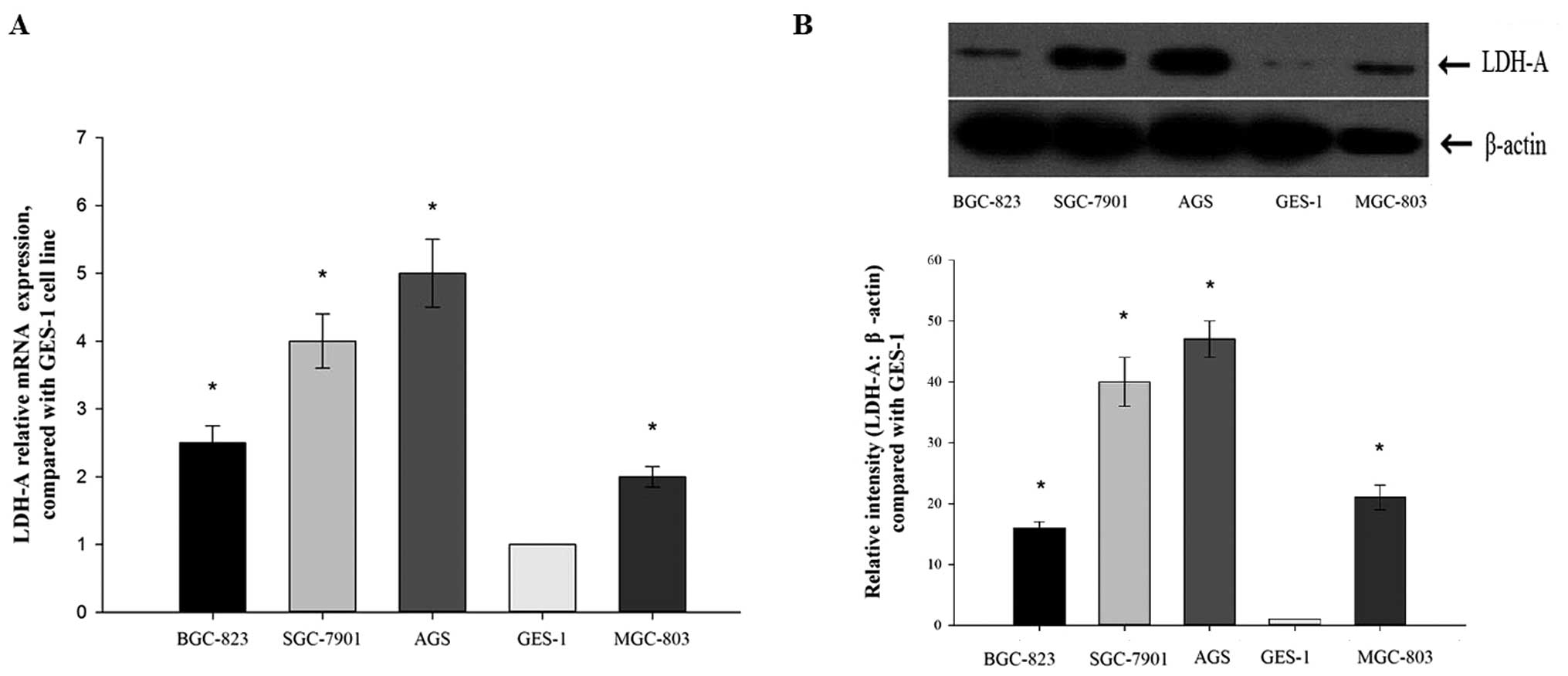
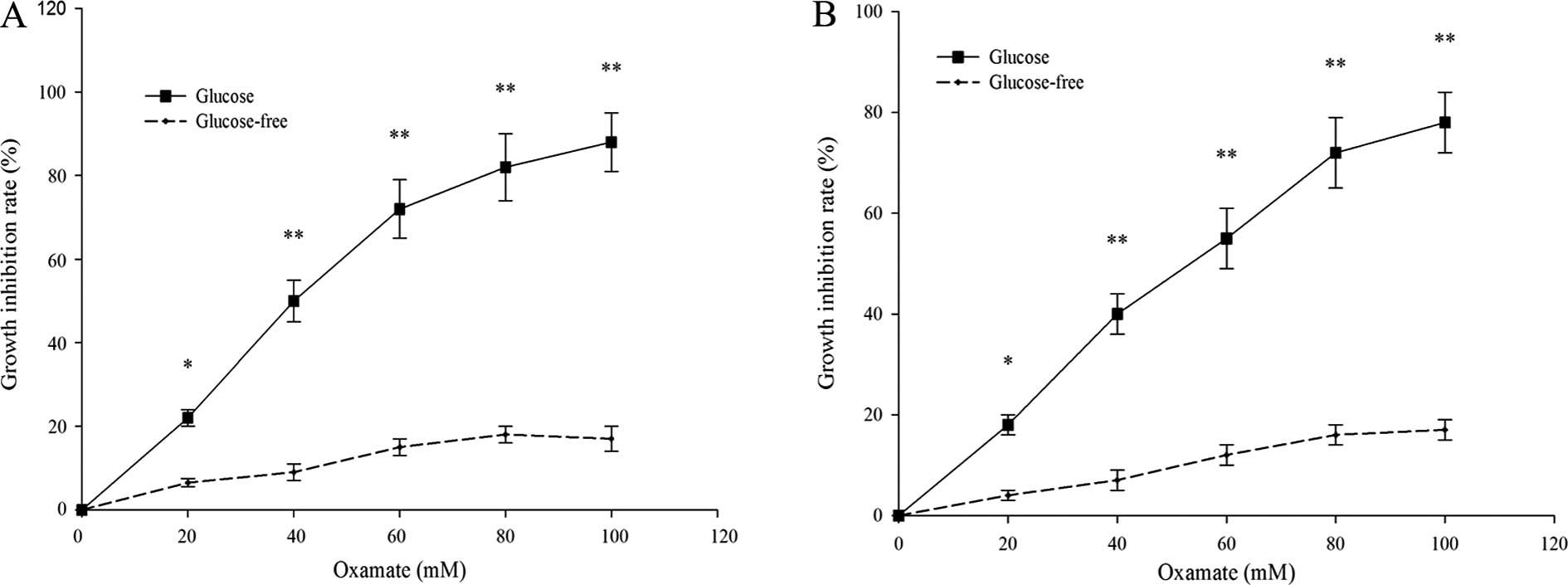
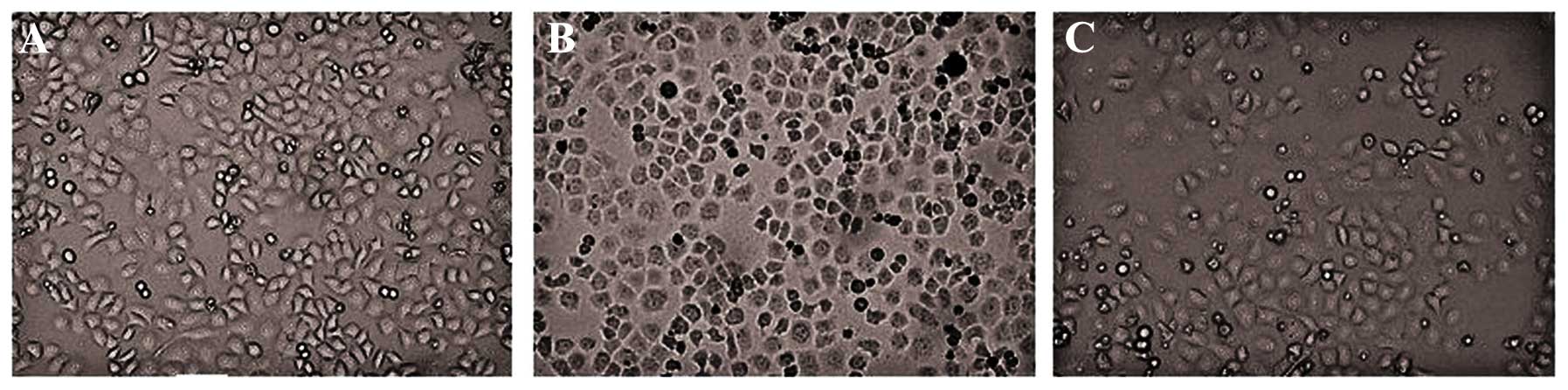
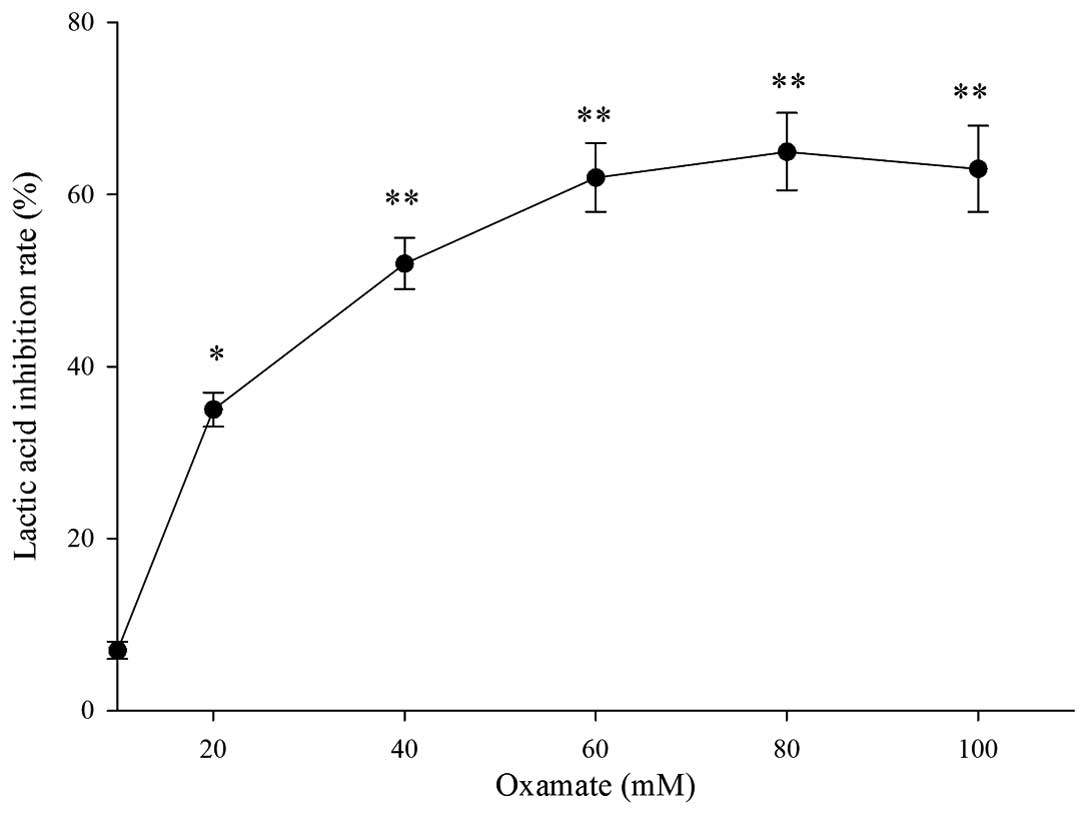
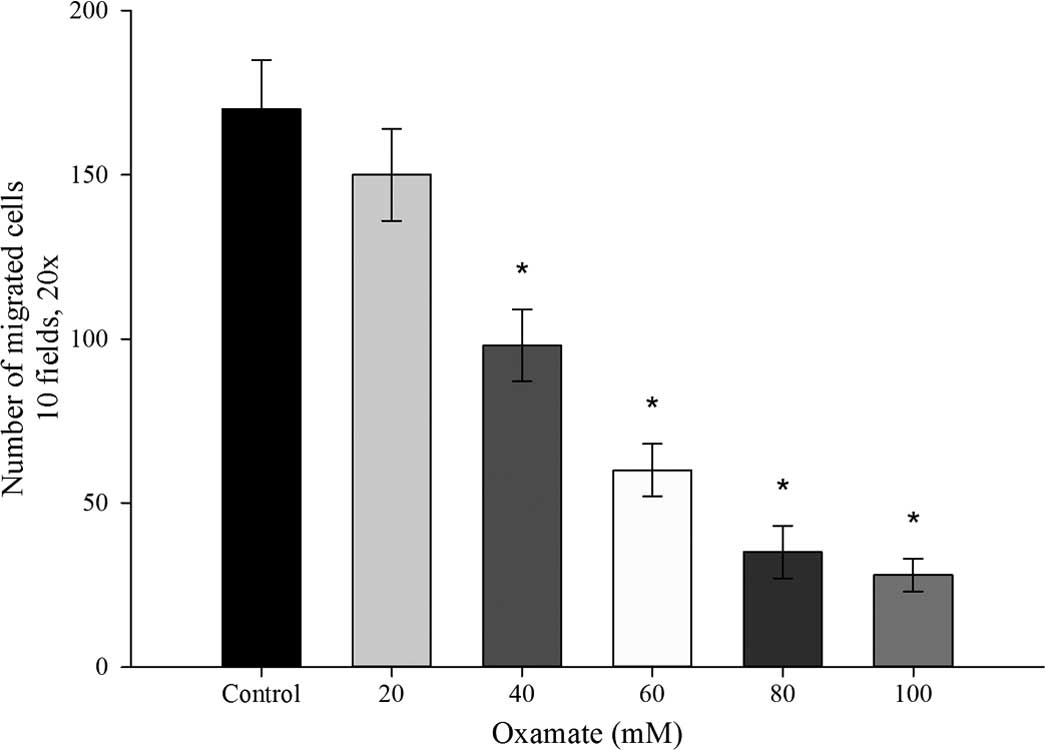
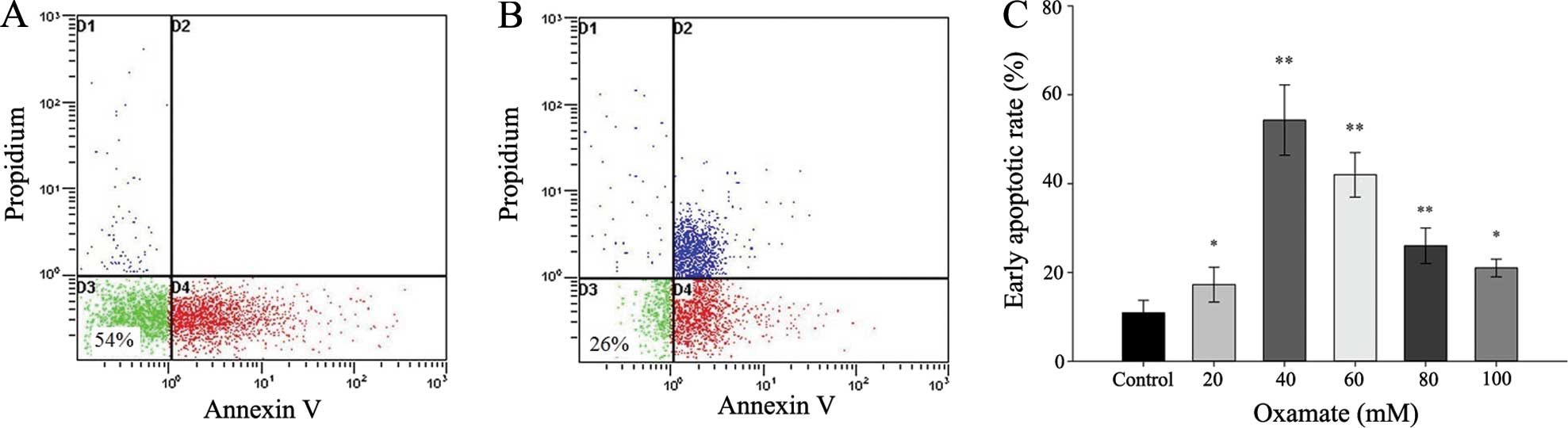
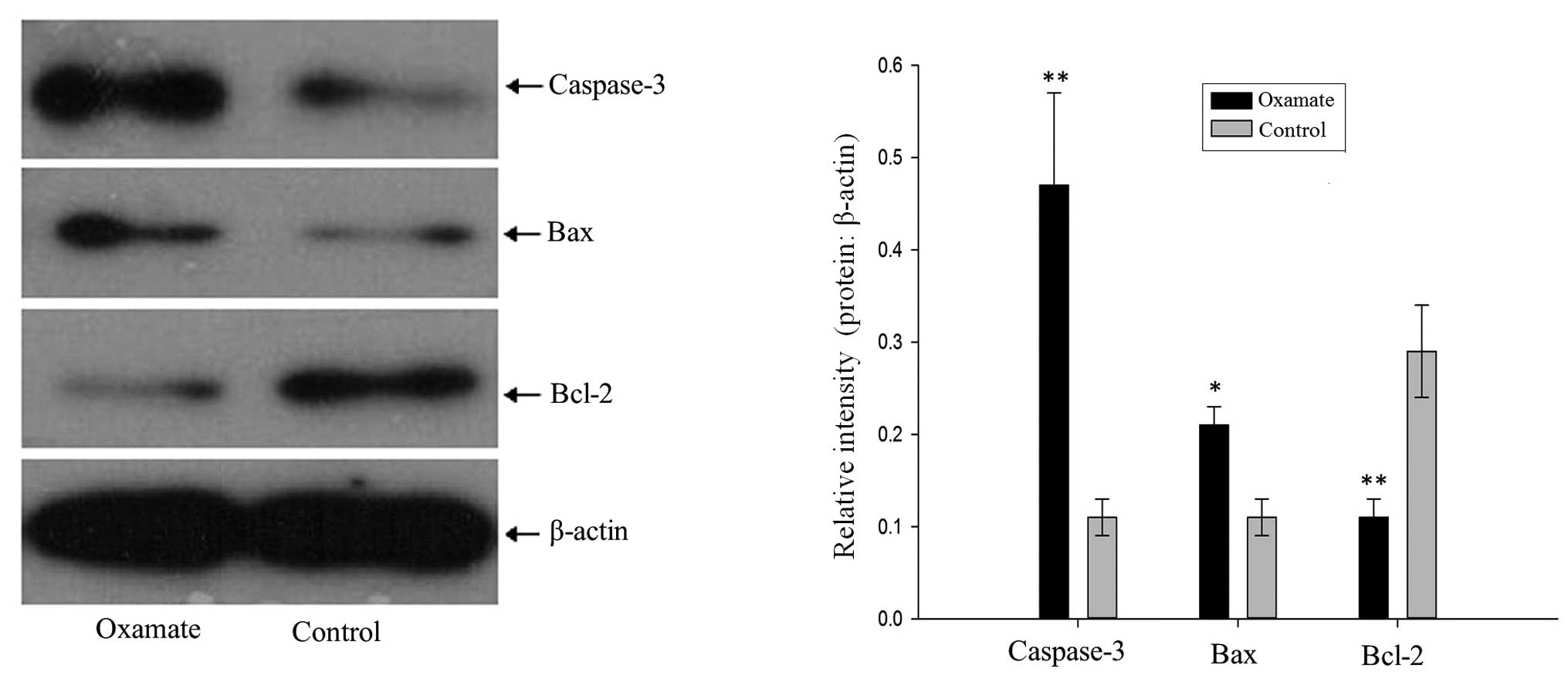
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, et al: Global
cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, et al:
Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int
J Cancer. 127:2893–2917. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Bertuccio P, Chatenoud L, Levi F, et al:
