|
1
|
Roe JS and Vakoc CR: C/EBPα: Critical at
the origin of leukemic transformation. J Exp Med. 211:1–4. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Rosenbauer F and Tenen DG: Transcription
factors in myeloid development: Balancing differentiation with
transformation. Nat Rev Immunol. 7:105–117. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
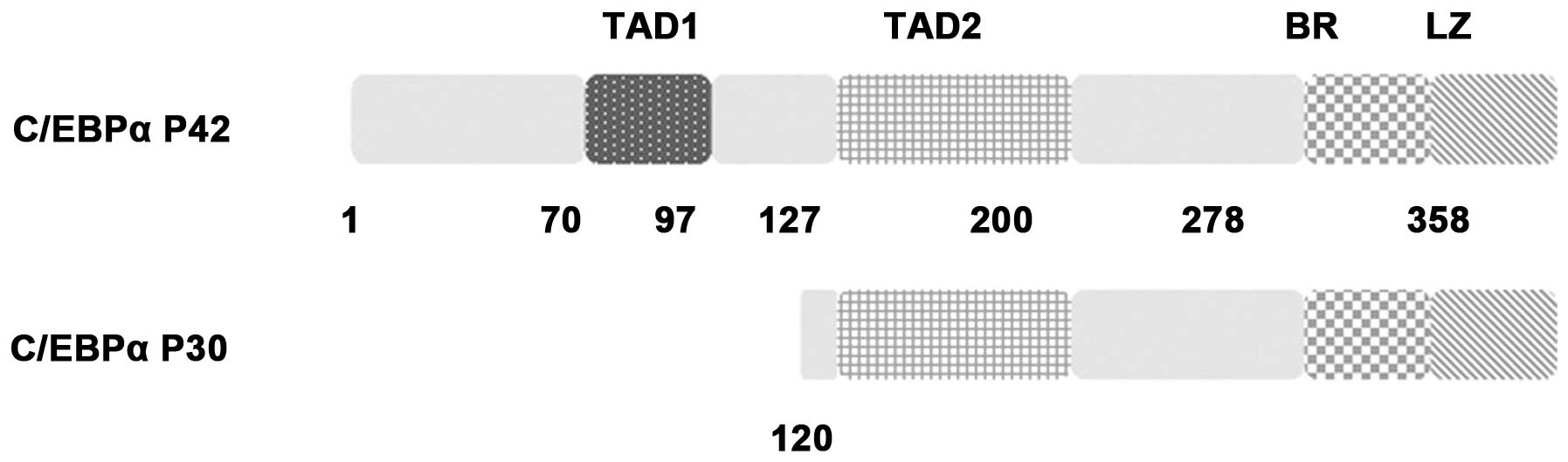
|
3
|
Scott LM, Civin CI, Rorth P and Friedman
AD: A novel temporal expression pattern of three C/EBP family
members in differentiating myelomonocytic cells. Blood.
