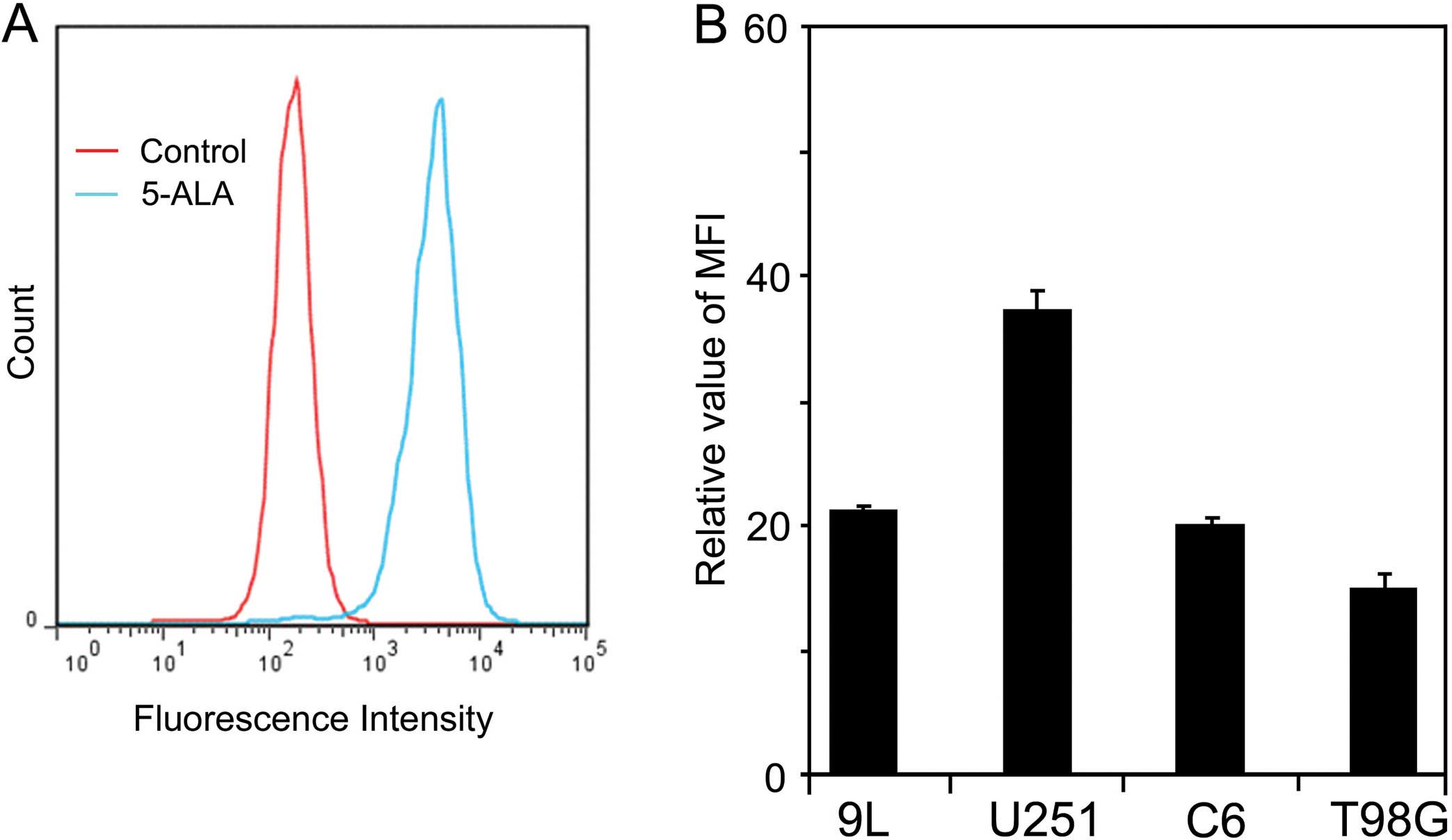
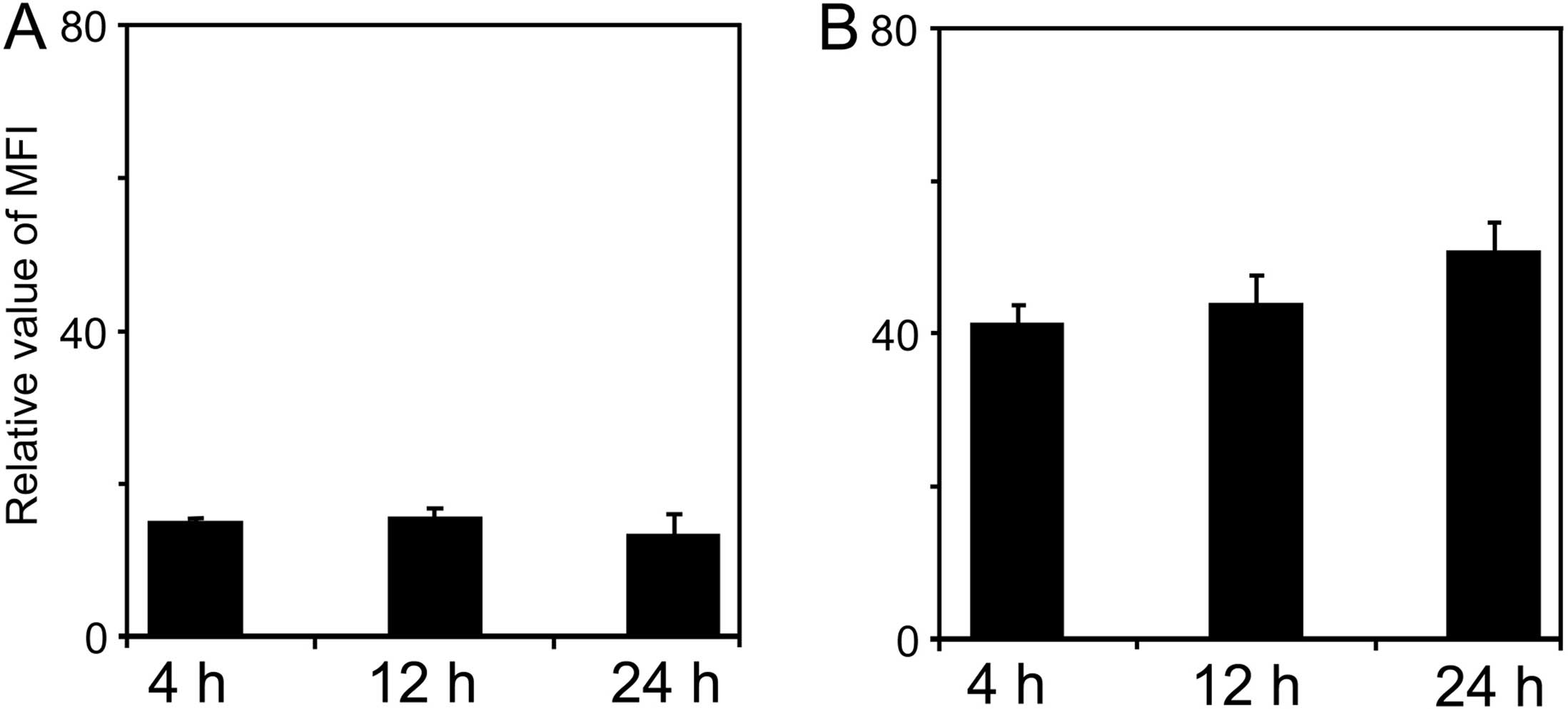
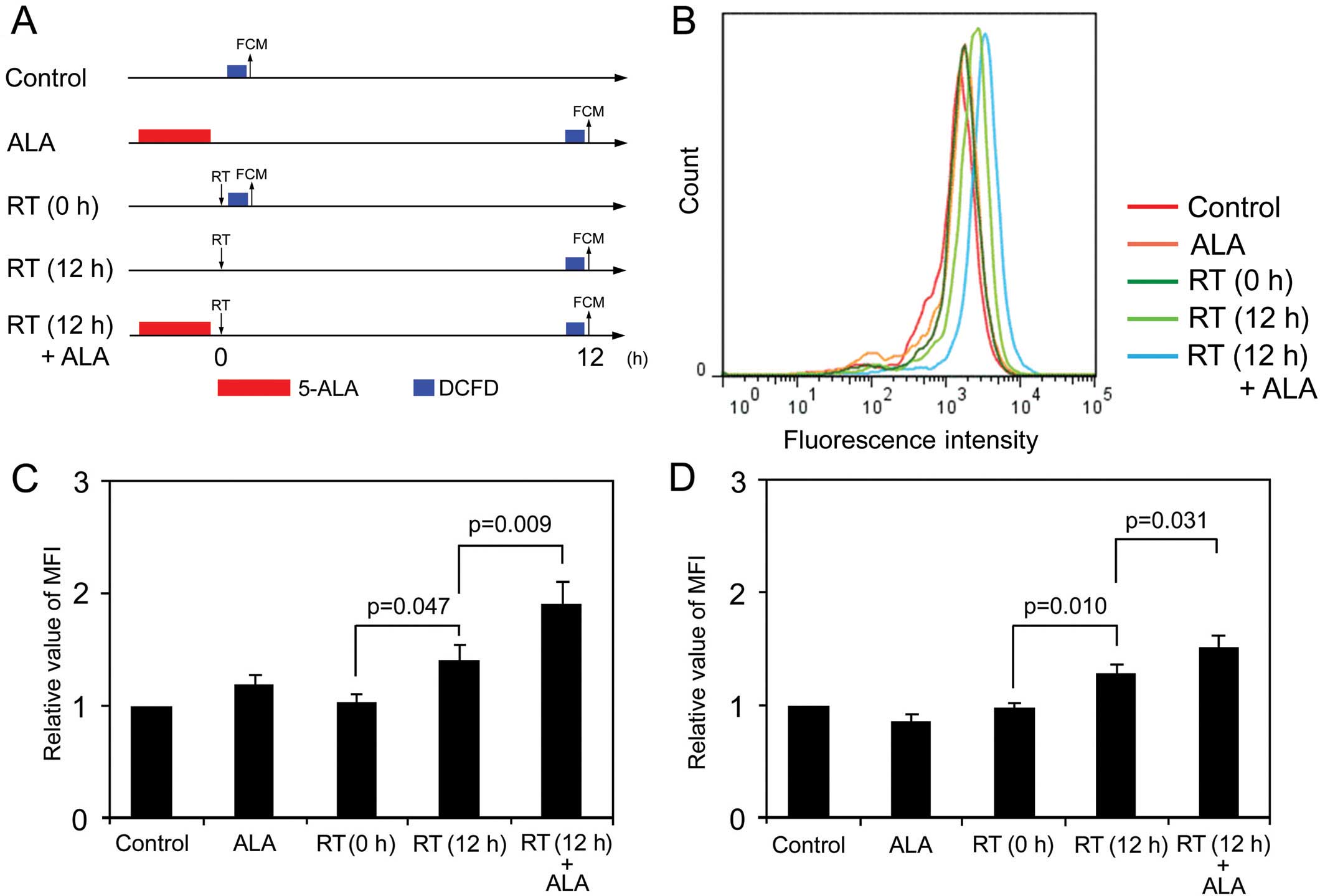
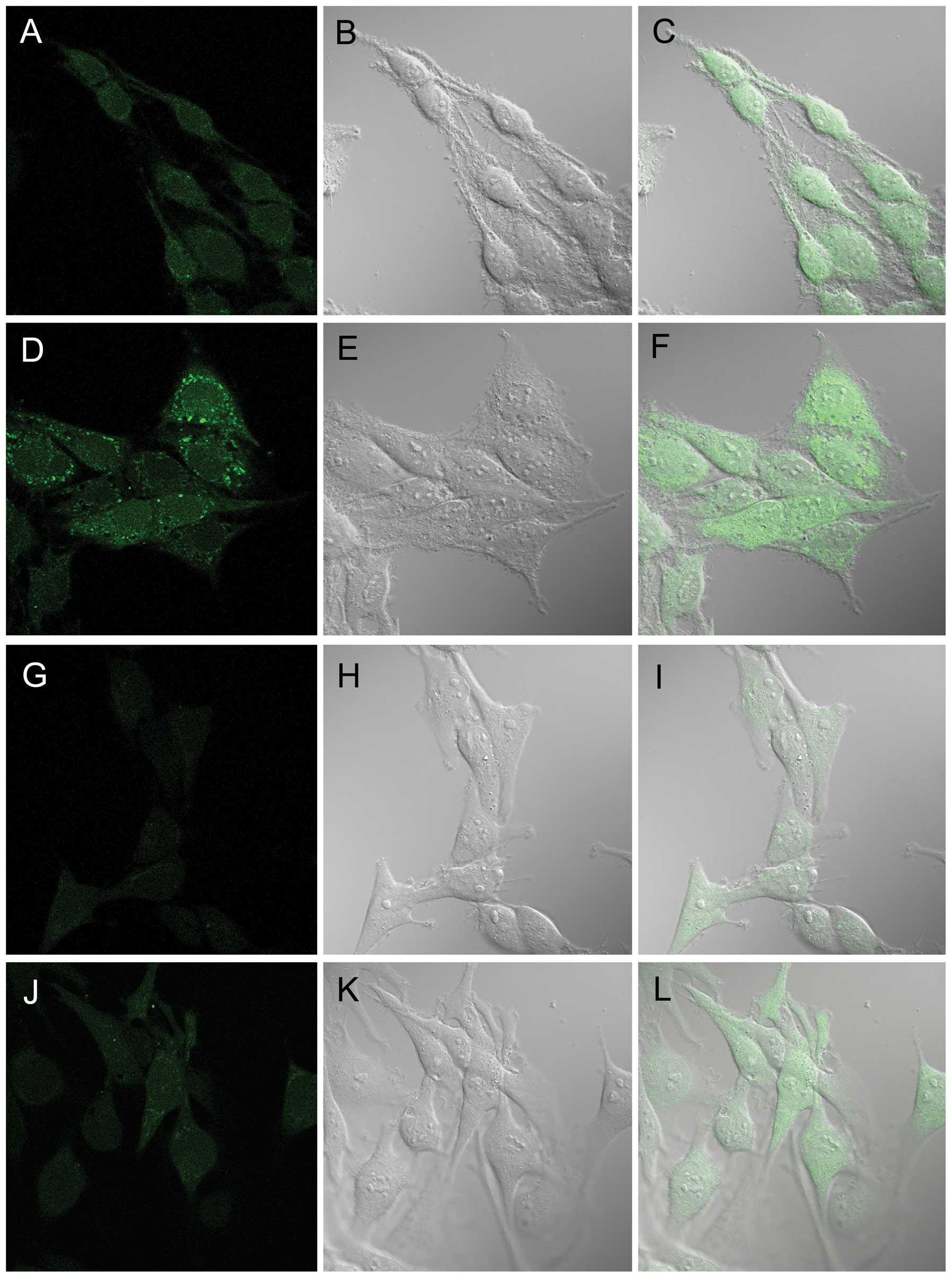
|
1
|
Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, et al:
Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for
glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 352:987–996. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Westphal M, Ram Z, Riddle V, Hilt D and
Bortey E; Executive Committee of the Gliadel Study Group. Gliadel
wafer in initial surgery for malignant glioma: long-term follow-up
of a multicenter controlled trial. Acta Neurochir. 148:269–275.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sanai N, Polley MY, McDermott MW, Parsa AT
and Berger MS: An extent of resection threshold for newly diagnosed
glioblastomas. J Neurosurg. 115:3–8. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lacroix M, Abi-Said D, Fourney DR, et al:
A multivariate analysis of 416 patients with glioblastoma
multiforme: prognosis, extent of resection, and survival. J
Neurosurg. 95:190–198. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Fischer F, Dickson EF, Kennedy JC and
Pottier RH: An affordable, portable fluorescence imaging device for
skin lesion detection using a dual wavelength approach for image
contrast enhancement and aminolaevulinic acid-induced
protoporphyrin IX. Part II In vivo testing. Lasers Med Sci.
