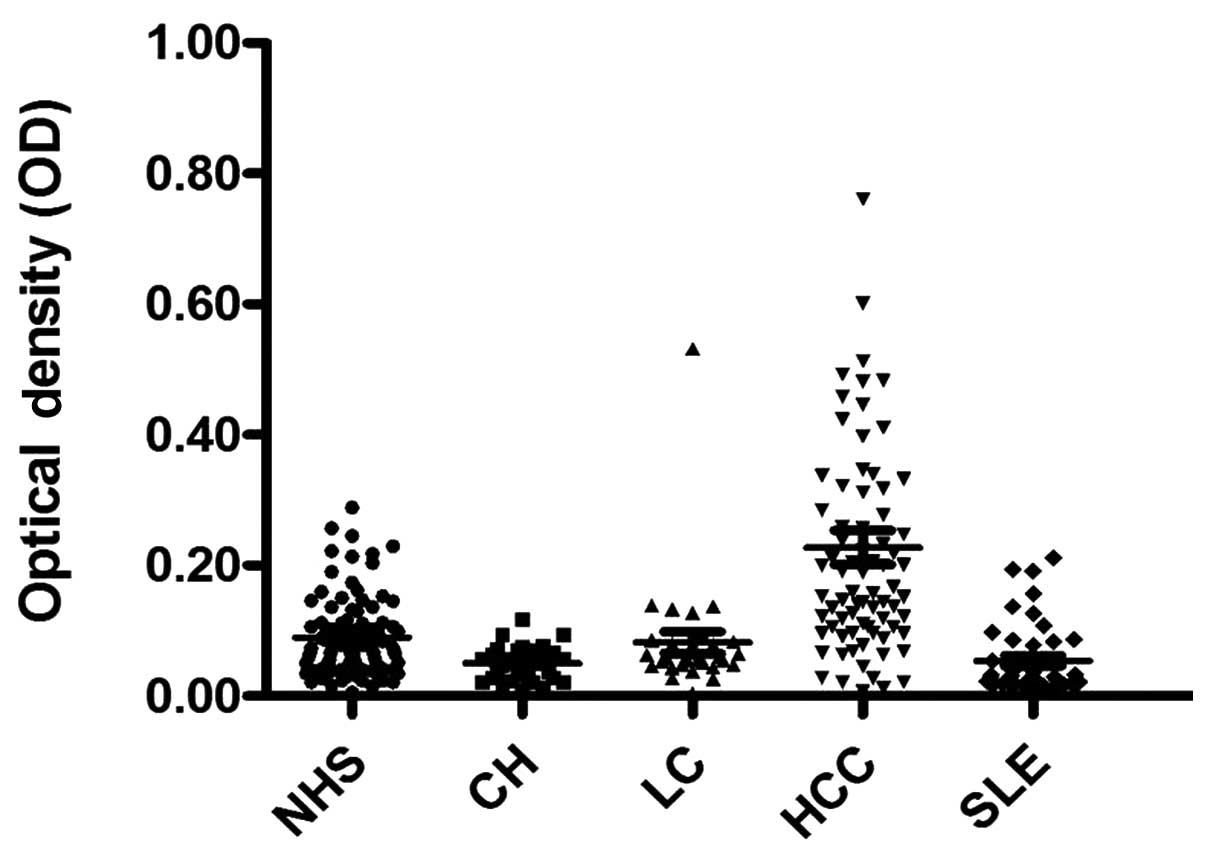
