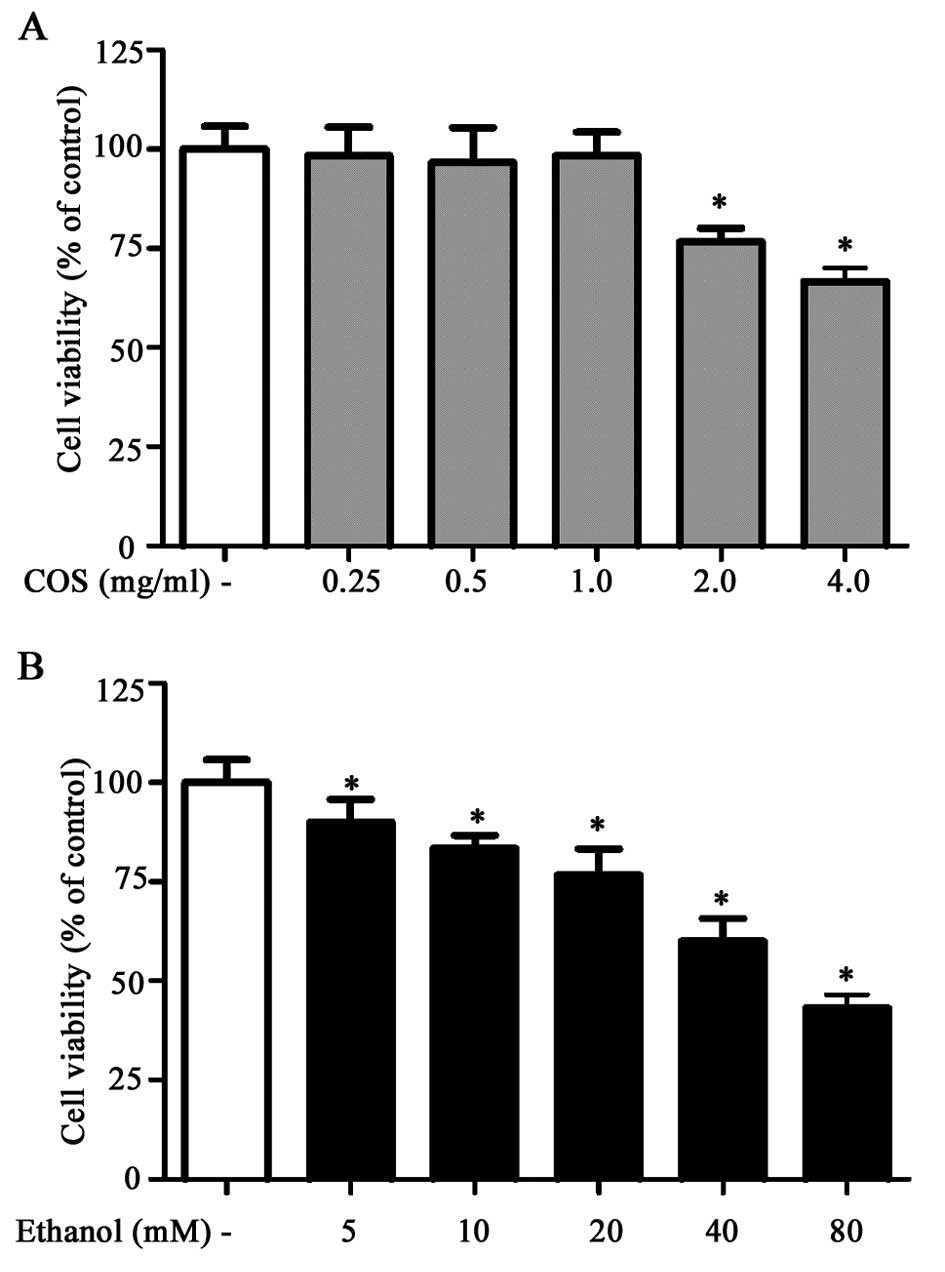
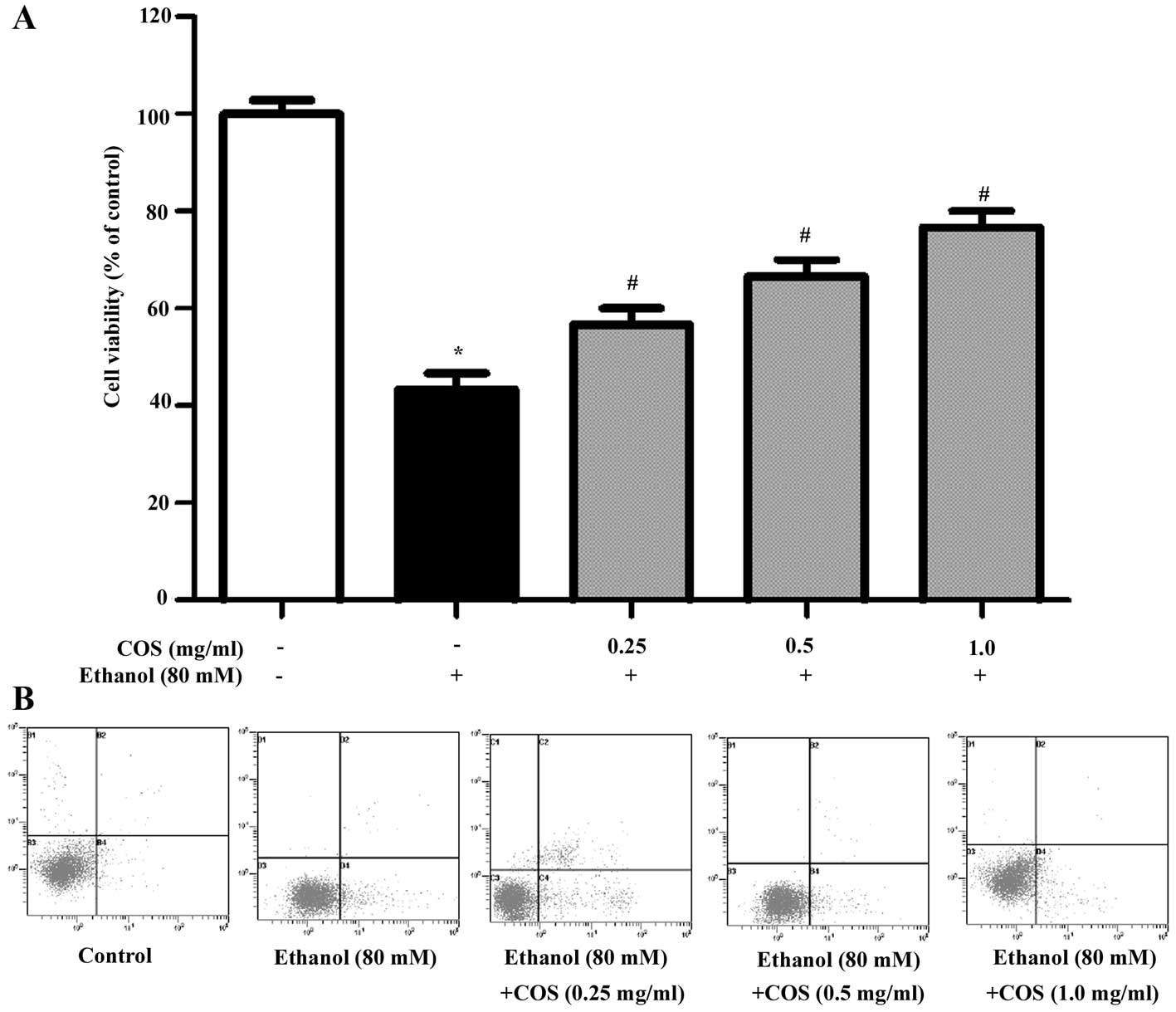
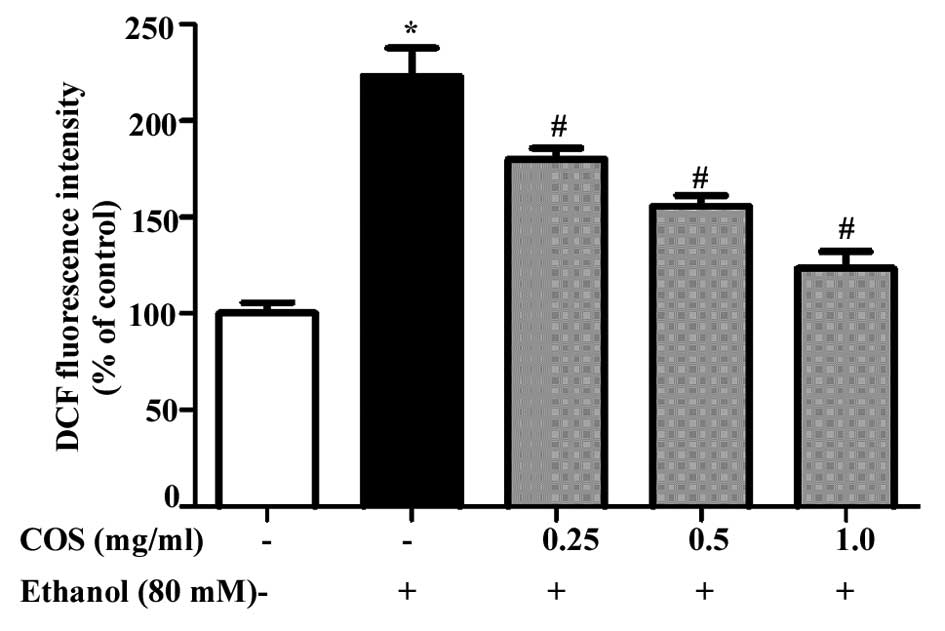
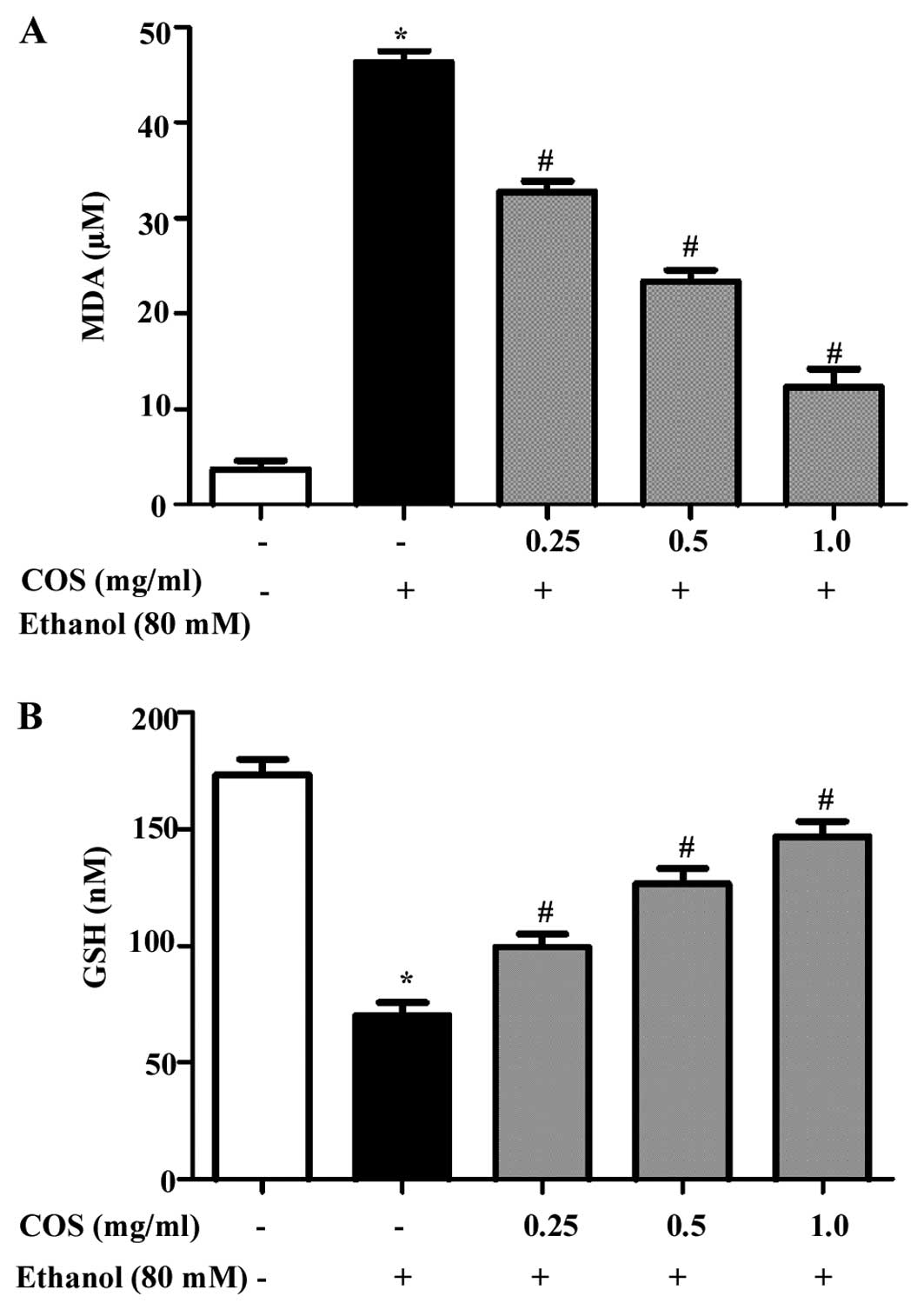
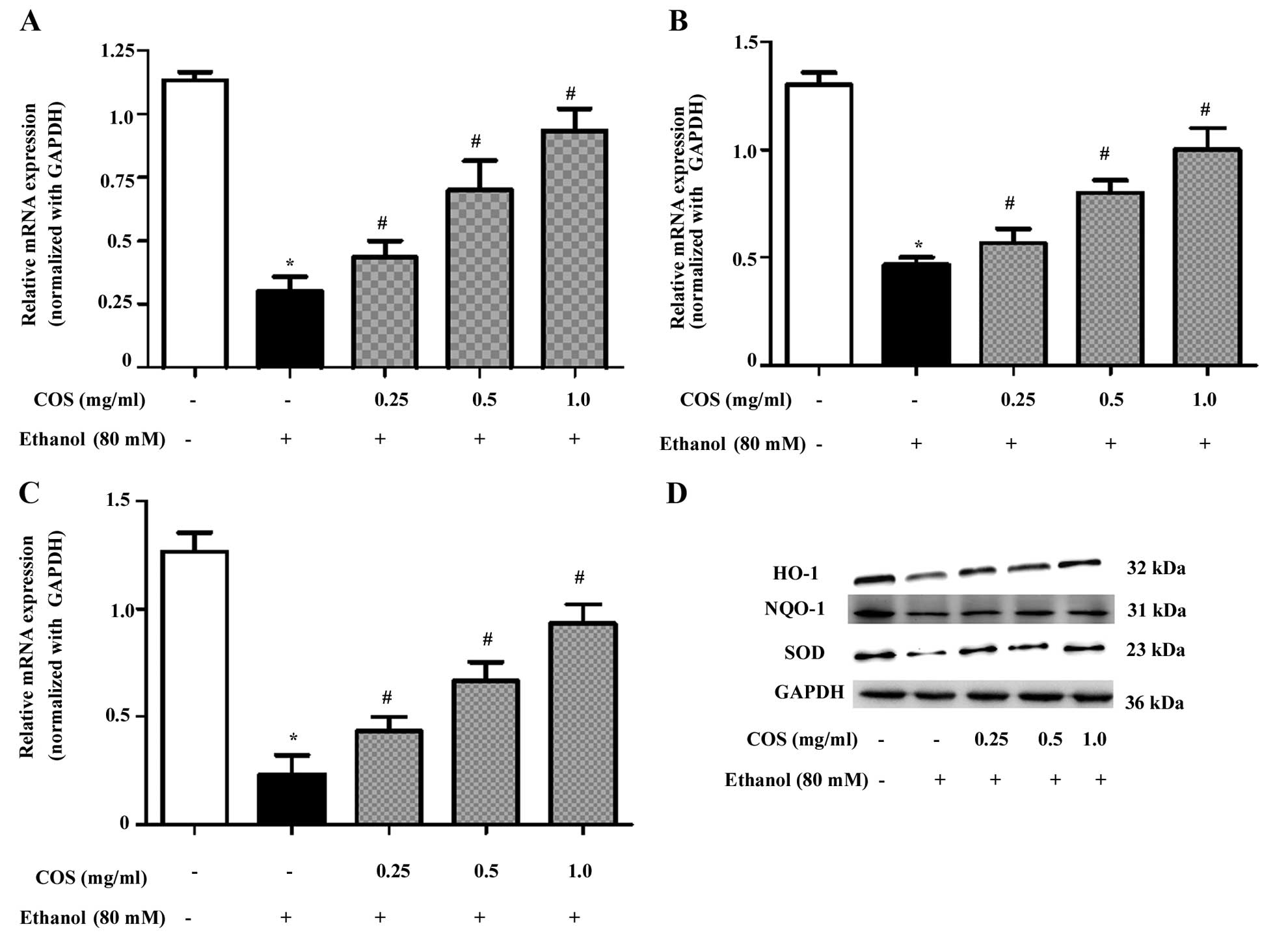
