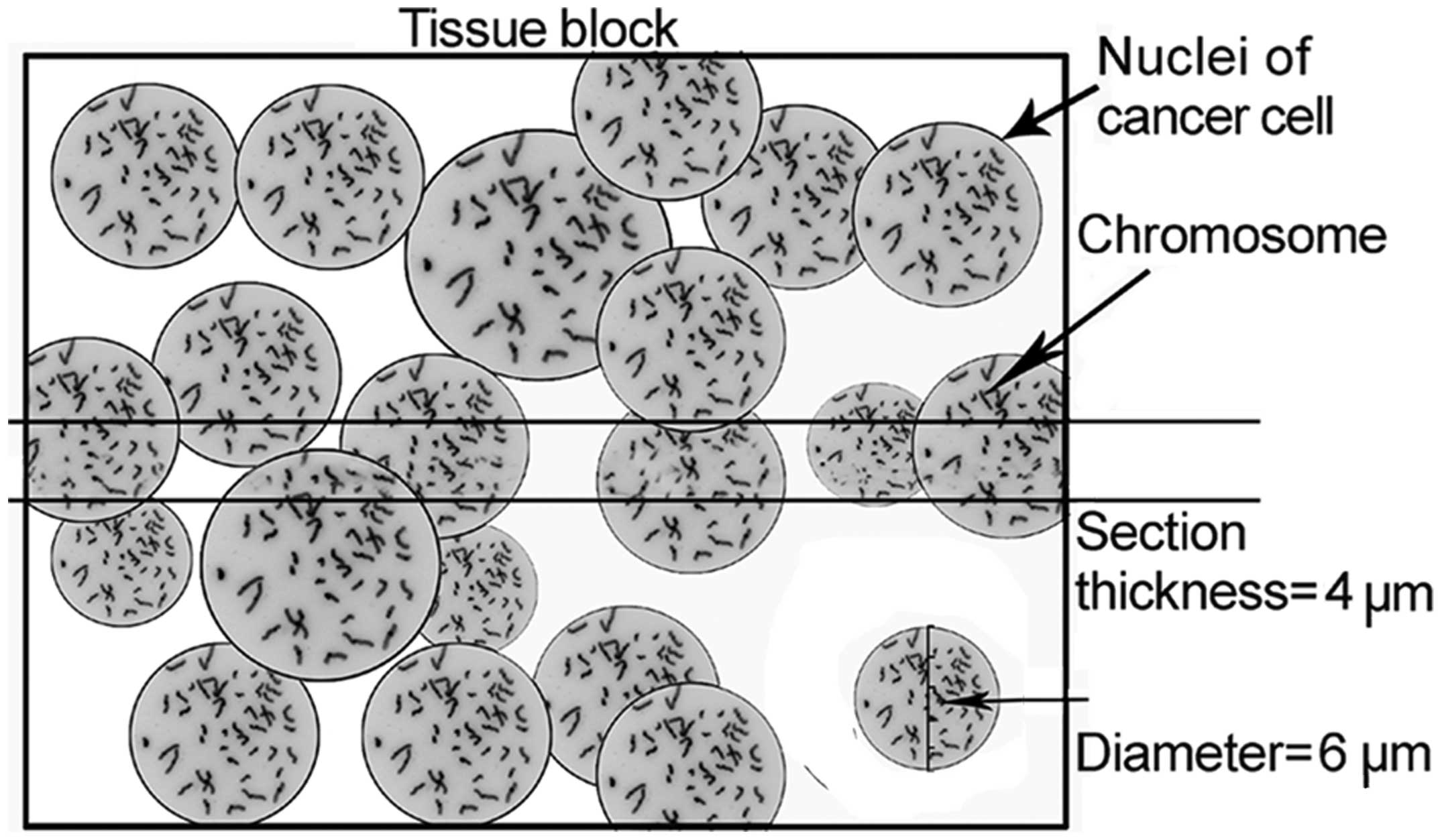
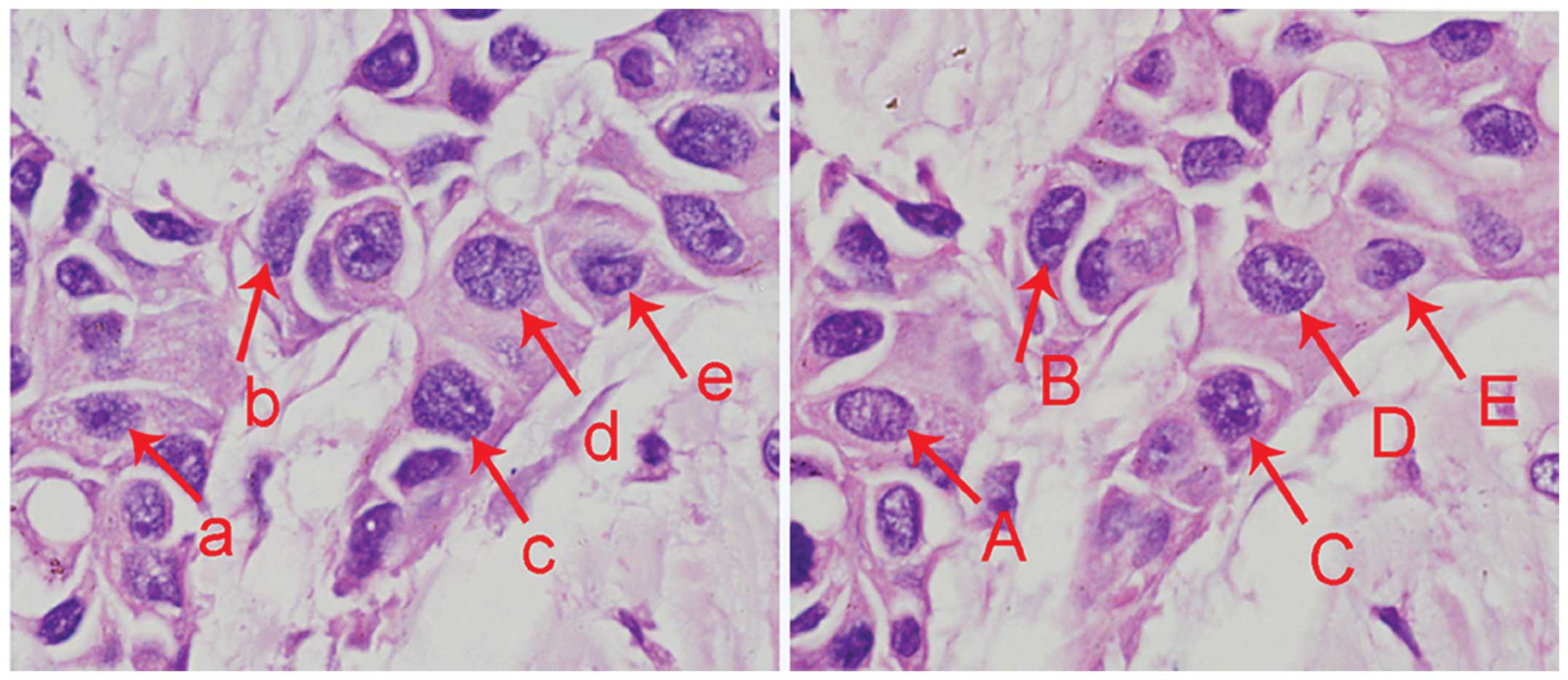
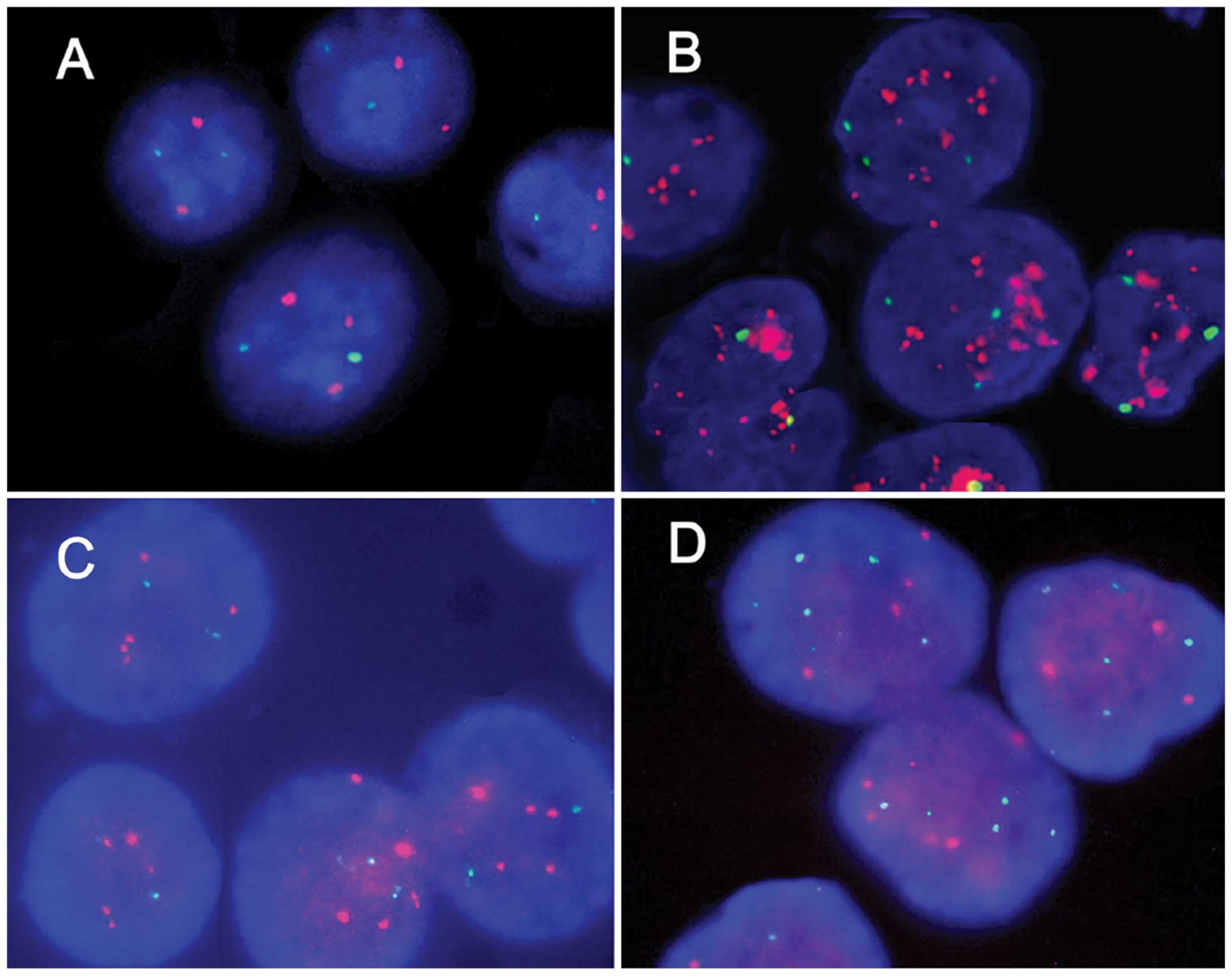
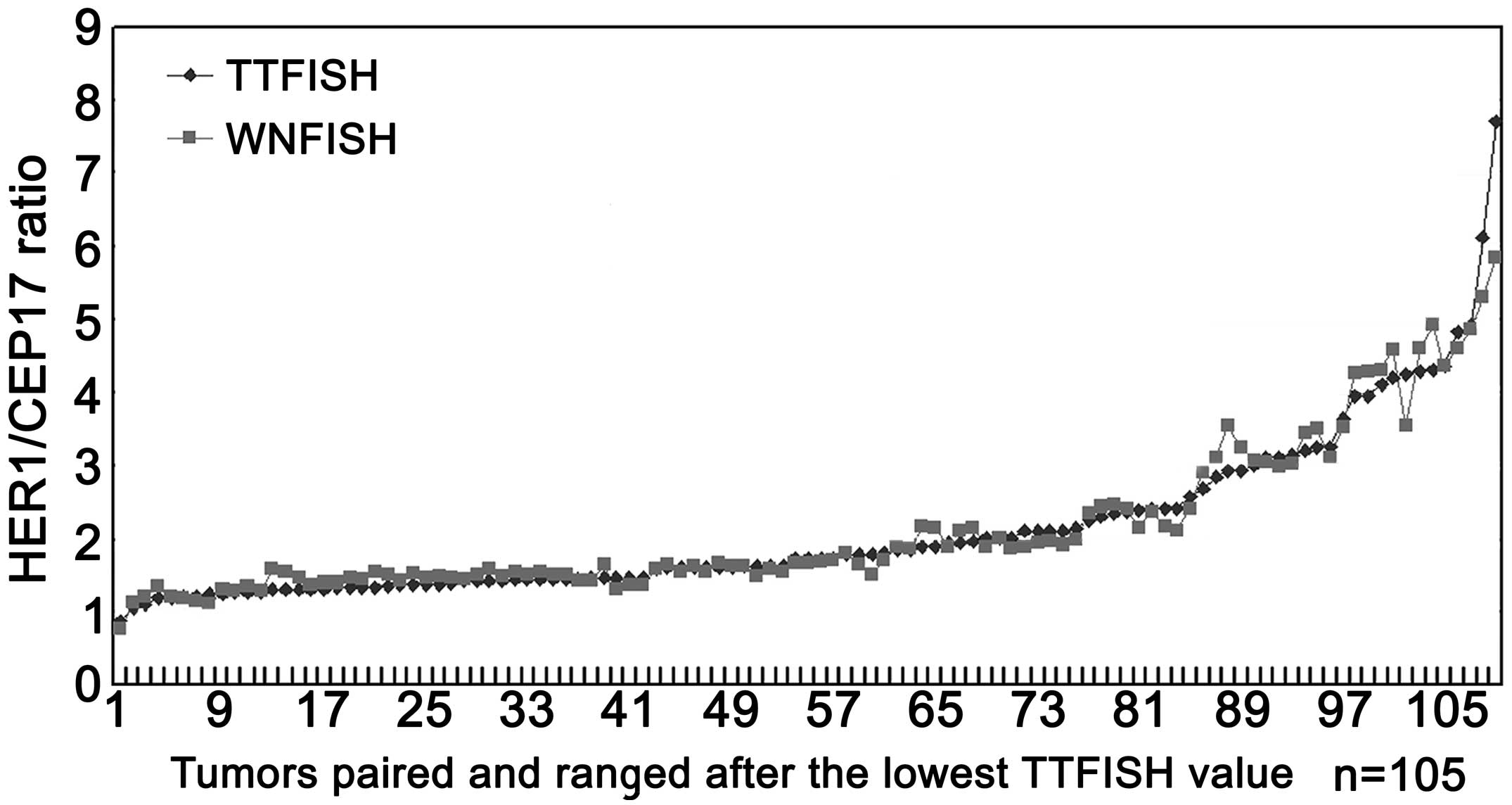
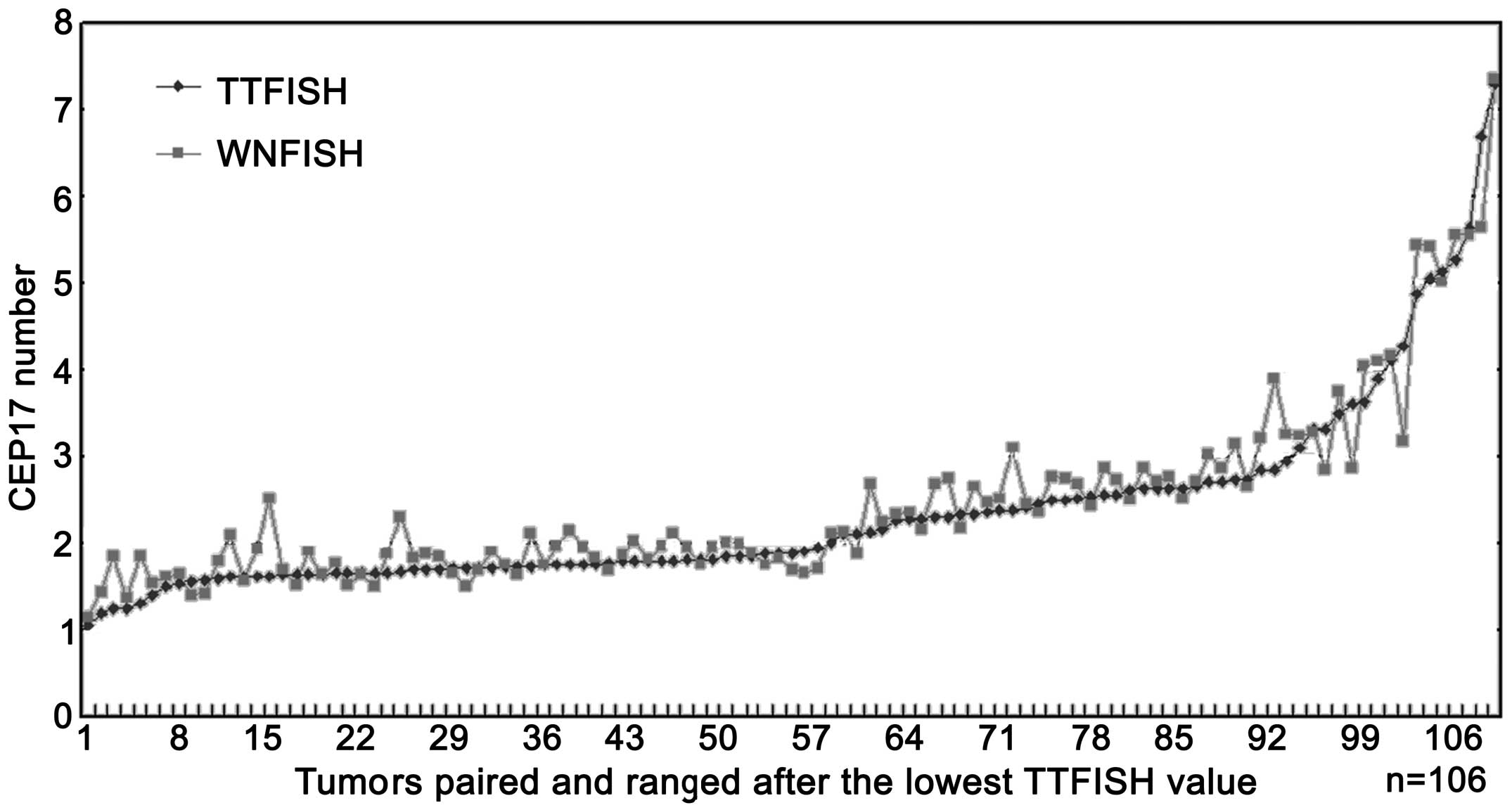
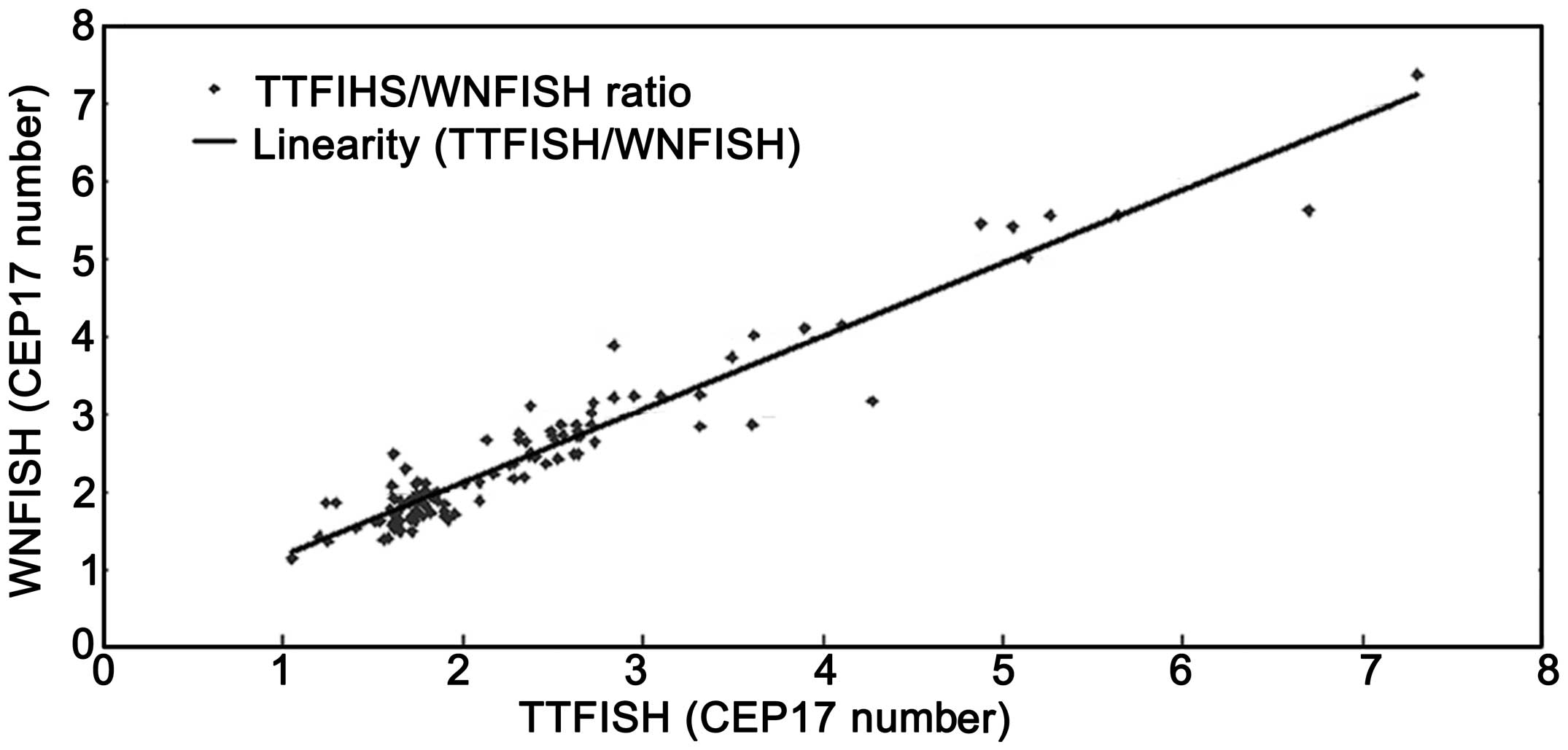
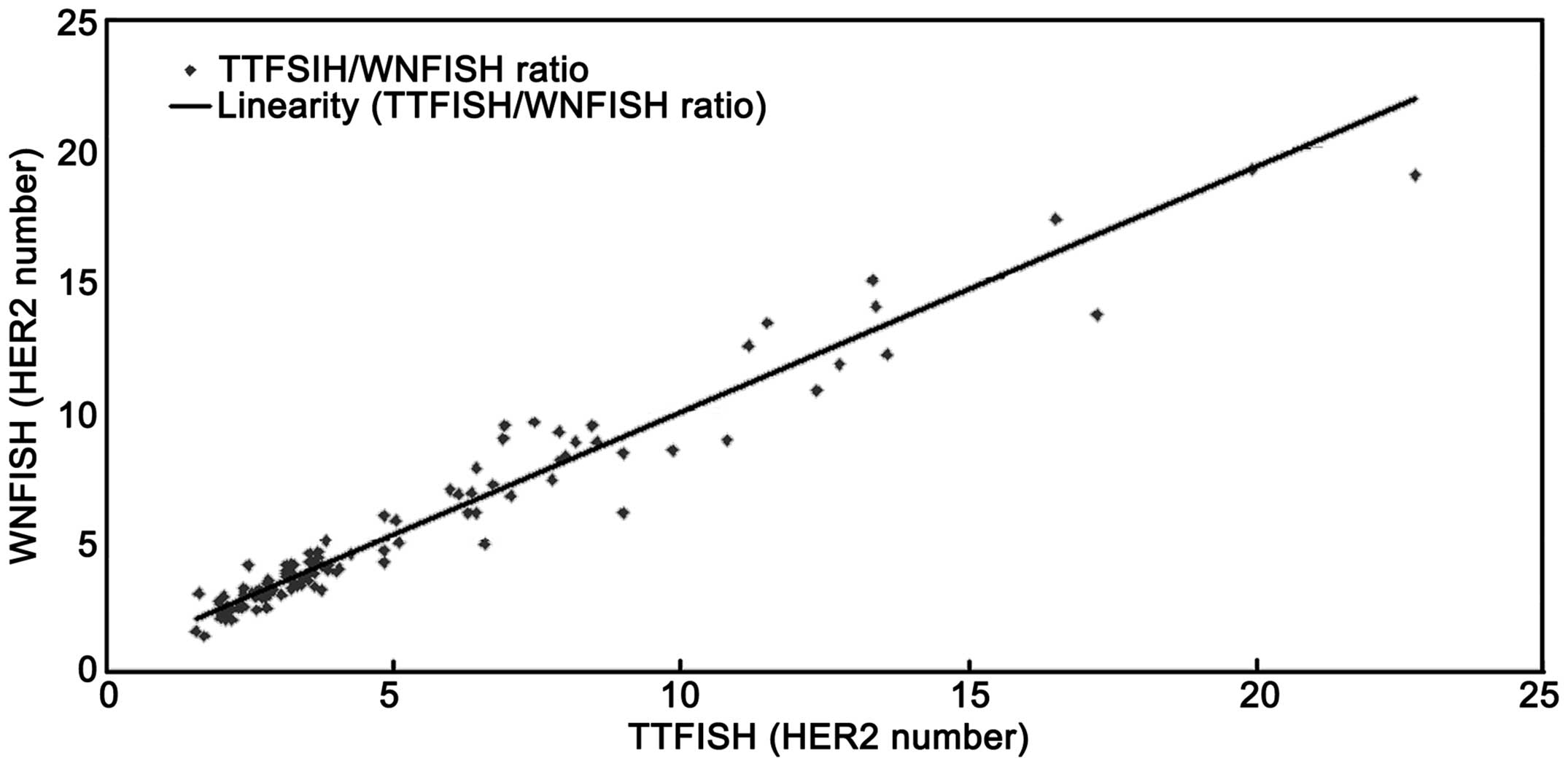
