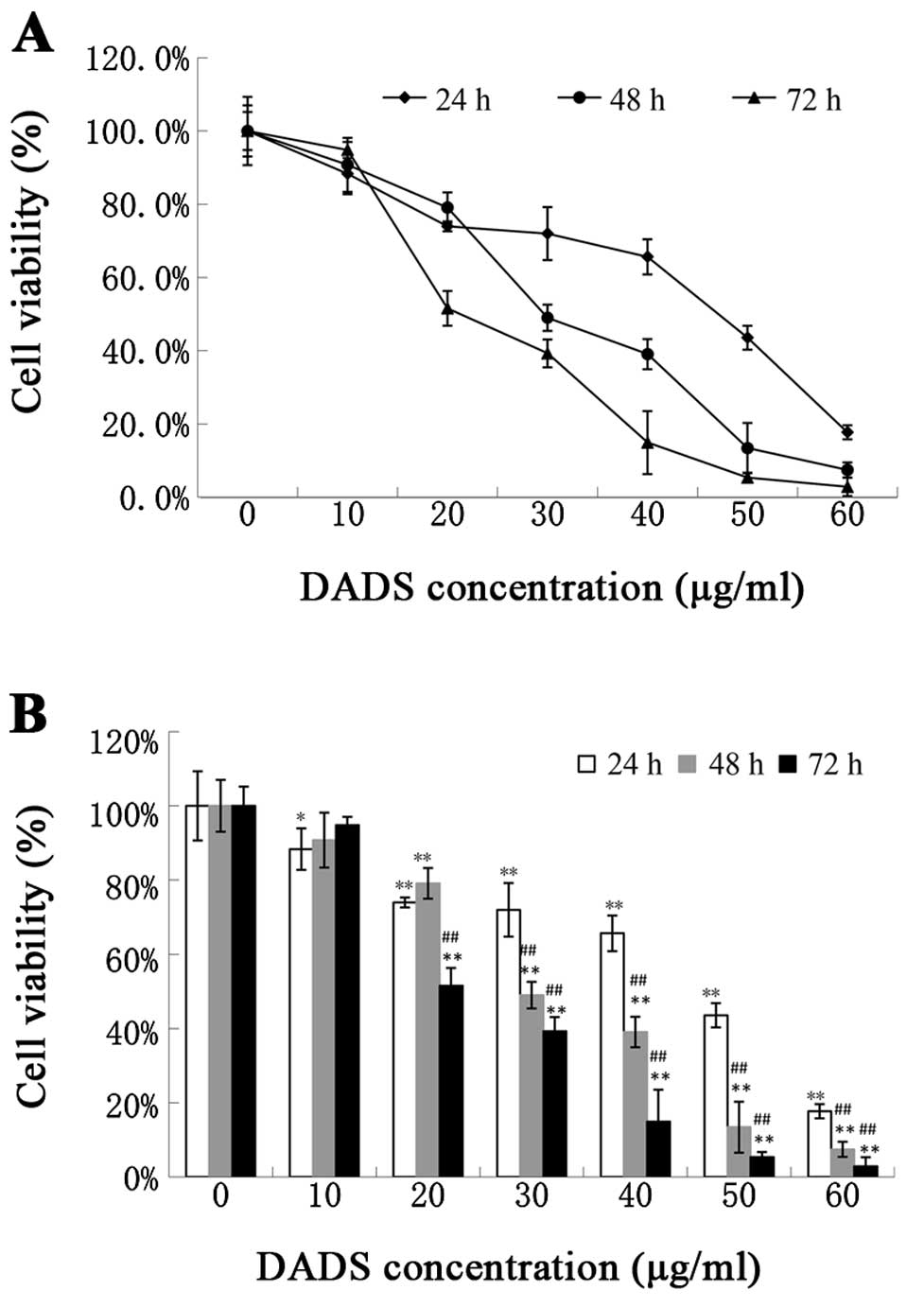
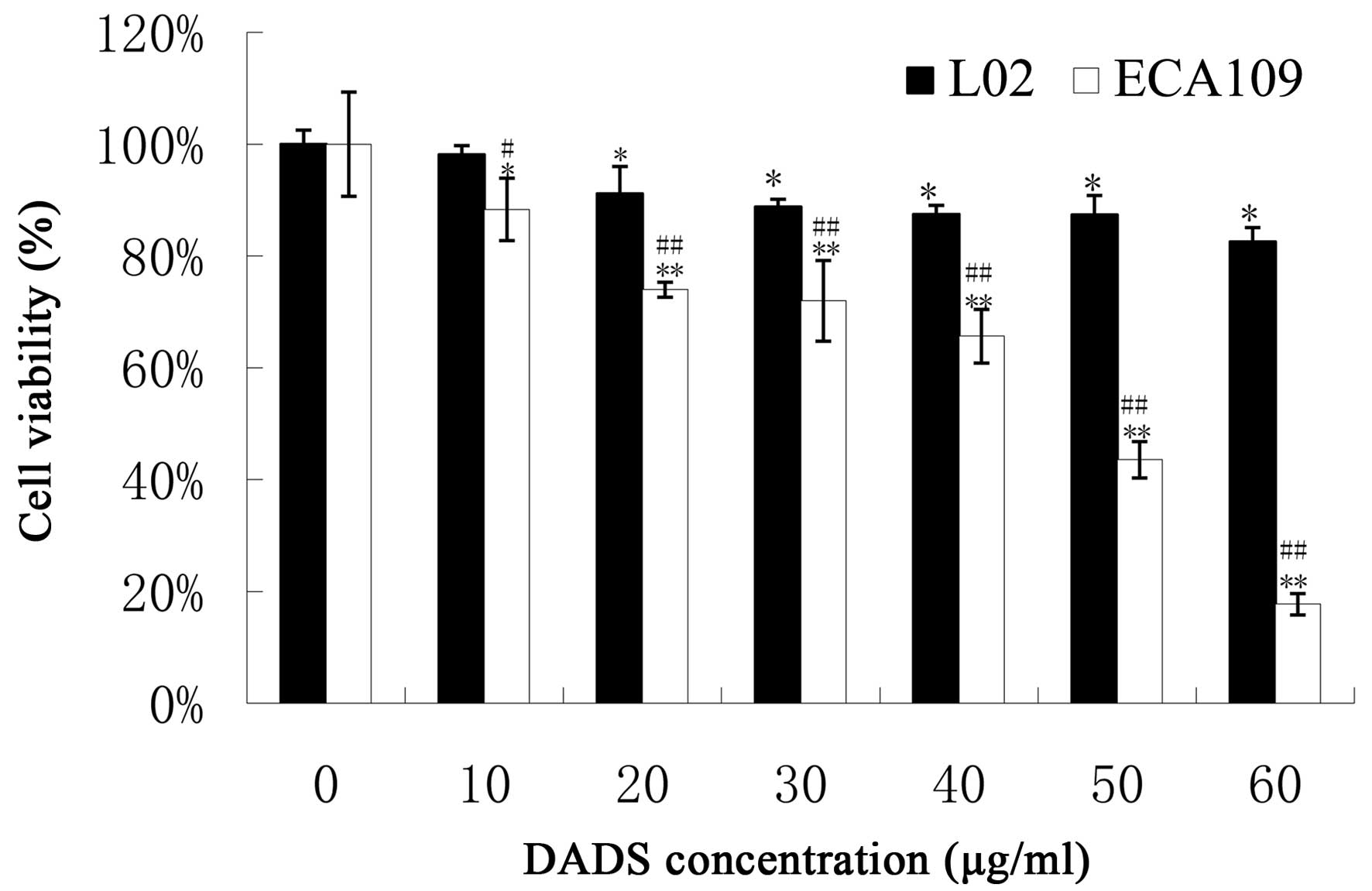
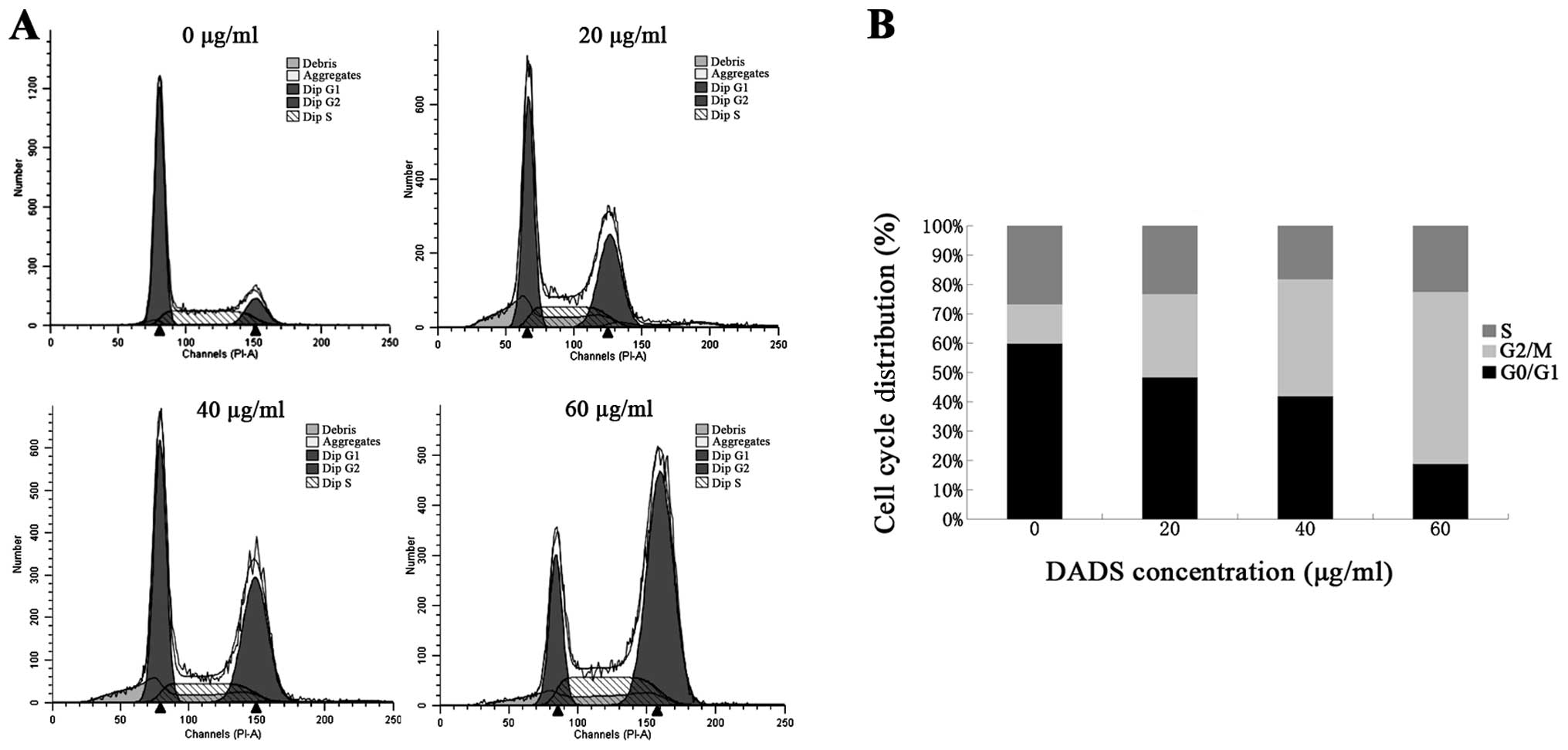
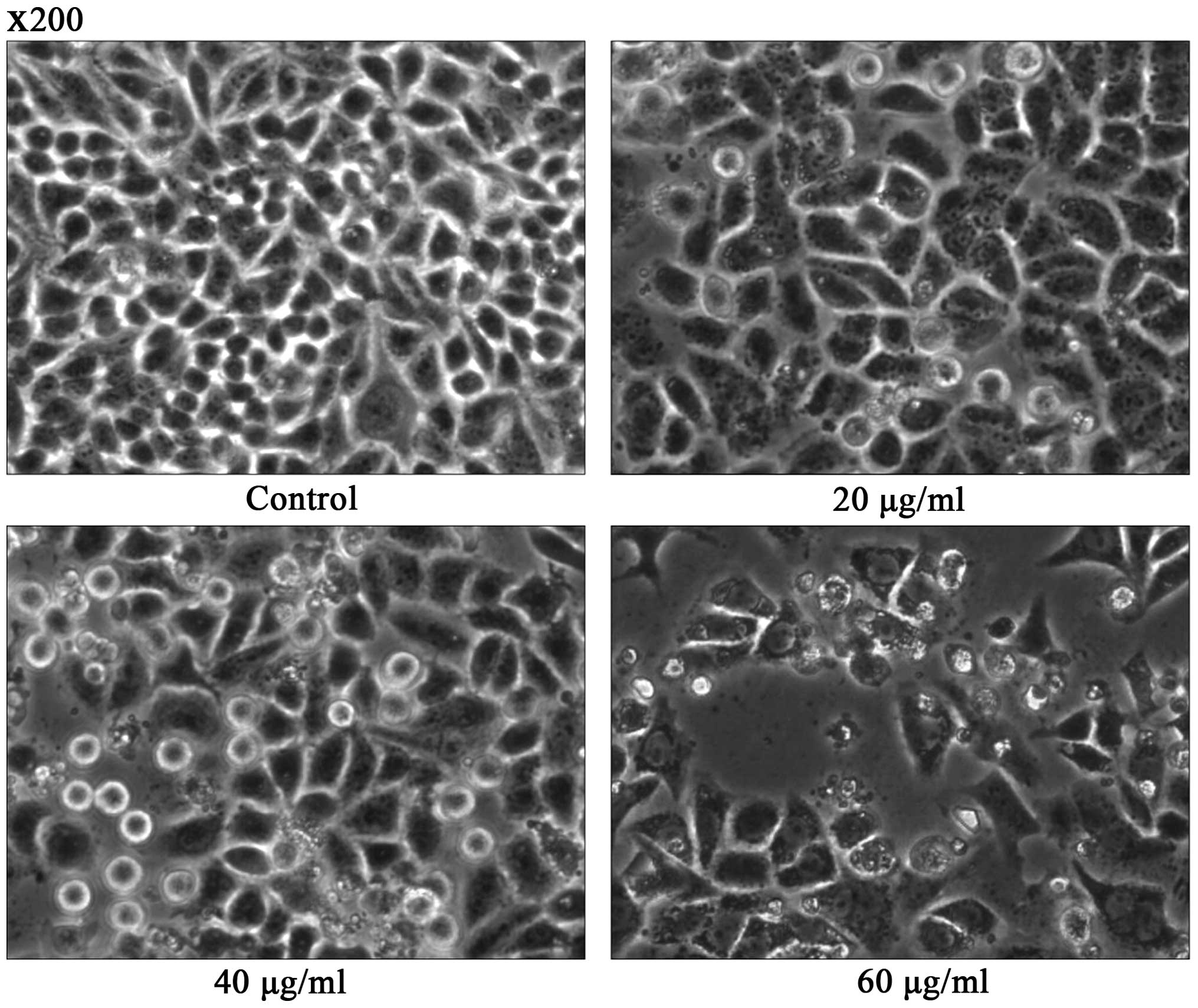
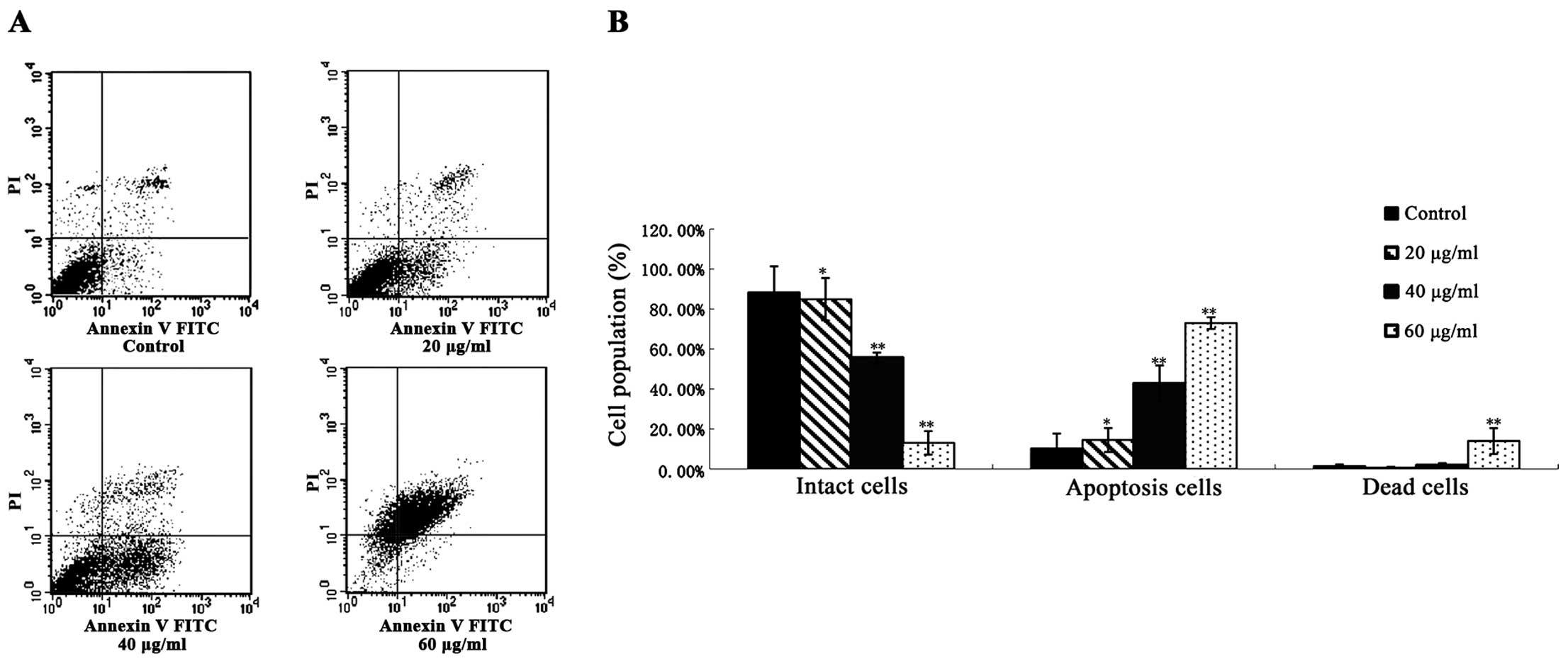
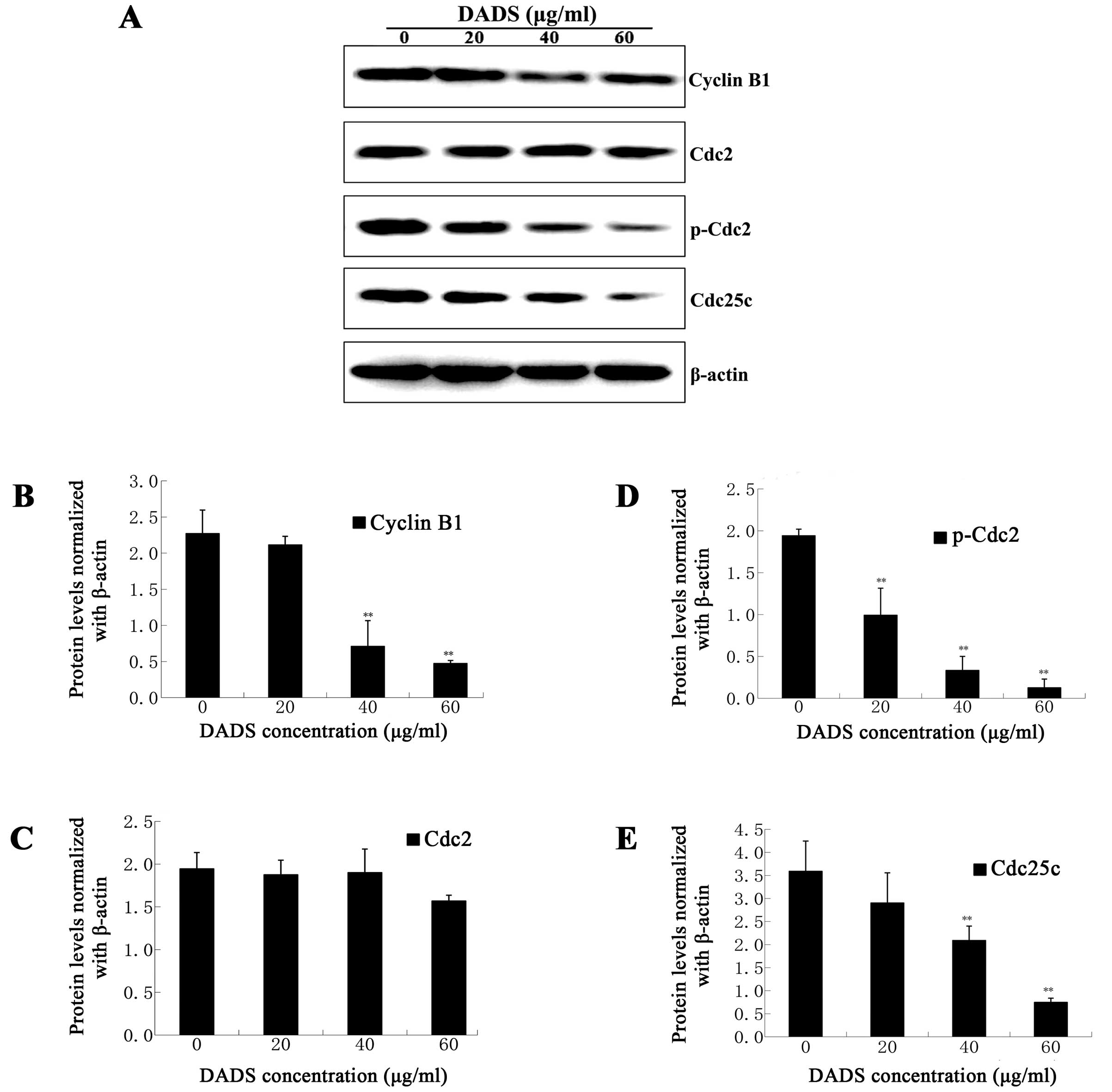
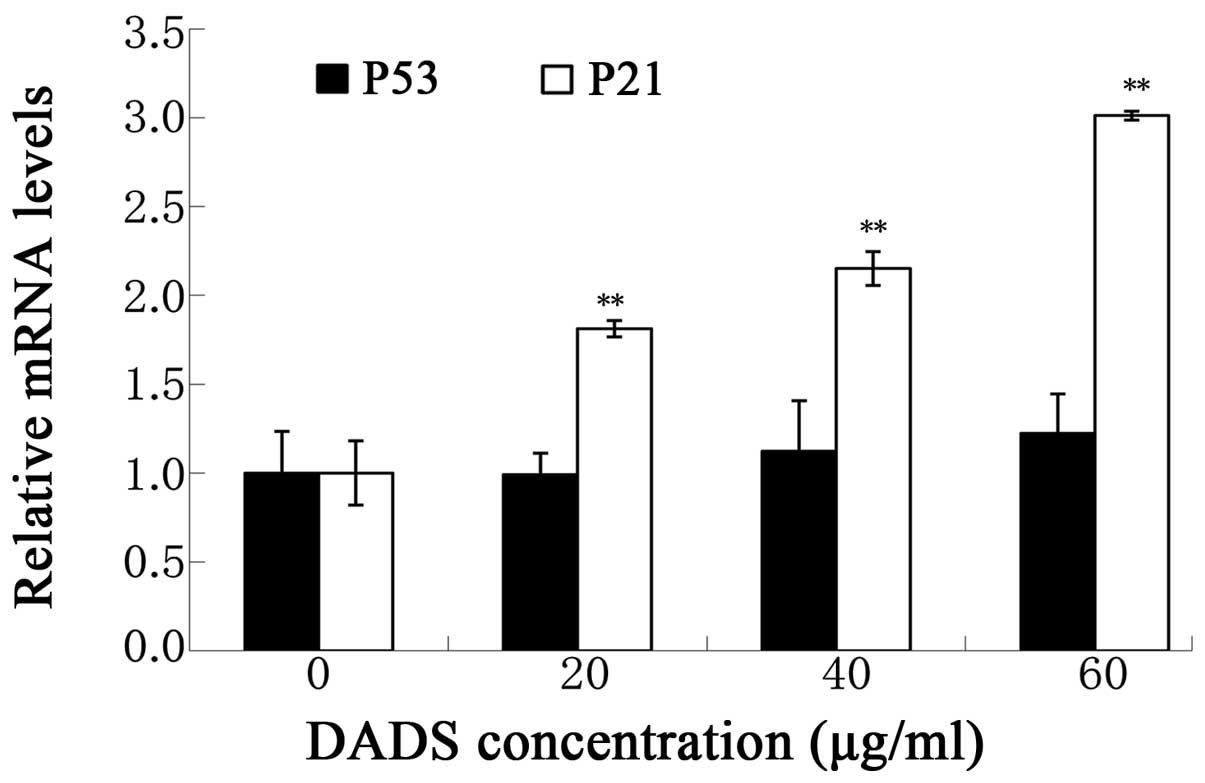
