|
1
|
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J and Pisani P:
Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 55:74–108. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Marioni G, Marchese-Ragona R, Cartei G,
Marchese F and Staffieri A: Current opinion in diagnosis and
treatment of laryngeal carcinoma. Cancer Treat Rev. 32:504–515.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Alhamarneh O, Amarnath SM, Stafford ND and
Greenman J: Regulatory T cells: what role do they play in antitumor
immunity in patients with head and neck cancer? Head Neck.
30:251–261. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zou W: Regulatory T cells, tumour immunity
and immunotherapy. Nat Rev Immunol. 6:295–307. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Curiel TJ, Coukos G, Zou L, et al:
Specific recruitment of regulatory T cells in ovarian carcinoma
fosters immune privilege and predicts reduced survival. Nat Med.
10:942–949. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kobayashi N, Hiraoka N, Yamagami W, et al:
FOXP3+ regulatory T cells affect the development and
progression of hepatocarcinogenesis. Clin Cancer Res. 13:902–911.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kono K, Kawaida H, Takahashi A, et al:
CD4(+) CD25high regulatory T cells increase with tumor
stage in patients with gastric and esophageal cancers. Cancer
Immunol Immunother. 55:1064–1071. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Pretscher D, Distel LV, Grabenbauer GG,
Wittlinger M, Buettner M and Niedobitek G: Distribution of immune
cells in head and neck cancer: CD8+ T-cells and
CD20+ B-cells in metastatic lymph nodes are associated
with favourable outcome in patients with oro- and hypopharyngeal
carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 9:2922009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Badoual C, Hans S, Rodriguez J, et al:
Prognostic value of tumor-infiltrating CD4+ T-cell
subpopulations in head and neck cancers. Clin Cancer Res.
12:465–472. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sakaguchi S, Sakaguchi N, Asano M, Itoh M
and Toda M: Immunological self-tolerance maintained by activated T
cells expressing IL-2 receptor alpha-chains (CD25). Breakdown of a
single mechanism of self-tolerance causes various autoimmune
diseases. J Immunol. 155:1151–1164. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Baecher-Allan C, Brown JA, Freeman GJ and
Hafler DA: CD4+CD25(high) regulatory cells in human
peripheral blood. J Immunol. 167:1245–1253. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hori S, Nomura T and Sakaguchi S: Control
of regulatory T cell development by the transcription factor Foxp3.
Science. 299:1057–1061. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Fontenot JD, Gavin MA and Rudensky AY:
Foxp3 programs the development and function of CD4(+)CD25(+)
regulatory T cells. Nat Immunol. 4:330–336. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Liu WH, Putnam AL, Xu-Yu Z, et al: CD127
expression inversely correlates with FoxP3 and suppressive function
of human CD4(+) T reg cells. J Exp Med. 203:1701–1711. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Drennan S, Stafford ND, Greenman J and
Green VL: Increased frequency and suppressive activity of
CD127(low/−) regulatory T cells in the peripheral circulation of
patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma are associated
with advanced stage and nodal involvement. Immunology. 140:335–343.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Miyara M, Yoshioka Y, Kitoh A, et al:
Functional delineation and differentiation dynamics of human
CD4+ T cells expressing the Foxp3 transcription factor.