80:1725–1735. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
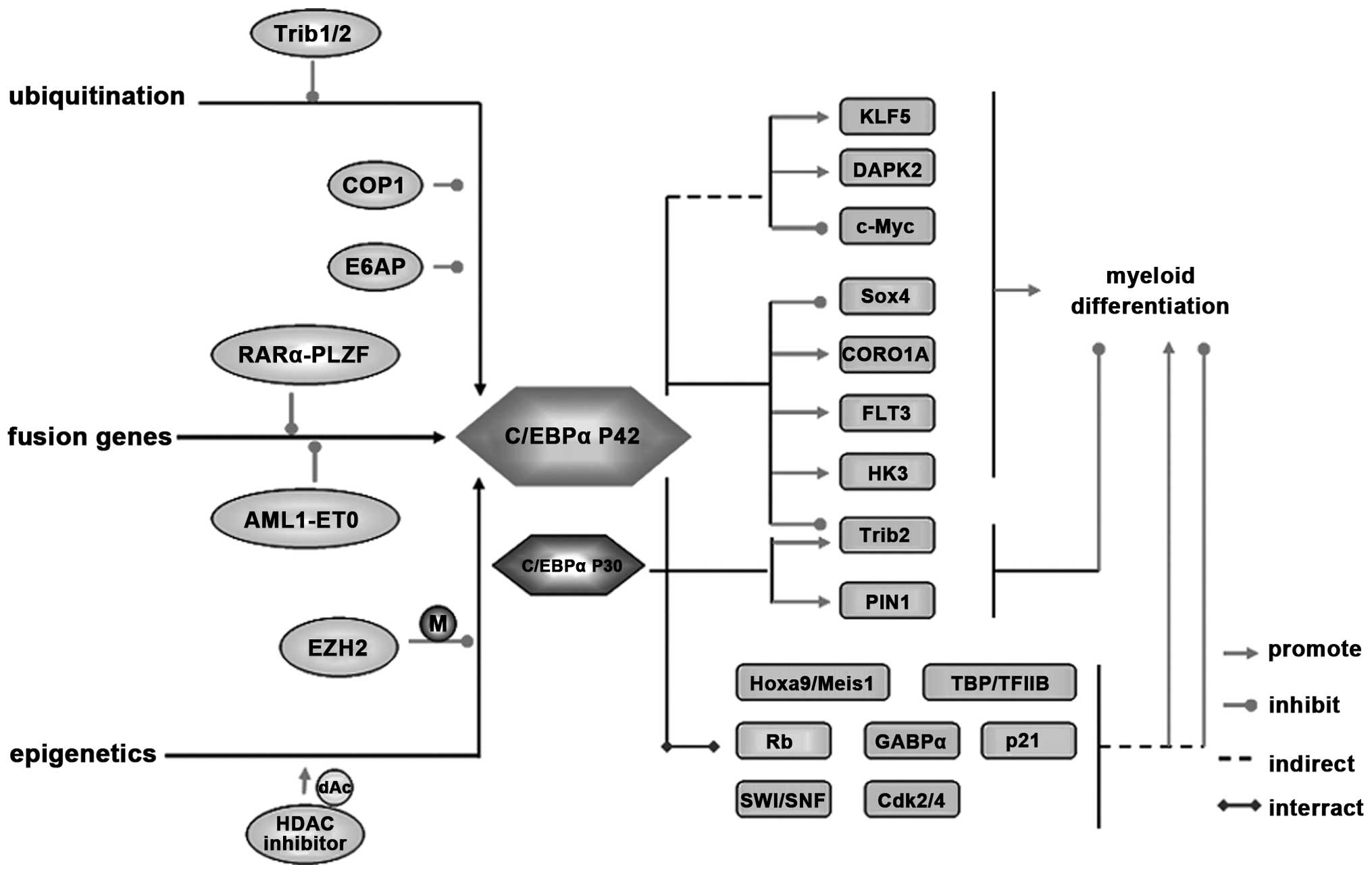
|
4
|
Birkenmeier EH, Gwynn B, Howard S, Jerry
J, Gordon JI, Landschulz WH and McKnight SL: Tissue-specific
expression, developmental regulation, and genetic mapping of the
gene encoding CCAAT/enhancer binding protein. Genes Dev.
