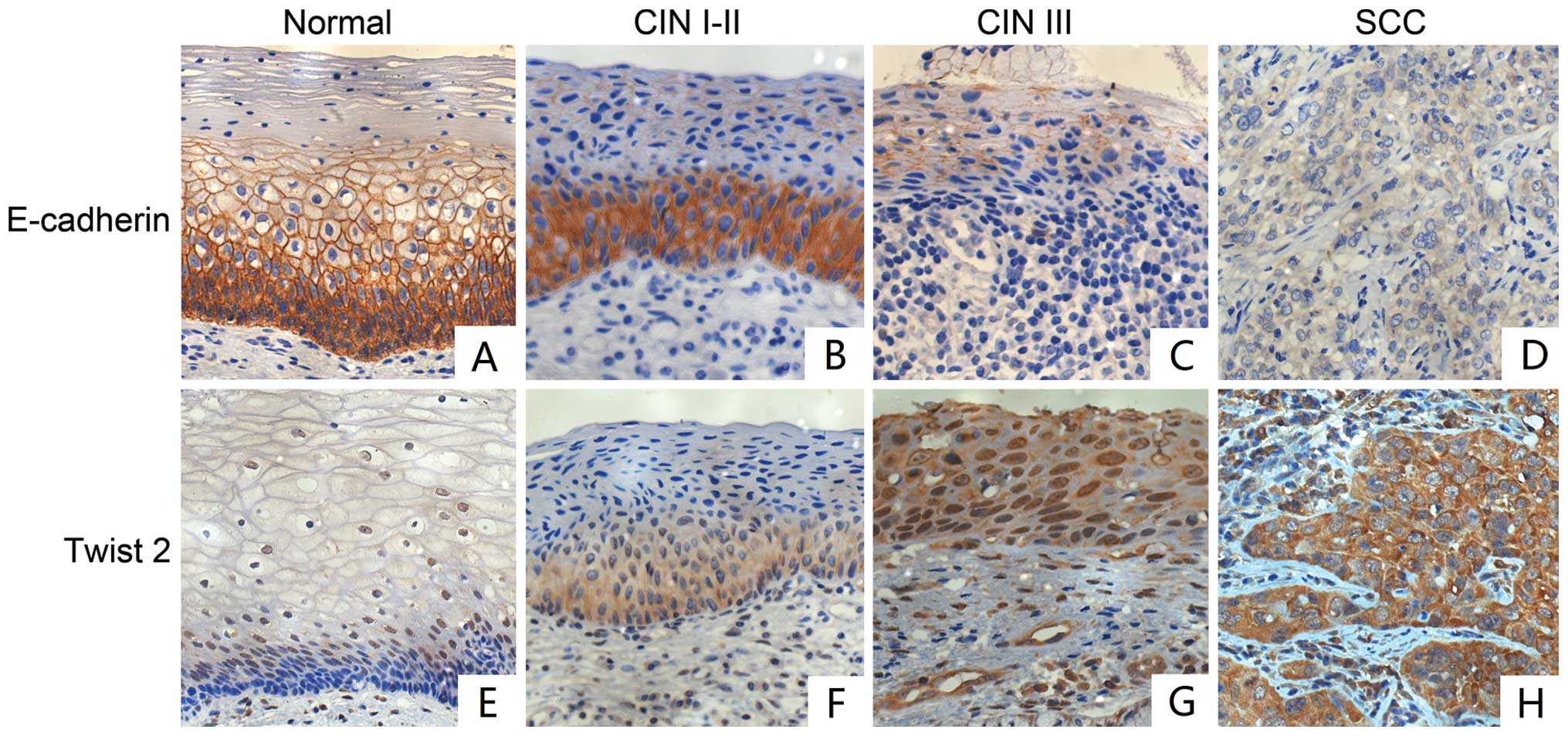
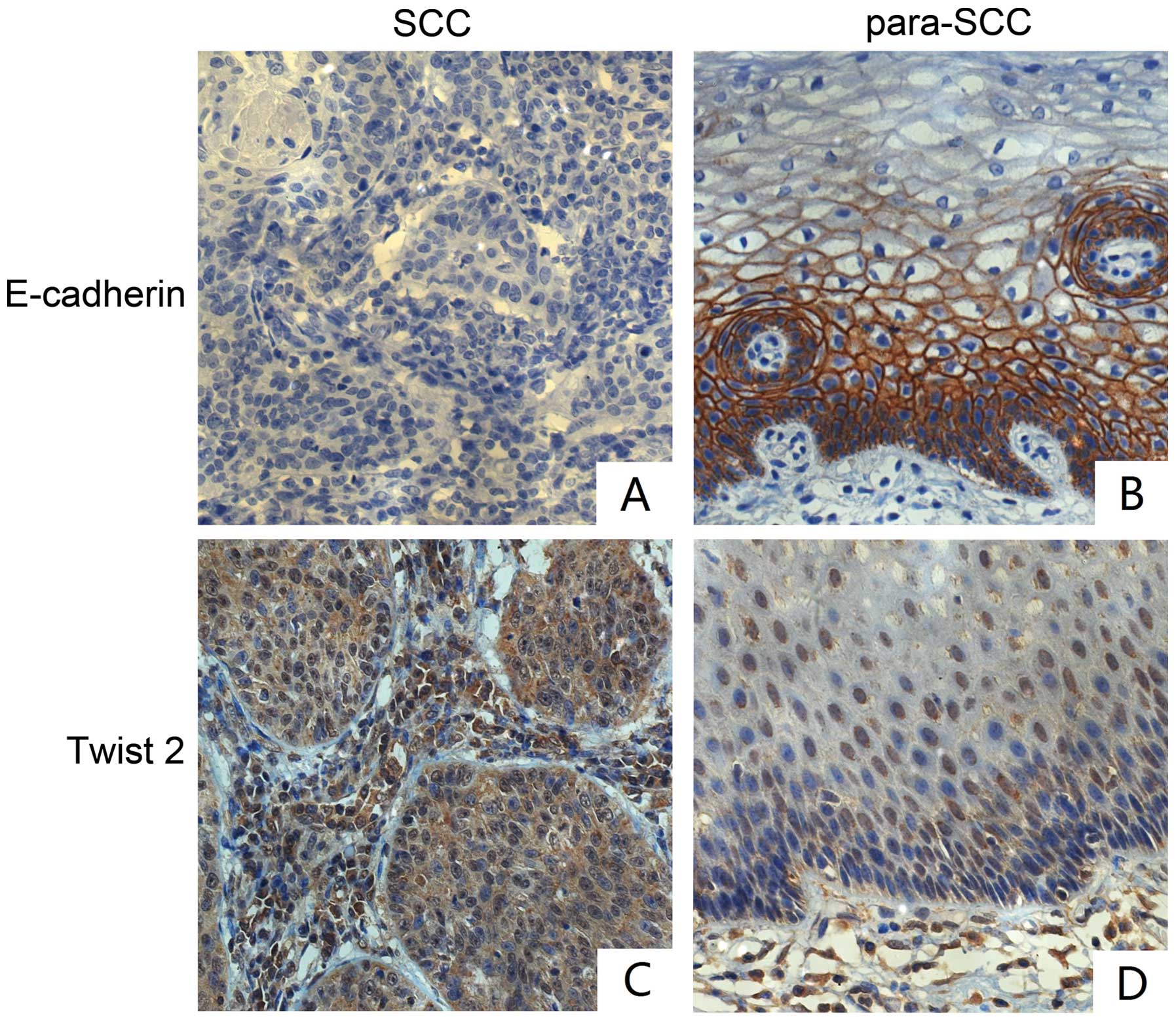
