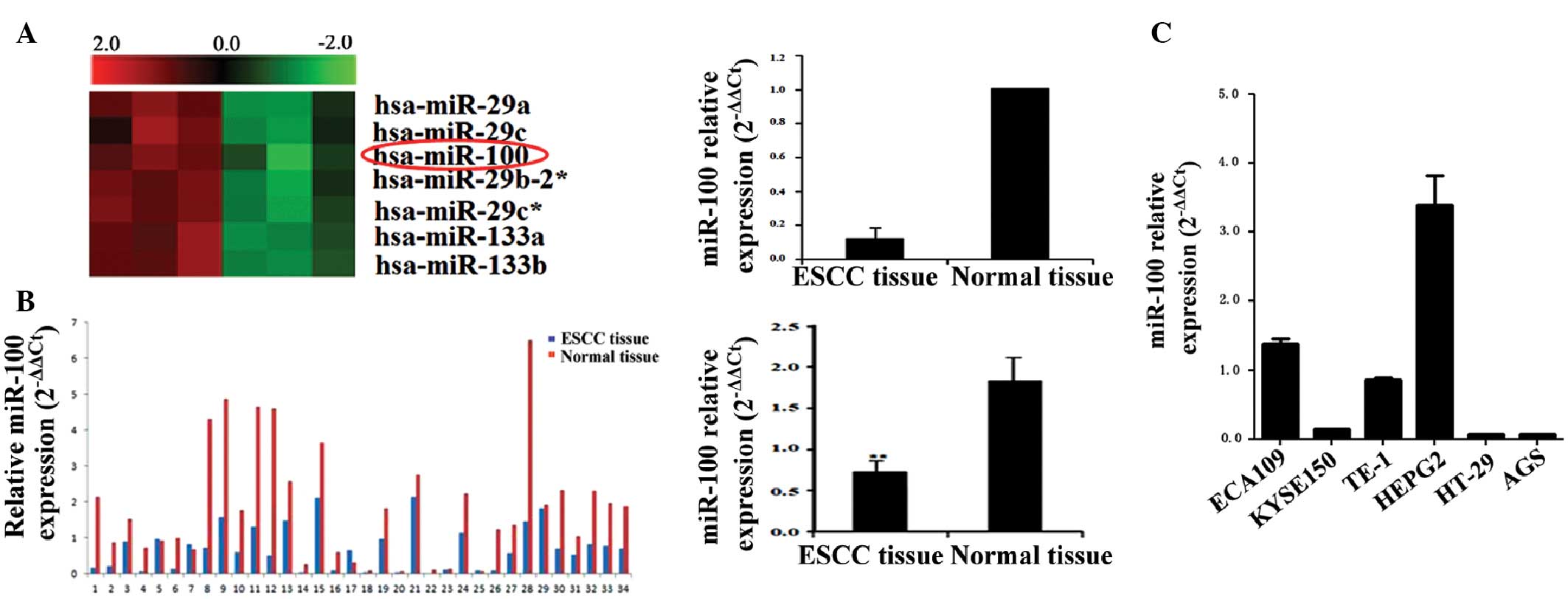
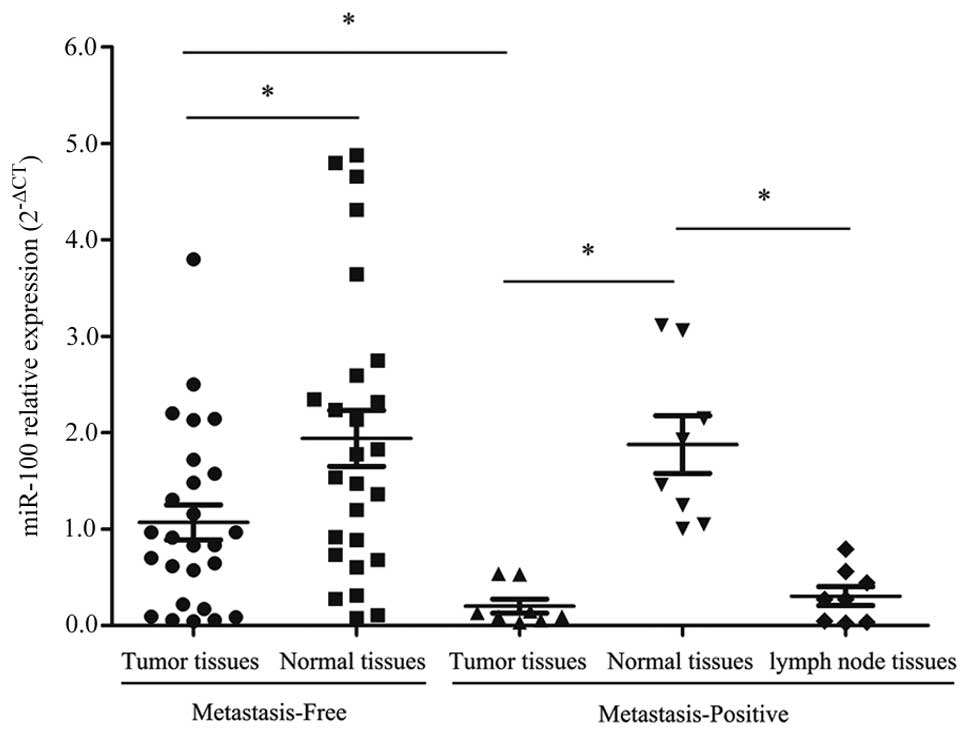
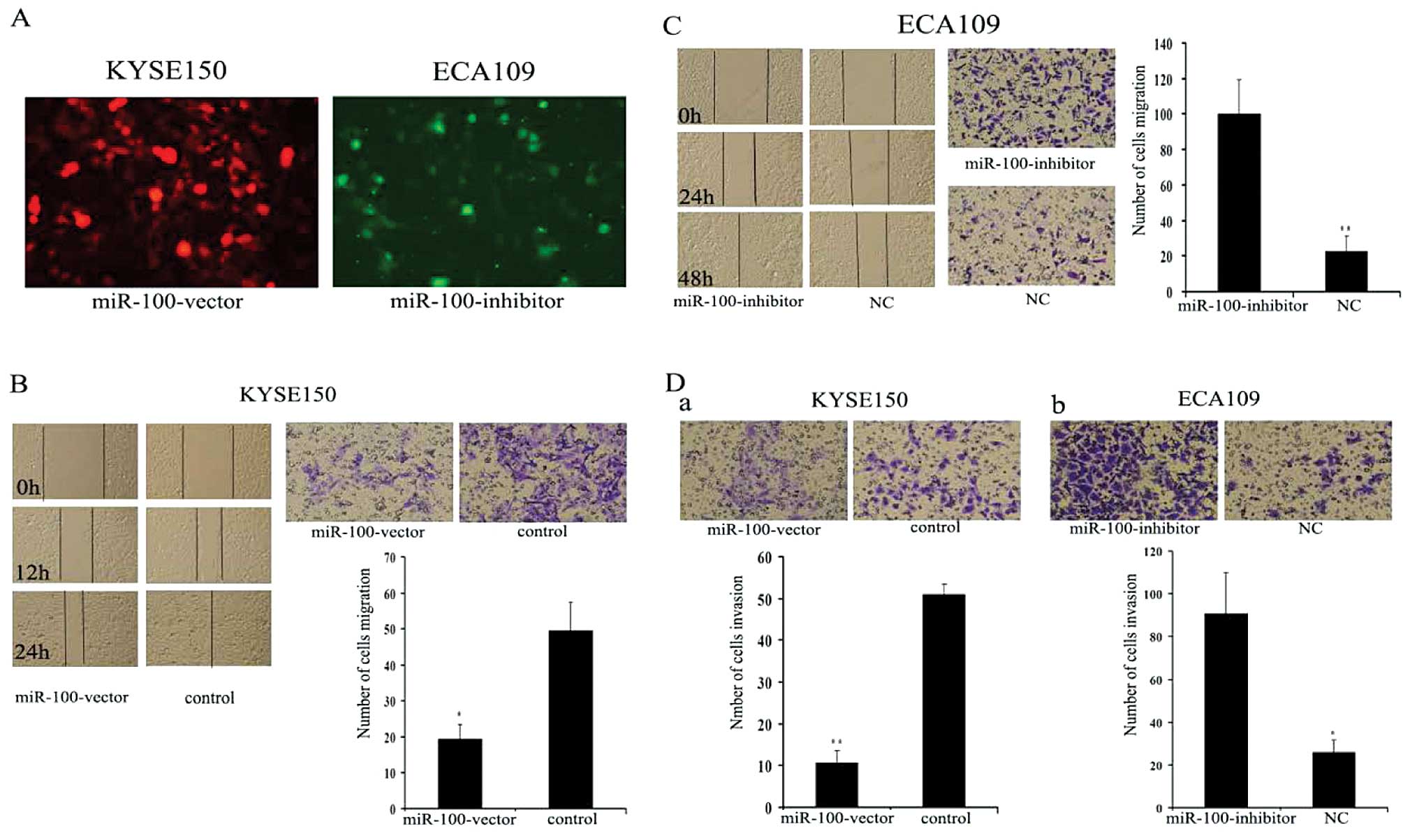
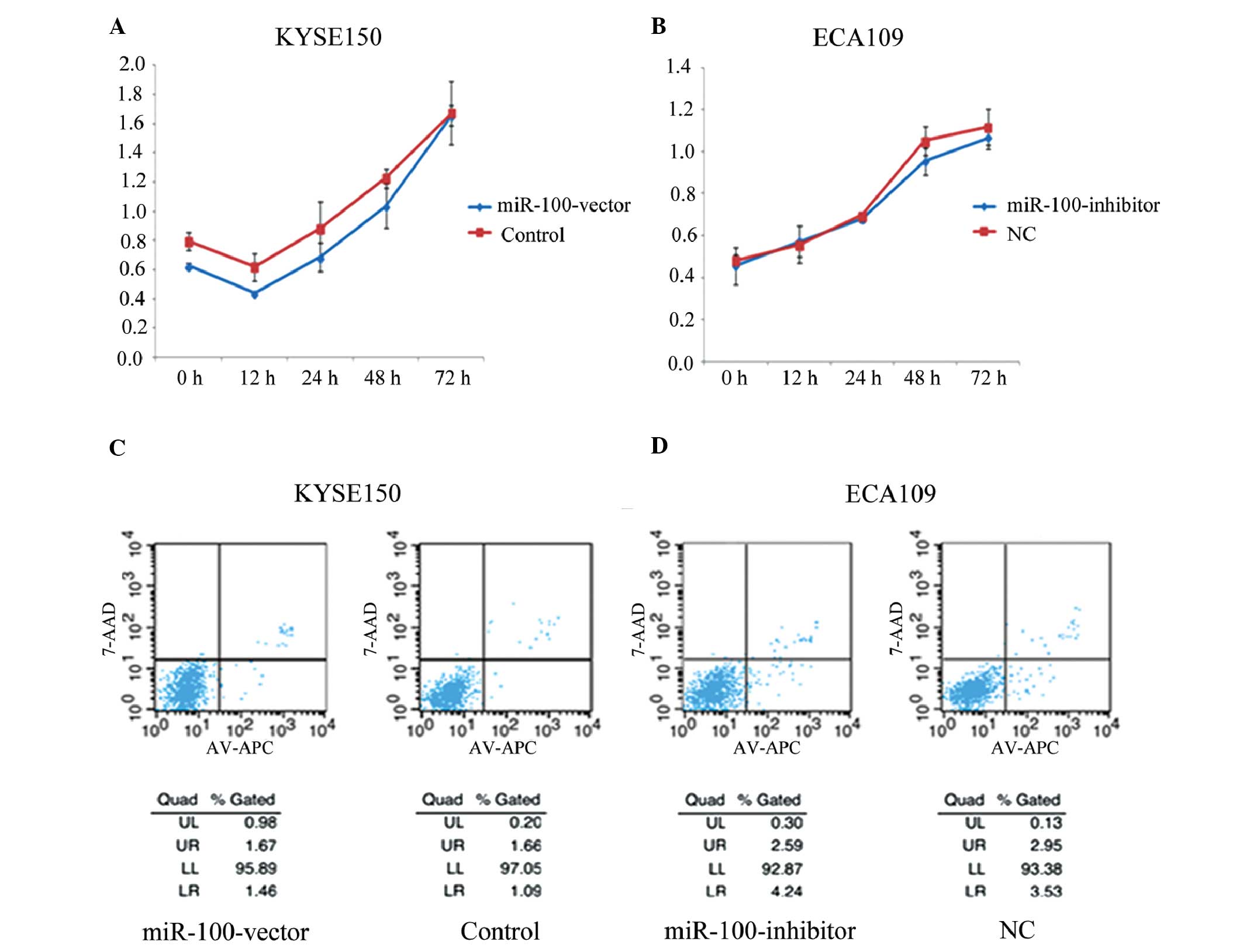
|
1
|
Enzinger PC and Mayer RJ: Esophageal
cancer. N Engl J Med. 349:2241–2252. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Orringer MB: Multimodality therapy for
esophageal carcinoma - update. Chest. 103:406S–409S. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Rice TW, Rusch VW, Apperson-Hansen C, et
al: Worldwide esophageal cancer collaboration. Dis Esophagus.