3:1146–1156. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
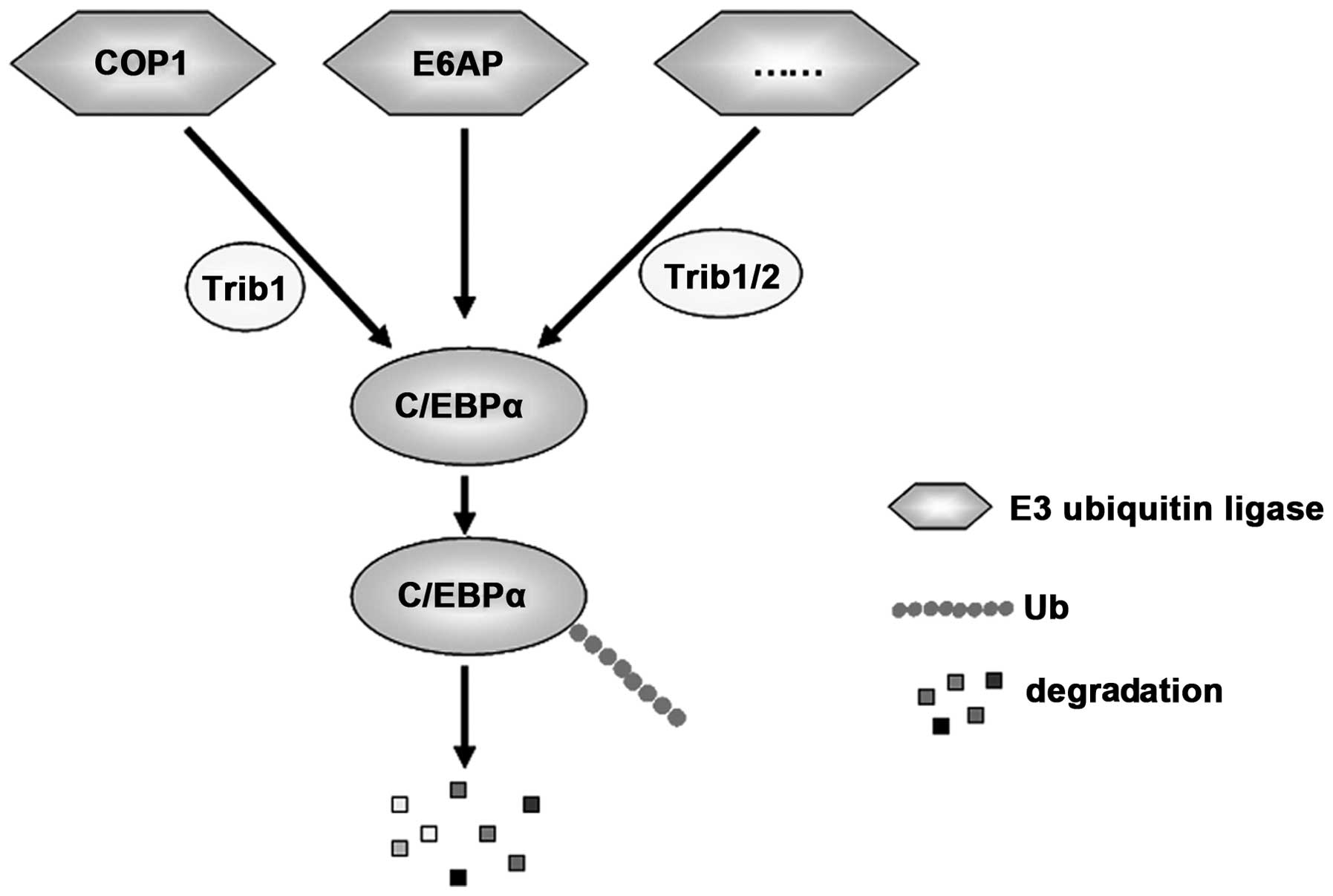
|
|
5
|
Koschmieder S, Halmos B, Levantini E and
Tenen DG: Dysregulation of the C/EBPalpha differentiation pathway
in human cancer. J Clin Oncol. 27:619–628. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
6
|
Mueller BU and Pabst T: C/EBPalpha and the
pathophysiology of acute myeloid leukemia. Curr Opin Hematol.