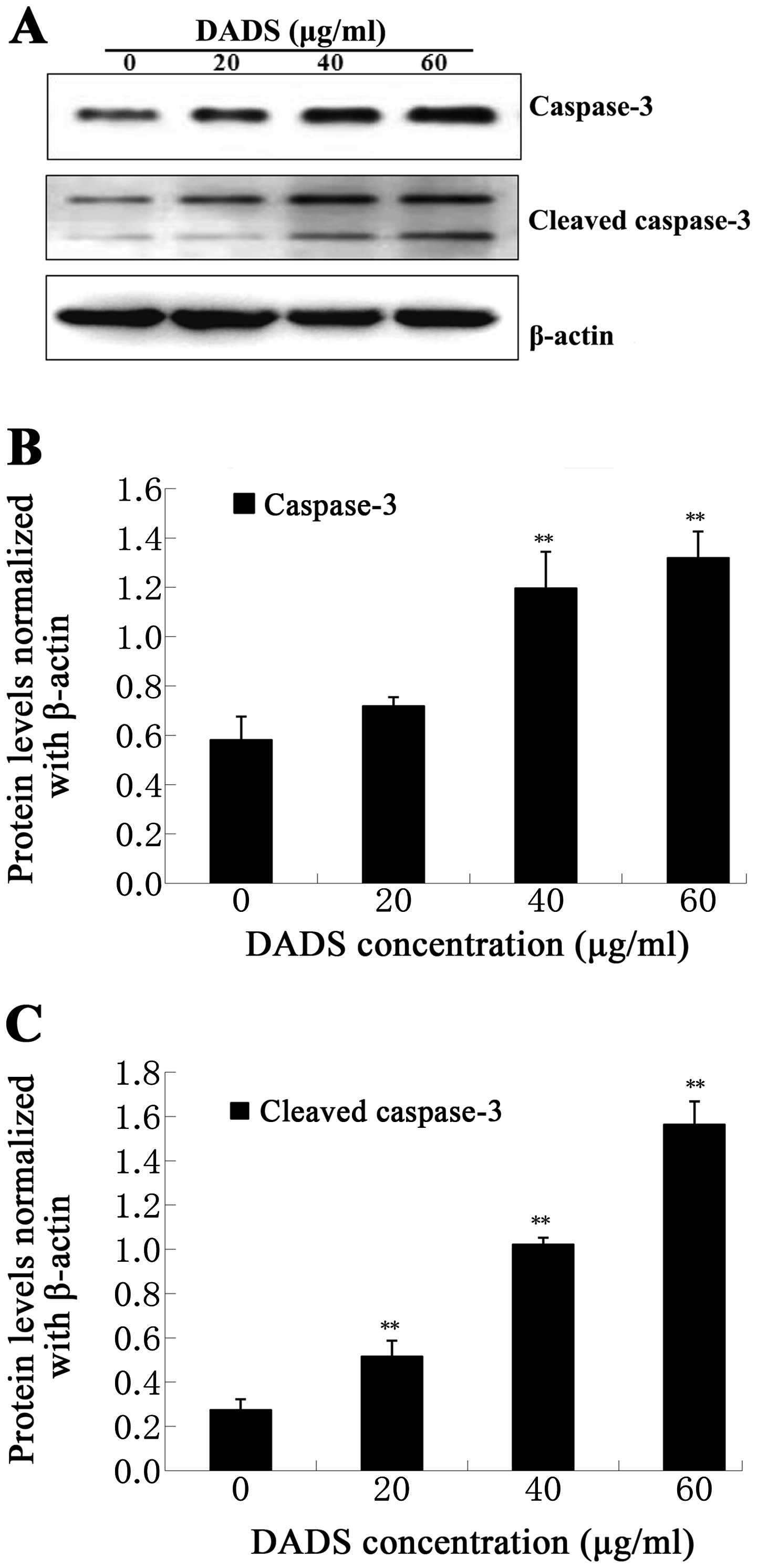
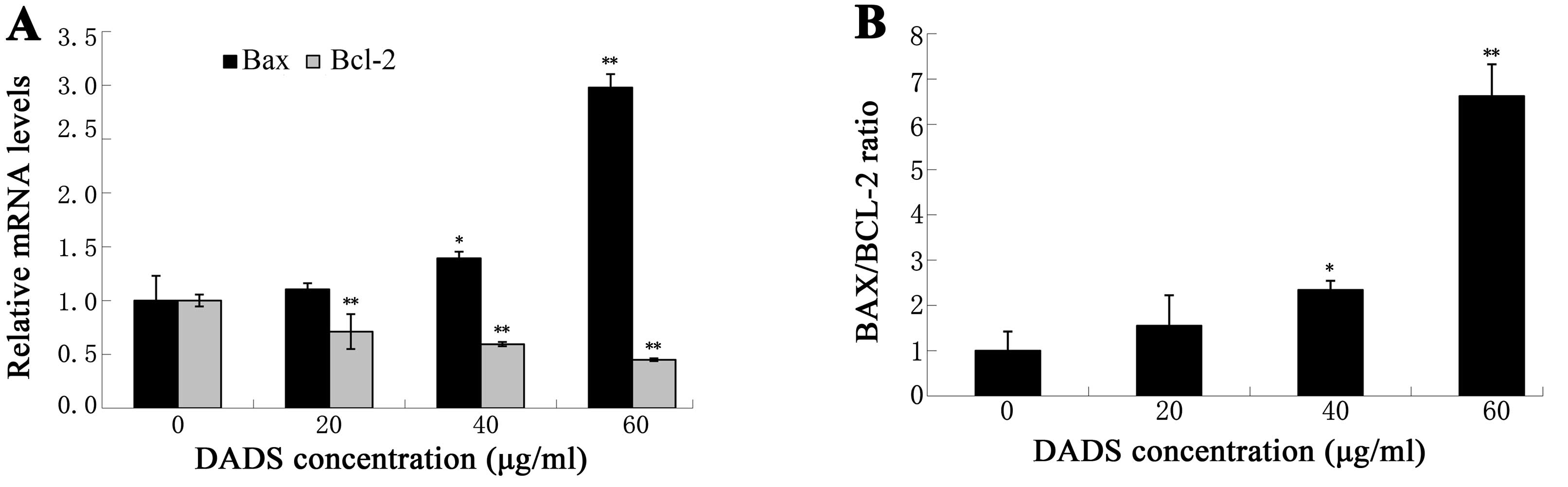
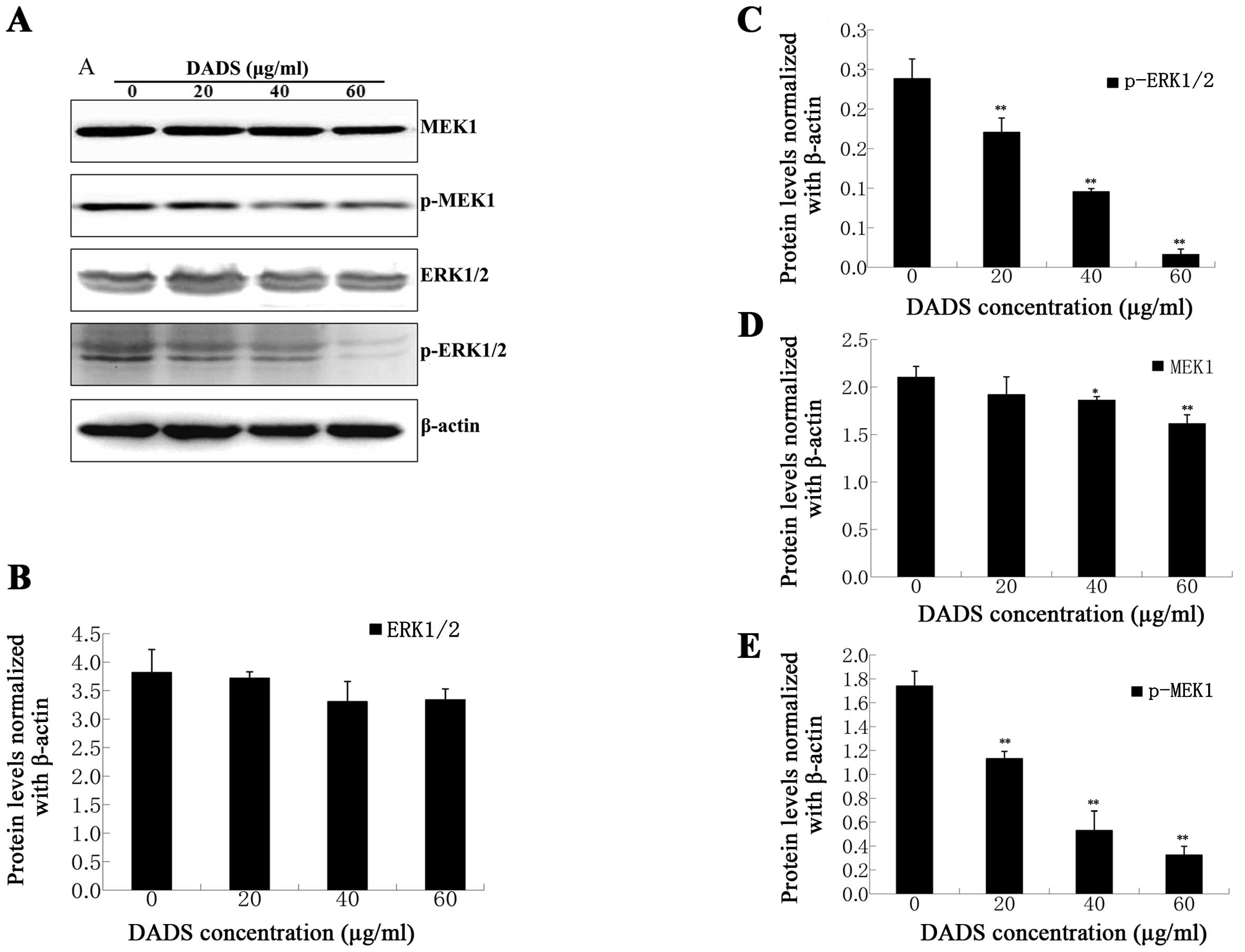
|
1
|
Cui X, Zhao Z, Liu D, et al: Inactivation
of miR-34a by aberrant CpG methylation in Kazakh patients with
esophageal carcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 33:20–33. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Orditura M, Galizia G, Fabozzi A, et al:
Preoperative treatment of locally advanced esophageal carcinoma.
Int J Oncol. 43:1745–1753. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Matés JM, Segura JA, Alonso FJ and Márquez
J: Anticancer antioxidant regulatory functions of phytochemicals.
Current Medicinal Chemistry. 18:2315–2338. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhou Y, Su J, Shi L, Liao Q and Su Q: DADS
downregulates the Rac1-ROCK1/PAK1-LIMK1-ADF/cofilin signaling
pathway, inhibiting cell migration and invasion. Oncol Rep.
29:605–612. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Alam M, Zubair S, Farazuddin M, et al:
Development, characterization and efficacy of niosomal diallyl
disulfide in treatment of disseminated murine candidiasis.
Nanomedicine. 9:247–256. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Maldonado PD, Chánez-Cárdenas ME and
Pedraza-Chaverrí J: Aged garlic extract, garlic powder extract,
S-allylcysteine, diallyl sulfide and diallyl disulfide do not
interfere with the antibiotic activity of gentamicin. Phytother
Res. 19:252–254. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Lissiman E, Bhasale AL and Cohen M: Garlic
for the common cold. Cochrane Database Syst Rev.