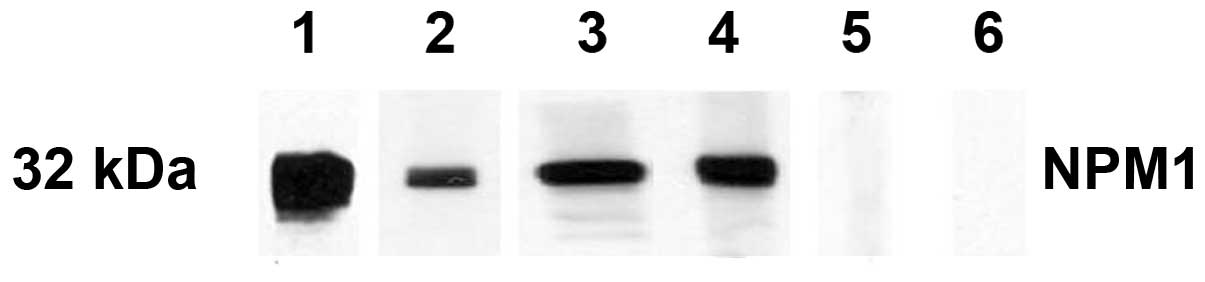
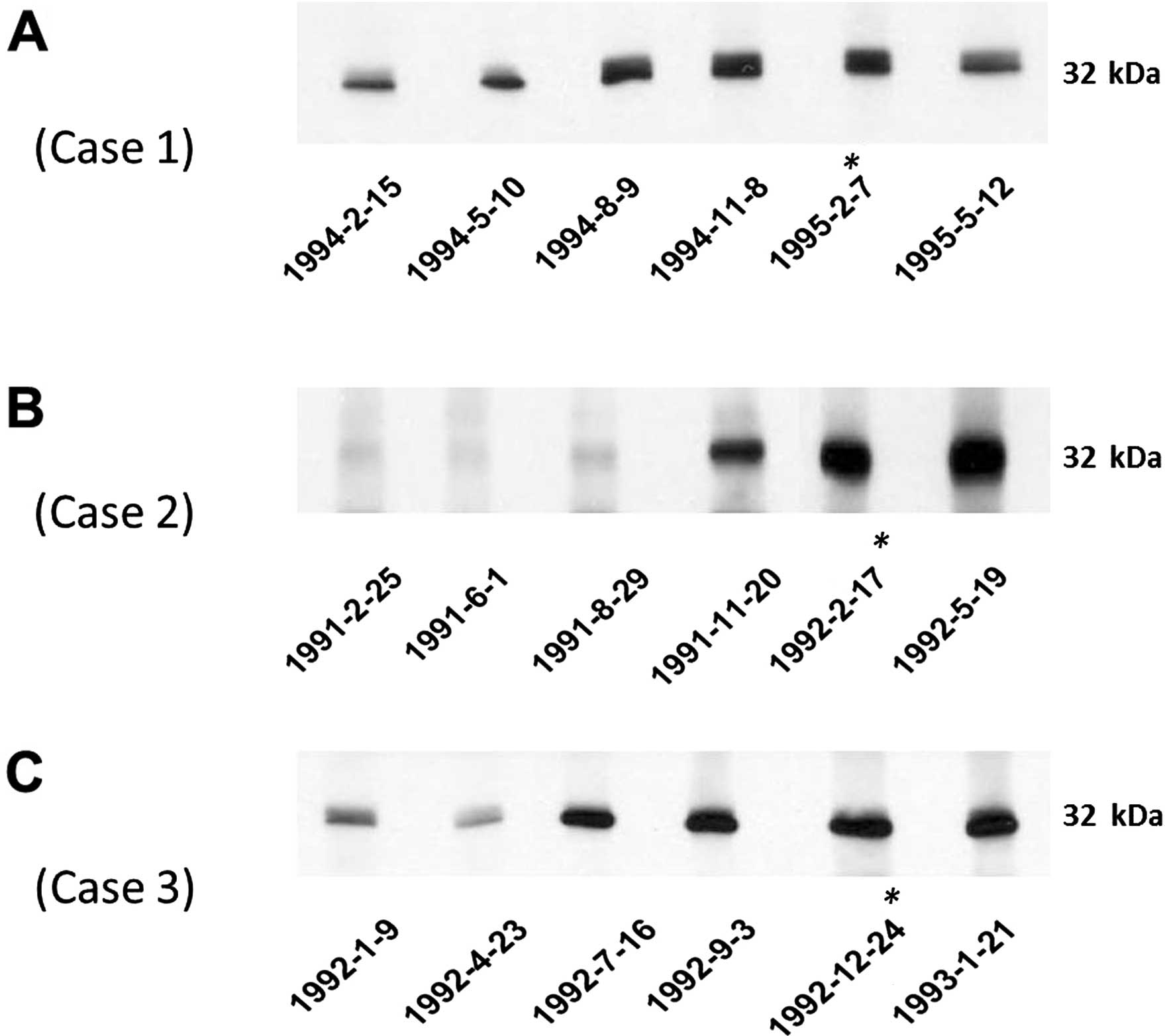