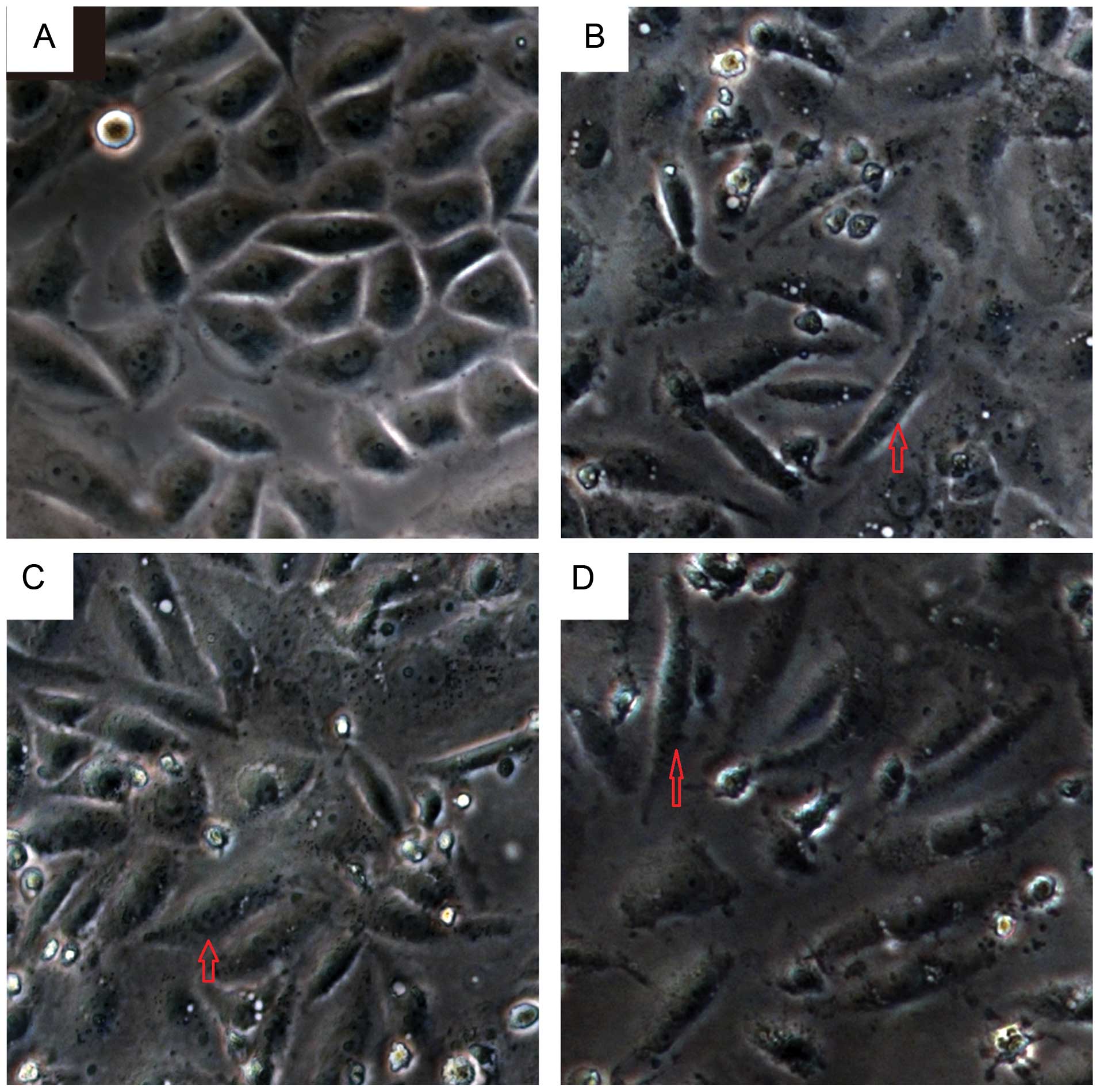
