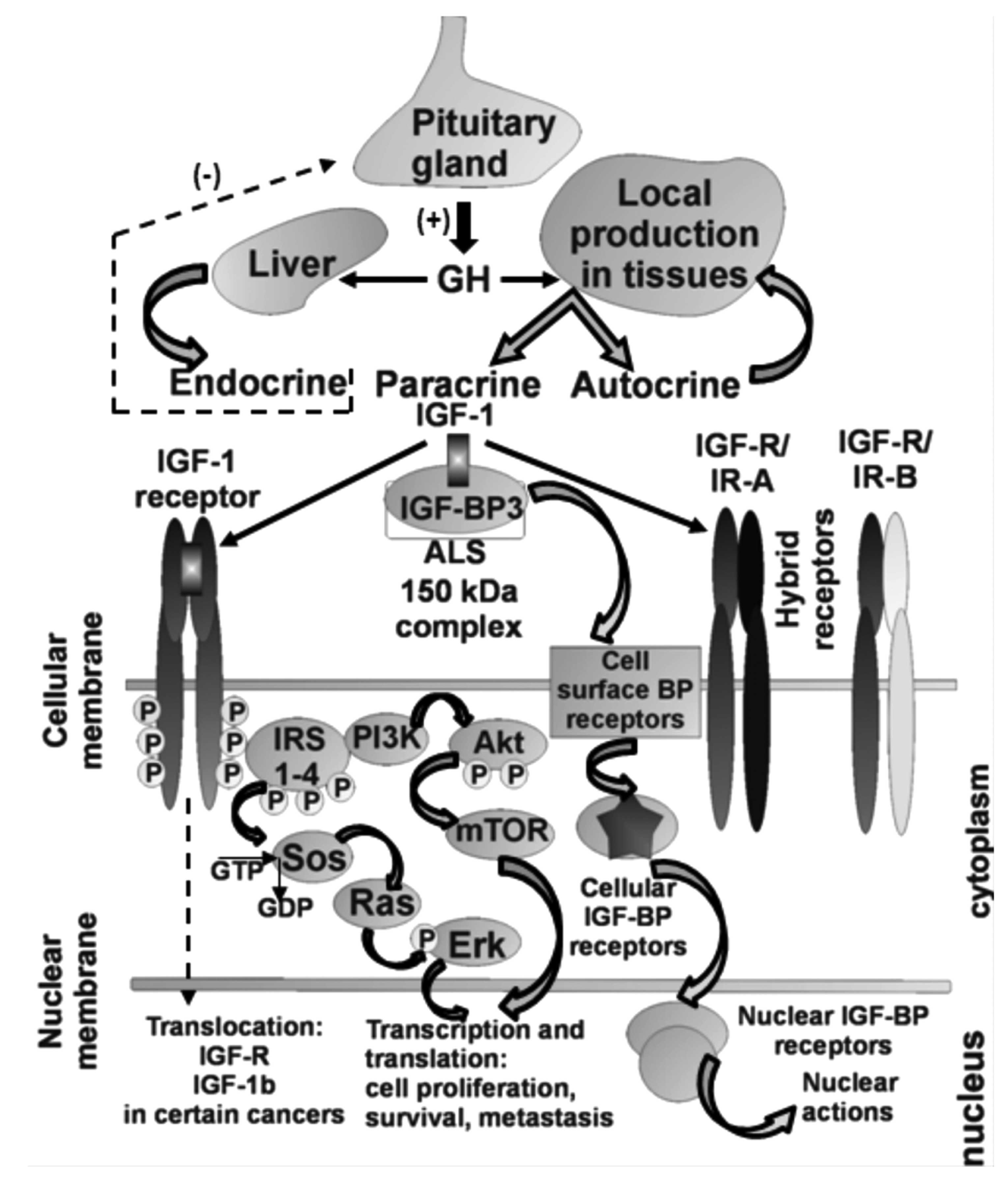
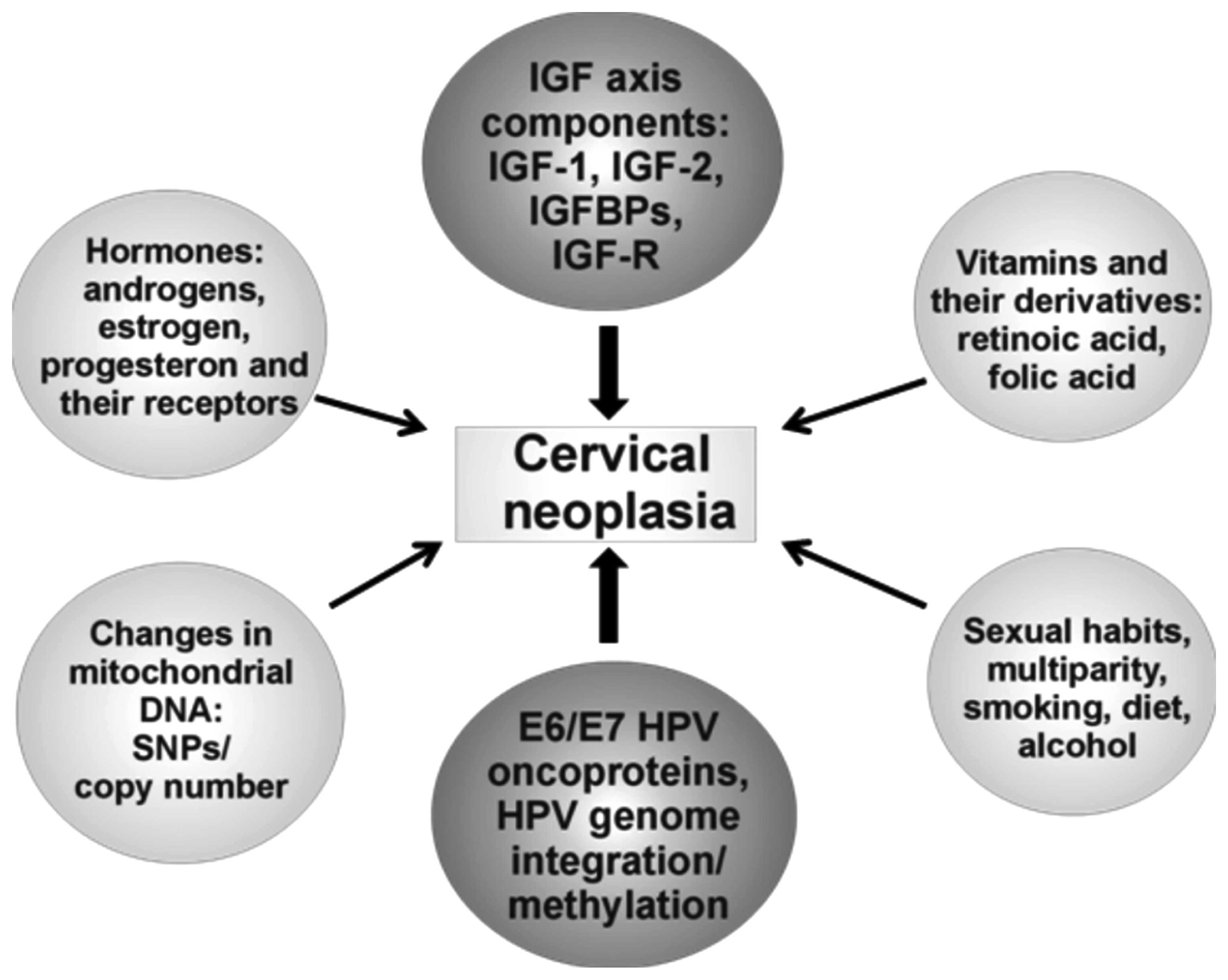
|
1
|
Pollak MN, Schernhammer ES and Hankinson
SE: Insulin-like growth factors and neoplasia. Nat Rev Cancer.