13:7–14. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Zhang P, Iwasaki-Arai J, Iwasaki H, et al:
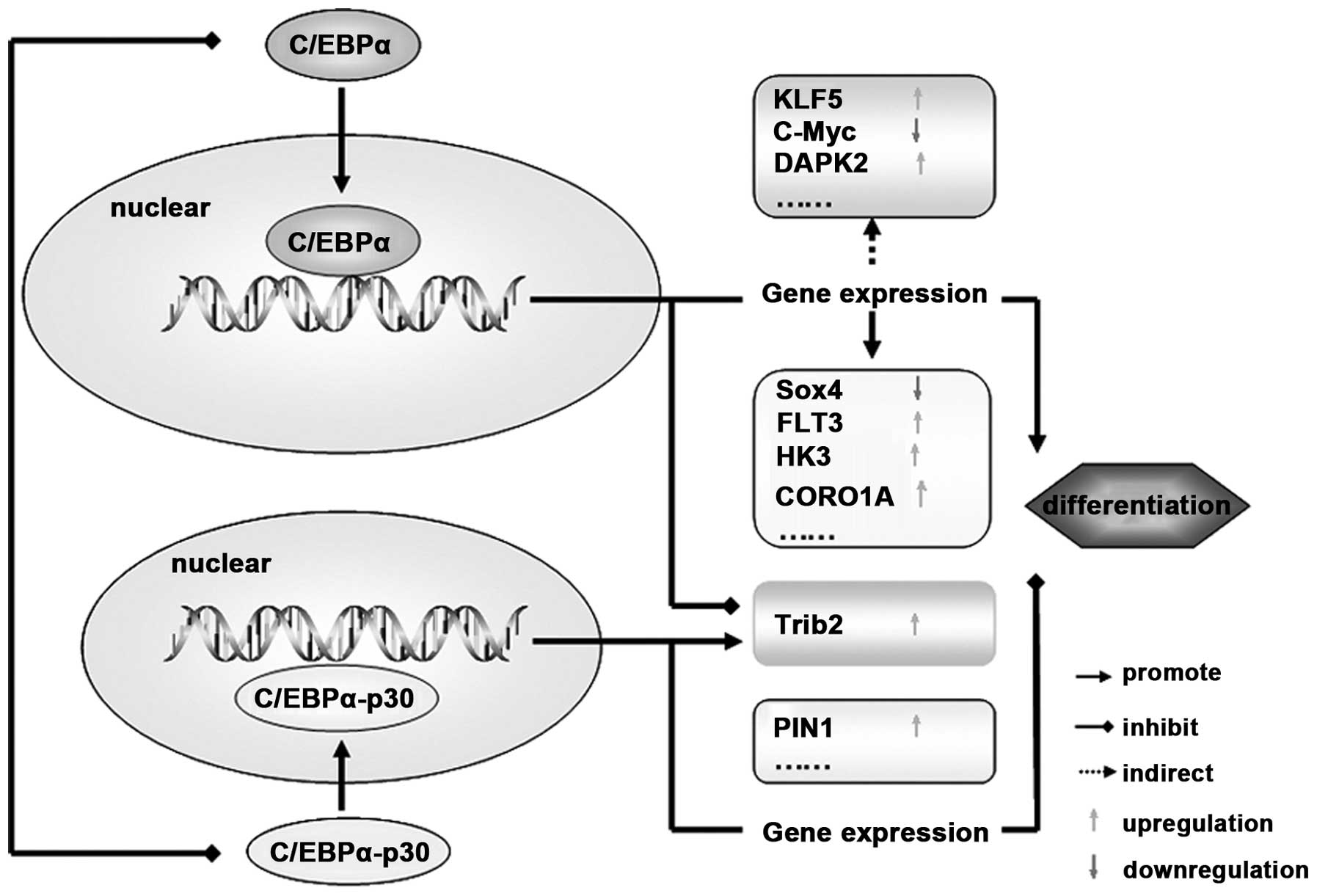
Enhancement of hematopoietic stem cell repopulating capacity and
self-renewal in the absence of the transcription factor C/EBP
alpha. Immunity. 21:853–863. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhang DE, Zhang P, Wang ND, Hetherington
CJ, Darlington GJ and Tenen DG: Absence of granulocyte
colony-stimulating factor signaling and neutrophil development in
CCAAT enhancer binding protein alpha-deficient mice. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 94:569–574. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Porse BT, Bryder D, Theilgaard-Mönch K,
Hasemann MS, Anderson K, Damgaard I, Jacobsen SE and Nerlov C: Loss
of C/EBP alpha cell cycle control increases myeloid progenitor
proliferation and transforms the neutrophil granulocyte lineage. J
Exp Med. 202:85–96. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang X, Scott E, Sawyers CL and Friedman
AD: C/EBPalpha bypasses granulocyte colony-stimulating factor
signals to rapidly induce PU.1 gene expression, stimulate
granulocytic differentiation, and limit proliferation in 32D cl3
myeloblasts. Blood. 94:560–571. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bereshchenko O, Mancini E, Moore S, Bilbao
D, Månsson R, Luc S, Grover A, Jacobsen SE, Bryder D and Nerlov C:
Hematopoietic stem cell expansion precedes the generation of
committed myeloid leukemia-initiating cells in C/EBPalpha mutant
AML. Cancer Cell. 16:390–400. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Pabst T, Mueller BU, Zhang P, Radomska HS,
Narravula S, Schnittger S, Behre G, Hiddemann W and Tenen DG:
Dominant-negative mutations of CEBPA, encoding CCAAT/enhancer
binding protein-alpha (C/EBPalpha), in acute myeloid leukemia. Nat
Genet. 27:263–270. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Preudhomme C, Sagot C, Boissel N, et al:
ALFA Group: Favorable prognostic significance of CEBPA mutations in
patients with de novo acute myeloid leukemia: A study from the
Acute Leukemia French Association (ALFA). Blood. 100:2717–2723.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Miller M, Shuman JD, Sebastian T, Dauter Z
and Johnson PF: Structural basis for DNA recognition by the basic
region leucine zipper transcription factor CCAAT/enhancer-binding
protein alpha. J Biol Chem. 278:15178–15184. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Pabst T and Mueller BU: Transcriptional
dysregulation during myeloid transformation in AML. Oncogene.
26:6829–6837. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Pabst T and Mueller BU: Complexity of
CEBPA dysregulation in human acute myeloid leukemia. Clin Cancer
Res. 15:5303–5307. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Cai DH, Wang D, Keefer J, Yeamans C,
Hensley K and Friedman AD: C/EBP alpha:AP-1 leucine zipper
heterodimers bind novel DNA elements, activate the PU.1 promoter
and direct monocyte lineage commitment more potently than C/EBP