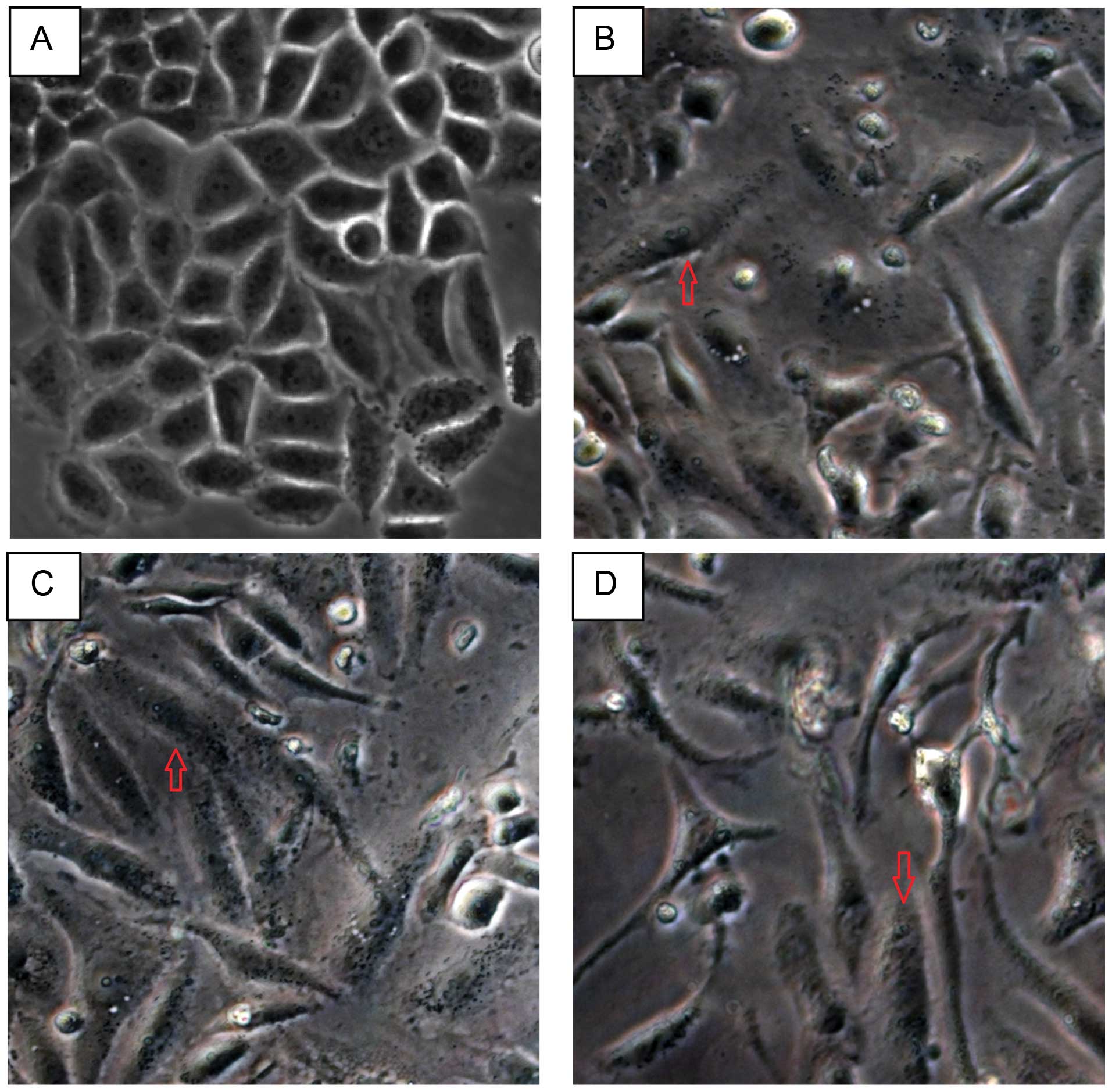
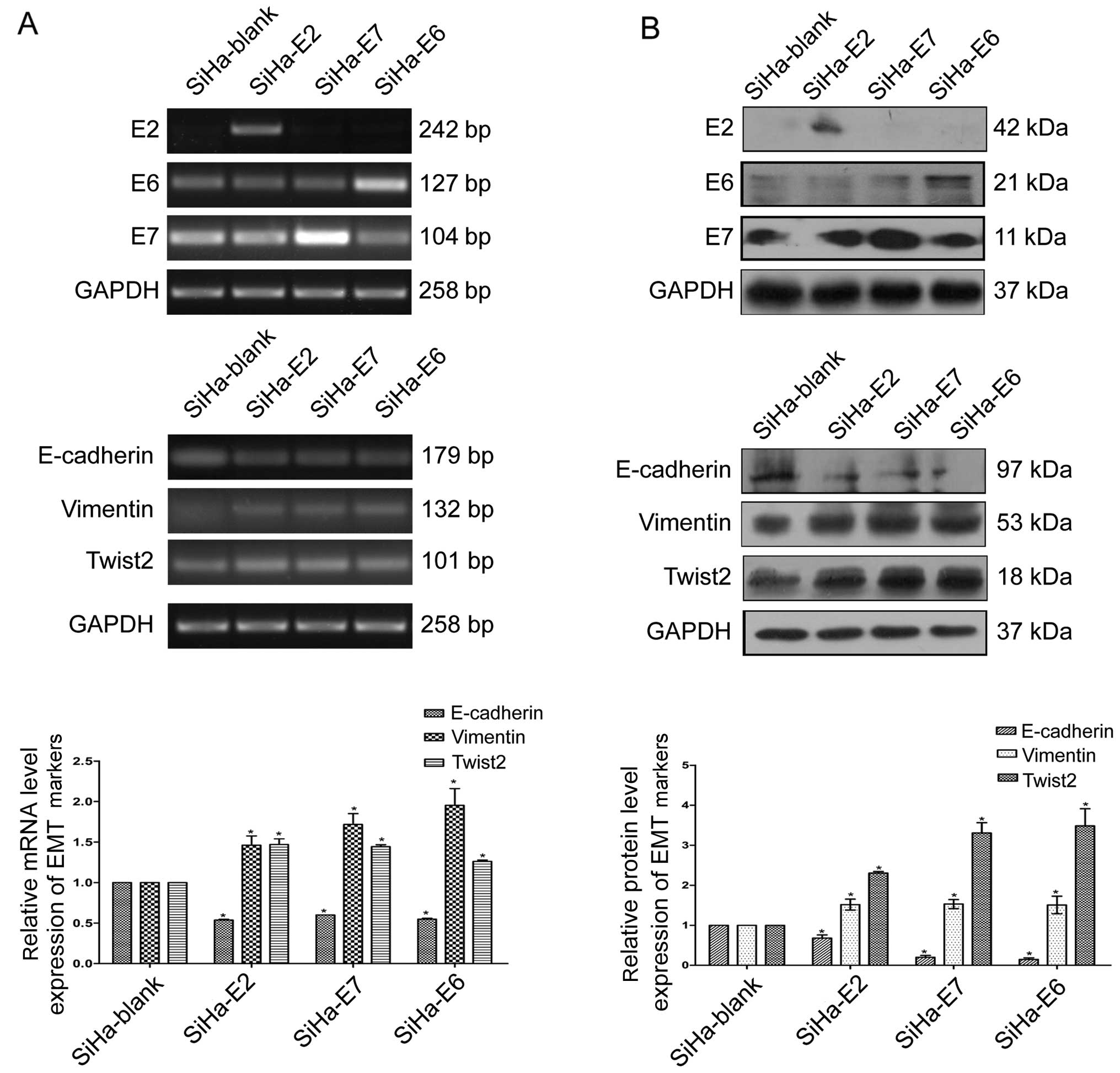
