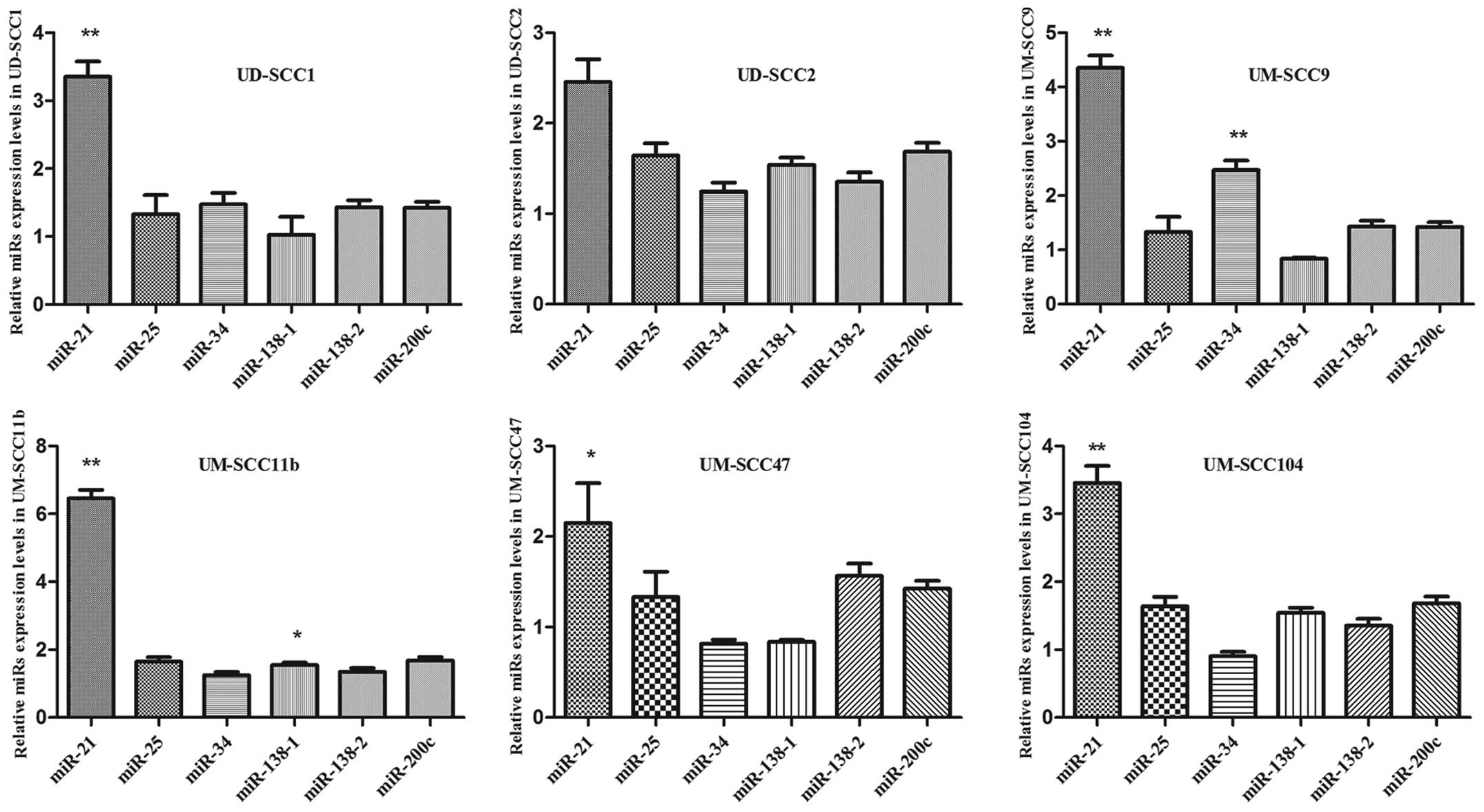
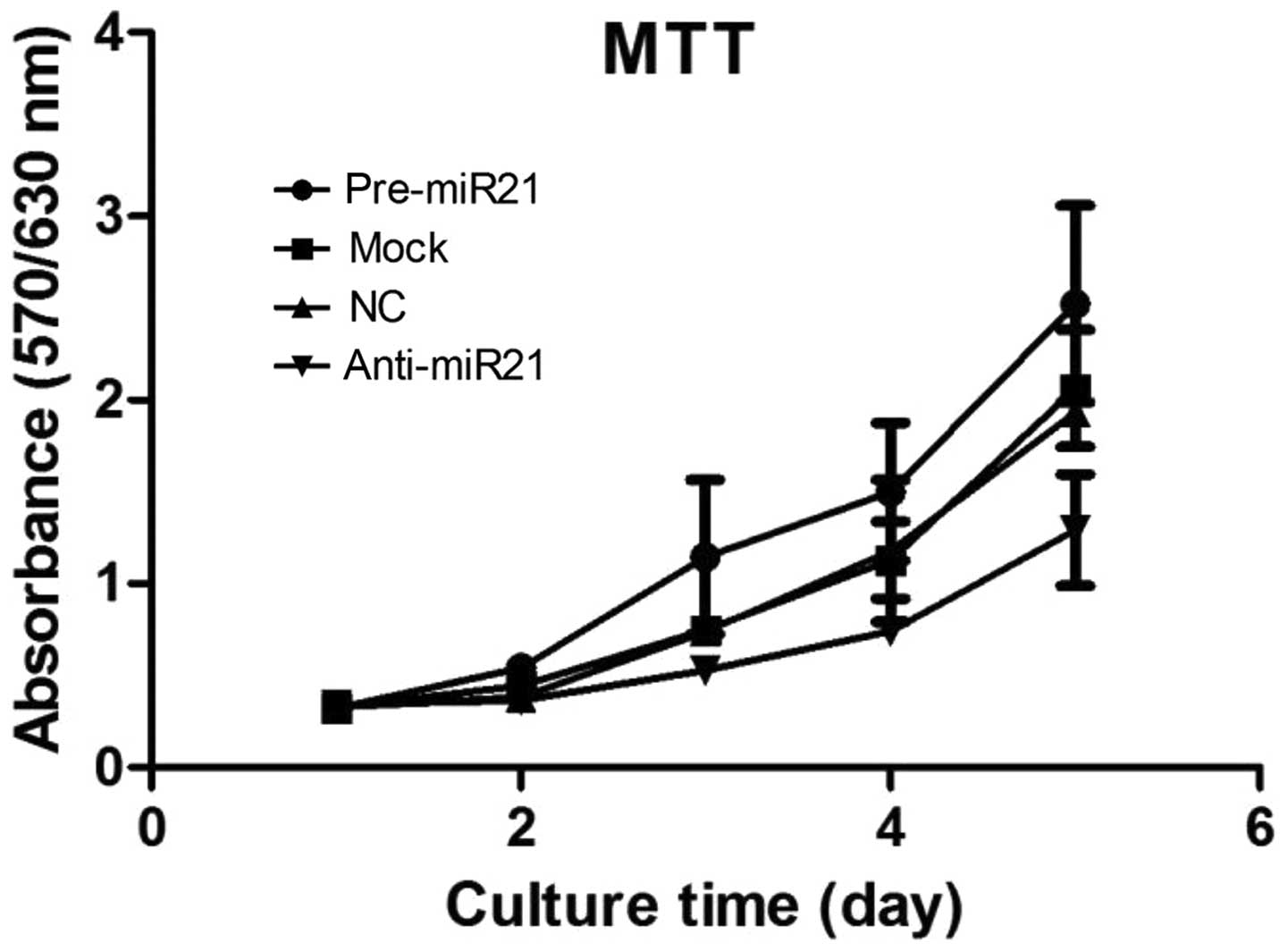
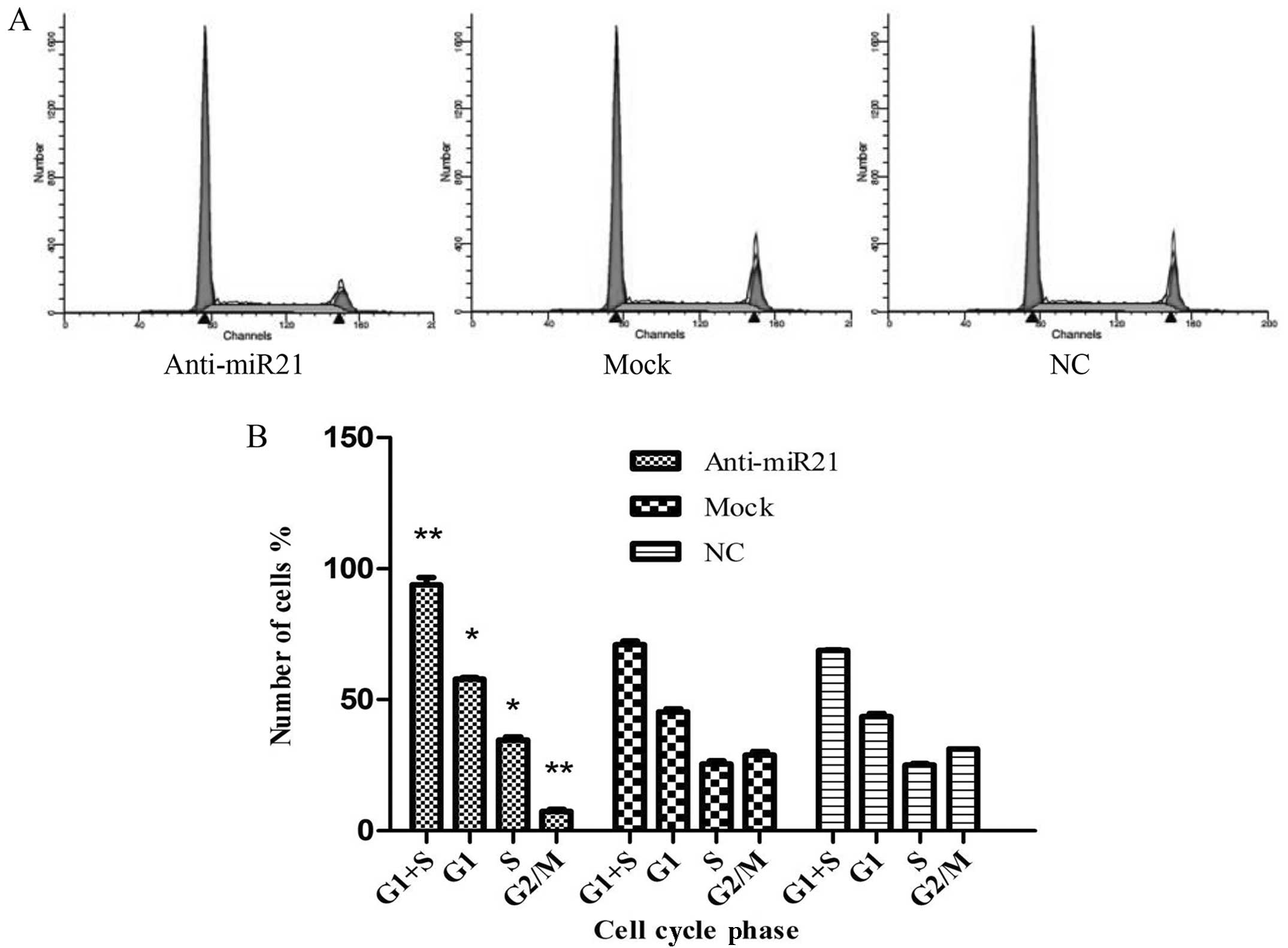
