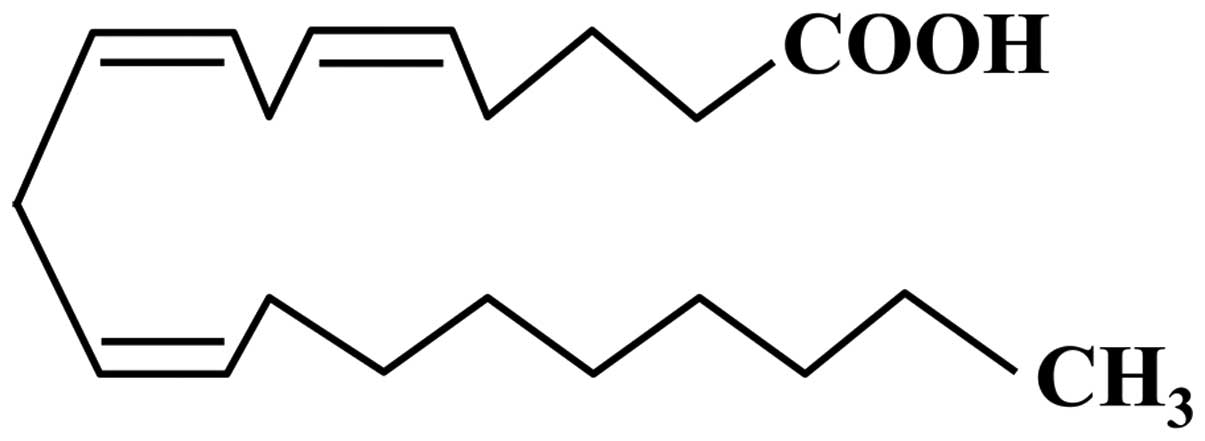
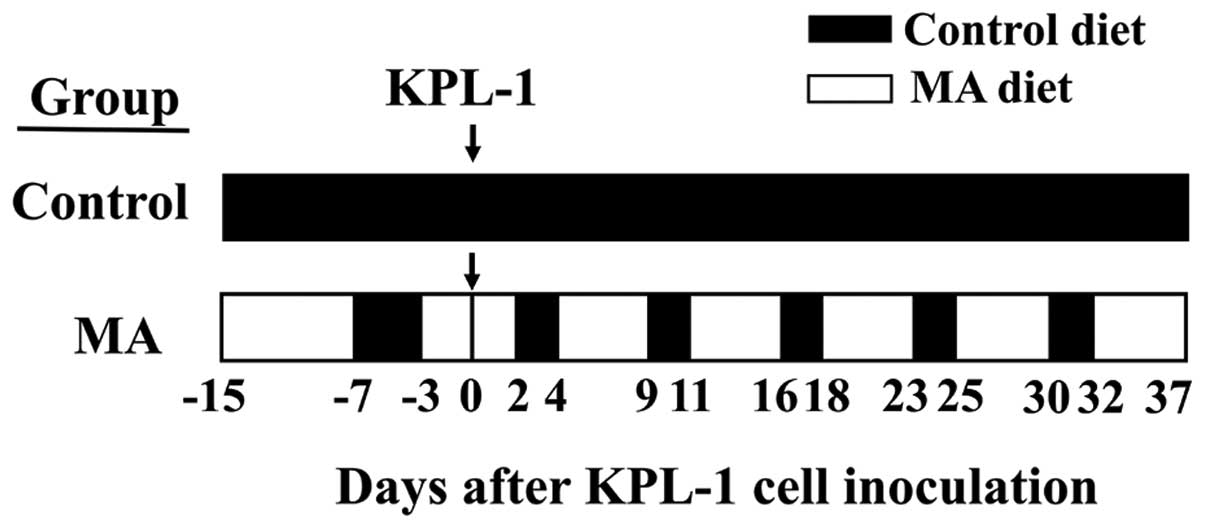
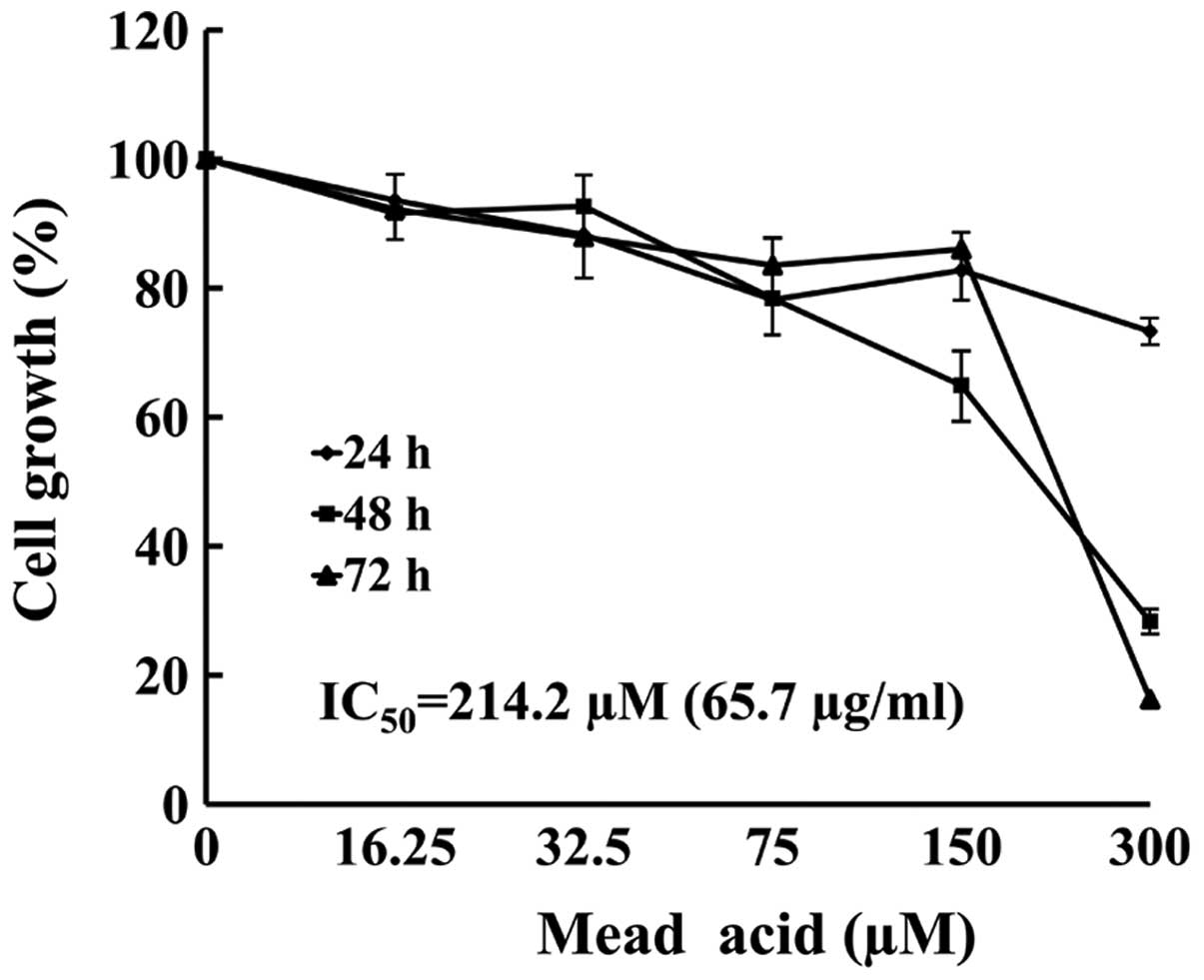
