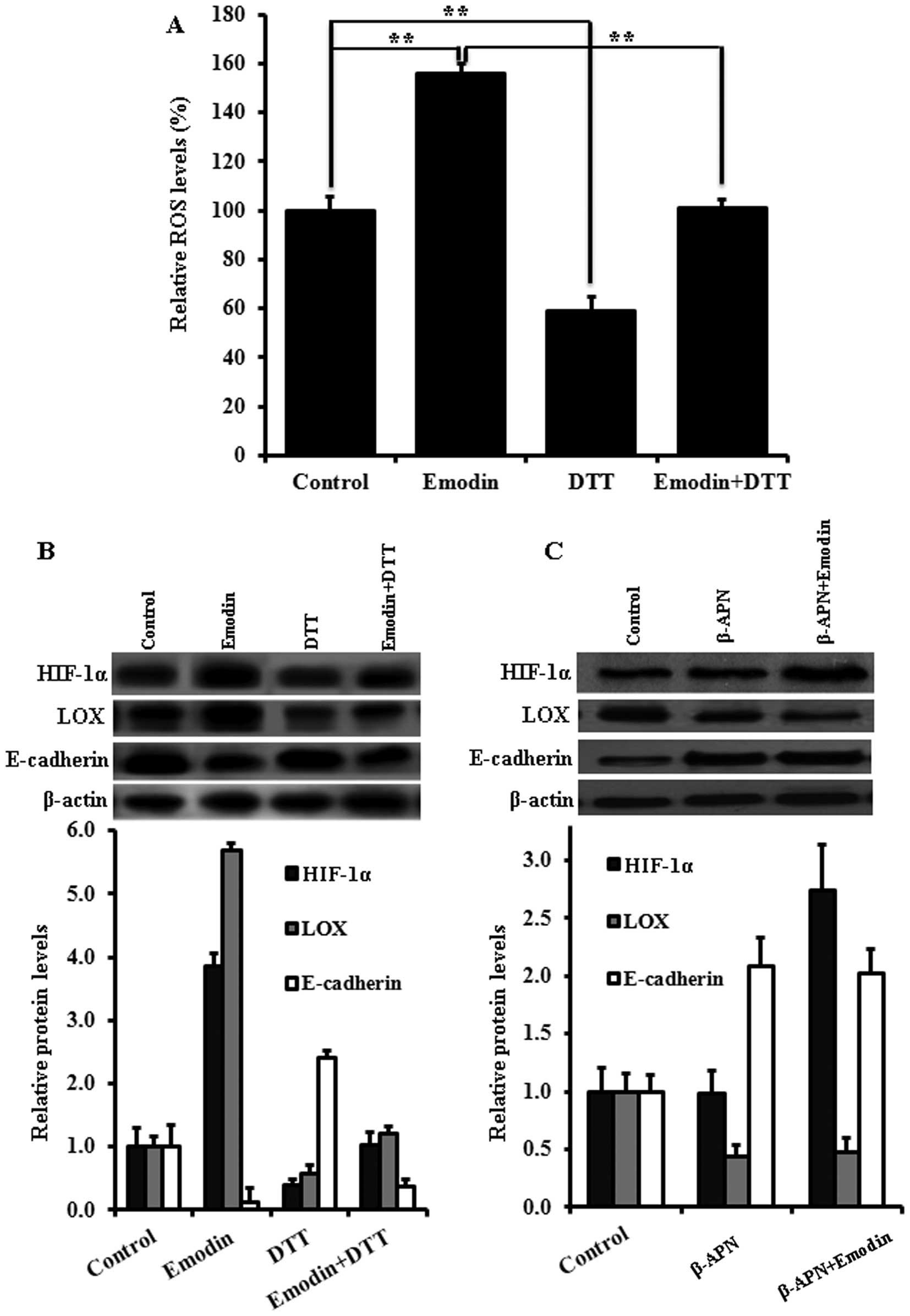
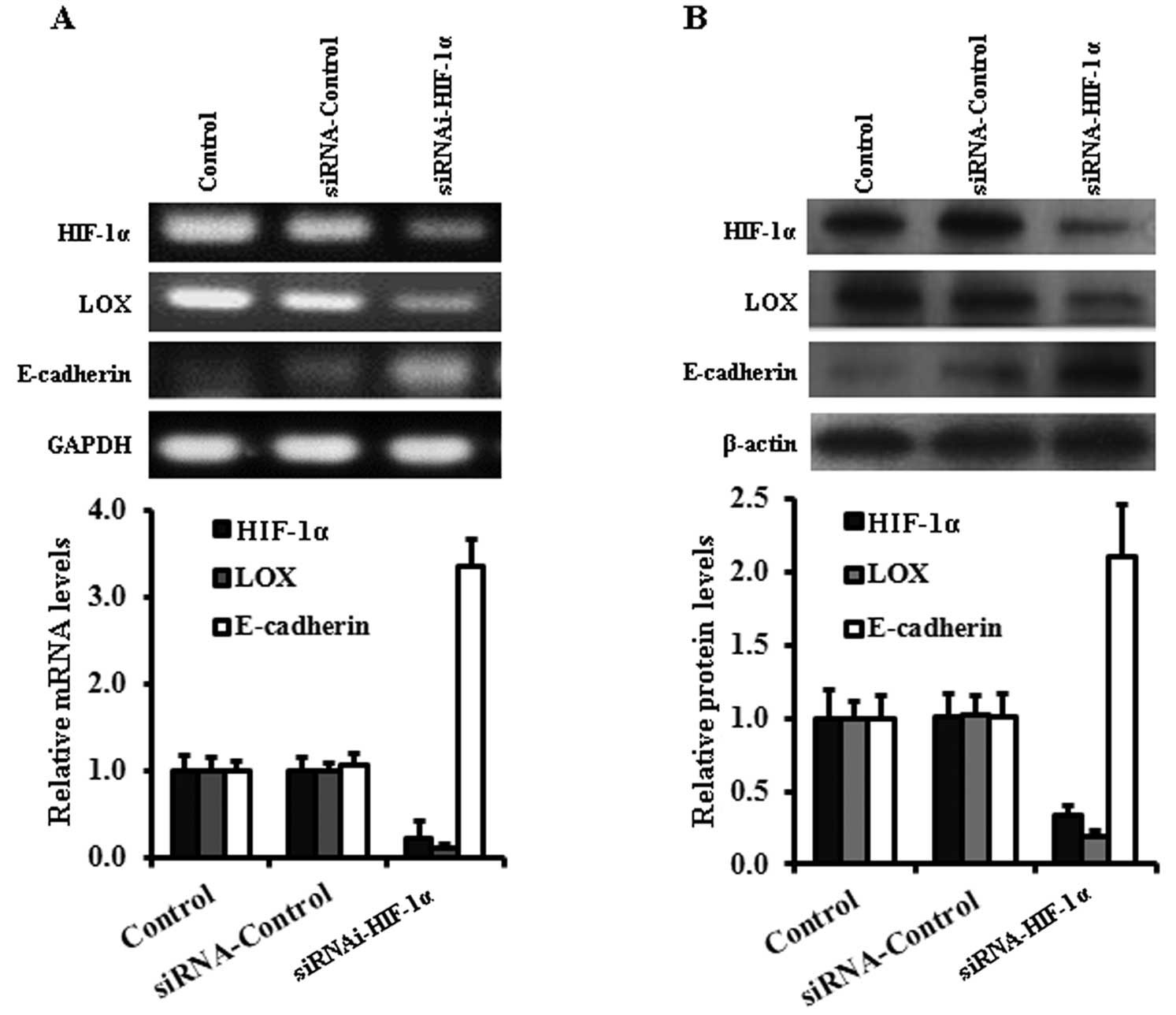
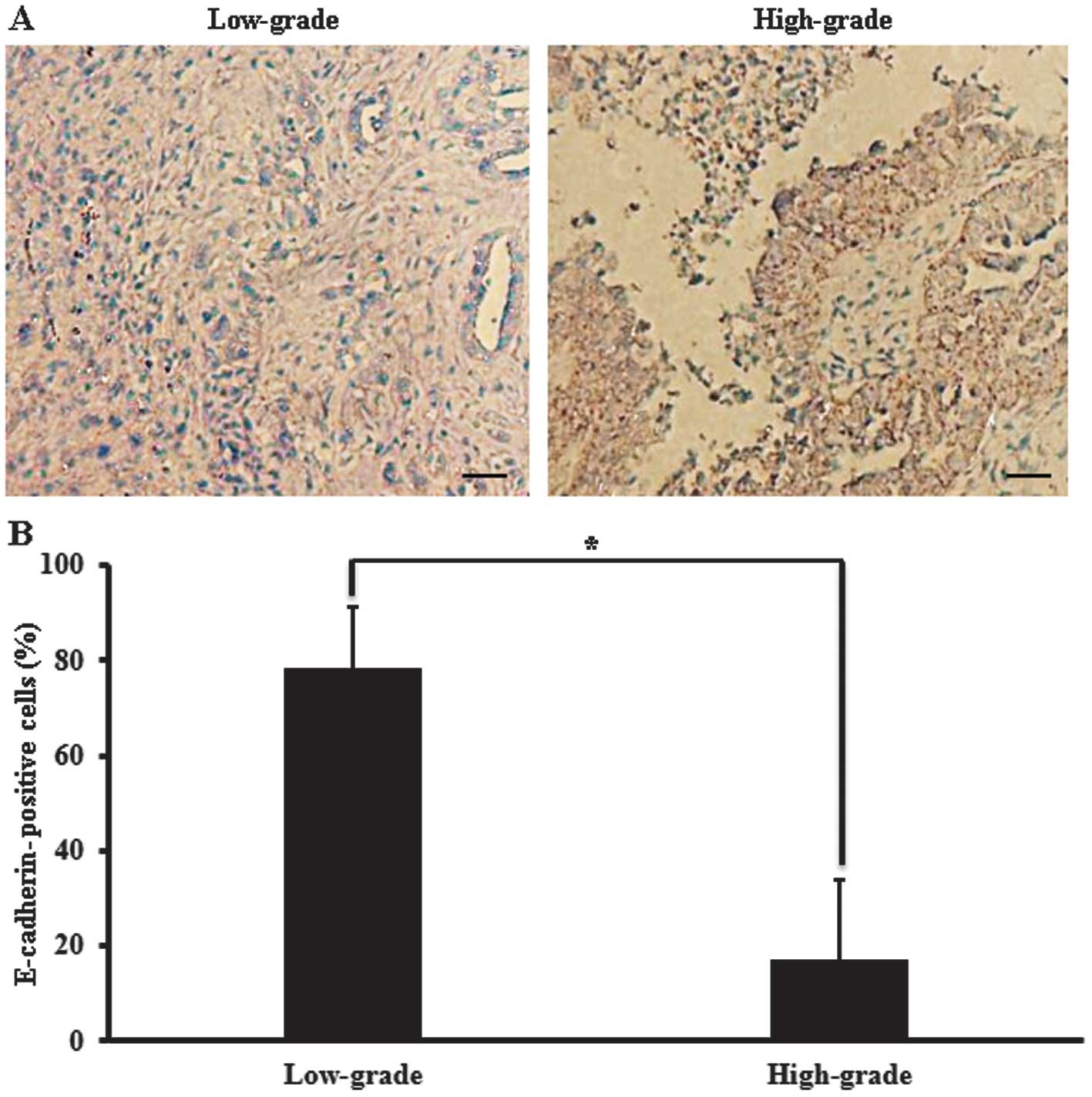
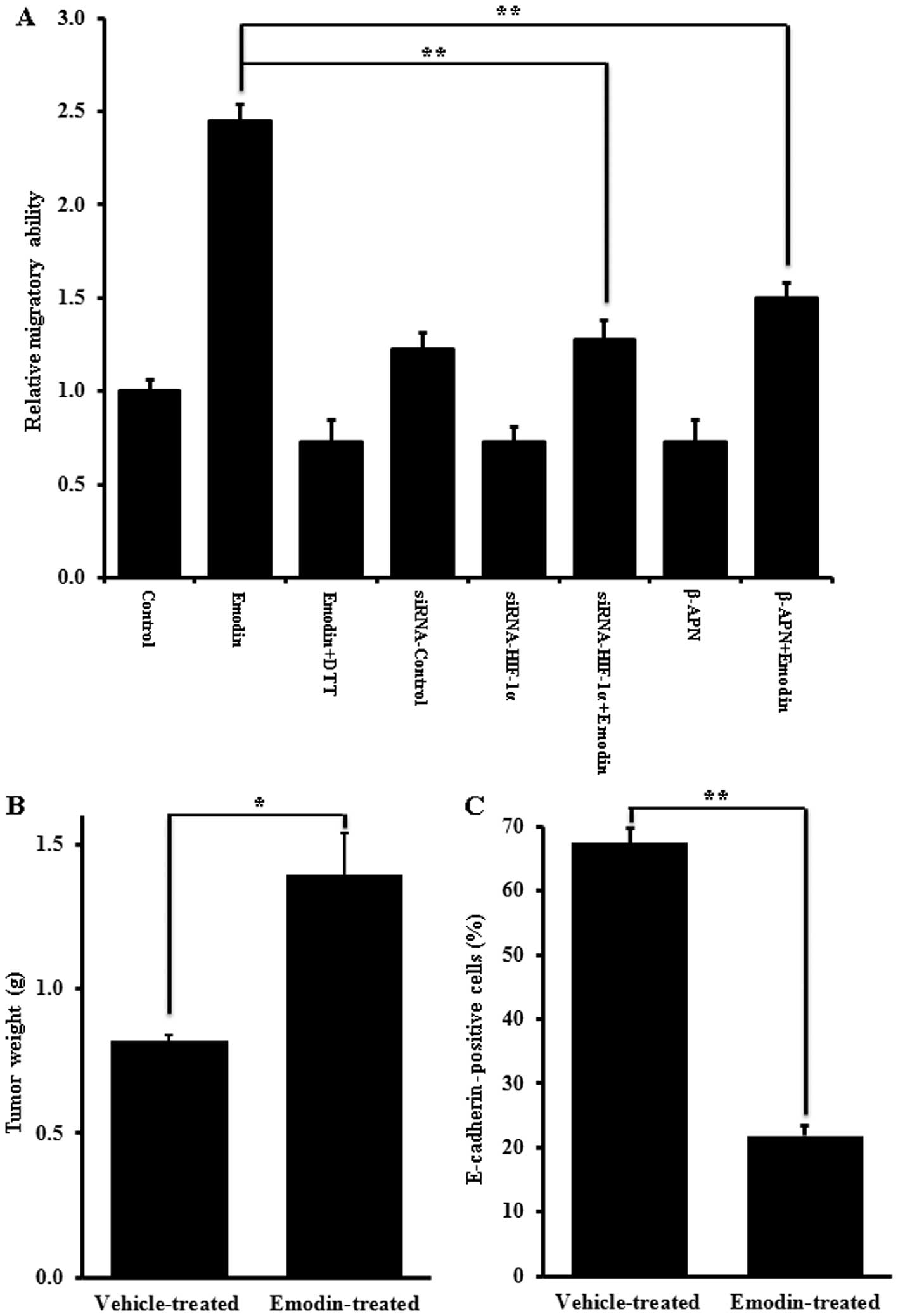
|
1
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 63:11–30. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Thibault B, Castells M, Delord JP and
Couderc B: Ovarian cancer microenvironment: implications for cancer
dissemination and chemoresistance acquisition. Cancer Metastasis
Rev. Dec 20–2013.(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
3
|
Ozols RF, Bundy BN, Greer BE, et al: Phase
III trial of carboplatin and paclitaxel compared with cisplatin and
paclitaxel in patients with optimally resected stage III ovarian
cancer: a Gynecologic Oncology Group study. J Clin Oncol.
