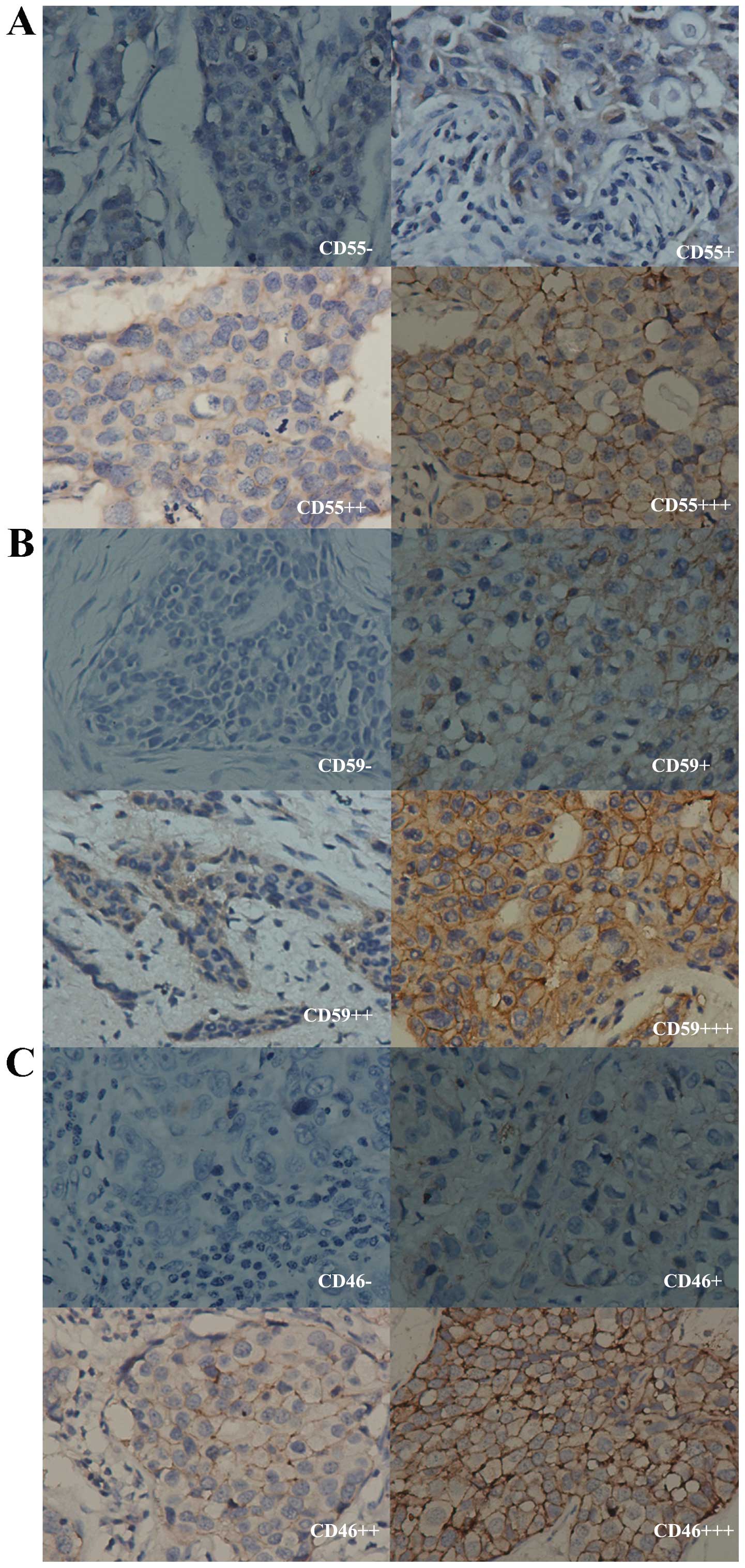
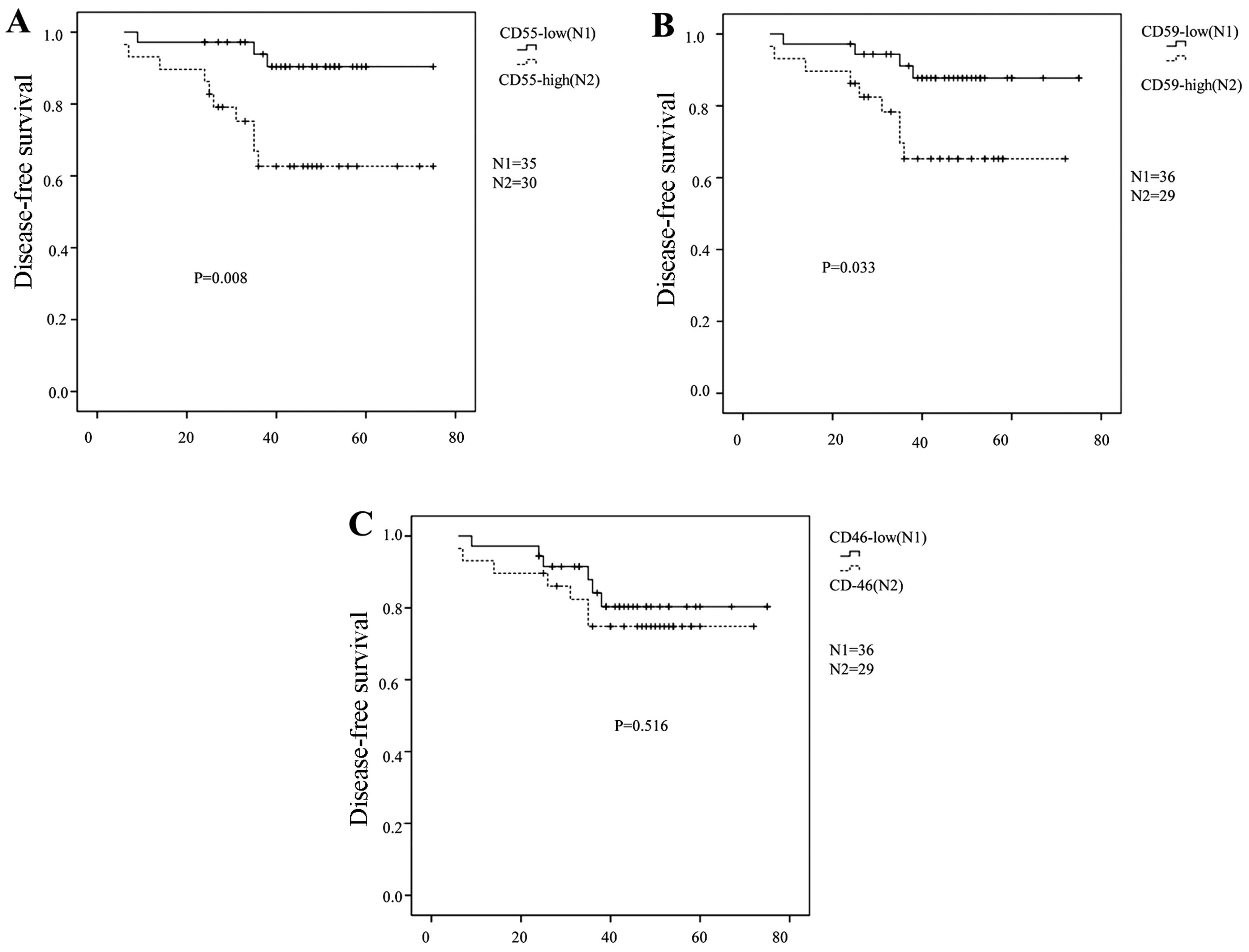
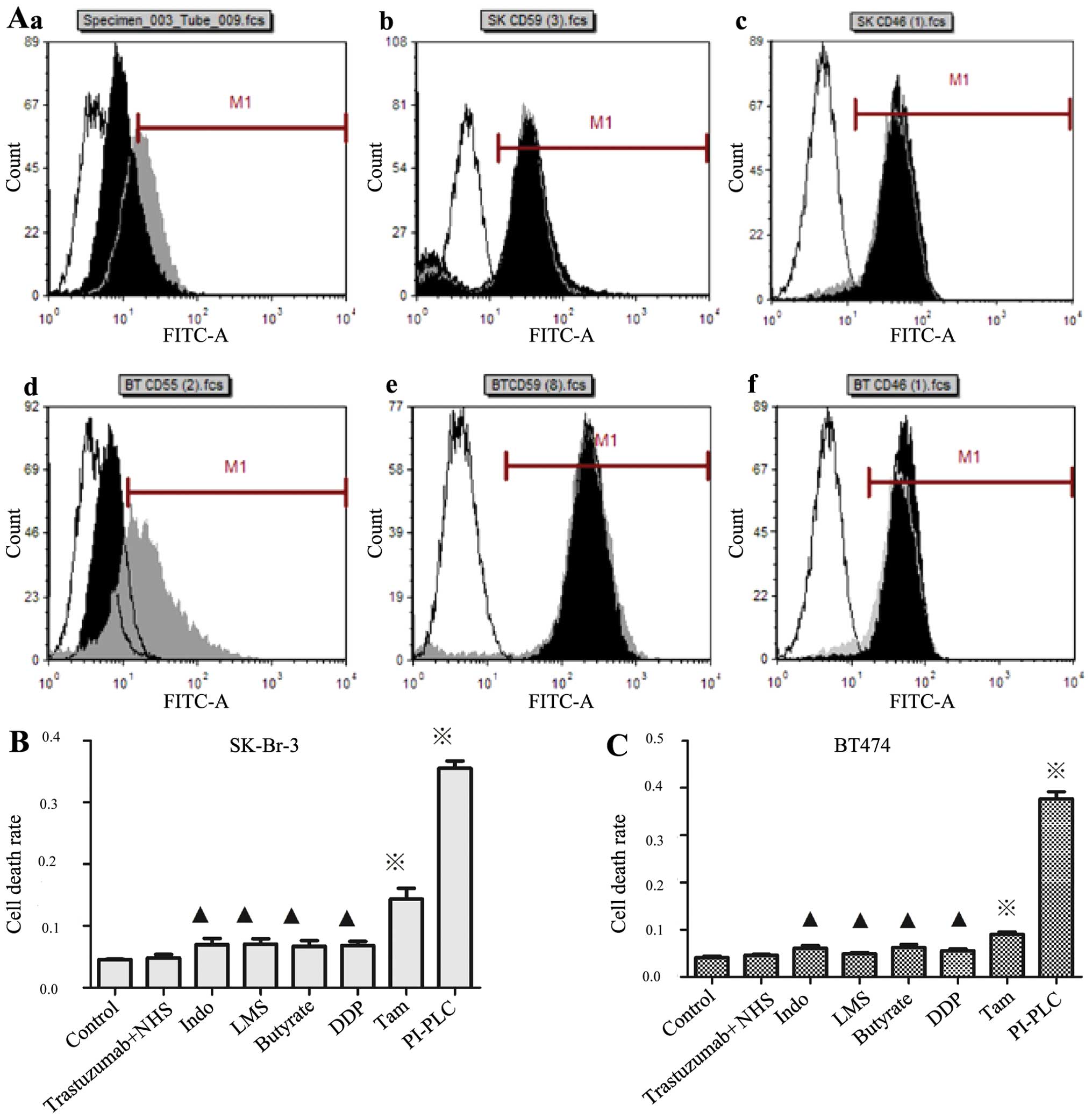
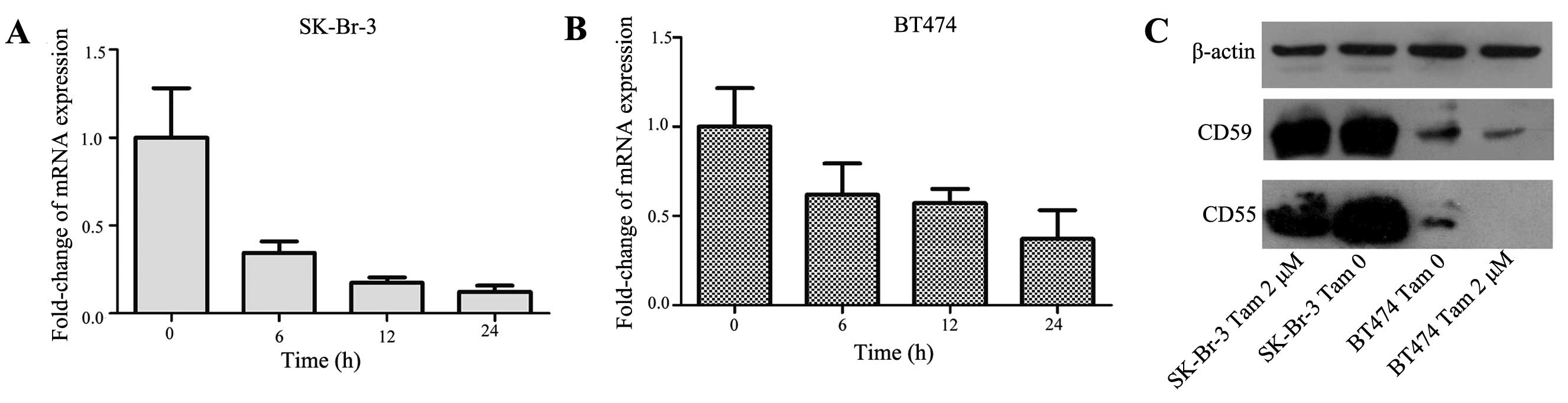
|
1
|
Natsume A, Niwa R and Satoh M: Improving
effector functions of antibodies for cancer treatment: Enhancing
ADCC and CDC. Drug Des Devel Ther. 3:7–16. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yamashita M, Katakura Y and Shirahata S:
Recent advances in the generation of human monoclonal antibody.
Cytotechnology. 55:55–60. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Piccart-Gebhart MJ, Procter M,
