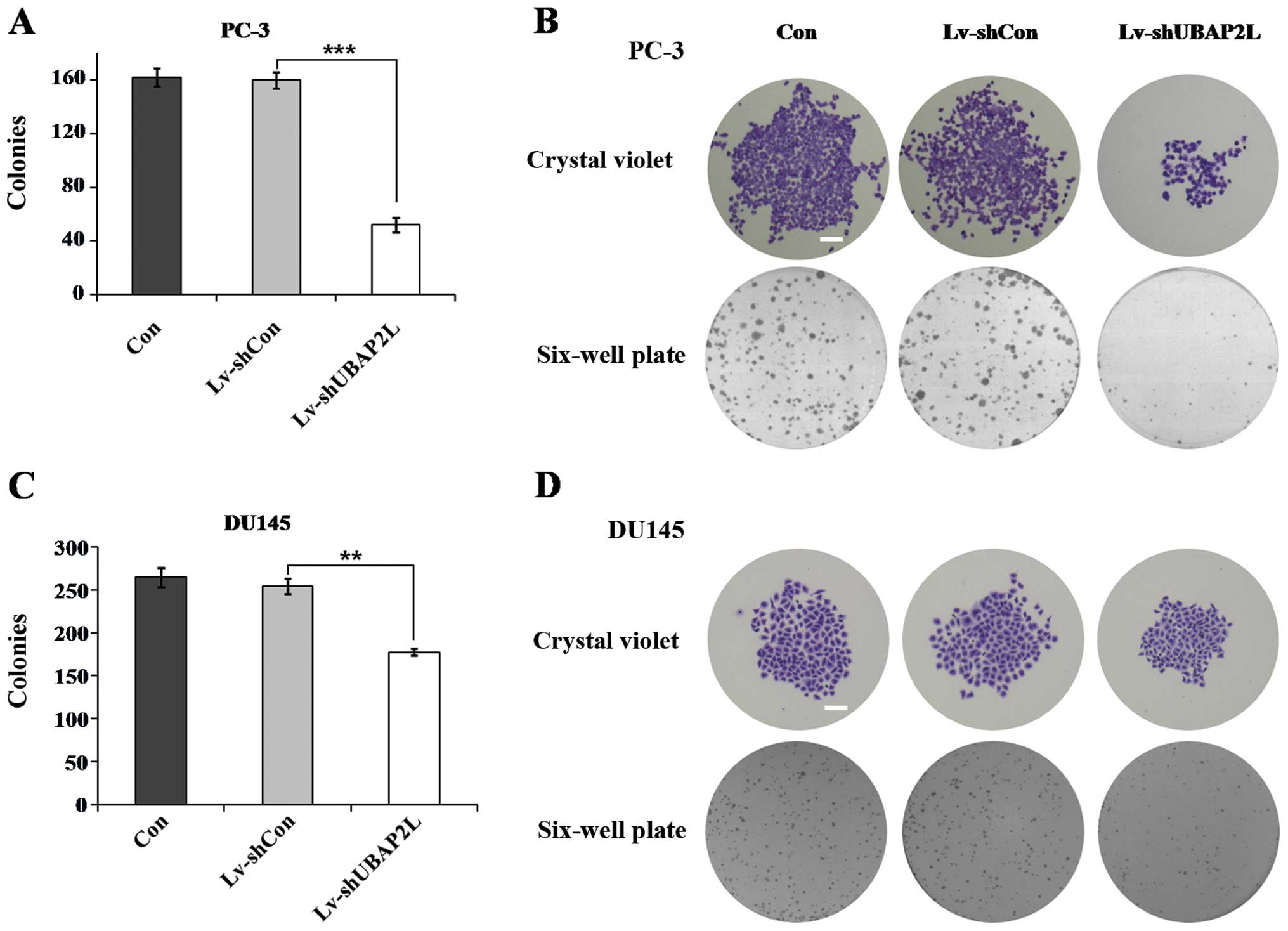
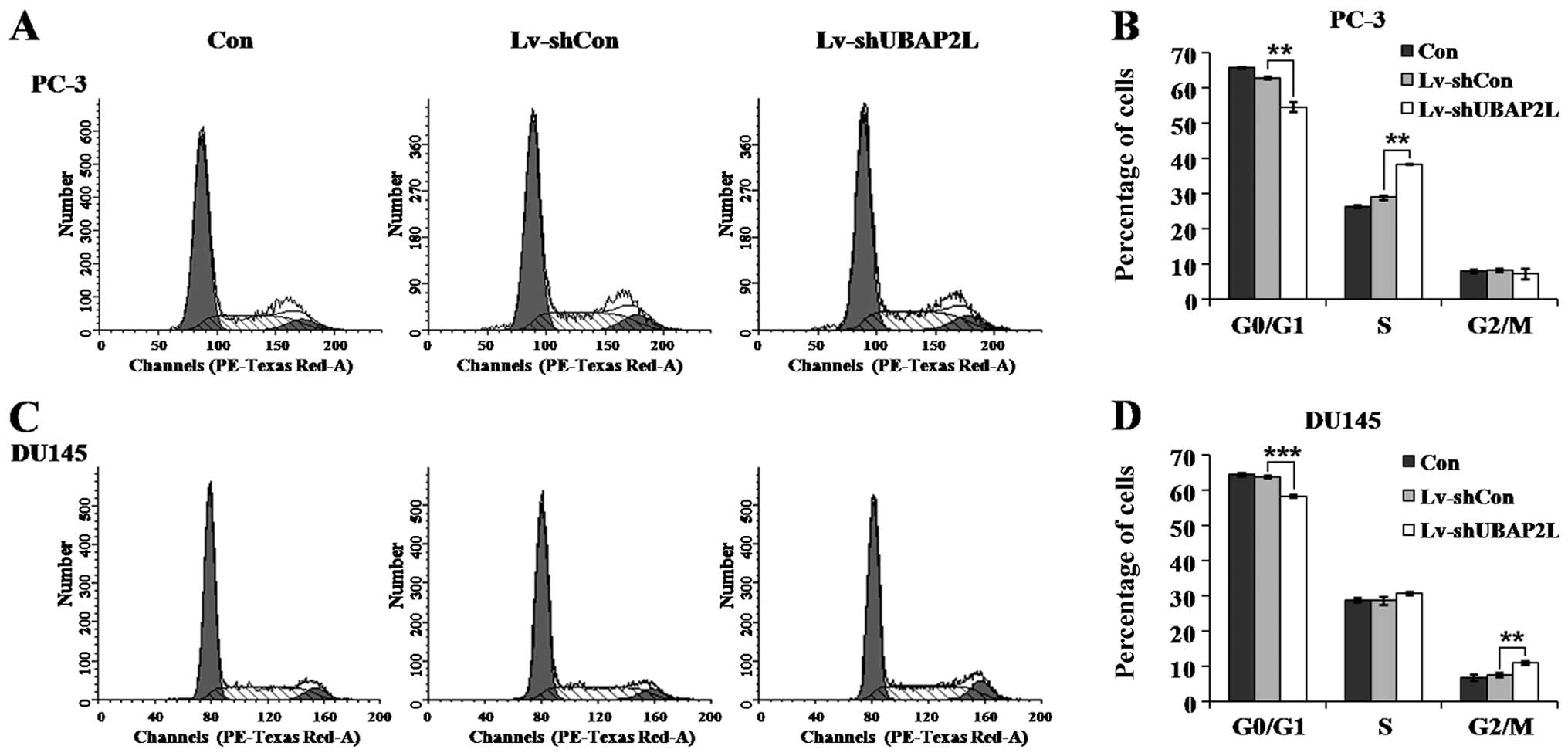
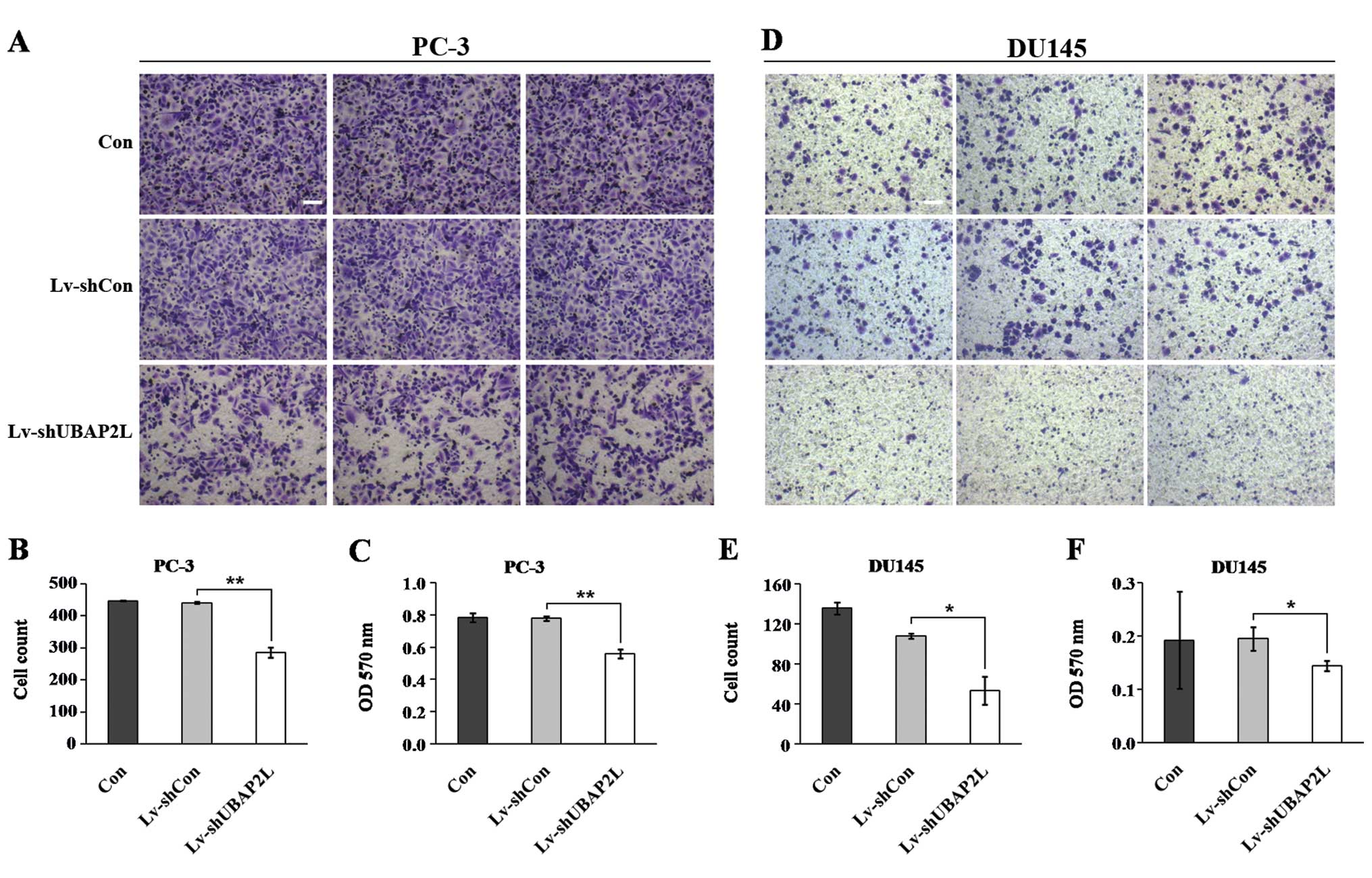
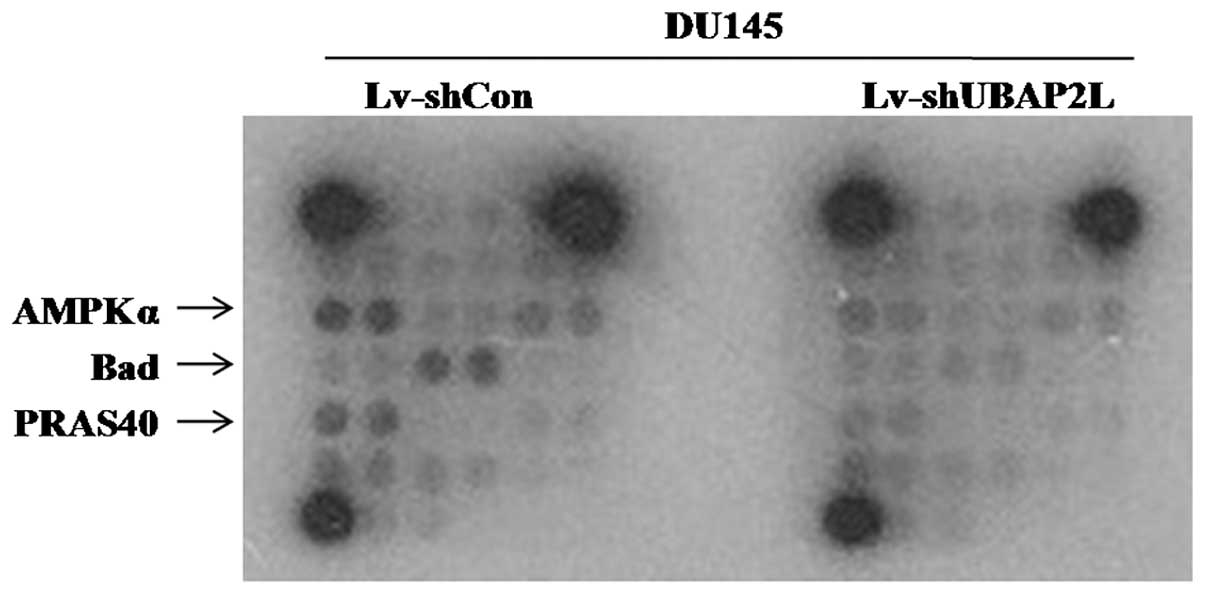
|
1
|
Baade PD, Youlden DR and Krnjacki LJ:
International epidemiology of prostate cancer: geographical
distribution and secular trends. Mol Nutr Food Res. 53:171–184.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
McGarrity GJ, Hoyah G, Winemiller A, et
al: Patient monitoring and follow-up in lentiviral clinical trials.