4:505–518. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Barton ER: The ABCs of IGF-I isoforms:
impact on muscle hypertrophy and implications for repair. Appl
Physiol Nutr Metab. 31:791–797. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Durzyńska J, Philippou A, Brisson BK,
Nguyen-McCarty M and Barton ER: The pro-forms of insulin-like
growth factor I (IGF-I) are predominant in skeletal muscle and
alter IGF-I receptor activation. Endocrinology. 154:1215–1224.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tan DS, Cook A and Chew SL: Nucleolar
localization of an isoform of the IGF-I precursor. BMC Cell Biol.
3:172002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Durzyńska J, Wardziński A, Koczorowska M,
Goździcka-Józefiak A and Barton ER: Human Eb peptide: not just a
by-product of pre-pro-IGF1b processing? Horm Metab Res. 45:415–422.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Siegfried JM, Kasprzyk PG, Treston AM,
Mulshine JL, Quinn KA and Cuttitta F: A mitogenic peptide amide
encoded within the E peptide domain of the insulin-like growth
factor IB prohormone. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 89:8107–8111. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kasprzak A, Szaflarski W, Szmeja J, et al:
Expression of various insulin-like growth factor-1 mRNA isoforms in
colorectal cancer. Contemp Oncol. 16:147–153. 2012.
|
|
8
|
Kasprzak A, Szaflarski W, Szmeja J, et al:
Differential expression of IGF-1 mRNA isoforms in colorectal
carcinoma and normal colon tissue. Int J Oncol. 42:305–316.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Koczorowska MM, Kwasniewska A and
Gozdzicka-Jozefiak A: IGF1 mRNA isoform expression in the cervix of
HPV-positive women with pre-cancerous and cancer lesions. Exp Ther
Med. 2:149–156. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Pollak M: Insulin and insulin-like growth
factor signaling in neoplasia. Nat Rev Cancer. 8:915–928. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Grimberg A: Mechanisms by which IGF-I may
promote cancer. Cancer Biol Ther. 2:630–635. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lukanova A, Lundin E, Toniolo P, et al:
Circulating levels of insulin-like growth factor-I and risk of
ovarian cancer. Int J Cancer. 101:549–554. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sell C, Rubini M, Rubin R, Liu JP,
Efstratiadis A and Baserga R: Simian virus 40 large tumor antigen
is unable to transform mouse embryonic fibroblasts lacking type 1
insulin-like growth factor receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
90:11217–11221. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
LeRoith D and Roberts CT Jr: The
insulin-like growth factor system and cancer. Cancer Lett.
195:127–137. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Loughran G, Huigsloot M, Kiely PA, Smith
LM, Floyd S, Ayllon V and O’Connor R: Gene expression profiles in
cells transformed by overexpression of the IGF-I receptor.
Oncogene. 24:6185–6193. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gallagher EJ and LeRoith D: Minireview:
IGF, insulin, and cancer. Endocrinology. 152:2546–2551. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Aleksic T, Chitnis MM, Perestenko OV, et
al: Type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor translocates to the
nucleus of human tumor cells. Cancer Res. 70:6412–6419. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Baserga R: The insulin receptor
substrate-1: a biomarker for cancer? Exp Cell Res. 315:727–732.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Baserga R: Customizing the targeting of
IGF-1 receptor. Future Oncol. 5:43–50. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
DePinho RA: The age of cancer. Nature.
408:248–254. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Laron Z: The GH-IGF1 axis and longevity.
The paradigm of IGF1 deficiency. Hormones. 7:24–27. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Steuerman R, Shevah O and Laron Z:
Congenital IGF1 deficiency tends to confer protection against
post-natal development of malignancies. Eur J Endocrinol.
164:485–489. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Laron Z: Laron syndrome (primary growth
hormone resistance or insensitivity): the personal experience
1958–2003. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 89:1031–1044. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Guevara-Aguirre J, Balasubramanian P,
Guevara-Aguirre M, et al: Growth hormone receptor deficiency is
associated with a major reduction in pro-aging signaling, cancer,
and diabetes in humans. Sci Transl Med. 3:70ra132011.(Epub ahead of
print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Wang SR, Carmichael H, Andrew SF, et al:
Large-scale pooled next-generation sequencing of 1077 genes to
identify genetic causes of short stature. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.