22:1–8. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lewis BP, Burge CB and Bartel DP:
Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that
thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell. 120:15–20.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, et al: MicroRNA
expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature. 435:834–838.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Calin GA and Croce CM: MicroRNA signatures
in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:857–866. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kong YW, Ferland-McCollough D, Jackson TJ
and Bushell M: microRNAs in cancer management. Lancet Oncol.
13:e249–e258. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Jia XQ, Cheng HQ, Qian X, et al:
Lentivirus-mediated overexpression of microRNA-199a inhibits cell
proliferation of human hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Biochem
Biophys. 62:237–244. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Calin GA, Sevignani C, Dumitru CD, et al:
Human microRNA genes are frequently located at fragile sites and
genomic regions involved in cancers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
101:2999–3004. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kong KL, Kwong DL, Chan TH, et al:
MicroRNA-375 inhibits tumour growth and metastasis in oesophageal
squamous cell carcinoma through repressing insulin-like growth
factor 1 receptor. Gut. 61:33–42. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhang HF, Zhang K, Liao LD, et al:
miR-200b suppresses invasiveness and modulates the cytoskeletal and
adhesive machinery in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells via
targeting Kindlin-2. Carcinogenesis. 35:292–301. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Fu HL, Wu de P, Wang XF, et al: Altered
miRNA expression is associated with differentiation, invasion, and
metastasis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) in patients
from Huaian, China. Cell Biochem Biophys. 67:657–668. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Leite KR, Tomiyama A, Reis ST,
Sousa-Canavez JM, Sanudo A, Camara-Lopes LH and Srougi M: MicroRNA
expression profiles in the progression of prostate cancer - from
high-grade prostate intraepithelial neoplasia to metastasis. Urol
Oncol. 31:796–801. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Feng B, Wang R and Chen LB: MiR-100
resensitizes docetaxel-resistant human lung adenocarcinoma cells
(SPC-A1) to docetaxel by targeting Plk1. Cancer Lett. 317:184–191.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zheng YS, Zhang H, Zhang XJ, et al:
MiR-100 regulates cell differentiation and survival by targeting
RBSP3, a phosphatase-like tumor suppressor in acute myeloid
leukemia. Oncogene. 31:80–92. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Peng DX, Luo M, Qiu LW, He YL and Wang XF:
Prognostic implications of microRNA-100 and its functional roles in
human epithelial ovarian cancer. Oncol Rep. 27:1238–1244.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Oliveira JC, Brassesco MS, Morales AG, et
al: MicroRNA-100 acts as a tumor suppressor in human bladder
carcinoma 5637 cells. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 12:3001–3004.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Henson BJ, Bhattacharjee S, O’Dee DM,
Feingold E and Gollin SM: Decreased expression of miR-125b and
miR-100 in oral cancer cells contributes to malignancy. Genes
Chromosomes Cancer. 48:569–582. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Gebeshuber CA and Martinez J: miR-100
suppresses IGF2 and inhibits breast tumorigenesis by interfering
with proliferation and survival signaling. Oncogene. 32:3306–3310.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhu Q, Hong A, Sheng N, et al:
microParaflo biochip for nucleic acid and protein analysis. Methods
Mol Biol. 382:287–312. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hutvagner G, McLachlan J, Pasquinelli AE,
Balint E, Tuschl T and Zamore PD: A cellular function for the
RNA-interference enzyme Dicer in the maturation of the let-7 small
temporal RNA. Science. 293:834–838. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Alvarez-Garcia I and Miska EA: MicroRNA
functions in animal development and human disease. Development.