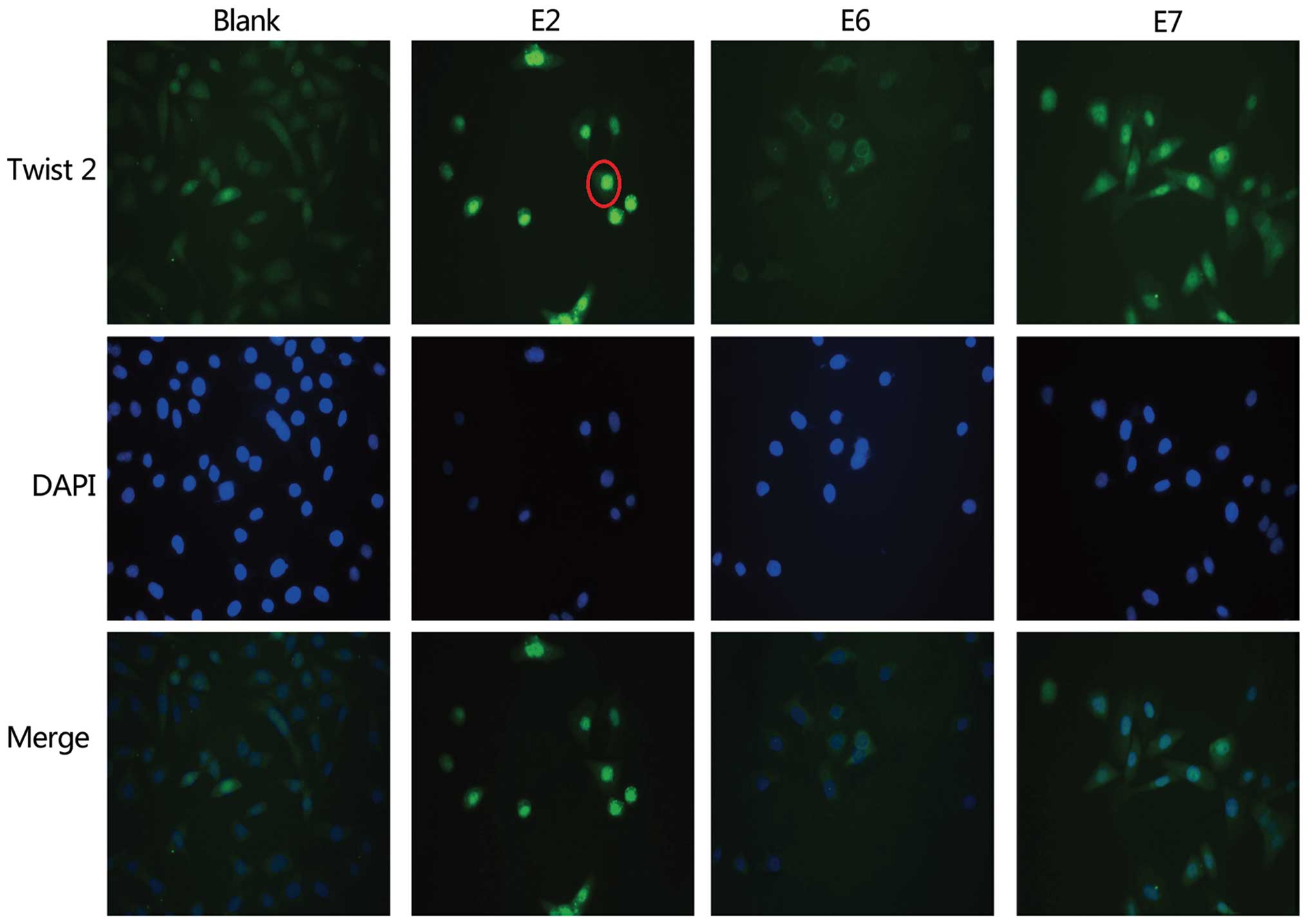