Immunity. 30:899–911. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kordasti S, Marsh J, Al-Khan S, et al:
Functional characterization of CD4+ T cells in aplastic
anemia. Blood. 119:2033–2043. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Buckner JH: Mechanisms of impaired
regulation by CD4(+) CD25(+)FOXP3(+) regulatory T cells in human
autoimmune diseases. Nat Rev Immunol. 10:849–859. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Benchetrit F, Gazagne A, Adotevi O, et al:
Cytotoxic T lymphocytes: role in immunosurveillance and in
immunotherapy. Bull Cancer. 90:677–685. 2003.(In French).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Bennett SR, Carbone FR, Karamalis F,
Miller JF and Heath WR: Induction of a CD8+ cytotoxic T
lymphocyte response by cross-priming requires cognate
CD4+ T cell help. J Exp Med. 186:65–70. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Cassel D and Forman J: Linked recognition
of helper and cytotoxic antigenic determinants for the generation
of cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Ann NY Acad Sci. 532:51–60. 1988.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
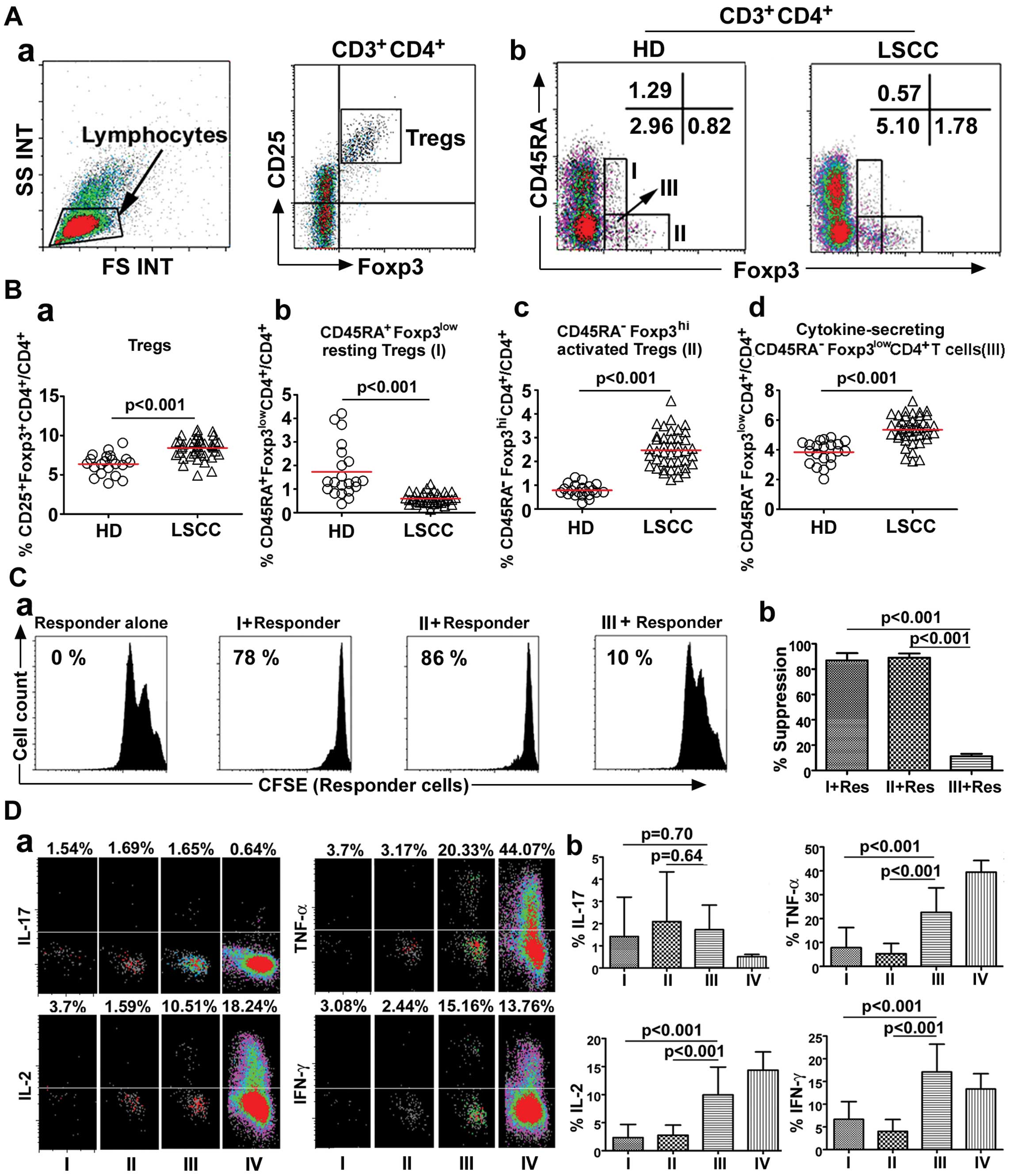
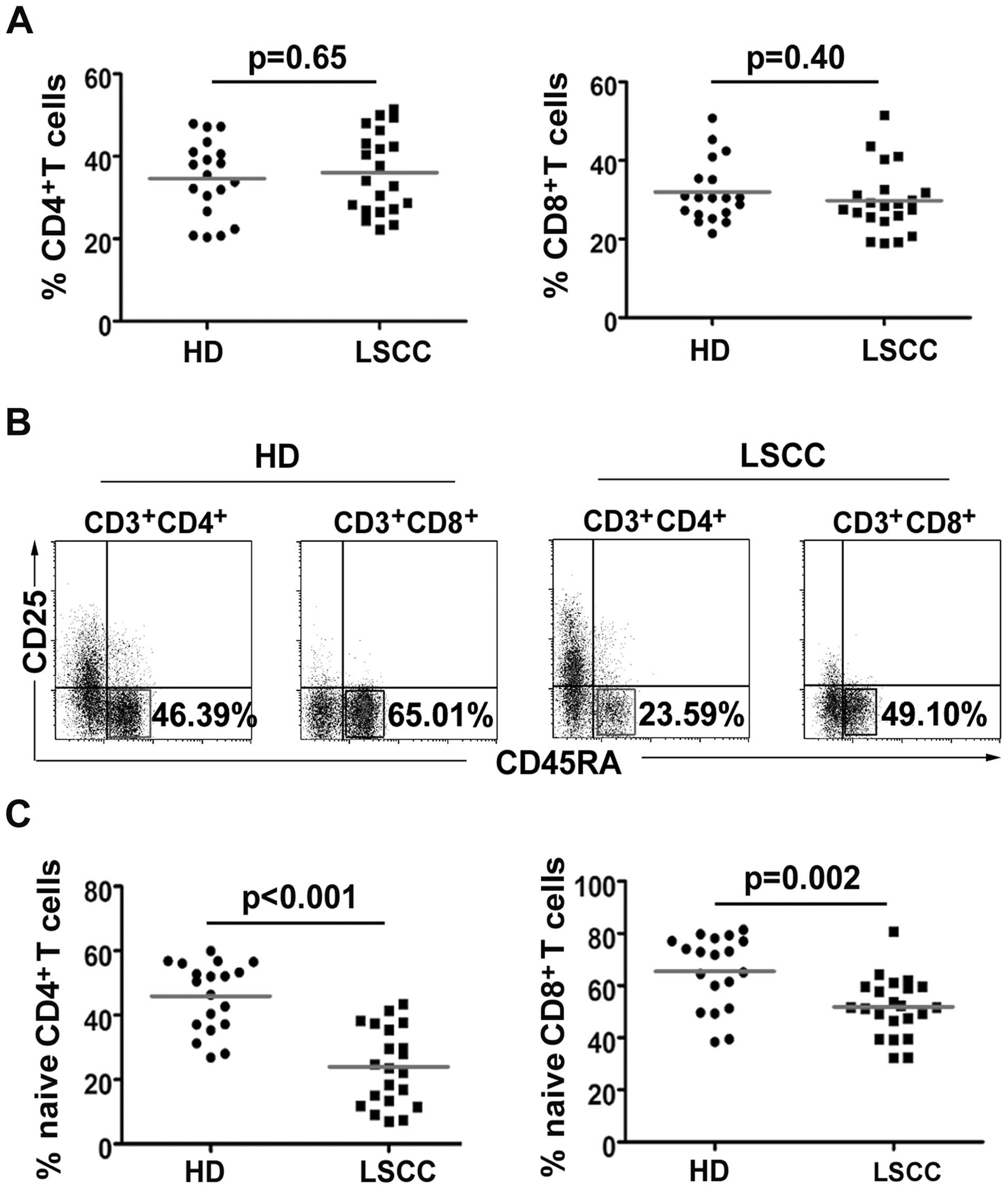
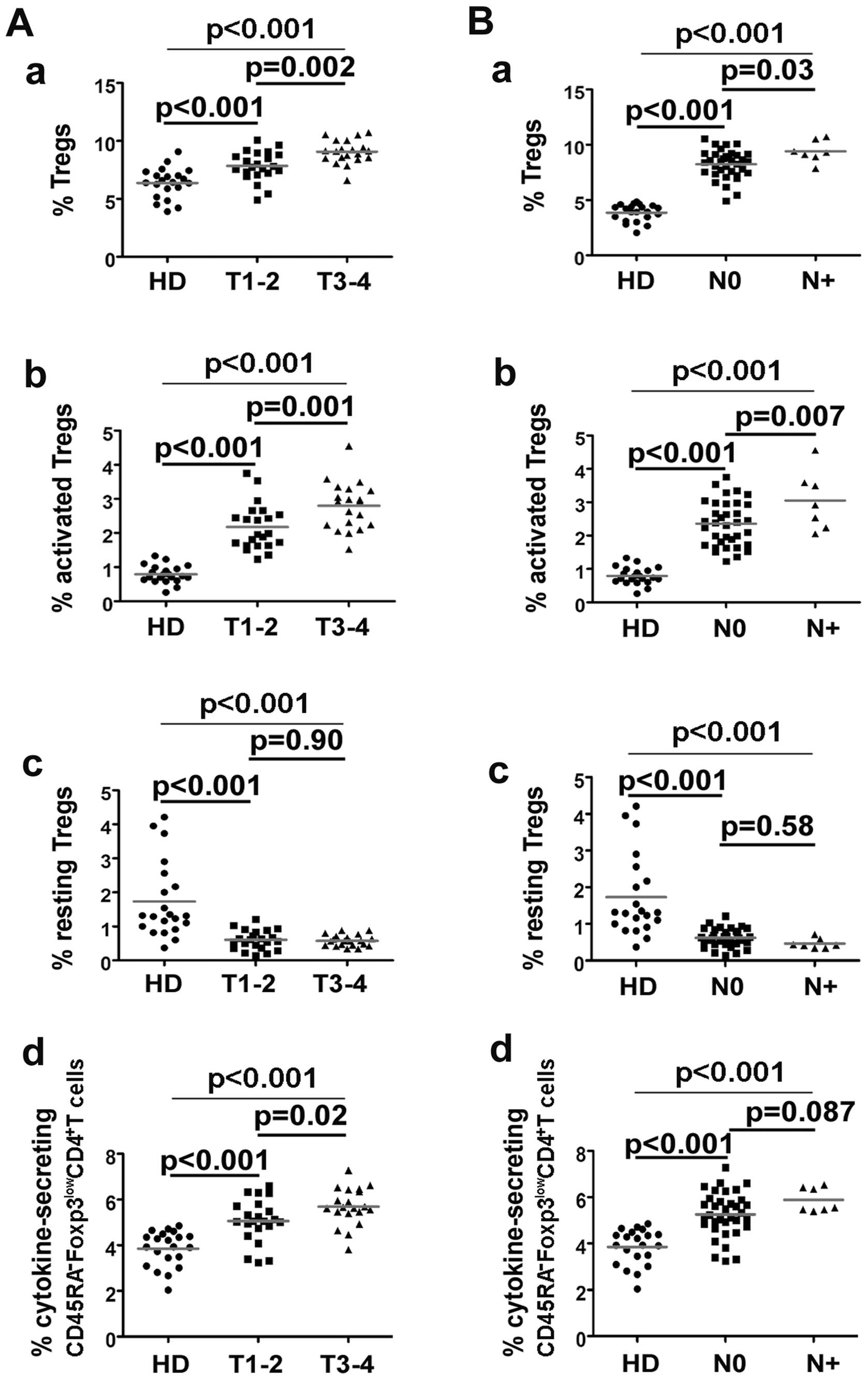