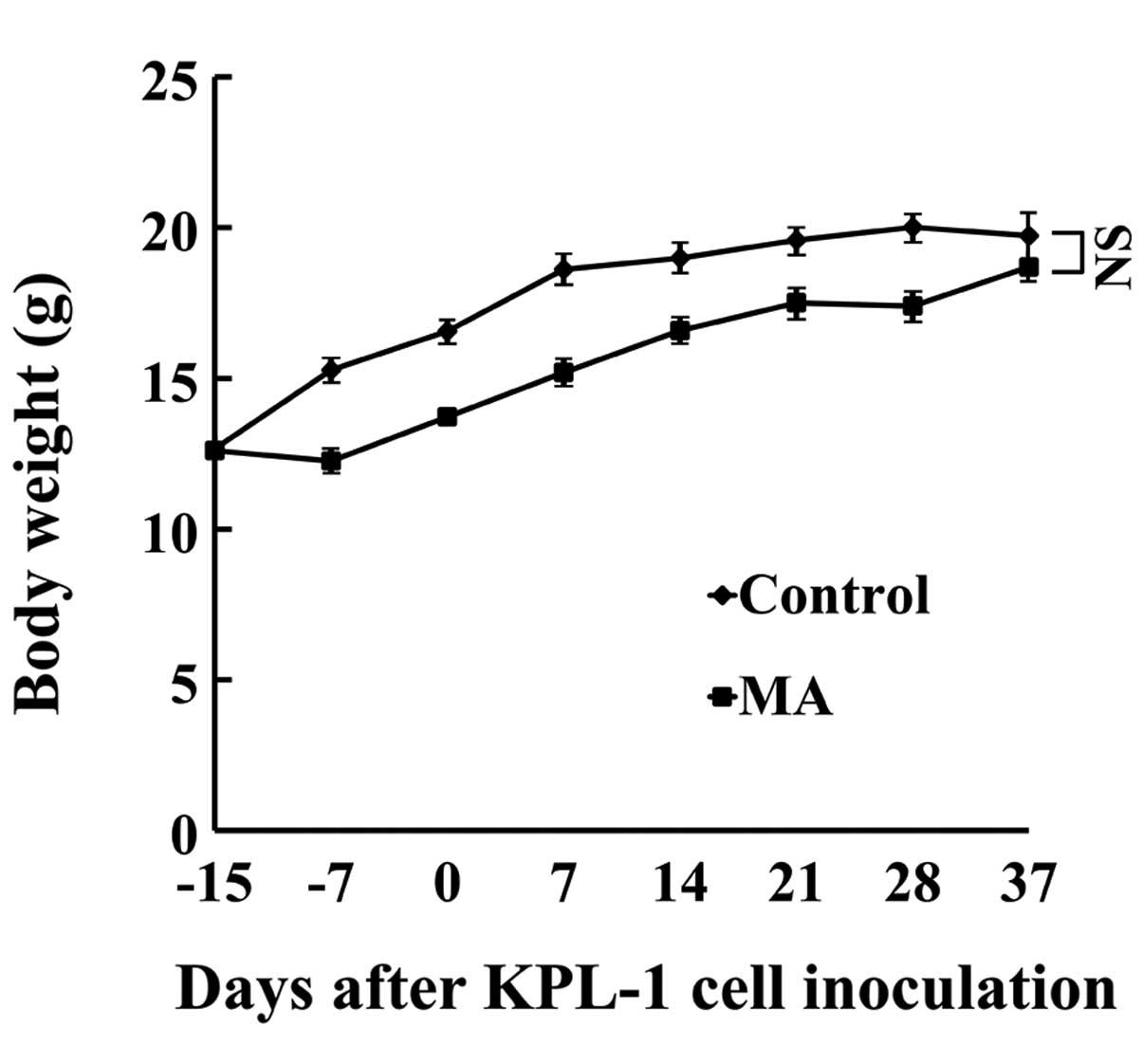
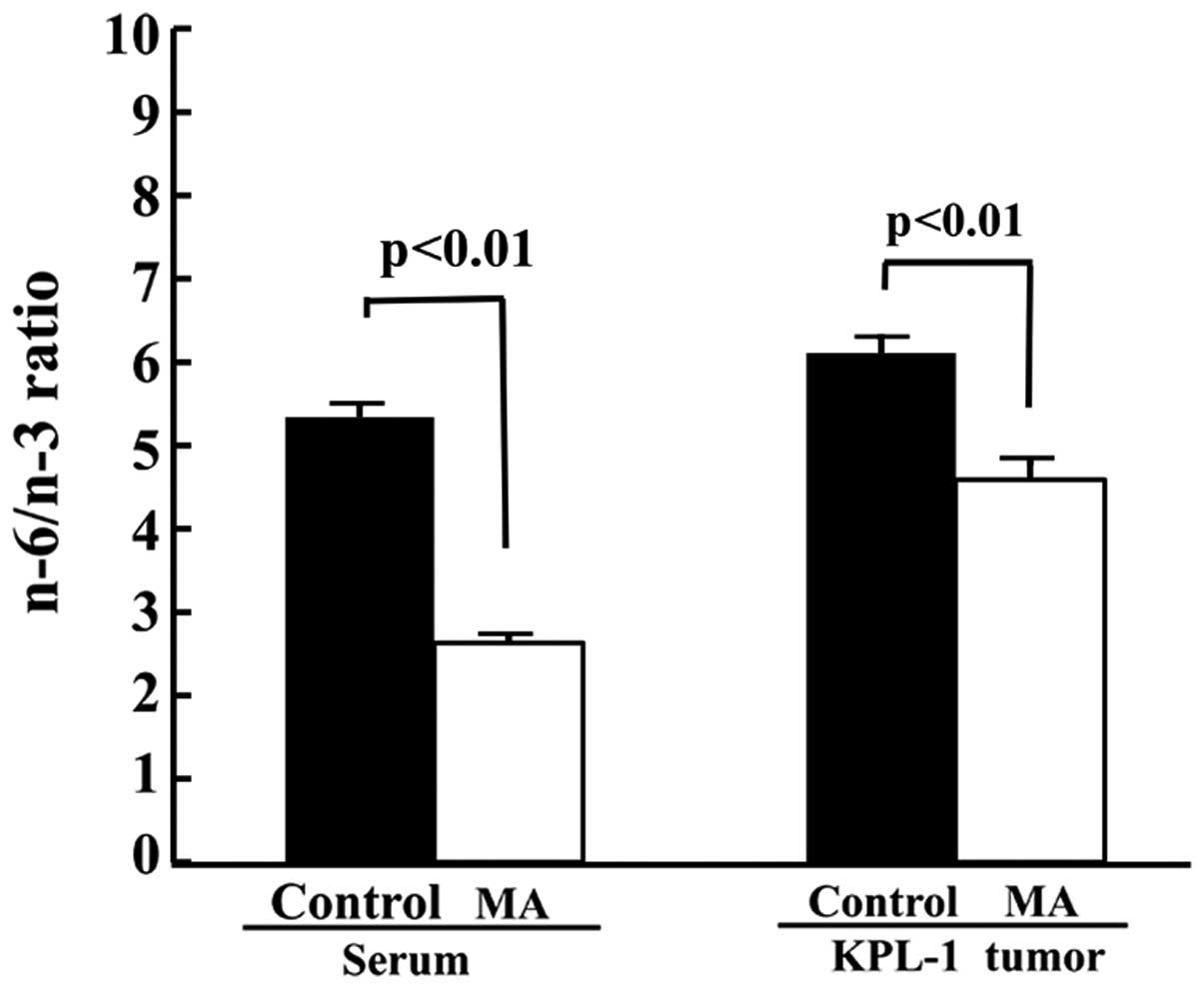
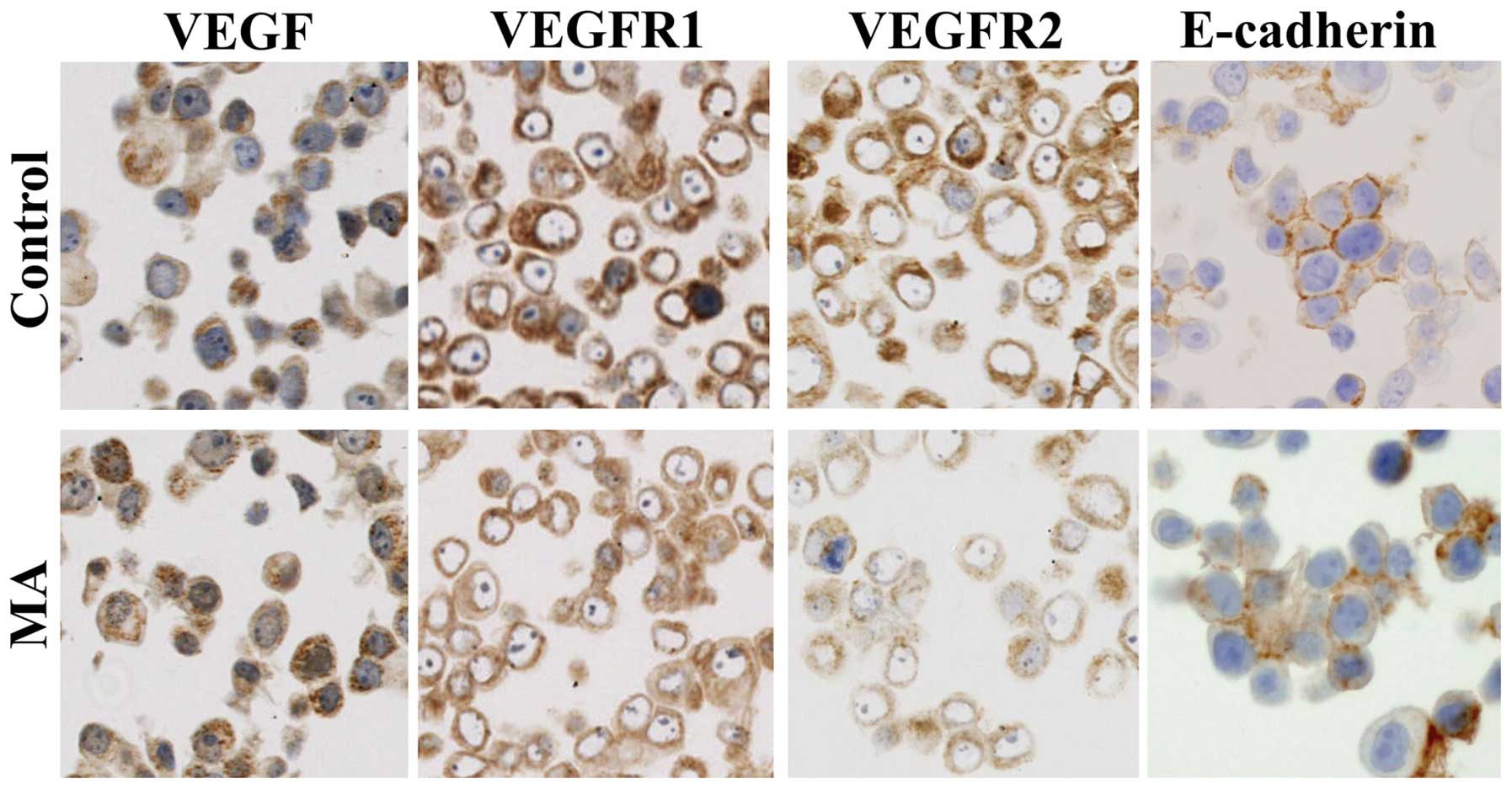