16:207–212. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Yamamoto J, Yamamoto S, Hirano T, et al:
Monitoring of singlet oxygen is useful for predicting the
photodynamic effects in the treatment for experimental glioma. Clin
Cancer Res. 12:7132–7139. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Stummer W, Novotny A, Stepp H, Goetz C,
Bise K and Reulen HJ: Fluorescence-guided resection of glioblastoma
multiforme by using 5-aminolevulinic acid-induced porphyrins: a
prospective study in 52 consecutive patients. J Neurosurg.
93:1003–1013. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tamura Y, Kuroiwa T, Kajimoto Y, Miki Y,
Miyatake S and Tsuji M: Endoscopic identification and biopsy
sampling of an intraventricular malignant glioma using a
5-aminolevulinic acid-induced protoporphyrin IX fluorescence
imaging system. Technical note. J Neurosurg. 106:507–510. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Della Puppa A, De Pellegrin S, d’Avella E,
et al: 5-aminolevulinic acid (5-ALA) fluorescence guided surgery of
high-grade gliomas in eloquent areas assisted by functional
mapping. Our experience and review of the literature. Acta
Neurochir. 155:965–972. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Shapiro WR, Green SB, Burger PC, et al:
Randomized trial of three chemotherapy regimens and two
radiotherapy regimens and two radiotherapy regimens in
postoperative treatment of malignant glioma. Brain Tumor
Cooperative Group Trial 8001. J Neurosurg. 71:1–9. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Laperriere N, Zuraw L and Cairncross G;
Cancer Care Ontario Practice Guidelines Initiative Neuro-Oncology
Disease Site Group. Radiotherapy for newly diagnosed malignant
glioma in adults: a systematic review. Radiother Oncol. 64:259–273.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mimura S, Ito Y, Nagayo T, et al:
Cooperative clinical trial of photodynamic therapy with photofrin
II and excimer dye laser for early gastric cancer. Lasers Surg Med.
19:168–172. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Mlkvy P, Messmann H, Pauer M, et al:
Distribution and photodynamic effects of
meso-tetrahydroxyphenylchlorin (mTHPC) in the pancreas and adjacent
tissues in the Syrian golden hamster. Br J Cancer. 73:1473–1479.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yamamoto J, Hirano T, Li S, et al:
Selective accumulation and strong photodynamic effects of a new
photosensitizer, ATX-S10. Na (II), in experimental malignant
glioma. Int J Oncol. 27:1207–1213. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Schaffer M, Ertl-Wagner B, Schaffer PM, et
al: Feasibility of photofrin II as a radiosensitizing agent in
solid tumors - preliminary results. Onkologie. 29:514–519. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Luksiene Z, Juzenas P and Moan J:
Radiosensitization of tumours by porphyrins. Cancer Lett.
235:40–47. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Berg K, Luksiene Z, Moan J and Ma L:
Combined treatment of ionizing radiation and photosensitization by
5-aminolevulinic acid-induced protoporphyrin IX. Radiat Res.
142:340–346. 1995. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yamamoto J, Ogura S, Tanaka T, et al:
Radiosensitizing effect of 5-aminolevulinic acid-induced
protoporphyrin IX in glioma cells in vitro. Oncol Rep.