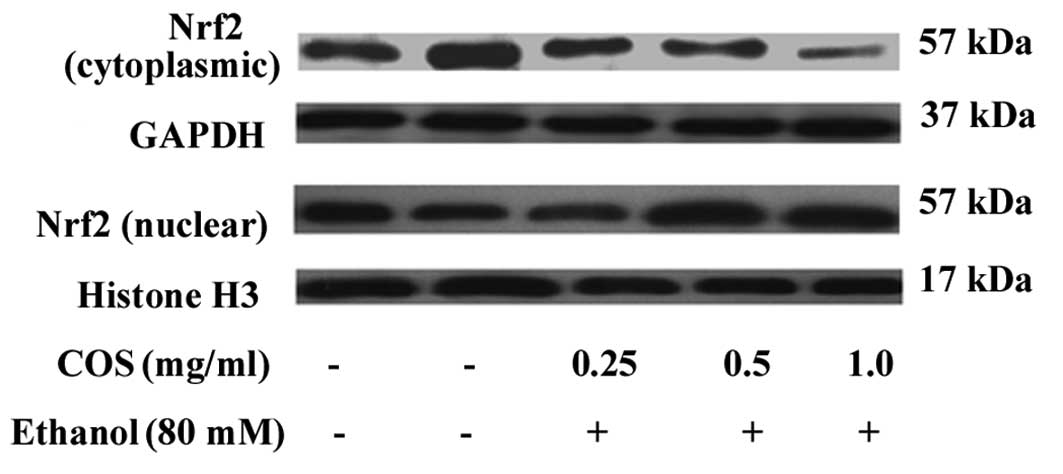
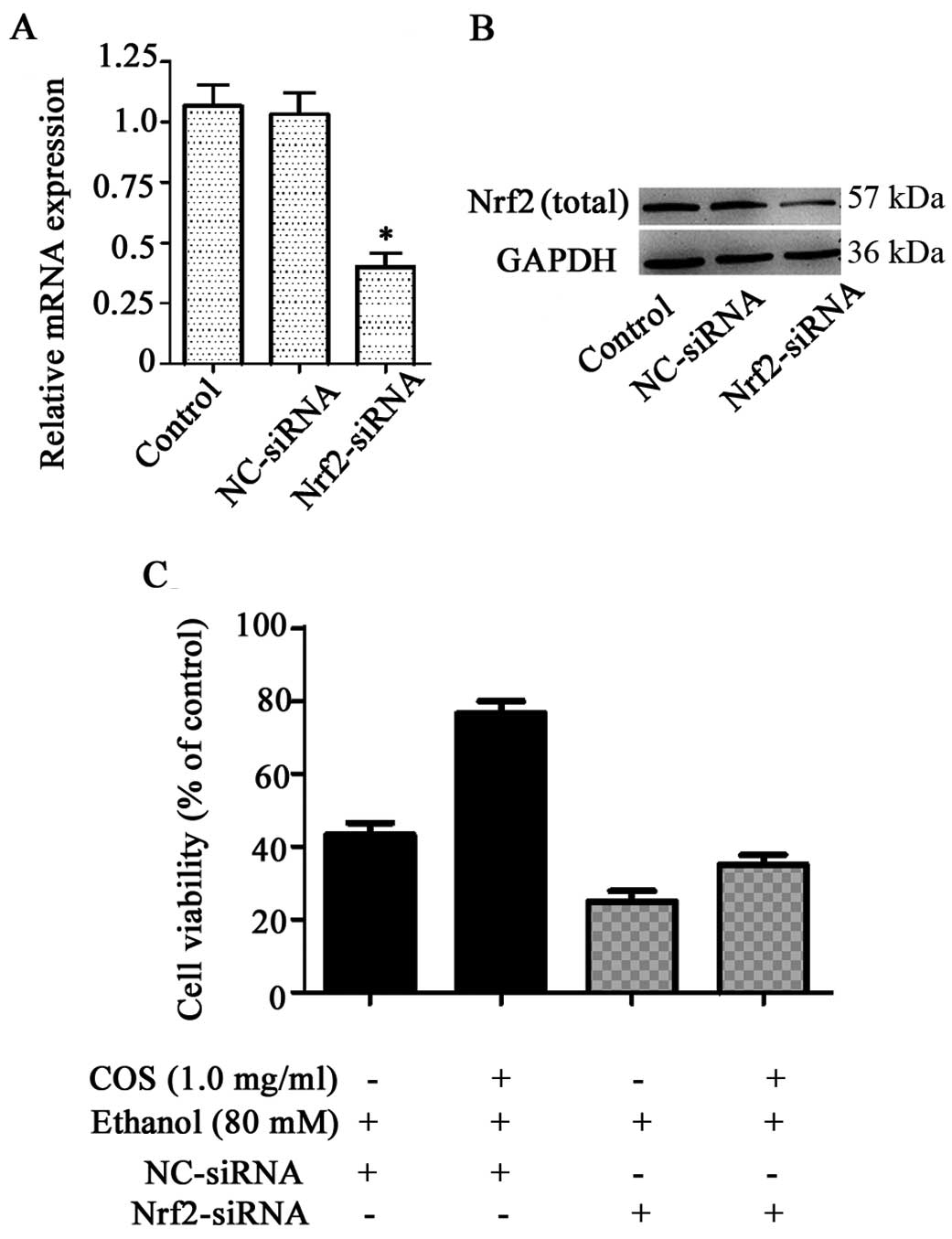
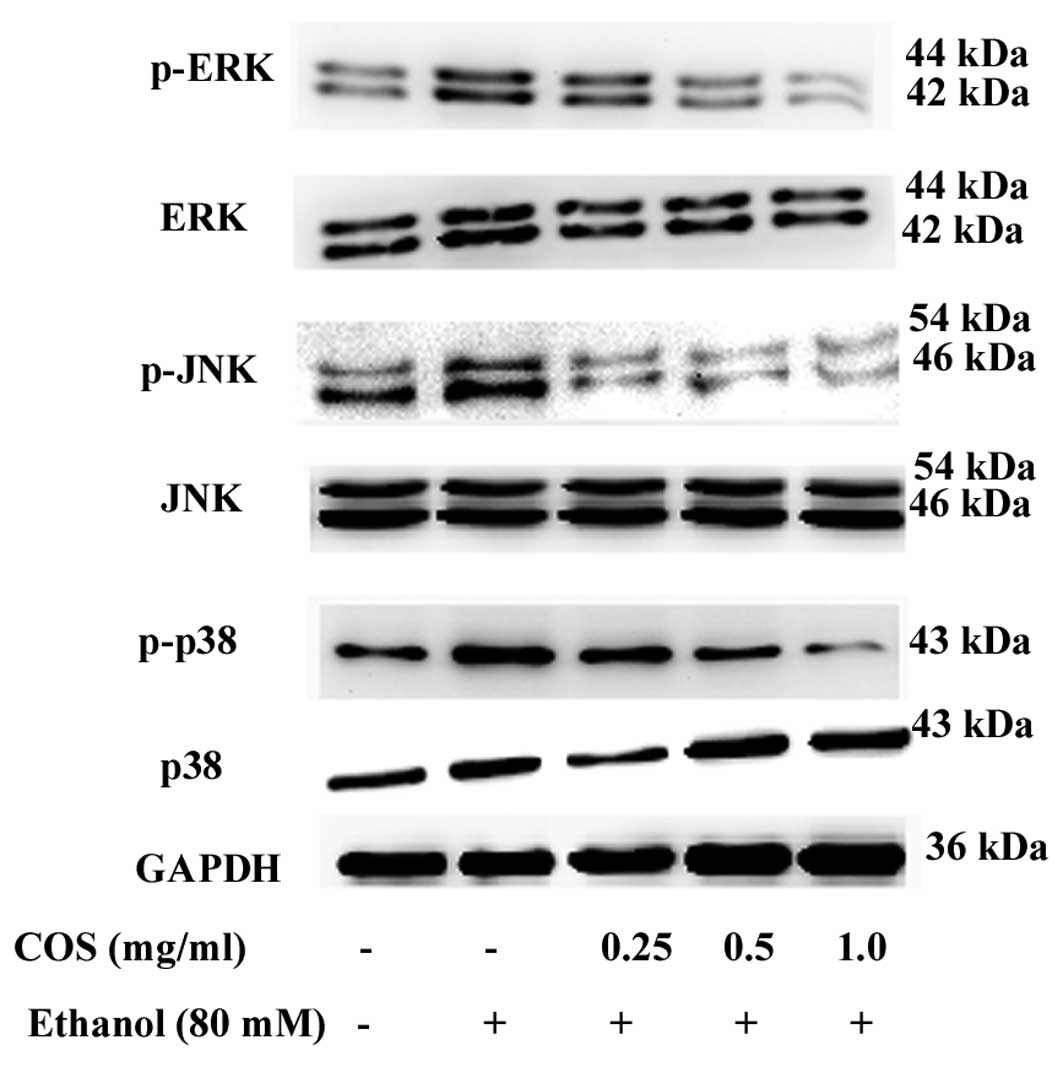
|
1
|
Lee HI, McGregor RA, Choi MS, et al: Low
doses of curcumin protect alcohol-induced liver damage by
modulation of the alcohol metabolic pathway, CYP2E1 and AMPK. Life
Sci. 93:693–699. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhu H, Jia Z, Misra H and Li YR: Oxidative
stress and redox signaling mechanisms of alcoholic liver disease:
updated experimental and clinical evidence. J Dig Dis. 13:133–142.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zeng T, Zhang CL, Song FY, et al: The
activation of HO-1/Nrf-2 contributes to the protective effects of
diallyl disulfide (DADS) against ethanol-induced oxidative stress.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1830:4848–4859. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hajji S, Younes I, Ghorbel-Bellaaj O, et
al: Structural differences between chitin and chitosan extracted
from three different marine sources. Int J Biol Macromol.