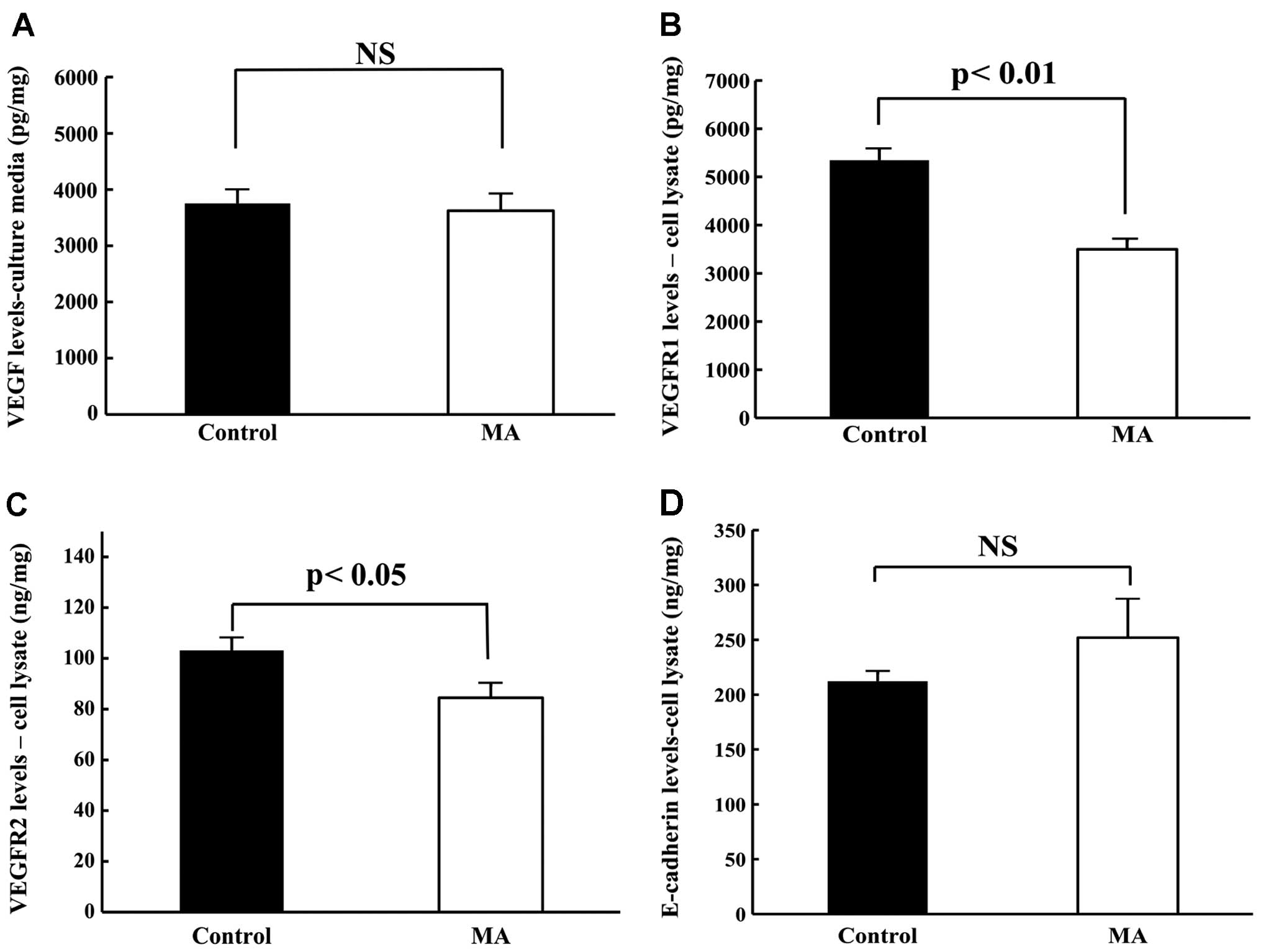
|
1
|
Adami HO, Signorello LB and Trichopoulos
D: Towards an understanding of breast cancer etiology. Semin Cancer
Biol. 8:255–262. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Tsubura A, Uehara N, Kiyozuka Y and
Shikata N: Dietary factors modifying breast cancer risk and
relation to time of intake. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia.