alpha homodimers or AP-1. Oncogene. 27:2772–2779. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Wang D, Paz-Priel I and Friedman AD:
NF-kappa B p50 regulates C/EBP alpha expression and inflammatory
cytokine-induced neutrophil production. J Immunol. 182:5757–5762.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Dahl R, Walsh JC, Lancki D, Laslo P, Iyer
SR, Singh H and Simon MC: Regulation of macrophage and neutrophil
cell fates by the PU.1:C/EBPalpha ratio and granulocyte
colony-stimulating factor. Nat Immunol. 4:1029–1036. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Licht JD, Chomienne C, Goy A, et al:
Clinical and molecular characterization of a rare syndrome of acute
promyelocytic leukemia associated with translocation (11;17).
Blood. 85:1083–1094. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chen Z, Brand NJ, Chen A, Chen SJ, Tong
JH, Wang ZY, Waxman S and Zelent A: Fusion between a novel
Krüppel-like zinc finger gene and the retinoic acid receptor-alpha
locus due to a variant t(11;17) translocation associated with acute
promyelocytic leukaemia. EMBO J. 12:1161–1167. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Girard N, Tremblay M, Humbert M, Grondin
B, Haman A, Labrecque J, Chen B, Chen Z, Chen SJ and Hoang T:
RARα-PLZF oncogene inhibits C/EBPα function in myeloid cells. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 110:13522–13527. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Pabst T, Mueller BU, Harakawa N, Schoch C,
Haferlach T, Behre G, Hiddemann W, Zhang DE and Tenen DG: AML1-ETO
downregulates the granulocytic differentiation factor C/EBP alpha
in t(8;21) myeloid leukemia. Nat Med. 7:444–451. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Baer C, Claus R, Frenzel LP, et al:
Extensive promoter DNA hypermethylation and hypomethylation is
associated with aberrant microRNA expression in chronic lymphocytic
leukemia. Cancer Res. 72:3775–3785. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chim CS, Wong AS and Kwong YL: Infrequent
hypermethylation of CEBPA promotor in acute myeloid leukaemia. Br J
Haematol. 119:988–990. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Annamaneni S, Kagita S, Gorre M, Digumarti
RR, Satti V and Battini MR: Methylation status of CEBPA gene
promoter in chronic myeloid leukemia. Hematology. 19:42–44. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Nikoloski G, Langemeijer SM, Kuiper RP, et
al: Somatic mutations of the histone methyltransferase gene EZH2 in
myelodysplastic syndromes. Nat Genet. 42:665–667. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Herrera-Merchan A, Arranz L, Ligos JM, de
Molina A, Dominguez O and Gonzalez S: Ectopic expression of the
histone methyltransferase Ezh2 in haematopoietic stem cells causes
myeloproliferative disease. Nat Commun. 3:6232012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Thiel AT, Feng Z, Pant DK, Chodosh LA and
Hua X: The trithorax protein partner menin acts in tandem with EZH2
to suppress C/EBPα and differentiation in MLL-AF9 leukemia.