98:1428–1437. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Mullis PE: Genetics of isolated growth
hormone deficiency. J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol. 2:52–62. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Forbes BE: Molecular mechanisms underlying
insulin-like growth factor action: How mutations in the GH: IGF
axis lead to short stature. Pediatr Endocrinol Rev. 8:374–381.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Petriczko E, Wikiera B, Horodnicka-Józwa
A, et al: A two year observation of the process of applying
recombinant IGF-1 to treat short stature in children with primary
IGF-1 deficiency - case reports of 3 patients. Pediatr Endocrinol
Diabetes Metab. 17:233–238. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kędzia A, Durzyńska J, Gabryelczyk B,
Petriczko E and Goździcka-Józefiak A: An analysis of the IGF-I
receptor coding sequence in the genome of children with growth
disorders. Pediatrc Endocrinol, Diabet and Metab. 19:96–99.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kasprzak A and Adamek A: The insulin-like
growth factor (IGF) signaling axis and hepatitis C virus-associated
carcinogenesis (Review). Int J Oncol. 41:1919–1931. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Trojanek J, Croul S, Ho T, et al:
T-antigen of the human polyomavirus JC attenuates faithful DNA
repair by forcing nuclear interaction between IRS-1 and Rad51. J
Cell Physiol. 206:35–46. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Reiss K, Khalili K, Giordano A and
Trojanek J: JC virus large T-antigen and IGF-I signaling system
merge to affect DNA repair and genomic integrity. J Cell Physiol.
206:295–300. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ramamoorthy S, Devaraj B, Miyai K, et al:
John Cunningham virus T-antigen expression in anal carcinoma.
Cancer. 117:2379–2385. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
de Villiers EM, Fauquet C, Broker TR,
Bernard HU and zur Hausen H: Classification of papillomaviruses.
Virology. 324:17–27. 2004.
|
|
35
|
Jo H and Kim JW: Implications of HPV
infection in uterine cervical cancer. Cancer Ther. 3:419–434.
2005.
|
|
36
|
Bernard HU: The clinical importance of the
nomenclature, evolution and taxonomy of human papillomaviruses. J
Clin Virol. 32:S1–S6. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
zur Hausen H: Papillomaviruses and cancer:
from basic studies to clinical application. Nat Rev Cancer.
2:342–350. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Pietsch EC and Murphy ME: Low risk HPV-E6
traps p53 in the cytoplasm and induces p53-dependent apoptosis.
Cancer Biol Ther. 7:1916–1918. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
zur Hausen H: Papillomaviruses in the
causation of human cancers - a brief historical account. Virology.
384:260–265. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ghittoni R, Accardi R, Hasan U, Gheit T,
Sylla B and Tommasino M: The biological properties of E6 and E7
oncoproteins from human papillomaviruses. Virus Genes. 40:1–13.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Doorbar J: Molecular biology of human
papillomavirus infection and cervical cancer. Clin Sci.
110:525–541. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Doorbar J, Quint W, Banks L, Bravo IG,
Stoler M, Broker TR and Stanley MA: The biology and life-cycle of
human papillomaviruses. Vaccine. 30:F55–F70. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Whiteside MA, Siegel EM and Unger ER:
Human papillomavirus and molecular considerations for cancer risk.
Cancer. 113:S2981–S2994. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
von Knebel Doeberitz M: New markers for
cervical dysplasia to visualise the genomic chaos created by
aberrant oncogenic papillomavirus infections. Eur J Cancer.
38:2229–2242. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Vinokurova S, Wentzensen N, Kraus I, et
al: Type-dependent integration frequency of human papillomavirus
genomes in cervical lesions. Cancer Res. 68:307–313. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Thorland EC, Myers SL, Gostout BS and
Smith DI: Common fragile sites are preferential targets for HPV16
integrations in cervical tumors. Oncogene. 22:1225–1237. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Cheung JL, Cheung TH, Yu MY and Chan PK:
Virological characteristics of cervical cancers carrying pure
episomal form of HPV16 genome. Gynecol Oncol. 131:374–379. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Yugawa T and Kiyono T: Molecular
mechanisms of cervical carcinogenesis by high-risk human
papillomaviruses: novel functions of E6 and E7 oncoproteins. Rev
Med Virol. 19:97–113. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Egawa K: Do human papillomaviruses target
epidermal stem cells? Dermatology. 207:251–254. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Wilson VG, West M, Woytek K and Rangasamy
D: Papillomavirus E1 proteins: form, function, and features. Virus
Genes. 24:275–290. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
You J, Croyle JL, Nishimura A, Ozato K and
Howley PM: Interaction of the bovine papillomavirus E2 protein with
Brd4 tethers the viral DNA to host mitotic chromosomes. Cell.