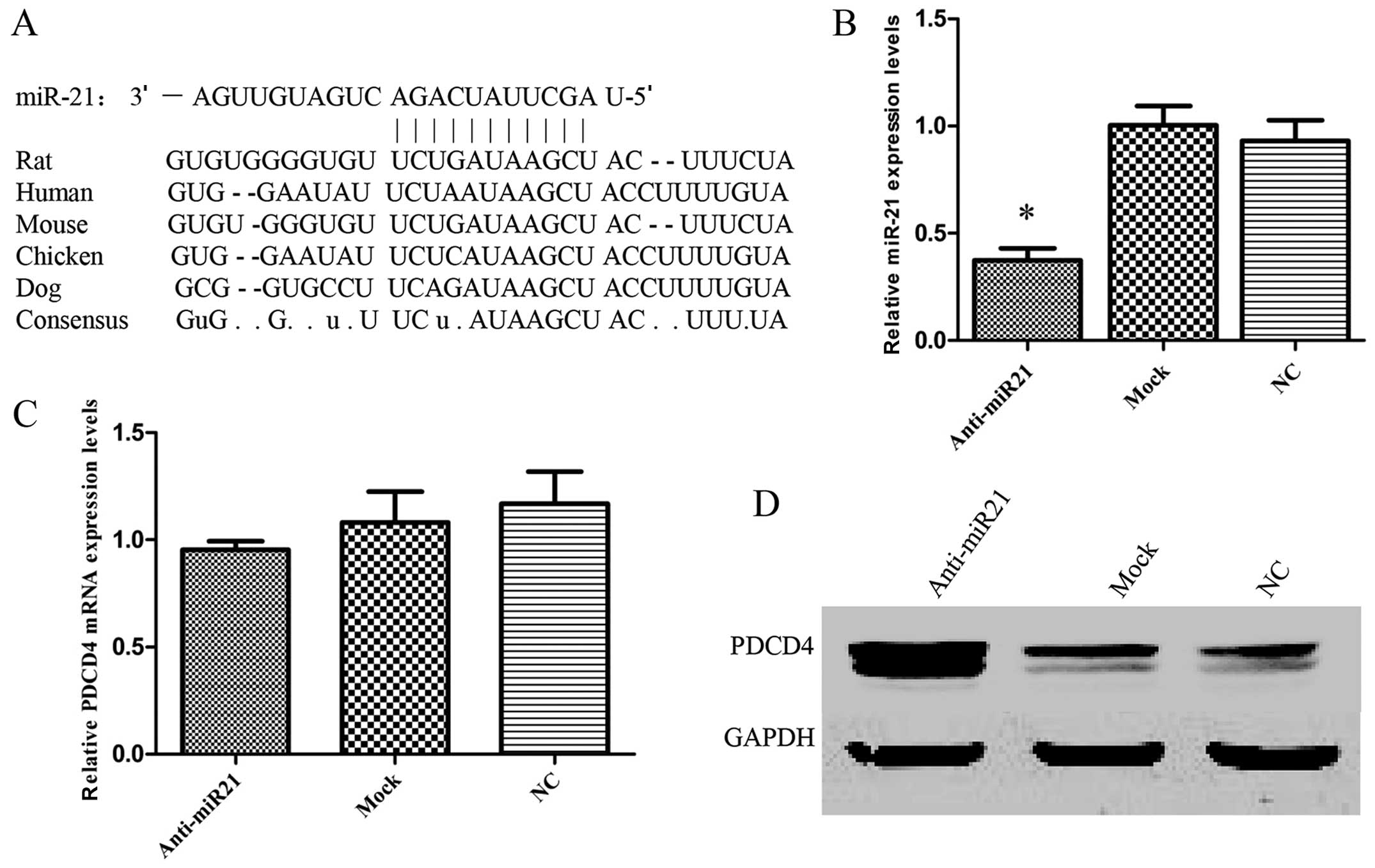
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Cheng ZX, Sun B, Wang SJ, et al: Nuclear
factor-κB-dependent epithelial to mesenchymal transition induced by
HIF-1α activation in pancreatic cancer cells under hypoxic
conditions. PLoS One. 6:e237522011.