10:87–100. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tsubura A, Yuri T, Yoshizawa K, Uehara N
and Takada H: Role of fatty acids in malignancy and visual
impairment: epidemiological evidence and experimental studies.
Histol Histopathol. 24:223–234. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chénais B and Blanckaert V: The Janus face
of lipids in human breast cancer: how polyunsaturated fatty acids
affect tumor cell hallmarks. Int J Breast Cancer.
2012:7125362012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
de Lorgeril M and Salen P: New insights
into the health effects of dietary saturated and omega-6 and
omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids. BMC Med. 10:502012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bartsch H, Nair J and Owen RW: Dietary
polyunsaturated fatty acids and cancers of the breast and
colorectum: emerging evidence for their role as risk modifiers.
Carcinogenesis. 20:2209–2218. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yuri T, Danbara N, Tsujita-Kyutoku M,
Fukunaga K, Takada H, Inoue Y, Hada T and Tsubura A: Dietary
docosahexaenoic acid suppresses N-methyl-N-nitrosourea-induced
mammary carcinogenesis in rats more effectively than
eicosapentaenoic acid. Nutr Cancer. 45:211–217. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wen ZH, Su YC, Lai PL, Zhang Y, Xu YF,
Zhao A, Yao GY, Jia CH, Lin J, Xu S, Wang L, Wang XK, Liu AL, Jiang
Y, Dai YF and Bai XC: Critical role of arachidonic acid-activated
mTOR signaling in breast carcinogenesis and angiogenesis. Oncogene.
32:160–170. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Patterson RE, Flatt SW, Newman VA,
Natarajan L, Rock CL, Thomson CA, Caan BJ, Parker BA and Pierce JP:
Marine fatty acid intake is associated with breast cancer
prognosis. J Nutr. 141:201–206. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Signori C, El-Bayoumy K, Russo J, Thompson
HJ, Richie JP, Hartman TJ and Manni A: Chemoprevention of breast
cancer by fish oil in preclinical models: trials and tribulations.
Cancer Res. 71:6091–6096. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Senzaki H, Iwamoto S, Ogura E, Kiyozuka Y,
Arita S, Kurebayashi J, Takada H, Hioki K and Tsubura A: Dietary
effects of fatty acids on growth and metastasis of KPL-1 human
breast cancer cells in vivo and in vitro. Anticancer Res.
18:1621–1627. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chang NW, Wu CT, Chen DR, Yeh CY and Lin
C: High levels of arachidonic acid and peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor-alpha in breast cancer tissues are
associated with promoting cancer cell proliferation. J Nutr
Biochem. 24:274–281. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Taioli E, Nicolosi A and Wynder EL:
Dietary habits and breast cancer: a comparative study of United
States and Italian data. Nutr Cancer. 16:259–265. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Cohen LA, Epstein M, Pittman B and
Rivenson A: The influence of different varieties of olive oil on
N-methylnitrosourea (NMU)-induced mammary tumorigenesis. Anticancer
Res. 20:2307–2312. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Rose DP: Dietary fatty acids and cancer.
Am J Clin Nutr. 66(Suppl 4): 998S–1003S. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hamazaki T, Suzuki N, Widyowati R,
Miyahara T, Kadota S, Ochiai H and Hamazaki K: The depressive
effects of 5,8,11-eicosatrienoic acid (20:3n-9) on osteoblasts.