Leyland-Jones B, et al: Trastuzumab after adjuvant chemotherapy in
HER2-positive breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 353:1659–1672. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Romond EH, Perez EA, Bryant J, et al:
Trastuzumab plus adjuvant chemotherapy for operable HER2-positive
breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 353:1673–1684. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Slamon D, Eiermann W, Robert N, et al:
Phase III randomized trial comparing doxorubicin and
cyclophosphamide followed by docetaxel (AC→T) with doxorubicin and
cyclophosphamide followed by docetaxel and trastuzumab (AC→TH) with
docetaxel, carboplatin and trastuzumab (TCH) in HER2 positive early
breast cancer patients: study. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
94:S52005.
|
|
6
|
Nahta R and Esteva FJ: HER2 therapy:
molecular mechanisms of trastuzumab resistance. Breast Cancer Res.
8:2152006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Valabrega G, Montemurro F and Aglietta M:
Trastuzumab: mechanism of action, resistance and future
perspectives in HER2-overexpressing breast cancer. Ann Oncol.
18:977–984. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Dalle S, Thieblemont C, Thomas L and
Dumontet C: Monoclonal antibodies in clinical oncology. Anticancer
Agents Med Chem. 8:523–532. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Drebin JA, Link VC and Greene MI:
Monoclonal antibodies specific for the neu oncogene product
directly mediate antitumor effects in vivo. Oncogene. 2:387–394.