117:349–360. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Doorbar J: The papillomavirus life cycle.
J Clin Virol. 32:S7–S15. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Watson RA, Thomas M, Banks L and Roberts
SJ: Activity of the human papillomavirus E6 PDZ-binding motif
correlates with an enhanced morphological transformation of
immortalized human keratinocytes. J Cell Sci. 116:4925–4934. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Sun L, Zhang G, Lei T, Huang C, Song T and
Si L: Two different HPV-11E6 fusion proteins trap p53 in the
cytoplasm and induce apoptosis. Cancer Biol Ther. 7:1909–1915.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Tommasino M, Accardi R, Caldeira S, Dong
W, Malanchi I, Smet A and Zehbe I: The role of TP53 in cervical
carcinogenesis. Hum Mutat. 21:307–312. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Ganguly N and Parihar SP: Human
papillomavirus E6 and E7 oncoproteins as risk factors for
tumorigenesis. J Biosci. 34:113–123. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
McLaughlin-Drubin ME and Münger K: The
human papillomavirus E7 oncoprotein. Virology. 384:335–344. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Psyrri A and DiMaio D: Human
papillomavirus in cervical and head-and-neck cancer. Nat Clin Pract
Oncol. 5:24–31. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Clifford GM, Smith JS, Plummer M, Muñoz N
and Franceschi S: Human papillomavirus types in invasive cervical
cancer worldwide: a meta-analysis. Br J Cancer. 88:63–73. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
zur Hausen H: Papillomaviruses causing
cancer: evasion from host-cell control in early events in
carcinogenesis. J Natl Cancer Inst. 92:690–698. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Lee SW, Lee SY, Lee SR, Ju W and Kim SC:
Plasma levels of insulin-like growth factor-1 and insulin-like
growth factor binding protein-3 in women with cervical neoplasia.
Gynecol Oncol. 21:174–180. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Wu X, Tortolero-Luna G, Zhao H, Phatak D,
Spitz MR and Follen M: Serum levels of insulin-like growth factor I
and risk of squamous intraepithelial lesions of the cervix. Clin
Cancer Res. 9:3356–3361. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Huang YF, Shen MR, Hsu KF, Cheng YM and
Chou CY: Clinical implications of insulin-like growth factor 1
system in early-stage cervical cancer. Br J Cancer. 99:1096–1102.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Schaffer A, Koushik A, Trottier H, et al:
Insulin-like growth factor-I and risk of high-grade cervical
intraepithelial neoplasia. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev.
16:716–722. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Serrano ML, Romero A, Cendales R,
Sánchez-Gómez M and Bravo MM: Serum levels of insulin-like growth
factor-I and -II and insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3
in women with squamous intraepithelial lesions and cervical cancer.
Biomedica. 26:258–268. 2006.
|
|
66
|
Serrano ML, Sánchez-Gómez M and Bravo MM:
Insulin-like growth factor system gene expression in cervical
scrapes from women with squamous intraepithelial lesions and
cervical cancer. Growth Horm IGF Res. 17:492–499. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Serrano ML, Sánchez-Gómez M, Bravo MM,
Yakar S and LeRoith: Differential expression of IGF-I and insulin
receptor isoforms in HPV positive and negative human cervical
cancer cell lines. Horm Metab Res. 40:661–667. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Serrano ML, Sánchez-Gómez M and Bravo MM:
Cervical scrapes levels of insulin-like growth factor-II and
insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3 in women with squamous
intraepithelial lesions and cervical cancer. Horm Metab Res.