Lipids. 44:97–102. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hamazaki T, Nagasawa T, Hamazaki K and
Itomura M: Inhibitory effect of 5,8,11-eicosatrienoic acid on
angiogenesis. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 86:221–224.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hicklin DJ and Ellis LM: Role of the
vascular endothelial growth factor pathway in tumor growth and
angiogenesis. J Clin Oncol. 23:1011–1027. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Fox SB, Generali DG and Harris AL: Breast
tumour angiogenesis. Breast Cancer Res. 9:2162007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Sharma PS, Sharma R and Tyagi T:
VEGF/VEGFR pathway inhibitors as anti-angiogenic agents: present
and future. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 11:624–653. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Eynard AR, Jiang WG and Mansel RE:
Eicosatrienoic acid (20:3 n-9) inhibits the expression of
E-cadherin and desmoglein in human squamous cell carcinoma in
vitro. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 59:371–377. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Heyd VL and Eynard AR: Effects of
eicosatrienoic acid (20:3 n-9, Mead’s acid) on some
promalignant-related properties of three human cancer cell lines.
Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 71:177–188. 2003.
|
|
23
|
Jones J and Walker R: Cell-cell and
cell-stromal interactions in breast cancer invasion and metastasis.
Int J Oncol. 11:609–616. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Scully OJ, Bay BH, Yip G and Yu Y: Breast
cancer metastasis. Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 9:311–320. 2012.
|
|
25
|
Pidgeon GP, Lysaght J, Krishnamoorthy S,
Reynolds JV, O’Byrne K, Nie D and Honn KV: Lipoxygenase metabolism:
roles in tumor progression and survival. Cancer Metastasis Rev.
26:503–524. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hu N, Li Y, Zhao Y, Wang Q, You JC, Zhang
XD and Ye LH: A novel positive feedback loop involving
FASN/p-ERK1/2/5-LOX/LTB4/FASN sustains high growth of breast cancer
cells. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 32:921–929. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
James MJ, Gibson RA, Neumann MA and
Cleland LG: Effect of dietary supplementation with n-9
eicosatrienoic acid on leukotriene B4 synthesis in rats:
a novel approach to inhibition of eicosanoid synthesis. J Exp Med.
178:2261–2265. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Cleland LG, Gibson RA, Neumann MA,
Hamazaki T, Akimoto K and James MJ: Dietary (n-9) eicosatrienoic
acid from a cultured fungus inhibits leukotriene B4
synthesis in rats and the effect is modified by dietary linoleic
acid. J Nutr. 126:1534–1540. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Pouchieu C, Chajès V, Laporte F,
Kesse-Guyot E, Galan P, Hercberg S, Latino-Martel P and Touvier M:
Prospective associations between plasma saturated, monounsaturated
and polyunsaturated fatty acids and overall and breast cancer risk
- modulation by antioxidants: a nested case-control study. PLoS
One. 9:e904422014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Kurebayashi J, Kurosumi M and Sonoo H: A
new human breast cancer cell line, KPL-1 secretes tumour-associated
antigens and grows rapidly in female athymic nude mice. Brit J
Cancer. 71:845–853. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kurebayashi J, Kanomata N, Moriya T,
Kozuka Y, Watanabe M and Sonoo H: Preferential antitumor effect of
the Src inhibitor dasatinib associated with a decreased proportion
of aldehyde dehydrogenase 1-positive cells in breast cancer cells
of the basal B subtype. BMC Cancer. 10:5682010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Kanematsu S, Uehara N, Miki H, Yoshizawa
K, Kawanaka A, Yuri T and Tsubura A: Autophagy inhibition enhances
sulforaphane-induced apoptosis in human breast cancer cells.
Anticancer Res. 30:3381–3390. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
No authors listed. Report of the American
Institute of Nutrition Ad Hoc Committee on Standards for
Nutritional Studies. J Nutr. 107:1340–1348. 1977.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Sakuradani E, Kamada N, Hirano Y,
Nishihara M, Kawashima H, Akimoto K, Higashiyama K, Ogawa J and
Shimizu S: Production of 5,8,11-eicosatrienoic acid by a Δ5 and Δ6
desaturation activity-enhanced mutant derived from a Δ12
desaturation activity-defective mutant of Mortierella alpina
1S-4. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 60:281–287. 2002.
|
|
35
|
Bligh EG and Dyer WJ: A rapid method of
total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol.