21:3194–3200. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Garcia AA, Hirte H, Fleming G, et al:
Phase II clinical trial of bevacizumab and low-dose metronomic oral
cyclophosphamide in recurrent ovarian cancer: a trial of the
California, Chicago, and Princess Margaret Hospital phase II
consortia. J Clin Oncol. 26:76–82. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Penson RT, Dizon DS, Cannistra SA, et al:
Phase II study of carboplatin, paclitaxel, and bevacizumab with
maintenance bevacizumab as first-line chemotherapy for advanced
mullerian tumors. J Clin Oncol. 28:154–159. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Berkenblit A, Seiden MV, Matulonis UA, et
al: A phase II trial of weekly docetaxel in patients with
platinum-resistant epithelial ovarian, primary peritoneal serous
cancer, or fallopian tube cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 95:624–631. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Agarwal R and Kaye SB: Ovarian cancer:
strategies for overcoming resistance to chemotherapy. Nat Rev
Cancer. 3:502–516. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Cannistra SA: Cancer of the ovary. N Engl
J Med. 351:2519–2529. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hennessy BT, Coleman RL and Markman M:
Ovarian cancer. Lancet. 374:1371–1382. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Joyce JA and Pollard JW:
Microenvironmental regulation of metastasis. Nat Rev Cancer.
9:239–252. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Vaupel P, Kallinowski F and Okunieff P:
Blood flow, oxygen and nutrient supply, and metabolic
microenvironment of human tumors: a review. Cancer Res.
49:6449–6465. 1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Anderson AR, Weaver AM, Cummings PT and
Quaranta V: Tumor morphology and phenotypic evolution driven by
selective pressure from the microenvironment. Cell. 127:905–915.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Rademakers SE, Span PN, Kaanders JH, Sweep
FC, van der Kogel AJ and Bussink J: Molecular aspects of tumour
hypoxia. Mol Oncol. 2:41–53. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Chan DA, Sutphin PD, Yen SE and Giaccia
AJ: Coordinate regulation of the oxygen-dependent degradation
domains of hypoxia-inducible factor 1α. Mol Cell Biol.
25:6415–6426. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ratcliffe PJ, O’Rourke JF, Maxwell PH and
Pugh CW: Oxygen sensing, hypoxia-inducible factor-1 and the
regulation of mammalian gene expression. J Exp Biol. 201:1153–1162.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Semenza GL: Defining the role of
hypoxia-inducible factor 1 in cancer biology and therapeutics.
Oncogene. 29:625–634. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bell EL, Klimova TA, Eisenbart J, et al:
The Qo site of the mitochondrial complex III is required for the
transduction of hypoxic signaling via reactive oxygen species
production. J Cell Biol. 177:1029–1036. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chandel NS, McClintock DS, Feliciano CE,
et al: Reactive oxygen species generated at mitochondrial complex
III stabilize hypoxia-inducible factor-1α during hypoxia: a
mechanism of O2 sensing. J Biol Chem. 275:25130–25138.
2000.
|
|
19
|
Callapina M, Zhou J, Schmid T, Köhl R and
Brüne B: NO restores HIF-1α hydroxylation during hypoxia: role of
reactive oxygen species. Free Radic Biol Med. 39:925–936. 2005.
|
|
20
|
Erler JT, Bennewith KL, Nicolau M, et al:
Lysyl oxidase is essential for hypoxia-induced metastasis. Nature.
440:1222–1226. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Stewart GD, Gray K, Pennington CJ, et al:
Analysis of hypoxia-associated gene expression in prostate cancer:
lysyl oxidase and glucose transporter-1 expression correlate with
Gleason score. Oncol Rep. 20:1561–1567. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Schietke R, Warnecke C, Wacker I, et al:
The lysyl oxidases LOX and LOXL2 are necessary and sufficient to
repress E-cadherin in hypoxia: insights into cellular
transformation processes mediated by HIF-1. J Biol Chem.
285:6658–6669. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Pez F, Dayan F, Durivault J, et al: The
HIF-1-inducible lysyl oxidase activates HIF-1 via the Akt pathway
in a positive regulation loop and synergizes with HIF-1 in
promoting tumor cell growth. Cancer Res. 71:1647–1657. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ji F, Wang Y, Qiu L, et al: Hypoxia
inducible factor 1α-mediated LOX expression correlates with
migration and invasion in epithelial ovarian cancer. Int J Oncol.