3:CD0062062012.
|
|
8
|
Lee IC, Kim SH, Baek HS, et al: The
involvement of Nrf2 in the protective effects of diallyl disulfide
on carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatic oxidative damage and
inflammatory response in rats. Food Chem Toxicol. 63:174–185. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Truong D, Hindmarsh W and O’Brien PJ: The
molecular mechanisms of diallyl disulfide and diallyl sulfide
induced hepatocyte cytotoxicity. Chem Biol Interact. 180:79–88.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Arunkumar R, Sharmila G, Elumalai P, et
al: Effect of diallyl disulfide on insulin-like growth factor
signaling molecules involved in cell survival and proliferation of
human prostate cancer cells in vitro and in silico approach through
docking analysis. Phytomedicine. 19:912–923. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Song JD, Lee SK, Kim KM, et al: Molecular
mechanism of diallyl disulfide in cell cycle arrest and apoptosis
in HCT-116 colon cancer cells. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 23:71–79.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Nkrumah-Elie YM, Reuben JS, Hudson AM, et
al: The attenuation of early benzo (a) pyrene-induced carcinogenic
insults by diallyl disulfide (DADS) in MCF-10A cells. Nutr Cancer.
64:1112–1121. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Ling H, Wen L, Ji XX, et al: Growth
inhibitory effect and Chk1-dependent signaling involved in G2/M
arrest on human gastric cancer cells induced by diallyl disulfide.
Braz J Med Biol Res. 43:271–278. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Jun Z, Suzuki M, Xiao J, Wen J, Talbot SG,
Li GC and Xu M: Comparative effects of natural and synthetic
diallyl disulfide on apoptosis of human breast-cancer MCF-7 cells.
Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 52:113–119. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhang XH, Zou ZQ, Xu CW, Shen YZ and Li D:
Myricetin induces G2/M phase arrest in HepG2 cells by inhibiting
the activity of the cyclin B/cdc2 complex. Mol Med Rep. 4:273–277.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sankari SL, Masthan KM, Babu NA,
Bhattacharjee T and Elumalai M: Apoptosis in cancer - an update.
Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 13:4873–4878. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Czepukojc B, Baltes AK, Cerella C, et al:
Synthetic polysulfane derivatives induce cell cycle arrest and
apoptotic cell death in human hematopoietic cancer cells. Food Chem
Toxicol. 64:249–257. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Tang H, Kong Y, Guo J, et al: Diallyl
disulfide suppresses proliferation and induces apoptosis in human
gastric cancer through Wnt-1 signaling pathway by upregulation of
miR-200b and miR-22. Cancer Lett. 340:72–81. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Haneji T, Hirashima K, Teramachi J and
Morimoto H: Okadaic acid activates the PKR pathway and induces
apoptosis through PKR stimulation in MG63 osteoblast-like cells.
Int J Oncol. 42:1904–1910. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hui C, Jun W, Ya LN and Ming X: Effect of
Allium sativum (garlic) diallyl disulfide (DADS) on human
non-small cell lung carcinoma H1299 cells. Trop Biomed. 25:37–45.
2008.
|
|
21
|
Tan H, Ling H, He J, Yi L, Zhou J, Lin M
and Su Q: Inhibition of ERK and activation of p38 are involved in
diallyl disulfide induced apoptosis of leukemia HL-60 cells. Arch
Pharm Res. 31:786–793. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Altonsy MO, Habib TN and Andrews SC:
Diallyl disulfide-induced apoptosis in a breast-cancer cell line
(MCF-7) may be caused by inhibition of histone deacetylation. Nutr
Cancer. 64:1251–1260. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Duong HQ, Hwang JS, Kim HJ, Seong YS and
Bae I: BML-275, an AMPK inhibitor, induces DNA damage, G2/M arrest
and apoptosis in human pancreatic cancer cells. Int J Oncol.
41:2227–2236. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Paul P, Rajendran SK, Peuhu E, Alshatwi
AA, Akbarsha MA, Hietanen S and Eriksson JE: Novel action modality
of the diterpenoid anisomelic acid causes depletion of E6 and E7
viral oncoproteins in HPV-transformed cervical carcinoma cells.
Biochem Pharmacol. 89:171–184. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Zhang Z, Wang CZ, Du GJ, et al: Genistein
induces G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis via ATM/p53-dependent
pathway in human colon cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 43:289–296.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Li B, Zhao J, Wang CZ, Searle J, He TC,
Yuan CS and Du W: Ginsenoside Rh2 induces apoptosis and
paraptosis-like cell death in colorectal cancer cells through
activation of p53. Cancer Lett. 301:185–192. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ding L, Huang Y, Du Q, et al: TGEV
nucleocapsid protein induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis
through activation of p53 signaling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
445:497–503. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Takahashi H, Chen MC, Pham H, et al:
Baicalein, a component of Scutellaria baicalensis, induces
apoptosis by Mcl-1 downregulation in human pancreatic cancer cells.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1813:1465–1474. 2011.
|
|
29
|
Lv C, Sun W, Sun H, Wei S, Chen R, Wang B
and Huang C: Asperolide A, a marine-derived tetranorditerpenoid,
induces G2/M arrest in human NCI-H460 lung carcinoma cells, is
mediated by p53-p21 stabilization and modulated by Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK
signaling pathway. Mar Drugs. 11:316–331. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|