3:911–917. 1959. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lai YC, Hamazaki K, Yoshizawa K, Kawanaka
A, Kuwata M, Kanematsu S, Hamazaki T, Takada H and Tsubura A:
Short-term pregnancy hormone treatment of
N-methyl-N-nitrosourea-induced mammary carcinogenesis
in relation to fatty acid composition of serum phospholipids in
female Lewis rats. In Vivo. 24:553–560. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Schoeffner DJ, Matheny SL, Akahane T,
Factor V, Berry A, Merlino G and Thorgeirsson UP: VEGF contributes
to mammary tumor growth in transgenic mice through paracrine and
autocrine mechanisms. Lab Invest. 85:608–623. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kanematsu S, Yoshizawa K, Uehara N, Miki
H, Sasaki T, Kuro M, Lai YC, Kimura A, Yuri T and Tsubura A:
Sulforaphane inhibits the growth of KPL-1 human breast cancer cells
in vitro and suppresses the growth and metastasis of
orthotopically transplanted KPL-1 cells in female athymic mice.
Oncol Rep. 26:603–608. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Redon CE, Weyemi U, Parekh PR, Huang D,
Burrell AS and Bonner WM: γ-H2AX and other histone
post-translational modifications in the clinic. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1819:743–756. 2012.
|
|
40
|
Perrot-Applanat M and Di Benedetto M:
Autocrine functions of VEGF in breast tumor cells: adhesion,
survival, migration and invasion. Cell Adh Migr. 6:547–553. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Price DJ, Miralem T, Jiang S, Steinberg R
and Avraham H: Role of vascular endothelial growth factor in the
stimulation of cellular invasion and signaling of breast cancer
cells. Cell Growth Differ. 12:129–135. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Weigand M, Hantel P, Kreienberg R and
Waltenberger J: Autocrine vascular endothelial growth factor
signalling in breast cancer. Evidence from cell lines and primary
breast cancer cultures in vitro. Angiogenesis. 8:197–204. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Wu Y, Hooper AT, Zhong Z, Witte L, Bohlen
P, Rafii S and Hicklin DJ: The vascular endothelial growth factor
receptor (VEGFR-1) supports growth and survival of human breast
carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 119:1519–1529. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Guo S, Colbert LS, Fuller M, Zhang Y and
Gonzalez-Perez RR: Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 in
breast cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1806:108–121. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Ghosh S, Sullivan CA, Zerkowski MP,
Molinaro AM, Rimm DL, Camp RL and Chung GG: High levels of vascular
endothelial growth factor and its receptors (VEGFR-1, VEGFR-2,
neuropilin-1) are associated with worse outcome in breast cancer.
Hum Pathol. 39:1835–1843. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Howard EM, Lau SK, Lyles RH, Birdsong GG,
Umbreit JN and Kochhar R: Expression of e-cadherin in high-risk
breast cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 131:14–18. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Wendt MK, Taylor MA, Schiemann BJ and
Schiemann WP: Downregulation of epithelial cadherin is required to
initiate metastatic outgrowth of breast cancer. Mol Biol Cell.
22:2423–2435. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Wanami LS, Chen HY, Peiró S, García de
Herreros A and Bachelder RE: Vascular endothelial growth factor-A
stimulates Snail expression in breast tumor cells: implications for
tumor progression. Exp Cell Res. 314:2448–2453. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Zhu ZR, Agren J, Männistö S, Pietinen P,
Eskelinen M, Syrjänen K and Uusitupa M: Fatty acid composition of
breast adipose tissue in breast cancer patients and in patients
with benign breast disease. Nutr Cancer. 24:151–160. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Maillard V, Bougnoux P, Ferrari P, Jourdan
ML, Pinault M, Lavillonnière F, Body G, Le Floch O and Chajès V:
N-3 and N-6 fatty acids in breast adipose tissue and relative risk
of breast cancer in a case-control study in Tours, France. Int J
Cancer. 98:78–83. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Okuyama H, Kobayashi T and Watanabe S:
Dietary fatty acids - the n-6/n-3 balance and chronic elderly
diseases. Excess linoleic acid and relative n-3 deficiency syndrome
seen in Japan. Prog Lipid Res. 35:409–457. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Cleland LG, Neumann MA, Gibson RA,
Hamazaki T, Akimoto K and James MJ: Effect of dietary n-9
eicosatrienoic acid on the fatty acid composition of plasma lipid
fractions and tissue phospholipids. Lipids. 31:829–837. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Ip C, Carter CA and Ip MM: Requirement of
essential fatty acid for mammary tumorigenesis in the rat. Cancer
Res. 45:1997–2001. 1985.PubMed/NCBI
|