42:977–981. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Shen MR, Hsu YM, Hsu KF, Chen YF, Tang MJ
and Chou CY: Insulin-like growth factor 1 is a potent stimulator of
cervical cancer cell invasiveness and proliferation that is
modulated by alphavbeta3 integrin signaling. Carcinogenesis.
27:962–971. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Steller MA, Delgado CH, Bartels CJ,
Woodworth CD and Zou Z: Overexpression of the insulin-like growth
factor-1 receptor and autocrine stimulation in human cervical
cancer cells. Cancer Res. 56:1761–1765. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Kuramoto H, Hongo A, Liu YX, et al:
Immunohistochemical evaluation of insulin-like growth factor I
receptor status in cervical cancer specimens. Acta Med Okayama.
62:251–259. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Voskuil DW, Bosma A, Vrieling A, Rookus MA
and van ‘t Veer LJ: Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-system mRNA
quantities in normal and tumor breast tissue of women with sporadic
and familial breast cancer risk. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
84:225–233. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Rosenzweig SA and Atreya HS: Defining the
pathway to insulin-like growth factor system targeting in cancer.
Biochem Pharmacol. 80:1115–1124. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Dal Maso L, Augustin LS, Franceschi S, et
al: Association between components of the insulin-like growth
factor system and epithelial ovarian cancer risk. Oncology.
67:225–230. 2004.
|
|
75
|
Hong J, Zhang G, Dong F and Rechler MM:
Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-binding protein-3 mutants that do
not bind IGF-I or IGF-II stimulate apoptosis in human prostate
cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 277:10489–10497. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Baege AC, Disbrow GL and Schlegel R:
IGFBP-3, a marker of cellular senescence, is overexpressed in human
papillomavirus-immortalized cervical cells and enhances
IGF-1-induced mitogenesis. J Virol. 78:5720–5727. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Berger AJ, Baege A, Guillemette T, et al:
Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 3 expression increases
during immortalization of cervical keratinocytes by human
papillomavirus type 16 E6 and E7 proteins. Am J Pathol.
161:603–610. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Harris TG, Burk RD, Yu H, et al:
Insulin-like growth factor axis and oncogenic human papillomavirus
natural history. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 17:245–248.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Mannhardt B, Weinzimer SA, Wagner M,
Fiedler M, Cohen P, Jansen-Dürr P and Zwerschke W: Human
papillomavirus type 16 E7 oncoprotein binds and inactivates
growth-inhibitory insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3. Mol
Cell Biol. 20:6483–6495. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Mathur SP, Mathur RS, Underwood PB, Kohler
MF and Creasman WT: Circulating levels of insulin-like growth
factor-II and IGF-binding protein 3 in cervical cancer. Gynecol
Oncol. 91:486–493. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Sharma M, Satyam A, Abhishek A, Khan R,
Rajappa M and Sharma A: Molecular and circulatory expression of
insulin growth factors in Indian females with advanced cervical
cancer. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 13:6475–6479. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Gariglio P, Gutiérrez J, Cortés E and
Vázquez J: The role of retinoid deficiency and estrogens as
cofactors in cervical cancer. Arch Med Res. 40:449–465. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Shai A, Brake T, Somoza C and Lambert PF:
The human papillomavirus E6 oncogene dysregulates the cell cycle
and contributes to cervical carcinogenesis through two independent
activities. Cancer Res. 67:1626–1635. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Chung SH, Franceschi S and Lambert PF:
Estrogen and ERalpha: culprits in cervical cancer? Trends
Endocrinol Metab. 21:504–511. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Brake T and Lambert PF: Estrogen
contributes to the onset, persistence, and malignant progression of
cervical cancer in a human papillomavirus-transgenic mouse model.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:2490–2495. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Yoo YA, Son J, Mehta FF, Demayo FJ, Lydon
JP and Chung SH: Progesterone signaling inhibits cervical
carcinogenesis in mice. Am J Pathol. 183:1679–1687. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Webster K, Taylor A and Gaston K:
Oestrogen and progesterone increase the levels of apoptosis induced
by the human papillomavirus type 16 E2 and E7 proteins. J Gen
Virol. 82:201–213. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