Recent patterns in gastric cancer: a global overview. Int J Cancer.
125:666–673. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 62:10–29. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: the next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Annibaldi A and Widmann C: Glucose
metabolism in cancer cells. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care.
13:466–470. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Cheong H, Lu C, Lindsten T and Thompson
CB: Therapeutic targets in cancer cell metabolism and autophagy.
Nat Biotechnol. 30:671–678. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Favoni RE and Florio T: Combined
chemotherapy with cytotoxic and targeted compounds for the
management of human malignant pleural mesothelioma. Trends
Pharmacol Sci. 32:463–479. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Vander Heiden MG, Cantley LC and Thompson
CB: Understanding the Warburg effect: the metabolic requirements of
cell proliferation. Science. 324:1029–1033. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kolev Y, Uetake H, Takagi Y and Sugihara
K: Lactate dehydrogenase-5 (LDH-5) expression in human gastric
cancer: association with hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF-1α) pathway,
angiogenic factors production and poor prognosis. Ann Surg Oncol.
15:2336–2344. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Koukourakis MI, Giatromanolaki A and
Sivridis E; Tumour and Angiogenesis Research Group. Lactate
dehydrogenase isoenzymes 1 and 5: differential expression by
neoplastic and stromal cells in non-small cell lung cancer and
other epithelial malignant tumors. Tumour Biol. 24:199–202. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Xie H, Valera VA, Merino MJ, et al: LDH-A
inhibition, a therapeutic strategy for treatment of hereditary
leiomyomatosis and renal cell cancer. Mol Cancer Ther. 8:626–635.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sudo K: Lactate dehydrogenase M subunit
deficiency. Rinsho Byori. 50:571–575. 2002.(In Japanese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kanno T, Sudo K, Maekawa M, et al: Lactate
dehydrogenase M-subunit deficiency: a new type of hereditary
exertional myopathy. Clin Chim Acta. 173:89–98. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Okumura N, Terasawa F, Ueno I, et al:
Genetic analyses in homozygous and heterozygous variants of lactate
dehydrogenase-B (H) subunit - LD-B Matsumoto I and II (LD-B W323R).