Haematologica. 98:918–927. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Dedhia PH, Keeshan K, Uljon S, Xu L, Vega
ME, Shestova O, Zaks-Zilberman M, Romany C, Blacklow SC and Pear
WS: Differential ability of Tribbles family members to promote
degradation of C/EBPalpha and induce acute myelogenous leukemia.
Blood. 116:1321–1328. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yoshida A, Kato JY, Nakamae I and
Yoneda-Kato N: COP1 targets C/EBPα for degradation and induces
acute myeloid leukemia via Trib1. Blood. 122:1750–1760. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Pal P, Lochab S, Kanaujiya JK, Kapoor I,
Sanyal S, Behre G and Trivedi AK: E6AP, an E3 ubiquitin ligase
negatively regulates granulopoiesis by targeting transcription
factor C/EBPα for ubiquitin-mediated proteasome degradation. Cell
Death Dis. 4:e5902013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Sandoval S, Kraus C, Cho EC, et al: Sox4
cooperates with CREB in myeloid transformation. Blood. 120:155–165.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Aue G, Du Y, Cleveland SM, et al: Sox4
cooperates with PU.1 haploinsufficiency in murine myeloid leukemia.
Blood. 118:4674–4681. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Fung TK, Leung AY and So CW: Sox4you: A
new player in C/EBPα leukemia. Cancer Cell. 24:557–559. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhang H, Alberich-Jorda M, Amabile G, et
al: Sox4 is a key oncogenic target in C/EBPα mutant acute myeloid
leukemia. Cancer Cell. 24:575–588. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kindler T, Lipka DB and Fischer T: FLT3 as
a therapeutic target in AML: Still challenging after all these
years. Blood. 116:5089–5102. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kelly LM, Liu Q, Kutok JL, Williams IR,
Boulton CL and Gilliland DG: FLT3 internal tandem duplication
mutations associated with human acute myeloid leukemias induce
myeloproliferative disease in a murine bone marrow transplant
model. Blood. 99:310–318. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Federzoni EA, Valk PJ, Torbett BE,
Haferlach T, Löwenberg B, Fey MF and Tschan MP: PU.1 is linking the
glycolytic enzyme HK3 in neutrophil differentiation and survival of
APL cells. Blood. 119:4963–4970. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Federzoni EA, Humbert M, Torbett BE, Behre
G, Fey MF and Tschan MP: CEBPA-dependent HK3 and KLF5 expression in
primary AML and during AML differentiation. Sci Rep. 4:42612014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Diakiw SM, Kok CH, To LB, Lewis ID, Brown
AL and D’Andrea RJ: The granulocyte-associated transcription factor
Krüppel-like factor 5 is silenced by hypermethylation in acute
myeloid leukemia. Leuk Res. 36:110–116. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Chan KT, Creed SJ and Bear JE: Unraveling
the enigma: Progress towards understanding the coronin family of
actin regulators. Trends Cell Biol. 21:481–488. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Moriceau S, Kantari C, Mocek J, et al:
Coronin-1 is associated with neutrophil survival and is cleaved
during apoptosis: Potential implication in neutrophils from cystic
fibrosis patients. J Immunol. 182:7254–7263. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Federzoni EA, Humbert M, Valk PJ, Behre G,
Leibundgut EO, Torbett BE, Fey MF and Tschan MP: The actin-binding