|
|
3
|
Semenza GL: HIF-1 and tumor progression:
pathophysiology and therapeutics. Trends Mol Med. 8(Suppl 4):
S62–S67. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Imai T, Horiuchi A, Wang C, et al: Hypoxia
attenuates the expression of E-cadherin via up-regulation of SNAIL
in ovarian carcinoma cells. Am J Pathol. 163:1437–1447. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, et al: MicroRNA
expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature. 435:834–838.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Volinia S, Calin GA, Liu CG, et al: A
microRNA expression signature of human solid tumors defines cancer
gene targets. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:2257–2261. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Rosenfeld N, Aharonov R, Meiri E, et al:
MicroRNAs accurately identify cancer tissue origin. Nat Biotechnol.
26:462–469. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chu Y, Zhu H, Lv L, Zhou Y and Huo J:
MiRNAs in oesophageal squamous cancer. Neth J Med. 71:69–75.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Janiszewska J, Szaumkessel M and Szyfter
K: microRNAs are important players in head and neck carcinoma: a
review. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 88:716–728. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wu Q, Wang C, Lu Z, Guo L and Ge Q:
Analysis of serum genome-wide microRNAs for breast cancer
detection. Clin Chim Acta. 413:1058–1065. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liang H, Gong F, Zhang S, Zhang CY, Zen K
and Chen X: The origin, function, and diagnostic potential of
extracellular microRNAs in human body fluids. Wiley Interdiscip Rev
RNA. 5:285–300. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Endo K, Weng H, Kito N, Fukushima Y and
Iwai N: miR-216a and miR-216b as markers for acute phased
pancreatic injury. Biomed Res. 34:179–188. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Olivieri F, Rippo MR, Procopio AD and
Fazioli F: Circulating inflamma-miRs in aging and
age-related diseases. Front Genet. 4:1212013.
|
|
14
|
de Yébenes VG, Bartolomé-Izquierdo N and
Ramiro AR: Regulation of B-cell development and function by
microRNAs. Immunol Rev. 253:25–39. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Stefani G: Roles of microRNAs and their
targets in cancer. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 7:1833–1840. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yang J, Hao Y and Xi JJ: Therapeutic
application of microRNAs against human cancers. J Lab Autom.
18:30–33. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Farazi TA, Spitzer JI, Morozov P and
Tuschl T: miRNAs in human cancer. J Pathol. 223:102–115. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Lo WL, Yu CC, Chiou GY, et al:
MicroRNA-200c attenuates tumour growth and metastasis of
presumptive head and neck squamous cell carcinoma stem cells. J
Pathol. 223:482–495. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liu X, Jiang L, Wang A, Yu J, Shi F and
Zhou X: MicroRNA-138 suppresses invasion and promotes apoptosis in
head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cell lines. Cancer Lett.
286:217–222. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chen HC, Chen GH, Chen YH, et al: MicroRNA
deregulation and pathway alterations in nasopharyngeal carcinoma.
Br J Cancer. 100:1002–1011. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Xu X, Chen Z, Zhao X, et al: MicroRNA-25
promotes cell migration and invasion in esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 421:640–645. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gao W, Xu J, Liu L, Shen H, Zeng H and Shu
Y: A systematic-analysis of predicted miR-21 targets identifies a
signature for lung cancer. Biomed Pharmacother. 66:21–28. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Schee K, Boye K, Abrahamsen TW, Fodstad Ø
and Flatmark K: Clinical relevance of microRNA miR-21, miR-31,
miR-92a, miR-101, miR-106a and miR-145 in colorectal cancer. BMC
Cancer. 12:5052012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Young MR, Santhanam AN, Yoshikawa N and
Colburn NH: Have tumor suppressor PDCD4 and its counteragent
oncogenic miR-21 gone rogue? Mol Interv. 10:76–79. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Allgayer H: Pdcd4, a colon cancer
prognostic that is regulated by a microRNA. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol.