27:1748–1752. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yamamoto J, Ogura S, Shimajiri S, et al:
5-Aminolevulinic acid-induced protoporphyrin IX with multi-dose
ionizing irradiation enhances host antitumor response and strongly
inhibits tumor growth in experimental glioma in vivo. Mol Med Rep.
(In press).
|
|
20
|
Riley PA: Free radicals in biology:
oxidative stress and the effects of ionizing radiation. Int J
Radiat Biol. 65:27–33. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hall EJ and Giaccia AJ: Physics and
chemistry of radiation absorption. Radiobiology for the
Radiologist. Hall EJ and Giaccia AJ: 6th edition. Lippincott
Williams & Wilkins; Philadelphia, PA: pp. 5–15. 2006
|
|
22
|
Chen Q, Chai YC, Mazumder S, et al: The
late increase in intracellular free radical oxygen species during
apoptosis is associated with cytochrome c release, caspase
activation, and mitochondrial dysfunction. Cell Death Differ.
10:323–334. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ogura A, Oowada S, Kon Y, et al: Redox
regulation in radiation-induced cytochrome c release from
mitochondria of human lung carcinoma A549 cells. Cancer Lett.
277:64–71. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Saenko Y, Cieslar-Pobuda A, Skonieczna M
and Rzeszowska-Wolny J: Changes of reactive oxygen and nitrogen
species and mitochondrial functioning in human K562 and HL60 cells
exposed to ionizing radiation. Radiat Res. 180:360–366. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yamamori T, Yasui H, Yamazumi M, et al:
Ionizing radiation induces mitochondrial reactive oxygen species
production accompanied by upregulation of mitochondrial electron
transport chain function and mitochondrial content under control of
the cell cycle checkpoint. Free Radic Biol Med. 53:260–270. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ishizuka M, Abe F, Sano Y, et al: Novel
development of 5-aminolevurinic acid (ALA) in cancer diagnoses and
therapy. Int Immunopharmacol. 11:358–365. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Ogura S, Maruyama K, Hagiya Y, et al: The
effect of 5-aminolevulinic acid on cytochrome c oxidase activity in
mouse liver. BMC Res Notes. 4:662011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sugiyama Y, Hagiya Y, Nakajima M, Ishizuka
M, Tanaka T and Ogura S: The heme precursor 5-aminolevulinic acid
disrupts the Warburg effect in tumor cells and induces
caspase-dependent apoptosis. Oncol Rep. 31:1282–1286. 2014.
|
|
29
|
Hosokawa Y, Sakakura Y, Tanaka L, Okumura
K, Yajima T and Kaneko M: Radiation-induced apoptosis is
independent of caspase-8 but dependent on cytochrome c and the
caspase-9 cascade in human leukemia HL60 cells. J Radiat Res.
46:293–303. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kowaltowski AJ, de Souza-Pinto NC,
Castilho RF and Vercesi AE: Mitochondria and reactive oxygen
species. Free Radic Biol Med. 47:333–343. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Le Caër S: Water radiolysis: influence of
oxide surfaces on H2 production under ionizing
radiation. Water. 3:235–253. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Wallace SS: Enzymatic processing of
radiation-induced free radical damage in DNA. Radiat Res. 150(Suppl
5): S60–S79. 1998. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ward JF: DNA damage produced by ionizing
radiation in mammalian cells: identities, mechanisms of formation,
and reparability. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 35:95–125. 1988.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Finkel T: Signal transduction by reactive
oxygen species. J Cell Biol. 194:7–15. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Matoba S, Kang JG, Patino WD, et al: p53
regulates mitochondrial respiration. Science. 312:1650–1653. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Herrmann PC, Gillespie JW, Charboneau L,
et al: Mitochondrial proteome: altered cytochrome c oxidase subunit
levels in prostate cancer. Proteomics. 3:1801–1810. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhou S, Kachhap S and Singh KK:
Mitochondrial impairment in p53-deficient human cancer cells.
Mutagenesis. 18:287–292. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Warburg O: On respiratory impairment in
cancer cells. Science. 124:269–270. 1956.PubMed/NCBI
|