López-Romero R, Garrido-Guerrero E,
Rangel-López A, et al: The cervical malignant cells display a down
regulation of ER-α but retain the ER-β expression. Int J Clin Exp
Pathol. 6:1594–1602. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Wang WM, Chung MH and Huang SM: Regulation
of nuclear receptor activities by two human papillomavirus type 18
oncoproteins, E6 and E7. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 303:932–939.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Mathur RS and Mathur SP: In vitro
downregulation of growth factors by insulin-like growth factor
binding protein-3 in cervical cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 91:410–415.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Piyathilake CJ, Henao OL, Macaluso M,
Cornwell PE, Meleth S, Heimburger DC and Partridge EE: Folate is
associated with the natural history of high-risk human
papillomaviruses. Cancer Res. 64:8788–8793. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Piyathilake CJ, Badiga S, Paul P, et al:
Indian women with higher serum concentrations of folate and vitamin
B12 are significantly less likely to be infected with carcinogenic
or high-risk (HR) types of human papillomaviruses (HPVs). Int J
Womens Health. 2:7–12. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
93
|
Warowicka A, Kwasniewska A and
Gozdzicka-Jozefiak A: Alterations in mtDNA: a qualitative and
quantitative study associated with cervical cancer development.
Gynecol Oncol. 129:193–198. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
94
|
Guo W, Yang D and Xu H: Mutations in the
D-loop region and increased copy number of mitochondrial DNA in
human laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Mol Biol Rep. 40:13–20.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Zhu W, Qin W, Bradley P, Wessel A, Puckett
CL and Sauter ER: Mitochondrial DNA mutations in breast cancer
tissue and in matched nipple aspirate fluid. Carcinogenesis.
26:145–152. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Gao J, Chang YS, Jallal B and Viner J:
Targeting the insulin-like growth factor axis for the development
of novel therapeutics in oncology. Cancer Res. 72:3–12. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Miller BS and Yee D: Type I insulin-like
growth factor receptor as a therapeutic target in cancer. Cancer
Res. 65:10123–10127. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Hartog H, Wesseling J, Boezen HM and van
der Graaf WT: The insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor in cancer:
old focus, new future. Eur J Cancer. 43:1895–1904. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Friedrich RE, Hagel C and Bartel-Friedrich
S: Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF-1R) in primary and
metastatic undifferentiated carcinoma of the head and neck: a
possible target of immunotherapy. Anticancer Res. 30:1641–1643.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Arcaro A: Targeting the insulin-like
growth factor-1 receptor in human cancer. Front Pharmacol.
4:302013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Pollak M: The insulin
receptor/insulin-like growth factor receptor family as a
therapeutic target in oncology. Clin Cancer Res. 18:40–50. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Samani AA, Yakar S, LeRoith D and Brodt P:
The role of the IGF system in cancer growth and metastasis:
overview and recent insights. Endocr Rev. 28:20–47. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Corvaia N, Beck A, Caussanel V and Goetsch
L: Insulin-like growth factor receptor type I as a target for
cancer therapy. Front Biosci. 5:439–450. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Baserga R: The decline and fall of the
IGF-I receptor. J Cell Physiol. 228:675–679. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Nakamura K, Hongo A, Kodama J, Miyagi Y,
Yoshinouchi M and Kudo T: Downregulation of the insulin-like growth
factor I receptor by antisense RNA can reverse the transformed
phenotype of human cervical cancer cell lines. Cancer Res.
60:760–765. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
McLaughlin-Drubin ME, Meyers J and Munger
K: Cancer associated human papillomaviruses. Curr Opin Virol.
2:459–466. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
107
|
Martignani E, Miretti S, Accornero P and
Baratta M: miRNAs highlights in stem and cancer cells. Mini Rev Med
Chem. 11:1165–1182. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Luo M, Shen D, Zhou X, Chen X and Wang W:
MicroRNA-497 is a potential prognostic marker in human cervical
cancer and functions as a tumor suppressor by targeting the
insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor. Surgery. 153:836–847. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Cheung TH, Man KN and Yu MY: Dysregulated
microRNAs in the pathogenesis and progression of cervical neoplasm.