J Gene Med. 15:78–82. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chen FZ and Zhao XK: Ubiquitin-proteasome
pathway and prostate cancer. Onkologie. 36:592–596. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Iqbal M, Messina McLaughlin PA, Dunn D, et
al: Proteasome inhibitors for cancer therapy. Bioorg Med Chem.
20:2362–2368. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Crawford LJ, Walker B and Irvine AE:
Proteasome inhibitors in cancer therapy. J Cell Commun Signal.
5:101–110. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Rastogi N and Mishra DP: Therapeutic
targeting of cancer cell cycle using proteasome inhibitors. Cell
Div. 7:262012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
San-Miguel JF, Richardson PG, Gunther A,
et al: Phase Ib study of panobinostat and bortezomib in relapsed or
relapsed and refractory multiple myeloma. J Clin Oncol.
31:3696–3703. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
O’Brien ME, Gaafar RM, Popat S, et al:
Phase II study of first-line bortezomib and cisplatin in malignant
pleural mesothelioma and prospective validation of progression free
survival rate as a primary end-point for mesothelioma clinical
trials (European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer
08052). Eur J Cancer. 49:2815–2822. 2013.
|
|
9
|
Wilde IB, Brack M, Winget JM and Mayor T:
Proteomic characterization of aggregating proteins after the
inhibition of the ubiquitin proteasome system. J Proteome Res.
10:1062–1072. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chuang HC, Chou CC, Kulp SK and Chen CS:
AMPK as a potential anticancer target - friend or foe? Curr Pharm
Des. 20:2607–2618. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kazi AA and Lang CH: PRAS40 regulates
protein synthesis and cell cycle in C2C12 myoblasts. Mol Med.
16:359–371. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Smith AJ, Karpova Y, D’Agostino R Jr,
Willingham M and Kulik G: Expression of the Bcl-2 protein BAD
promotes prostate cancer growth. PLoS One. 4:e62242009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li J, Coven DL, Miller EJ, et al:
Activation of AMPK alpha- and gamma-isoform complexes in the intact
ischemic rat heart. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
291:H1927–H1934. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sastry KS, Smith AJ, Karpova Y, Datta SR
and Kulik G: Diverse antiapoptotic signaling pathways activated by
vasoactive intestinal polypeptide, epidermal growth factor, and
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in prostate cancer cells converge on
BAD. J Biol Chem. 281:20891–20901. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Datta SR, Katsov A, Hu L, et al: 14-3-3
proteins and survival kinases cooperate to inactivate BAD by BH3
domain phosphorylation. Mol Cell. 6:41–51. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Fang X, Yu S, Eder A, et al: Regulation of
BAD phosphorylation at serine 112 by the Ras-mitogen-activated
protein kinase pathway. Oncogene. 18:6635–6640. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tan Y, Demeter MR, Ruan H and Comb MJ: BAD
Ser-155 phosphorylation regulates BAD/Bcl-XL interaction and cell
survival. J Biol Chem. 275:25865–25869. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sancak Y, Thoreen CC, Peterson TR, et al:
PRAS40 is an insulin-regulated inhibitor of the mTORC1 protein
kinase. Mol Cell. 25:903–915. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|