65:298–306. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lu X, Guo H, Sun L, Zhang L and Zhang Y:
Protective effects of sulfated chitooligosaccharides with different
degrees of substitution in MIN6 cells. Int J Biol Macromol.
52:92–98. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cho SY, Yun JW, Park PJ, et al: Effects of
chitooligosaccharide lactate salt on activity of acetaldehyde
dehydrogenase. J Med Food. 13:1061–1068. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Qiang W, Cahill JM, Liu J, et al:
Activation of transcription factor Nrf-2 and its downstream targets
in response to moloney murine leukemia virus ts1-induced
thiol depletion and oxidative stress in astrocytes. J Virol.
78:11926–11938. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ryu EY, Park AJ, Park SY, et al:
Inhibitory effects of Ginkgo biloba extract on inflammatory
mediator production by Porphyromonas gingivalis
lipopolysaccharide in murine macrophages via Nrf-2 mediated heme
oxygenase-1 signaling pathways. Inflammation. 35:1477–1486.
2012.
|
|
9
|
Gao D, Gao Z and Zhu G: Antioxidant
effects of Lactobacillus plantarum via activation of
transcription factor Nrf2. Food Funct. 4:982–989. 2013.
|
|
10
|
Senthil Kumar KJ, Liao JW, Xiao JH, Gokila
Vani M and Wang SY: Hepatoprotective effect of lucidone against
alcohol-induced oxidative stress in human hepatic HepG2 cells
through the up-regulation of HO-1/Nrf-2 antioxidant genes. Toxicol
In Vitro. 26:700–708. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kumar KJ, Chu FH, Hsieh HW, et al:
Antroquinonol from ethanolic extract of mycelium of Antrodia
cinnamomea protects hepatic cells from ethanol-induced
oxidative stress through Nrf-2 activation. J Ethnopharmacol.
136:168–177. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Joodi G, Ansari N and Khodagholi F:
Chitooligosaccharide-mediated neuroprotection is associated with
modulation of Hsps expression and reduction of MAPK
phosphorylation. Int J Biol Macromol. 48:726–735. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Woo CC, Hsu A, Kumar AP, Sethi G and Tan
KH: Thymoquinone inhibits tumor growth and induces apoptosis in a
breast cancer xenograft mouse model: the role of p38 MAPK and ROS.
PLoS One. 8:e753562013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ku BM, Lee YK, Jeong JY, et al:
Ethanol-induced oxidative stress is mediated by p38 MAPK pathway in
mouse hippocampal cells. Neurosci Lett. 419:64–67. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Barzegar A and Moosavi-Movahedi AA:
Intracellular ROS protection efficiency and free radical-scavenging
activity of curcumin. PLoS One. 6:e260122011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kaviarasan S, Ramamurthy N, Gunasekaran P,
Varalakshmi E and Anuradha CV:
Epigallocatechin-3-gallate(−)protects Chang liver cells against
ethanol-induced cytotoxicity and apoptosis. Basic Clin Pharmacol
Toxicol. 100:151–156. 2007.
|
|
17
|
Tahir M, Rehman MU, Lateef A, et al:
Diosmin protects against ethanol-induced hepatic injury via
alleviation of inflammation and regulation of TNF-α and NF-κB
activation. Alcohol. 47:131–139. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Shen Y, Yang T, Guo S, et al: Increased
serum ox-LDL levels correlated with lung function, inflammation,
and oxidative stress in COPD. Mediators Inflamm.