Cell Cycle. 11:2876–2884. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Butz K, Ristriani T, Hengstermann A, Denk
C, Scheffner M and Hoppe-Seyler F: siRNA targeting of the viral E6
oncogene efficiently kills human papillomavirus-positive cancer
cells. Oncogene. 22:5938–5945. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
111
|
Hall AH and Alexander KA: RNA interference
of human papillomavirus type 18 E6 and E7 induces senescence in
HeLa cells. J Virol. 77:6066–6069. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Kafri T, van Praag H, Gage FH and Verma
IM: Lentiviral vectors: regulated gene expression. Mol Ther.
1:516–521. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Gu W, Putral L, Hengst K, Minto K,
Saunders NA, Leggatt G and McMillan NA: Inhibition of cervical
cancer cell growth in vitro and in vivo with lentiviral-vector
delivered short hairpin RNA targeting human papillomavirus E6 and
E7 oncogenes. Cancer Gene Ther. 13:1023–1032. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Copreni E, Penzo M, Carrabino S and Conese
M: Lentivirus-mediated gene transfer to the respiratory epithelium:
a promising approach to gene therapy of cystic fibrosis. Gene Ther.
11:S67–S75. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Zhou J, Li B, Peng C, et al: Inhibition of
cervical cancer cell growth in vitro and in vivo by
lentiviral-vector mediated shRNA targeting the common promoter of
HPV16 E6 and E7 oncogenes. Antiviral Res. 98:305–313. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Bousarghin L, Touze A, Gaud G, et al:
Inhibition of cervical cancer cell growth by human papillomavirus
virus-like particles packaged with human papillomavirus oncoprotein
short hairpin RNAs. Mol Cancer Ther. 8:357–365. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
117
|
Remy-Ziller C, Germain C, Spindler A, et
al: Immunological characterization of a modified vaccinia virus
Ankara vector expressing the human papillomavirus 16 E1 protein.
Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2:147–155. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Markowitz LE, Tsu V, Deeks SL, Cubie H,
Wang SA, Vicari AS and Brotherton JM: Human papillomavirus vaccine
introduction - the first five years. Vaccine. 30:F139–F148.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Han KT and Sin JI: DNA vaccines targeting
human papillomavirus-associated diseases: progresses in animal and
clinical studies. Clin Exp Vaccine Res. 2:106–114. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Frazer IH: Prevention of cervical cancer
through papillomavirus vaccination. Nat Rev Immunol. 4:46–54. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Berraondo P, Nouzé C, Préville X, Ladant D
and Leclerc C: Eradication of large tumors in mice by a tritherapy
targeting the innate, adaptive, and regulatory components of the
immune system. Cancer Res. 67:8847–8855. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Peng S, Ji H, Trimble C, et al:
Development of a DNA vaccine targeting human papillomavirus type 16
oncoprotein E6. J Virol. 78:8468–8476. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Jin HS, Park EK, Lee JM, et al:
Immunization with adenoviral vectors carrying recombinant IL-12 and
E7 enhanced the antitumor immunity to human papillomavirus
16-associated tumor. Gynecol Oncol. 97:559–567. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
124
|
Gunn GR, Zubair A, Peters C, Pan ZK, Wu TC
and Paterson Y: Two Listeria monocytogenes vaccine vectors that
express different molecular forms of human papilloma virus-16
(HPV-16) E7 induce qualitatively different T cell immunity that
correlates with their ability to induce regression of established
tumors immortalized by HPV-16. J Immunol. 167:6471–6479. 2001.
|
|
125
|
Chandy AG, Nurkkala M, Josefsson A and
Eriksson K: Therapeutic dendritic cell vaccination with Ag coupled
to cholera toxin in combination with intratumoural CpG injection
leads to complete tumour eradication in mice bearing HPV 16
expressing tumours. Vaccine. 25:6037–6046. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
126
|
Da Silva DM, Schiller JT and Kast WM:
Heterologous boosting increases immunogenicity of chimeric
papillomavirus virus-like particle vaccines. Vaccine. 21:3219–3227.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|