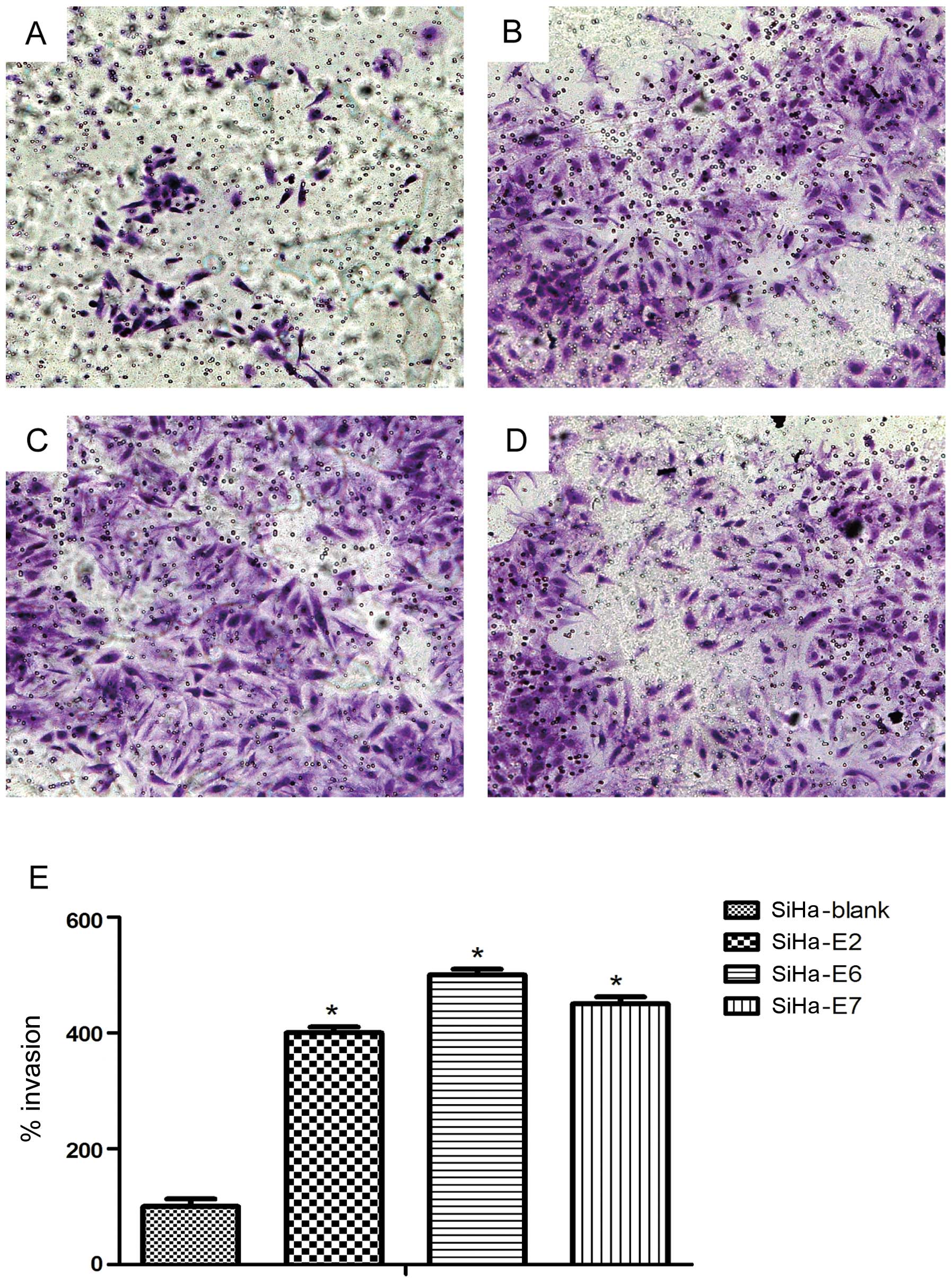
|
1
|
zur Hausen H: Papillomaviruses and cancer:
from basic studies to clinical application. Nat Rev Cancer.