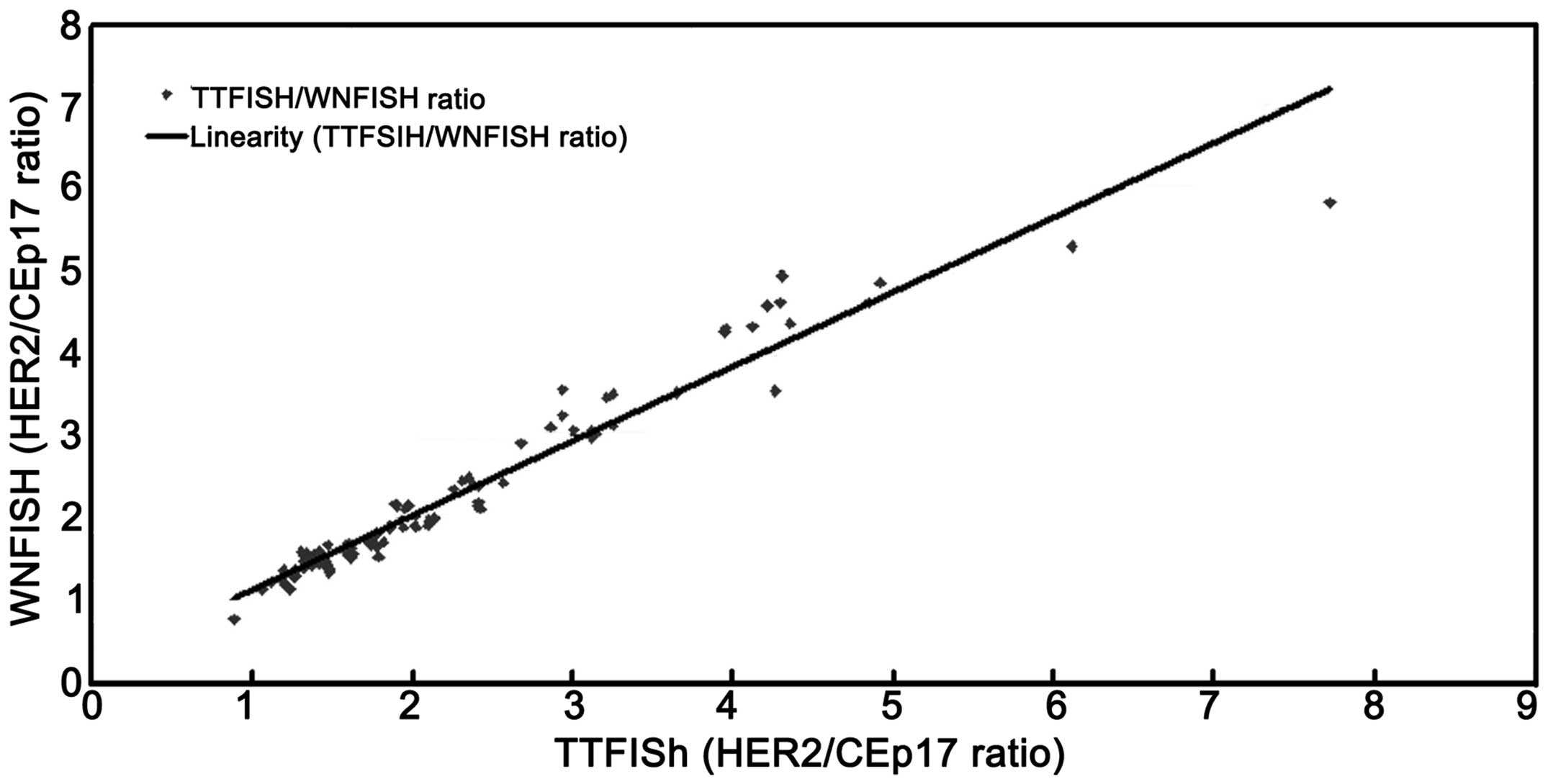
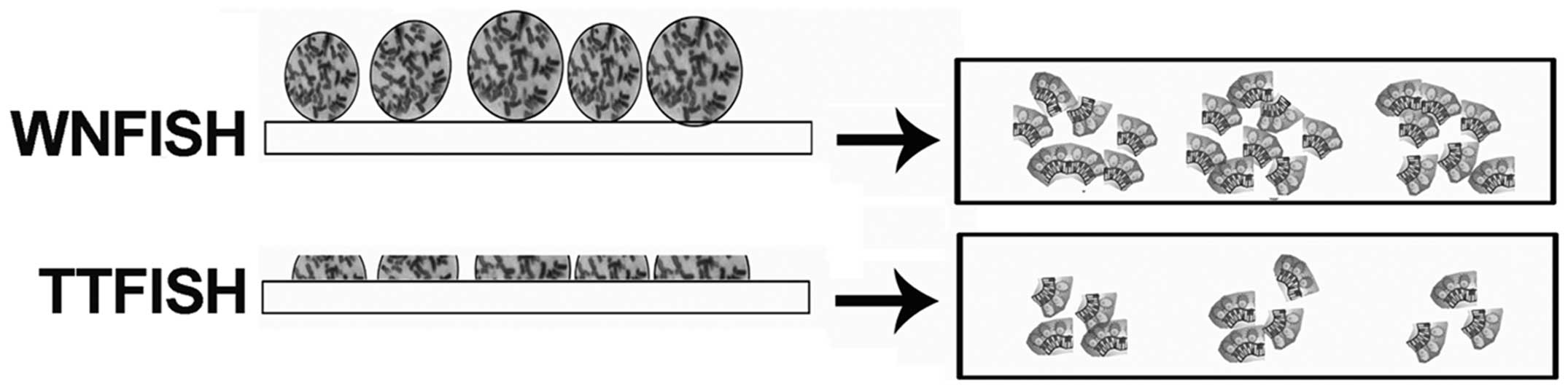
|
1
|
Gschwind A, Fischer OM and Ullrich A: The
discovery of receptor tyrosine kinases: targets for cancer therapy.
Nat Rev Cancer. 4:361–370. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lal P, Salazar PA, Hudis CA, Ladanyi M and