1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mamidi S, Cinci M, Hasmann M, Fehring V
and Kirschfink M: Lipoplex mediated silencing of membrane
regulators (CD46, CD55 and CD59) enhances complement-dependent
antitumor activity of trastuzumab and pertuzumab. Mol Oncol.
7:580–594. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Prang N, Preithner S, Brischwein K, et al:
Cellular and complement-dependent cytotoxicity of Ep-CAM-specific
monoclonal antibody MT201 against breast cancer cell lines. Br J
Cancer. 92:342–349. 2005.
|
|
12
|
Yu J, Caragine T, Chen S, Morgan BP, Frey
AB and Tomlinson S: Protection of human breast cancer cells from
complement-mediated lysis by expression of heterologous CD59. Clin
Exp Immunol. 115:13–18. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Mineo JF, Bordron A, Quintin-Roue I, et
al: Recombinant humanised anti-HER2/neu antibody (Herceptin)
induces cellular death of glioblastomas. Br J Cancer. 91:1195–1199.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Fishelson Z, Donin N, Zell S, Schultz S
and Kirschfink M: Obstacles to cancer immunotherapy: expression of
membrane complement regulatory proteins (mCRPs) in tumors. Mol
Immunol. 40:109–123. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Gancz D and Fishelson Z: Cancer resistance
to complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC): Problem-oriented
research and development. Mol Immunol. 46:2794–2800. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Macor P and Tedesco F: Complement as
effector system in cancer immunotherapy. Immunol Lett. 111:6–13.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hosch SB, Scheunemann P, Lüth M, et al:
Expression of 17-1A antigen and complement resistance factors CD55
and CD59 on liver metastasis in colorectal cancer. J Gastrointest
Surg. 5:673–679. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Koretz K, Brüderlein S, Henne C and Möller
P: Decay-accelerating factor (DAF, CD55) in normal colorectal
mucosa, adenomas and carcinomas. Br J Cancer. 66:810–814. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liu YC, Chen L, Peng SY and Hoang-Vu C:
Role of CD97 (stalk) and CD55 as molecular markers for prognosis
and therapy of gastric carcinoma patients. J Zhejiang Univ Sci.
6:913–918. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Loberg RD, Day LL, Dunn R, Kalikin LM and
Pienta KJ: Inhibition of decay-accelerating factor (CD55)
attenuates prostate cancer growth and survival in vivo. Neoplasia.
8:69–78. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhao WP, Zhu B, Duan YZ and Chen ZT:
Neutralization of complement regulatory proteins CD55 and CD59
augments therapeutic effect of herceptin against lung carcinoma
cells. Oncol Rep. 21:1405–1411. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Terui Y, Sakurai T, Mishima Y, et al:
Blockade of bulky lymphoma-associated CD55 expression by RNA
interference overcomes resistance to complement-dependent
cytotoxicity with rituximab. Cancer Sci. 97:72–79. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Golay J, Lazzari M, Facchinetti V, et al:
CD20 levels determine the in vitro susceptibility to rituximab and
complement of B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia: further
regulation by CD55 and CD59. Blood. 98:3383–3389. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Andoh A, Shimada M, Araki Y, Fujiyama Y
and Bamba T: Sodium butyrate enhances complement-mediated cell
injury via down-regulation of decay-accelerating factor expression
in colonic cancer cells. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 50:663–672.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Holla VR, Wang D, Brown JR, Mann JR,
Katkuri S and DuBois RN: Prostaglandin E2 regulates the complement
inhibitor CD55/decay-accelerating factor in colorectal cancer. J
Biol Chem. 280:476–483. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Xin YC, Gui SH and Ge SQ: Tamoxifen
modulates the expression of complement inhibitory proteins on
chorio-carcinoma cell line JAR. Shanghai J Immunol. 1:20–23.