Sun W, Li WJ, Wu CY, Zhong H and Wen WP:
CD45RA−Foxp3high but not
CD45RA+Foxp3low suppressive T regulatory
cells increased in the peripheral circulation of patients with head
and neck squamous cell carcinoma and correlated with tumor
progression. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 33:352014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Strauss L, Bergmann C, Gooding W, et al:
The frequency and suppressor function of
CD4+CD25highFoxp3+ T cells in the
circulation of patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the head
and neck. Clin Cancer Res. 13:6301–6311. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lau KM, Cheng SH, Lo KW, et al: Increase
in circulating Foxp3+CD4+CD25(high)
regulatory T cells in nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients. Br J
Cancer. 96:617–622. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
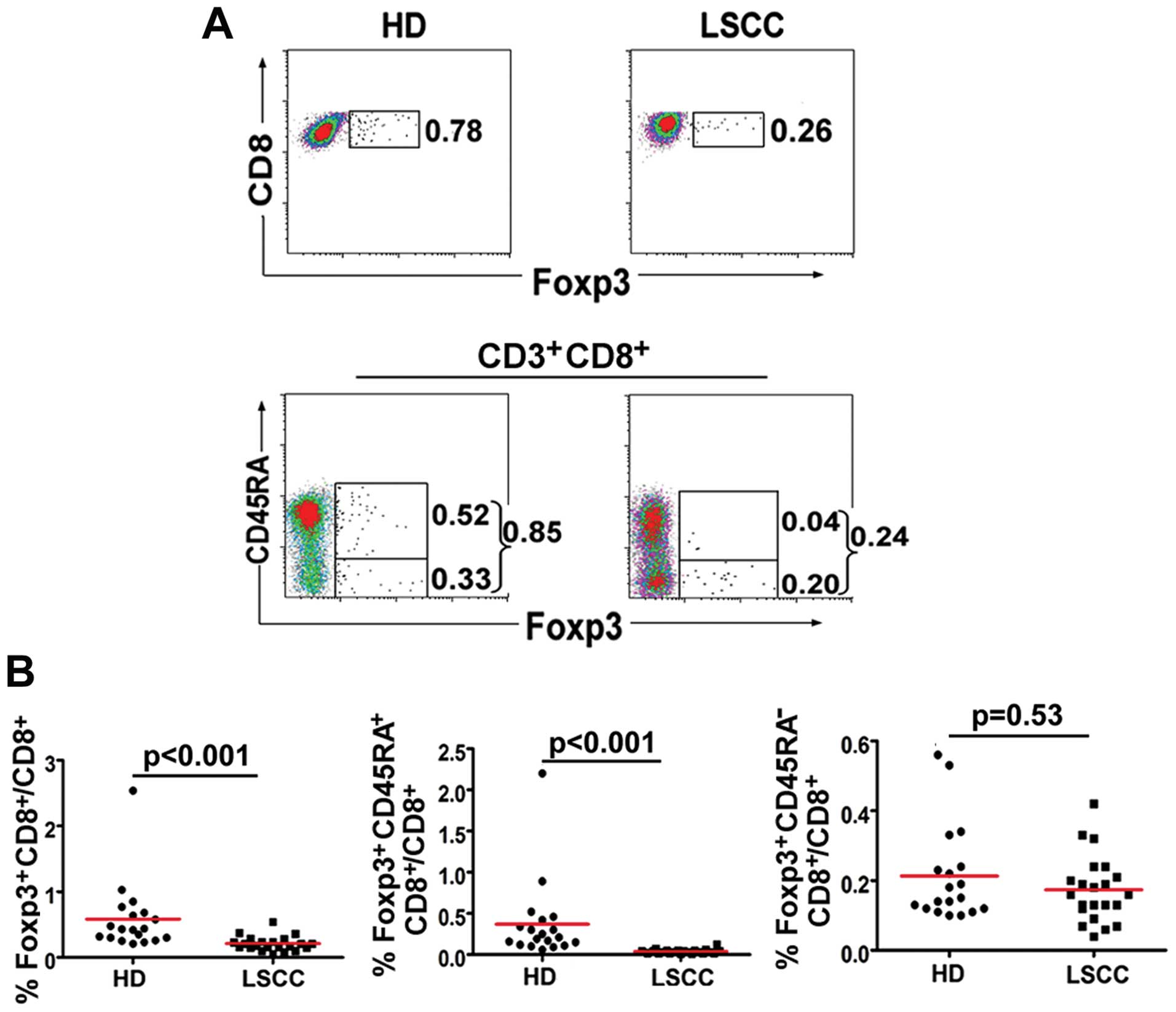
Chikamatsu K, Sakakura K, Whiteside TL and
Furuya N: Relationships between regulatory T cells and
CD8+ effector populations in patients with squamous cell
carcinoma of the head and neck. Head Neck. 29:120–127. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Shevach EM: Mechanisms of
Foxp3+ T regulatory cell-mediated suppression. Immunity.