2013:9723472013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Prietsch RF, Monte LG, da Silva FA, et al:
Genistein induces apoptosis and autophagy in human breast MCF-7
cells by modulating the expression of proapoptotic factors and
oxidative stress enzymes. Mol Cell Biochem. 390:235–242. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hoek JB and Pastorino JG: Ethanol,
oxidative stress, and cytokine-induced liver cell injury. Alcohol.
27:63–68. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kim YS, Lee SJ, Hwang JW, et al: In vitro
protective effects of Thymus quinquecostatus Celak extracts
on t-BHP-induced cell damage through antioxidant activity.
Food Chem Toxicol. 50:4191–4198. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kim YS, Hwang JW, Han YK, et al:
Antioxidant activity and protective effects of Trapa
japonica pericarp extracts against
tert-butylhydroperoxide-induced oxidative damage in Chang
cells. Food Chem Toxicol. 64:49–56. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Gokila Vani M, Kumar KJ, Liao JW, et al:
Antcin C from Antrodia cinnamomea protects liver cells
against free radical-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in
vitro and in vivo through Nrf2-dependent mechanism. Evid Based
Complement Alternat Med. 2013:2960822013.
|
|
24
|
De K, Roy K and Sengupta C: Inhibition of
lipid peroxidation induced by hydroxyprogesterone caproate by some
conventional antioxidants in goat liver homogenates. Acta Pol
Pharm. 64:201–210. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Townsend DM, Tew KD and Tapiero H: The
importance of glutathione in human disease. Biomed Pharmacother.
57:145–155. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Narasimhan M, Rathinam M, Patel D,
Henderson G and Mahimainathan L: Astrocytes prevent ethanol induced
apoptosis of Nrf2 depleted neurons by maintaining GSH homeostasis.
Open J Apoptosis. 1: View Article : Google Scholar : 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Matés JM: Effects of antioxidant enzymes
in the molecular control of reactive oxygen species toxicology.
Toxicology. 153:83–104. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Birrane G, Li H, Yang S, Tachado SD and
Seng S: Cigarette smoke induces nuclear translocation of heme
oxygenase 1 (HO-1) in prostate cancer cells: Nuclear HO-1 promotes
vascular endothelial growth factor secretion. Int J Oncol.
42:1919–1928. 2013.
|
|
29
|
Bao W, Li K, Rong S, et al: Curcumin
alleviates ethanol-induced hepatocytes oxidative damage involving
heme oxygenase-1 induction. J Ethnopharmacol. 128:549–553. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kim JY, Kim do Y, Son H, Kim YJ and Oh SH:
Protease-activated receptor-2 activates NQO-1 via Nrf2
stabilization in keratinocytes. J Dermatol Sci. 74:48–55. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
You H, Wei L, Sun WL, et al: The green tea
extract epigallocatechin-3-gallate inhibits irradiation-induced
pulmonary fibrosis in adult rats. Int J Mol Med. 34:92–102.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yao P, Nussler A, Liu L, et al: Quercetin
protects human hepatocytes from ethanol-derived oxidative stress by
inducing heme oxygenase-1 via the MAPK/Nrf2 pathways. J Hepatol.
47:253–261. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Son Y, Cheong YK, Kim NH, Chung HT, Kang
DG and Pae HO: Mitogen-activated protein kinases and reactive
oxygen species: how can ROS activate MAPK pathways? J Signal
Transduct. 2011:7926392011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Li J, He J and Yu C: Chitosan
oligosaccharide inhibits LPS-induced apoptosis of vascular
endothelial cells through the BKCa channel and the p38 signaling
pathway. Int J Mol Med. 30:157–164. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Venugopal SK, Chen J, Zhang Y, Clemens D,
Follenzi A and Zern MA: Role of MAPK phosphatase-1 in sustained
activation of JNK during ethanol-induced apoptosis in
hepatocyte-like VL-17A cells. J Biol Chem. 282:31900–31908. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wei P, Ma P, Xu QS, et al: Chitosan
oligosaccharides suppress production of nitric oxide in
lipopolysaccharide-induced N9 murine microglial cells in vitro.
Glycoconj J. 29:285–295. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|