2:342–350. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Faridi R, Zahra A, Khan K and Idrees M:
Oncogenic potential of human papillomavirus (HPV) and its relation
with cervical cancer. Virol J. 8:2692011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Panjković M and Ivković-Kapicl T: Etiology
and pathogenesis of precancerous lesions and invasive cervical
carcinoma. Med Pregl. 61:364–368. 2008.(In Serbian). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Snijders PJ, Steenbergen RD, Heideman DA
and Meijer CJ: HPV-mediated cervical carcinogenesis: concepts and
clinical implications. J Pathol. 208:152–164. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Javier MG and Sastre-Garau X: Uterine
cervix carcinoma: recent biological data and update for improving
follow-up and treatment. Isr Med Assoc J. 14:700–704.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ghittoni R, Accardi R, Hasan U, Gheit T,
Sylla B and Tommasino M: The biological properties of E6 and E7
oncoproteins from human papillomaviruses. Virus Genes. 40:1–13.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
De Craene B and Berx G: Regulatory
networks defining EMT during cancer initiation and progression. Nat
Rev Cancer. 13:97–110. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Stewart CJ and McCluggage WG:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in carcinomas of the female
genital tract. Histopathology. 62:31–43. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Lim J and Thiery JP:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions: insights from development.
Development. 139:3471–3486. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Le Bras GF, Taubenslag KJ and Andl CD: The
regulation of cell-cell adhesion during epithelial-mesenchymal
transition, motility and tumor progression. Cell Adh Migr.
6:365–373. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Rodriguez FJ, Lewis-Tuffin LJ and
Anastasiadis PZ: E-cadherin’s dark side: possible role in tumor
progression. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1826:23–31. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Iwatsuki M, Mimori K, Yokobori T, et al:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer development and its
clinical significance. Cancer Sci. 101:293–299. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Sanchez-Tillo E, Liu Y, de Barrios O, et
al: EMT-activating transcription factors in cancer: beyond EMT and
tumor invasiveness. Cell Mol Life Sci. 69:3429–3456. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lee MY and Shen MR: Epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in cervical carcinoma. Am J Transl Res. 4:1–13.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li Y, Wang W, Wang W, et al: Correlation
of TWIST2 up-regulation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition
during tumorigenesis and progression of cervical carcinoma. Gynecol
Oncol. 124:112–118. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Chamulitrat W, Schmidt R, Chunglok W, Kohl
A and Tomakidi P: Epithelium and fibroblast-like phenotypes derived
from HPV16 E6/E7-immortalized human gingival keratinocytes
following chronic ethanol treatment. Eur J Cell Biol. 82:313–322.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hellner K, Mar J, Fang F, Quackenbush J
and Munger K: HPV16 E7 oncogene expression in normal human
epithelial cells causes molecular changes indicative of an
epithelial to mesenchymal transition. Virology. 391:57–63. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cheng YM, Chou CY, Hsu YC, Chen MJ and
Wing LY: The role of human papillomavirus type 16 E6/E7
oncoproteins in cervical epithelial-mesenchymal transition and
carcinogenesis. Oncol Lett. 3:667–671. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Caberg JH, Hubert PM, Begon DY, et al:
Silencing of E7 oncogene restores functional E-cadherin expression
in human papillomavirus 16-transformed keratinocytes.