73:185–191. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Fassan M, Pizzi M, Battaglia G, et al:
Programmed cell death 4 (PDCD4) expression during multistep
Barrett’s carcinogenesis. J Clin Pathol. 63:692–696.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Fassan M, Pizzi M, Giacomelli L, et al:
PDCD4 nuclear loss inversely correlates with miR-21 levels in colon
carcinogenesis. Virchows Arch. 458:413–419. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chen C, Ridzon DA, Broomer AJ, et al:
Real-time quantification of microRNAs by stem-loop RT-PCR. Nucleic
Acids Res. 33:e1792005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wolf JS, Chen Z, Dong G, et al: IL
(interleukin)-1α promotes nuclear factor-κB and AP-1-induced IL-8
expression, cell survival, and proliferation in head and neck
squamous cell carcinomas. Clin Cancer Res. 7:1812–1820. 2001.
|
|
30
|
Itani S, Kunisada T, Morimoto Y, et al:
MicroRNA-21 correlates with tumorigenesis in malignant peripheral
nerve sheath tumor (MPNST) via programmed cell death protein 4
(PDCD4). J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 138:1501–1509. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Horiuchi A, Iinuma H, Akahane T, Shimada R
and Watanabe T: Prognostic significance of PDCD4 expression and
association with microRNA-21 in each Dukes’ stage of colorectal
cancer patients. Oncol Rep. 27:1384–1392. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang J and Zhang Y: Expression of
programmed cell death 4 protein is closely correlated with
laryngeal squamous cell carcinomas. Lin Chung Er Bi Yan Hou Tou
Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 25:539–541. 2011.(In Chinese).
|
|
33
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Iorio MV, Ferracin M, Liu CG, et al:
MicroRNA gene expression deregulation in human breast cancer.
Cancer Res. 65:7065–7070. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chan JA, Krichevsky AM and Kosik KS:
MicroRNA-21 is an antiapoptotic factor in human glioblastoma cells.
Cancer Res. 65:6029–6033. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Shi GH, Ye DW, Yao XD, et al: Involvement
of microRNA-21 in mediating chemo-resistance to docetaxel in
androgen-independent prostate cancer PC3 cells. Acta Pharmacol Sin.
31:867–873. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Xu YZ, Xi QH, Ge WL and Zhang XQ:
Identification of serum microRNA-21 as a biomarker for early
detection and prognosis in human epithelial ovarian cancer. Asian
Pac J Cancer Prev. 14:1057–1060. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Giovannetti E, Funel N, Peters GJ, et al:
MicroRNA-21 in pancreatic cancer: correlation with clinical outcome
and pharmacologic aspects underlying its role in the modulation of
gemcitabine activity. Cancer Res. 70:4528–4538. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Feng YH, Wu CL, Tsao CJ, et al:
Deregulated expression of sprouty2 and microRNA-21 in human colon
cancer: correlation with the clinical stage of the disease. Cancer
Biol Ther. 11:111–121. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhang BG, Li JF, Yu BQ, Zhu ZG, Liu BY and
Yan M: microRNA-21 promotes tumor proliferation and invasion in
gastric cancer by targeting PTEN. Oncol Rep. 27:1019–1026.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Selaru FM, Olaru AV, Kan T, et al:
MicroRNA-21 is overexpressed in human cholangiocarcinoma and
regulates programmed cell death 4 and tissue inhibitor of
metalloproteinase 3. Hepatology. 49:1595–1601. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Meng F, Henson R, Wehbe-Janek H, Ghoshal
K, Jacob ST and Patel T: MicroRNA-21 regulates expression of the
PTEN tumor suppressor gene in human hepatocellular cancer.