132:4653–4662. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hiyoshi Y, Kamohara H, Karashima R, et al:
MicroRNA-21 regulates the proliferation and invasion in esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 15:1915–1922. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Guo Y, Chen Z, Zhang L, et al: Distinctive
microRNA profiles relating to patient survival in esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Res. 68:26–33. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Smith CM, Watson DI, Michael MZ and Hussey
DJ: MicroRNAs, development of Barrett’s esophagus, and progression
to esophageal adenocarcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 16:531–537.
2010.
|
|
27
|
Kinoshita T, Hanazawa T, Nohata N, et al:
Tumor suppressive microRNA-218 inhibits cancer cell migration and
invasion through targeting laminin-332 in head and neck squamous
cell carcinoma. Oncotarget. 3:1386–1400. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Majid S, Dar AA, Saini S, et al:
MicroRNA-1280 inhibits invasion and metastasis by targeting ROCK1
in bladder cancer. PLoS One. 7:e467432012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Liu W, Gong YH, Chao TF, et al:
Identification of differentially expressed microRNAs by microarray:
a possible role for microRNAs gene in medulloblastomas. Chin Med J.
122:2405–2411. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li BH, Zhou JS, Ye F, Cheng XD, Zhou CY,
Lu WG and Xie X: Reduced miR-100 expression in cervical cancer and
precursors and its carcinogenic effect through targeting PLK1
protein. Eur J Cancer. 47:2166–2174. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hildebrandt MA, Yang H, Hung MC, et al:
Genetic variations in the PI3K/PTEN/AKT/mTOR pathway are associated
with clinical outcomes in esophageal cancer patients treated with
chemoradiotherapy. J Clin Oncol. 27:857–871. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Oyama K, Okawa T, Nakagawa H, et al: AKT
induces senescence in primary esophageal epithelial cells but is
permissive for differentiation as revealed in organotypic culture.
Oncogene. 26:2353–2364. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Okano J, Gaslightwala I, Birnbaum MJ,
Rustgi AK and Nakagawa H: Akt/protein kinase B isoforms are
differentially regulated by epidermal growth factor stimulation. J
Biol Chem. 275:30934–30942. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Baba Y, Iyama KI, Hirashima K, et al:
Laminin-332 promotes the invasion of oesophageal squamous cell
carcinoma via PI3K activation. Br J Cancer. 98:974–980. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Li B, Tsao SW, Li YY, et al: Id-1 promotes
tumorigenicity and metastasis of human esophageal cancer cells
through activation of PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Int J Cancer.
125:2576–2585. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hay N and Sonenberg N: Upstream and
downstream of mTOR. Genes Dev. 18:1926–1945. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Kim JE and Chen J: Cytoplasmic-nuclear
shuttling of FKBP12-rapamycin-associated protein is involved in
rapamycin-sensitive signaling and translation initiation. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 97:14340–14345. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Martin DE and Hall MN: The expanding TOR
signaling network. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 17:158–166. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Sun SY, Rosenberg LM, Wang X, Zhou Z, Yue
P, Fu H and Khuri FR: Activation of Akt and eIF4E survival pathways
by rapamycin-mediated mammalian target of rapamycin inhibition.
Cancer Res. 65:7052–7058. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Treeck O, Wackwitz B, Haus U and Ortmann
O: Effects of a combined treatment with mTOR inhibitor RAD001 and
tamoxifen in vitro on growth and apoptosis of human cancer cells.
Gynecol Oncol. 102:292–299. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
DeGraffenried LA, Friedrichs WE, Russell
DH, et al: Inhibition of mTOR activity restores tamoxifen response
in breast cancer cells with aberrant Akt activity. Clin Cancer Res.
10:8059–8067. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|