Carcinogenesis. 29:1441–1447. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mühlen S, Behren A, Iftner T and Simon C:
Influence of HPV16 E2 and its localisation on the expression of
matrix metalloproteinase-9. Int J Oncol. 37:337–345.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang J, Yang Y, Zhang Z, et al: Gankyrin
plays an essential role in estrogen-driven and GPR30-mediated
endometrial carcinoma cell proliferation via the PTEN/PI3K/AKT
signaling pathway. Cancer Lett. 339:279–287. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Wang YX, Zhang XY, Zhang BF, Yang CQ and
Gao HJ: Study on the clinical significance of Argonaute2 expression
in colonic carcinoma by tissue microarray. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
6:476–484. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Franco HL, Casasnovas J, Rodriguez-Medina
JR and Cadilla CL: Redundant or separate entities? - roles of
Twist1 and Twist2 as molecular switches during gene transcription.
Nucleic Acids Res. 39:1177–1186. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
24
|
Zeisberg M and Neilson EG: Biomarkers for
epithelial-mesenchymal transitions. J Clin Invest. 119:1429–1437.
2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Thiery JP, Acloque H, Huang RY and Nieto
MA: Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease.
Cell. 139:871–890. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Gasparotto D, Polesel J, Marzotto A, et
al: Overexpression of TWIST2 correlates with poor prognosis in head
and neck squamous cell carcinomas. Oncotarget. 2:1165–1175.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Mao Y, Zhang N, Xu J, Ding Z, Zong R and
Liu Z: Significance of heterogeneous Twist2 expression in human
breast cancers. PloS One. 7:e481782012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Myong NH: Loss of E-cadherin and
acquisition of vimentin in epithelial-mesenchymal transition are
noble indicators of uterine cervix cancer progression. Korean J
Pathol. 46:341–348. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Thiery JP and Sleeman JP: Complex networks
orchestrate epithelial-mesenchymal transitions. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 7:131–142. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Reik W: Stability and flexibility of
epigenetic gene regulation in mammalian development. Nature.
447:425–432. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lee MY, Chou CY, Tang MJ and Shen MR:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cervical cancer: correlation
with tumor progression, epidermal growth factor receptor
overexpression, and snail up-regulation. Clin Cancer Res.
14:4743–4750. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hsu YM, Chen YF, Chou CY, et al: KCl
cotransporter-3 down-regulates E-cadherin/beta-catenin complex to
promote epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Res.
67:11064–11073. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
van Roy F and Berx G: The cell-cell
adhesion molecule E-cadherin. Cell Mol Life Sci. 65:3756–3788.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Jung YS, Kato I and Kim HR: A novel
function of HPV16-E6/E7 in epithelial-mesenchymal transition.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 435:339–344. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Watson RA, Thomas M, Banks L and Roberts
S: Activity of the human papillomavirus E6 PDZ-binding motif
correlates with an enhanced morphological transformation of
immortalized human keratinocytes. J Cell Sci. 116:4925–4934. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Duffy CL, Phillips SL and Klingelhutz AJ:
Microarray analysis identifies differentiation-associated genes
regulated by human papillomavirus type 16 E6. Virology.
314:196–205. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Thierry F: Transcriptional regulation of
the papillomavirus oncogenes by cellular and viral transcription
factors in cervical carcinoma. Virology. 384:375–379. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Forma E, Wójcik-Krowiranda K, Bieńkiewicz
A and Bryś M: Molecular basis of gynecological oncology - TopBP1
protein and its participation in the transcription process. Ginekol
Pol. 83:363–367. 2012.(In Polish). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Bodily JM, Hennigan C, Wrobel GA and
Rodriguez CM: Regulation of the human papillomavirus type 16 late
promoter by E7 and the cell cycle. Virology. 443:11–19. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Xue Y, Lim D, Zhi L, He P, Abastado JP and
Thierry F: Loss of HPV16 E2 protein expression without disruption
of the E2 ORF correlates with carcinogenic progression. Open Virol
J. 6:163–172. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Ramirez-Salazar E, Centeno F, Nieto K,
Valencia-Hernandez A, Salcedo M and Garrido E: HPV16 E2 could act
as down-regulator in cellular genes implicated in apoptosis,
proliferation and cell differentiation. Virol J. 8:2472011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Bellanger S, Tan CL, Xue YZ, Teissier S
and Thierry F: Tumor suppressor or oncogene? A critical role of the
human papillomavirus (HPV) E2 protein in cervical cancer
progression. Am J Cancer Res. 1:373–389. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|