Gastroenterology. 133:647–658. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Tran N, McLean T, Zhang X, et al: MicroRNA
expression profiles in head and neck cancer cell lines. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 358:12–17. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Huang S, Li XQ, Chen X, Che SM, Chen W and
Zhang XZ: Inhibition of microRNA-21 increases radiosensitivity of
esophageal cancer cells through phosphatase and tensin homolog
deleted on chromosome 10 activation. Dis Esophagus. 26:823–831.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Schetter AJ, Leung SY, Sohn JJ, et al:
MicroRNA expression profiles associated with prognosis and
therapeutic outcome in colon adenocarcinoma. JAMA. 299:425–436.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Dillhoff M, Liu J, Frankel W, Croce C and
Bloomston M: MicroRNA-21 is overexpressed in pancreatic cancer and
a potential predictor of survival. J Gastrointest Surg.
12:2171–2176. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Asangani IA, Rasheed SA, Nikolova DA, et
al: MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) post-transcriptionally downregulates tumor
suppressor Pdcd4 and stimulates invasion, intravasation and
metastasis in colorectal cancer. Oncogene. 27:2128–2136. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Feber A, Xi L, Luketich JD, et al:
MicroRNA expression profiles of esophageal cancer. J Thorac
Cardiovasc Surg. 135:255–260. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Fulci V, Chiaretti S, Goldoni M, et al:
Quantitative technologies establish a novel microRNA profile of
chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood. 109:4944–4951. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Iorio MV, Visone R, Di Leva G, et al:
MicroRNA signatures in human ovarian cancer. Cancer Res.
67:8699–8707. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Markou A, Tsaroucha EG, Kaklamanis L,
Fotinou M, Georgoulias V and Lianidou ES: Prognostic value of
mature microRNA-21 and microRNA-205 overexpression in non-small
cell lung cancer by quantitative real-time RT-PCR. Clin Chem.
54:1696–1704. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Yang HS, Jansen AP, Nair R, et al: A novel
transformation suppressor, Pdcd4, inhibits AP-1 transactivation but
not NF-κB or ODC transactivation. Oncogene. 20:669–676.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Jansen AP, Camalier CE, Stark C and
Colburn NH: Characterization of programmed cell death 4 in multiple
human cancers reveals a novel enhancer of drug sensitivity. Mol
Cancer Ther. 3:103–110. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Jansen AP, Camalier CE and Colburn NH:
Epidermal expression of the translation inhibitor programmed cell
death 4 suppresses tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 65:6034–6041. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Göke A, Göke R, Knolle A, et al: DUG is a
novel homologue of translation initiation factor 4G that binds
eIF4A. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 297:78–82. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Yang HS, Jansen AP, Komar AA, et al: The
transformation suppressor Pdcd4 is a novel eukaryotic translation
initiation factor 4A binding protein that inhibits translation. Mol
Cell Biol. 23:26–37. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Göke R, Barth P, Schmidt A, Samans B and
Lankat-Buttgereit B: Programmed cell death protein 4 suppresses
CDK1/cdc2 via induction of p21Waf1/Cip1. Am J Physiol
Cell Physiol. 287:C1541–C1546. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Frankel LB, Christoffersen NR, Jacobsen A,
Lindow M, Krogh A and Lund AH: Programmed cell death 4 (PDCD4) is
an important functional target of the microRNA miR-21 in
breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 283:1026–1033. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Xu L, Dai WQ, Xu XF, Wang F, He L and Guo
CY: Effects of multiple-target anti-microRNA antisense
oligodeoxyribonucleotides on proliferation and migration of gastric
cancer cells. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 13:3203–3207. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Lennox KA and Behlke MA: A direct
comparison of anti-microRNA oligonucleotide potency. Pharm Res.
27:1788–1799. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|