30:636–645. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Schmidt A, Oberle N and Krammer PH:
Molecular mechanisms of Treg-mediated T cell suppression. Front
Immunol. 3:512012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
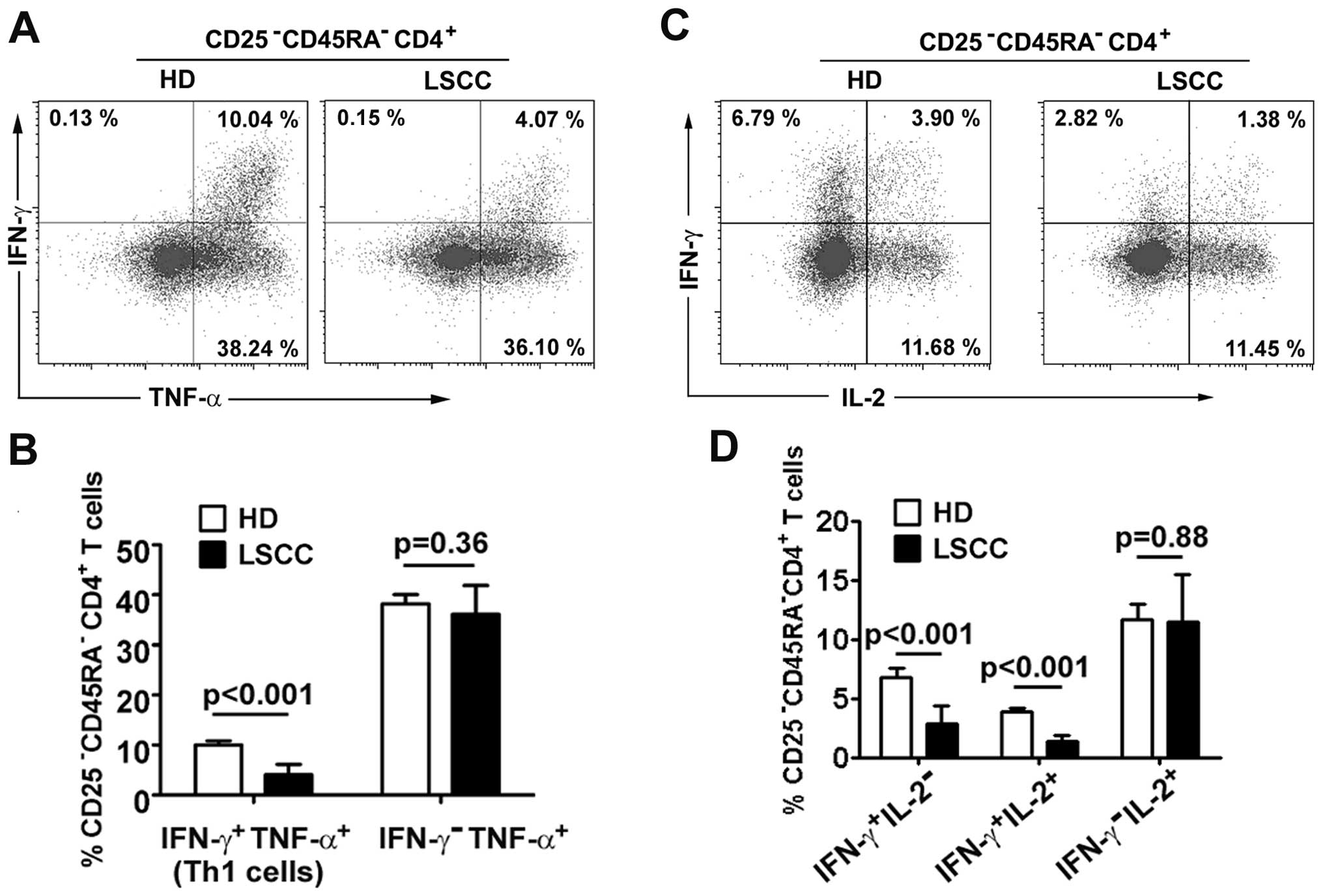
Foulds KE, Rotte MJ, Paley MA, et al:
IFN-gamma mediates the death of Th1 cells in a paracrine manner. J
Immunol. 180:842–849. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhou X, Bailey-Bucktrout SL, Jeker LT, et
al: Instability of the transcription factor Foxp3 leads to the
generation of pathogenic memory T cells in vivo. Nat Immunol.
10:1000–1007. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Allan SE, Crome SQ, Crellin NK, et al:
Activation-induced FOXP3 in human T effector cells does not
suppress proliferation or cytokine production. Int Immunol.
19:345–354. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Erfani N, Khademi B, Haghshenas MR,
Mojtahedi Z, Khademi B and Ghaderi A: Intracellular CTLA4 and
regulatory T cells in patients with laryngeal squamous cell
carcinoma. Immunol Invest. 42:81–90. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Schaefer C, Kim GG, Albers A, Hoermann K,
Myers EN and Whiteside TL: Characteristics of
CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells in the
peripheral circulation of patients with head and neck cancer. Br J
Cancer. 92:913–920. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Attig S, Hennenlotter J, Pawelec G, et al:
Simultaneous infiltration of polyfunctional effector and suppressor
T cells into renal cell carcinomas. Cancer Res. 69:8412–8419. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|