protein CORO1A is a novel PU.1 (SPI1)- and CEBPA-regulated gene
with significantly lower expression in APL and CEBPA-mutated AML
patients. Br J Haematol. 160:855–859. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Bao L, Kimzey A, Sauter G, Sowadski JM, Lu
KP and Wang DG: Prevalent overexpression of prolyl isomerase Pin1
in human cancers. Am J Pathol. 164:1727–1737. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Wulf GM, Ryo A, Wulf GG, Lee SW, Niu T,
Petkova V and Lu KP: Pin1 is overexpressed in breast cancer and
cooperates with Ras signaling in increasing the transcriptional
activity of c-Jun towards cyclin D1. EMBO J. 20:3459–3472. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Rinehart-Kim J, Johnston M, Birrer M and
Bos T: Alterations in the gene expression profile of MCF-7 breast
tumor cells in response to c-Jun. Int J Cancer. 88:180–190. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Pulikkan JA, Dengler V, Peer Zada AA,
Kawasaki A, Geletu M, Pasalic Z, Bohlander SK, Ryo A, Tenen DG and
Behre G: Elevated PIN1 expression by C/EBPalpha-p30 blocks
C/EBPalpha-induced granulocytic differentiation through c-Jun in
AML. Leukemia. 24:914–923. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Rishi L, Hannon M, Salomè M, et al:
Regulation of Trib2 by an E2F1-C/EBPα feedback loop in AML cell
proliferation. Blood. 123:2389–2400. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Humbert M, Halter V, Shan D, Laedrach J,
Leibundgut EO, Baerlocher GM, Tobler A, Fey MF and Tschan MP:
Deregulated expression of Kruppel-like factors in acute myeloid
leukemia. Leuk Res. 35:909–913. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Britschgi A, Trinh E, Rizzi M, Jenal M,
Ress A, Tobler A, Fey MF, Helin K and Tschan MP: DAPK2 is a novel
E2F1/KLF6 target gene involved in their proapoptotic function.
Oncogene. 27:5706–5716. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Britschgi A, Simon HU, Tobler A, Fey MF
and Tschan MP: Epigallocatechin-3-gallate induces cell death in
acute myeloid leukaemia cells and supports all-trans retinoic
acid-induced neutrophil differentiation via death-associated
protein kinase 2. Br J Haematol. 149:55–64. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Rizzi M, Tschan MP, Britschgi C, et al:
The death-associated protein kinase 2 is up-regulated during normal
myeloid differentiation and enhances neutrophil maturation in
myeloid leukemic cells. J Leukoc Biol. 81:1599–1608. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Fang J, Menon M, Zhang D, Torbett B,
Oxburgh L, Tschan M, Houde E and Wojchowski DM: Attenuation of
EPO-dependent erythroblast formation by death-associated protein
kinase-2. Blood. 112:886–890. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Humbert M, Federzoni EA, Britschgi A, et
al: The tumor suppressor gene DAPK2 is induced by the myeloid
transcription factors PU.1 and C/EBPα during granulocytic
differentiation but repressed by PML-RARα in APL. J Leukoc Biol.
95:83–93. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
56
|
Porse BT, Pedersen TA, Xu X, Lindberg B,
Wewer UM, Friis-Hansen L and Nerlov C: E2F repression by C/EBPalpha
is required for adipogenesis and granulopoiesis in vivo. Cell.
107:247–258. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Song G, Li Y, Zhang Z, et al: c-myc but
not Hif-1α-dependent downregulation of VEGF influences the
proliferation and differentiation of HL-60 cells induced by ATRA.