42:1578–1588. 2013.
|
|
25
|
Wang V, Davis DA, Haque M, Huang LE and
Yarchoan R: Differential gene up-regulation by hypoxia-inducible
factor-1α and hypoxia-inducible factor-2α in HEK293T cells. Cancer
Res. 65:3299–3306. 2005.
|
|
26
|
Elvidge GP, Glenny L, Appelhoff RJ,
Ratcliffe PJ, Ragoussis J and Gleadle JM: Concordant regulation of
gene expression by hypoxia and 2-oxoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase
inhibition: the role of HIF-1α, HIF-2α, and other pathways. J Biol
Chem. 281:15215–15226. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Warnecke C, Weidemann A, Volke M, et al:
The specific contribution of hypoxia-inducible factor-2α to hypoxic
gene expression in vitro is limited and modulated by cell
type-specific and exogenous factors. Exp Cell Res. 314:2016–2027.
2008.
|
|
28
|
Kagan HM and Li W: Lysyl oxidase:
properties, specificity, and biological roles inside and outside of
the cell. J Cell Biochem. 88:660–672. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Payne SL, Hendrix MJ and Kirschmann DA:
Paradoxical roles for lysyl oxidases in cancer - a prospect. J Cell
Biochem. 101:1338–1354. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Polgar N, Fogelgren B, Shipley JM and
Csiszar K: Lysyl oxidase interacts with hormone placental lactogen
and synergistically promotes breast epithelial cell proliferation
and migration. J Biol Chem. 282:3262–3272. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sullivan R and Graham CH: Hypoxia-driven
selection of the metastatic phenotype. Cancer Metastasis Rev.
26:319–331. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Axelson H, Fredlund E, Ovenberger M,
Landberg G and Påhlman S: Hypoxia-induced dedifferentiation of
tumor cells - a mechanism behind heterogeneity and aggressiveness
of solid tumors. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 16:554–563. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: the next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Imai T, Horiuchi A, Wang C, et al: Hypoxia
attenuates the expression of E-cadherin via up-regulation of SNAIL
in ovarian carcinoma cells. Am J Pathol. 163:1437–1447. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Esteban MA, Tran MG, Harten SK, et al:
Regulation of E-cadherin expression by VHL and
hypoxia-inducible factor. Cancer Res. 66:3567–3575. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Krishnamachary B, Zagzag D, Nagasawa H, et
al: Hypoxia-inducible factor-1-dependent repression of
E-cadherin in von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor-null renal
cell carcinoma mediated by TCF3, ZFHX1A, and ZFHX1B. Cancer Res.
66:2725–2731. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Peinado H, Del Carmen Iglesias-de la Cruz
M, Olmeda D, et al: A molecular role for lysyl oxidase-like 2
enzyme in snail regulation and tumor progression. EMBO J.
24:3446–3458. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Peng HL, He L and Zhao X: Association of
reduced immunohistochemical expression of E-cadherin with a poor
ovarian cancer prognosis - results of a meta-analysis. Asian Pac J
Cancer Prev. 13:2003–2007. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Cai J, Niu X, Chen Y, et al:
Emodin-induced generation of reactive oxygen species inhibits RhoA
activation to sensitize gastric carcinoma cells to anoikis.
Neoplasia. 10:41–51. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Dinh P, Harnett P, Piccart-Gebhart MJ and
Awada A: New therapies for ovarian cancer: cytotoxics and
molecularly targeted agents. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 67:103–112.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Galanis A, Pappa A, Giannakakis A, Lanitis
E, Dangaj D and Sandaltzopoulos R: Reactive oxygen species and
HIF-1 signalling in cancer. Cancer Lett. 266:12–20. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Kirschmann DA, Seftor EA, Fong SF, et al:
A molecular role for lysyl oxidase in breast cancer invasion.
Cancer Res. 62:4478–4483. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Yoon SO, Park SJ, Yoon SY, Yun CH and
Chung AS: Sustained production of H2O2
activates pro-matrix metalloproteinase-2 through receptor tyrosine
kinases/phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/NF-κB pathway. J Biol Chem.
277:30271–30282. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Woznick AR, Braddock AL, Dulai M, et al:
Lysyl oxidase expression in bronchogenic carcinoma. Am J Surg.
189:297–301. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|