2003.
|
|
27
|
Bjørge L and Matre R: Down-regulation of
CD59 (protectin) expression on human colorectal adenocarcinoma cell
lines by levamisole. Scand J Immunol. 42:512–516. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Eisenhauer EA, Therasse P, Bogaerts J, et
al: New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: revised
RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur J Cancer. 45:228–247. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Ikeda J, Morii E, Liu Y, et al: Prognostic
significance of CD55 expression in breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
14:4780–4786. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Molina MA, Codony-Servat J, Albanell J,
Rojo F, Arribas J and Baselga J: Trastuzumab (Herceptin), a
humanized anti-Her2 receptor monoclonal antibody, inhibits basal
and activated Her2 ectodomain cleavage in breast cancer cells.
Cancer Res. 61:4744–4749. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Subik K, Lee JF, Baxter L, et al: The
expression patterns of ER, PR, HER2, CK5/6, EGFR, Ki-67 and AR by
immunohistochemical analysis in breast cancer cell lines. Breast
Cancer. 4:35–41. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Spear GT, Lurain NS, Parker CJ, Ghassemi
M, Payne GH and Saifuddin M: Host cell-derived complement control
proteins CD55 and CD59 are incorporated into the virions of two
unrelated enveloped viruses. Human T cell leukemia/lymphoma virus
type I (HTLV-I) and human cytomegalovirus (HCMV). J Immunol.
155:4376–4381. 1995.
|
|
33
|
Kolev MV, Tediose T, Sivasankar B, et al:
Upregulating CD59: a new strategy for protection of neurons from
complement-mediated degeneration. Pharmacogenomics J. 10:12–19.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Durrant LG, Chapman MA, Buckley DJ,
Spendlove I, Robins RA and Armitage NC: Enhanced expression of the
complement regulatory protein CD55 predicts a poor prognosis in
colorectal cancer patients. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 52:638–642.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Loberg RD, Wojno KJ, Day LL and Pienta KJ:
Analysis of membrane-bound complement regulatory proteins in
prostate cancer. Urology. 66:1321–1326. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Madjd Z, Durrant LG, Pinder SE, et al: Do
poor-prognosis breast tumours express membrane cofactor proteins
(CD46)? Cancer Immunol Immunother. 54:149–156. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Macor P, Tripodo C, Zorzet S, et al: In
vivo targeting of human neutralizing antibodies against CD55 and
CD59 to lymphoma cells increases the antitumor activity of
rituximab. Cancer Res. 67:10556–10563. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Bannerji R, Kitada S, Flinn IW, et al:
Apoptotic regulatory and complement-protecting protein expression
in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: relationship to in vivo rituximab
resistance. J Clin Oncol. 21:1466–1471. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Bellone S, Roque D, Cocco E, et al:
Downregulation of membrane complement inhibitors CD55 and CD59 by
siRNA sensitises uterine serous carcinoma overexpressing Her2/neu
to complement and antibody-dependent cell cytotoxicity in vitro:
implications for trastuzumab-based immunotherapy. Br J Cancer.
106:1543–1550. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Gelderman KA, Kuppen PJ, Okada N, Fleuren
GJ and Gorter A: Tumor-specific inhibition of membrane-bound
complement regulatory protein Crry with bispecific monoclonal
antibodies prevents tumor outgrowth in a rat colorectal cancer lung
metastases model. Cancer Res. 64:4366–4372. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Argiris A, Wang CX, Whalen SG and
DiGiovanna MP: Synergistic interactions between tamoxifen and
trastuzumab (Herceptin). Clin Cancer Res. 10:1409–1420. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wang CX, Koay DC, Edwards A, et al: In
vitro and in vivo effects of combination of trastuzumab (Herceptin)
and tamoxifen in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
92:251–263. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Schild-Hay LJ, Leil TA, Divi RL, Olivero
OA, Weston A and Poirier MC: Tamoxifen induces expression of immune
response-related genes in cultured normal human mammary epithelial
cells. Cancer Res. 69:1150–1155. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|