Chen B: HER-2 testing in breast cancer using immunohistochemical
analysis and fluorescence in situ hybridization: a
single-institution experience of 2,279 cases and comparison of
dual-color and single-color scoring. Am J Clin Pathol. 121:631–636.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Owens MA, Horten BC and Da Silva MM: HER2
amplification ratios by fluorescence in situ hybridization and
correlation with immunohistochemistry in a cohort of 6556 breast
cancer tissues. Clin Breast Cancer. 5:63–69. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yaziji H, Goldstein LC, Barry TS, et al:
HER-2 testing in breast cancer using parallel tissue-based methods.
JAMA. 291:1972–1977. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Baselga J, Bradbury I, Eidtmann H, et al:
Lapatinib with trastuzumab for HER2-positive early breast cancer
(NeoALTTO): a randomised, open-label, multicentre, phase 3 trial.
Lancet. 379:633–640. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Valabrega G, Capellero S, Cavalloni G, et
al: HER2-positive breast cancer cells resistant to trastuzumab and
lapatinib lose reliance upon HER2 and are sensitive to the
multitargeted kinase inhibitor sorafenib. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
130:29–40. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Carr JA, Havstad S, Zarbo RJ, Divine G,
Mackowiak P and Velanovich V: The association of HER-2/neu
amplification with breast cancer recurrence. Arch Surg.