Clin Chim Acta. 287:163–171. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Fotakis G and Timbrell JA: In vitro
cytotoxicity assays: comparison of LDH, neutral red, MTT and
protein assay in hepatoma cell lines following exposure to cadmium
chloride. Toxicol Lett. 160:171–177. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Chou TC and Talalay P: Quantitative
analysis of dose-effect relationships: the combined effects of
multiple drugs or enzyme inhibitors. Adv Enzyme Regul. 22:27–55.
1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Fiume L, Manerba M, Vettraino M and Di
Stefano G: Impairment of aerobic glycolysis by inhibitors of lactic
dehydrogenase hinders the growth of human hepatocellular carcinoma
cell lines. Pharmacology. 86:157–162. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Fantin VR, St-Pierre J and Leder P:
Attenuation of LDH-A expression uncovers a link between glycolysis,
mitochondrial physiology, and tumor maintenance. Cancer Cell.
9:425–434. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ward PS and Thompson CB: Metabolic
reprogramming: a cancer hallmark even Warburg did not anticipate.
Cancer Cell. 21:297–308. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ferreira LM: Cancer metabolism: the
Warburg effect today. Exp Mol Pathol. 89:372–380. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lunt SY and Vander Heiden MG: Aerobic
glycolysis: meeting the metabolic requirements of cell
proliferation. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 27:441–464. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Rong Y, Wu W, Ni X, et al: Lactate
dehydrogenase A is over-expressed in pancreatic cancer and promotes
the growth of pancreatic cancer cells. Tumour Biol. 34:1523–1530.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hamanaka RB and Chandel NS: Targeting
glucose metabolism for cancer therapy. J Exp Med. 209:211–215.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Bayley JP and Devilee P: The Warburg
effect in 2012. Curr Opin Oncol. 24:62–67. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Tennant DA, Durán RV and Gottlieb E:
Targeting metabolic transformation for cancer therapy. Nat Rev
Cancer. 10:267–277. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wolf A, Agnihotri S, Micallef J, et al:
Hexokinase 2 is a key mediator of aerobic glycolysis and promotes
tumor growth in human glioblastoma multiforme. J Exp Med.
208:313–326. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chan DA, Sutphin PD, Nguyen P, et al:
Targeting GLUT1 and the Warburg effect in renal cell carcinoma by
chemical synthetic lethality. Sci Transl Med. 3:94ra702011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hirschhaeuser F, Sattler UG and
Mueller-Klieser W: Lactate: a metabolic key player in cancer.
Cancer Res. 71:6921–6925. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Qing G, Skuli N, Mayes PA, et al:
Combinatorial regulation of neuroblastoma tumor progression by
N-Myc and hypoxia inducible factor HIF-1α. Cancer Res.
70:10351–10361. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Shim H, Dolde C, Lewis BC, et al: c-Myc
transactivation of LDH-A: implications for tumor metabolism and
growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 94:6658–6663. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Le A, Cooper CR, Gouw AM, et al:
Inhibition of lactate dehydrogenase A induces oxidative stress and
inhibits tumor progression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 107:2037–2042.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhao Y, Butler EB and Tan M: Targeting
cellular metabolism to improve cancer therapeutics. Cell Death Dis.
4:e5322013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Sheng SL, Liu JJ, Dai YH, et al: Knockdown
of lactate dehydrogenase A suppresses tumor growth and metastasis
of human hepatocellular carcinoma. FEBS J. 279:3898–3910. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Farabegoli F, Vettraino M, Manerba M, et
al: Galloflavin, a new lactate dehydrogenase inhibitor, induces the
death of human breast cancer cells with different glycolytic
attitude by affecting distinct signaling pathways. Eur J Pharm Sci.
47:729–738. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhang Y, Zhang X, Wang X, et al:
Inhibition of LDH-A by lentivirus-mediated small interfering RNA
suppresses intestinal-type gastric cancer tumorigenicity through
the downregulation of Oct4. Cancer Lett. 321:45–54. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|