Oncol Rep. 29:2378–2384. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Eklund E: The role of Hox proteins in
leukemogenesis: Insights into key regulatory events in
hematopoiesis. Crit Rev Oncog. 16:65–76. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Kroon E, Krosl J, Thorsteinsdottir U,
Baban S, Buchberg AM and Sauvageau G: Hoxa9 transforms primary bone
marrow cells through specific collaboration with Meis1a but not
Pbx1b. EMBO J. 17:3714–3725. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Collins C, Wang J, Miao H, Bronstein J,
Nawer H, Xu T, Figueroa M, Muntean AG and Hess JL: C/EBPα is an
essential collaborator in Hoxa9/Meis1-mediated leukemogenesis. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 111:9899–9904. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Nerlov C and Ziff EB: CCAAT/enhancer
binding protein-alpha amino acid motifs with dual TBP and TFIIB
binding ability co-operate to activate transcription in both yeast
and mammalian cells. EMBO J. 14:4318–4328. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Müller C, Calkhoven CF, Sha X and Leutz A:
The CCAAT enhancer-binding protein alpha (C/EBPalpha) requires a
SWI/SNF complex for proliferation arrest. J Biol Chem.
279:7353–7358. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Chen PL, Riley DJ, Chen Y and Lee WH:
Retinoblastoma protein positively regulates terminal adipocyte
differentiation through direct interaction with C/EBPs. Genes Dev.
10:2794–2804. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Wang H, Iakova P, Wilde M, Welm A, Goode
T, Roesler WJ and Timchenko NA: C/EBPalpha arrests cell
proliferation through direct inhibition of Cdk2 and Cdk4. Mol Cell.
8:817–828. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Shimokawa T, Nunomura S, Enomoto Y and Ra
C: Amino acid residues in the beta3 strand and subsequent loop of
the conserved ETS domain that mediate basic leucine zipper (bZIP)
recruitment and potentially distinguish functional attributes of
ETS proteins. Biochem J. 430:129–139. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Shimokawa T, Nunomura S, Fujisawa D and Ra
C: Identification of the C/EBPα C-terminal tail residues involved
in the protein interaction with GABP and their potency in myeloid
differentiation of K562 cells. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1829:1207–1217. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Lin RJ, Nagy L, Inoue S, Shao W, Miller WH
Jr and Evans RM: Role of the histone deacetylase complex in acute
promyelocytic leukaemia. Nature. 391:811–814. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Zapotocky M, Mejstrikova E, Smetana K,
Stary J, Trka J and Starkova J: Valproic acid triggers
differentiation and apoptosis in AML1/ETO-positive leukemic cells
specifically. Cancer Lett. 319:144–153. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Tallman MS, Gilliland DG and Rowe JM: Drug
therapy for acute myeloid leukemia. Blood. 106:1154–1163. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Chen P, Aimiuwu J, Xie Z, Wei X, Liu S,
Klisovic R, Marcucci G and Chan KK: Biochemical modulation of
aracytidine (Ara-C) effects by GTI-2040, a ribonucleotide reductase
inhibitor, in K562 human leukemia cells. AAPS J. 13:131–140. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
71
|
Uy GL, Rettig MP, Motabi IH, et al: A
phase 1/2 study of chemosensitization with the CXCR4 antagonist
plerixafor in relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia. Blood.
119:3917–3924. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Bai H, Cao Z, Deng C, Zhou L and Wang C:
miR-181a sensitizes resistant leukaemia HL-60/Ara-C cells to Ara-C
by inducing apoptosis. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 138:595–602. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Hickey CJ, Schwind S, Radomska HS, et al:
Lenalidomide-mediated enhanced translation of C/EBPα-p30 protein
up-regulates expression of the antileukemic microRNA-181a in acute
myeloid leukemia. Blood. 121:159–169. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
74
|
Ko YC, Fang WH, Lin TC, Hou HA, Chen CY,
Tien HF and Lin LI: MicroRNA let-7a-3 gene methylation is
associated with karyotyping, CEBPA promoter methylation, and
survival in acute myeloid leukemia. Leuk Res. 38:625–631. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|