135:1469–1474. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Arteaga CL, Sliwkowski MX, Osborne CK,
Perez EA, Puglisi F and Gianni L: Treatment of HER2-positive breast
cancer: current status and future perspectives. Nat Rev Clin Oncol.
9:16–32. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wolff AC, Hammond ME, Schwartz JN, et al:
American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American
Pathologists guideline recommendations for human epidermal growth
factor receptor 2 testing in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol.
25:118–145. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Ohlschlegel C, Zahel K, Kradolfer D, Hell
M and Jochum W: HER2 genetic heterogeneity in breast
carcinoma. J Clin Pathol. 64:1112–1116. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Dal Lago L, Durbecq V, Desmedt C, et al:
Correction for chromosome-17 is critical for the determination of
true Her-2/neu gene amplification status in breast cancer. Mol
Cancer Ther. 5:2572–2579. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ma Y, Lespagnard L, Durbecq V, et al:
Polysomy 17 in HER-2/neu status elaboration in breast
cancer: effect on daily practice. Clin Cancer Res. 11:4393–4399.
2005.
|
|
13
|
Reddy JC, Reimann JD, Anderson SM and
Klein PM: Concordance between central and local laboratory HER2
testing from a community-based clinical study. Clin Breast Cancer.
7:153–157. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Reinholz MM, Bruzek AK, Visscher DW, et
al: Breast cancer and aneusomy 17: implications for carcinogenesis
and therapeutic response. Lancet Oncol. 10:267–277. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhang W and Yu Y: The important molecular
markers on chromosome 17 and their clinical impact in breast
cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 12:5672–5683. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Downs-Kelly E, Yoder BJ, Stoler M, et al:
The influence of polysomy 17 on HER2 gene and protein expression in
adenocarcinoma of the breast: a fluorescent in situ hybridization,
immunohistochemical, and isotopic mRNA in situ hybridization study.
Am J Surg Pathol. 29:1221–1227. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Bose S, Mohammed M, Shintaku P and Rao PN:
Her-2/neu gene amplification in low to moderately expressing breast
cancers: possible role of chromosome 17/Her-2/neu polysomy. Breast
J. 7:337–344. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Farabegoli F, Ceccarelli C, Santini D, et
al: c-erbB-2 over-expression in amplified and non-amplified breast
carcinoma samples. Int J Cancer. 84:273–277. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Pritchard KI, Munro A, O’Malley FP, et al:
Chromosome 17 centromere (CEP17) duplication as a predictor of
anthracycline response: evidence from the NCIC Clinical Trials
Group (NCIC CTG) MA.5 Trial. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 131:541–551.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lal P, Salazar PA, Ladanyi M and Chen B:
Impact of polysomy 17 on HER-2/neu immunohistochemistry in breast
carcinomas without HER-2/neu gene amplification. J Mol Diagn.
5:155–159. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Varshney D, Zhou YY, Geller SA and Alsabeh
R: Determination of HER-2 status and chromosome 17 polysomy in
breast carcinomas comparing HercepTest and PathVysion FISH assay.
Am J Clin Pathol. 121:70–77. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Rosenberg CL: Polysomy 17 and HER-2
amplification: true, true, and unrelated. J Clin Oncol.
26:4856–4858. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Vanden Bempt I, Van Loo P, Drijkoningen M,
et al: Polysomy 17 in breast cancer: clinicopathologic significance
and impact on HER-2 testing. J Clin Oncol. 26:4869–4874.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Pritchard KI, Shepherd LE, O’Malley FP, et
al: HER2 and responsiveness of breast cancer to adjuvant
chemotherapy. N Engl J Med. 354:2103–2111. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Shah SS, Wang Y, Tull J and Zhang S:
Effect of high copy number of HER2 associated with polysomy 17 on
HER2 protein expression in invasive breast carcinoma. Diagn Mol
Pathol. 18:30–33. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kouvaras E, Papandreou CN, Daliani DD,
Athanasiadis A and Koukoulis GK: Comparative study of spatial
localization of HER-2 and CEP17 signals and of HER-2/CEP17 ratios,
in ‘thin’ and ‘thick’ tissue sections. Breast. 21:34–39.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Tse CH, Hwang HC, Goldstein LC, et al:
Determining true HER2 gene status in breast cancers with
polysomy by using alternative chromosome 17 reference genes:
implications for anti-HER2 targeted therapy. J Clin Oncol.
29:4168–4174. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
JRL and GGK: A one-way components of
variance model for categorical data. Biometrics. 334:671–679.
1977.
|
|
29
|
Watters AD, Going JJ, Cooke TG and
Bartlett JM: Chromosome 17 aneusomy is associated with poor
prognostic factors in invasive breast carcinoma. Breast Cancer Res
Treat. 77:109–114. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|