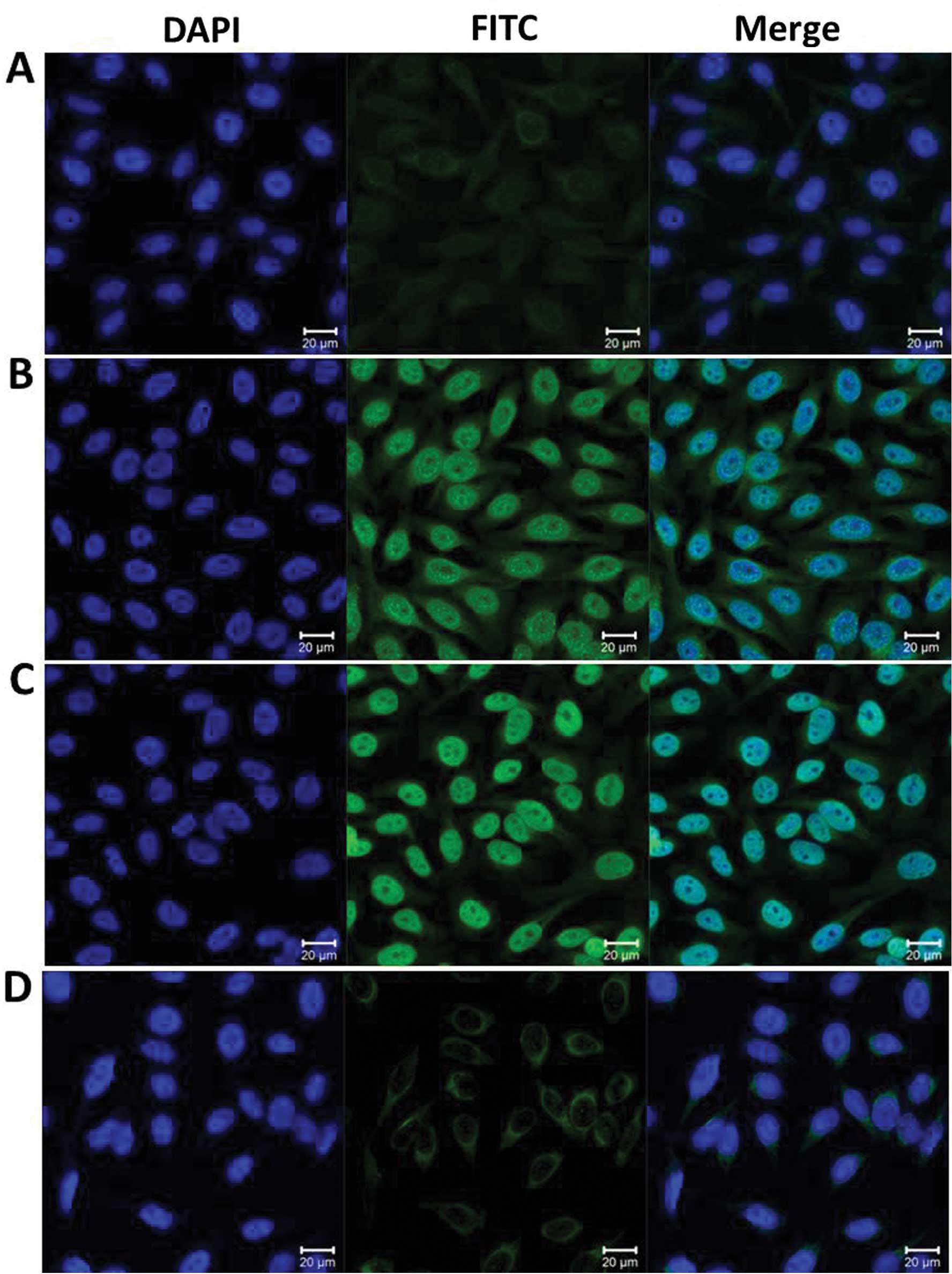
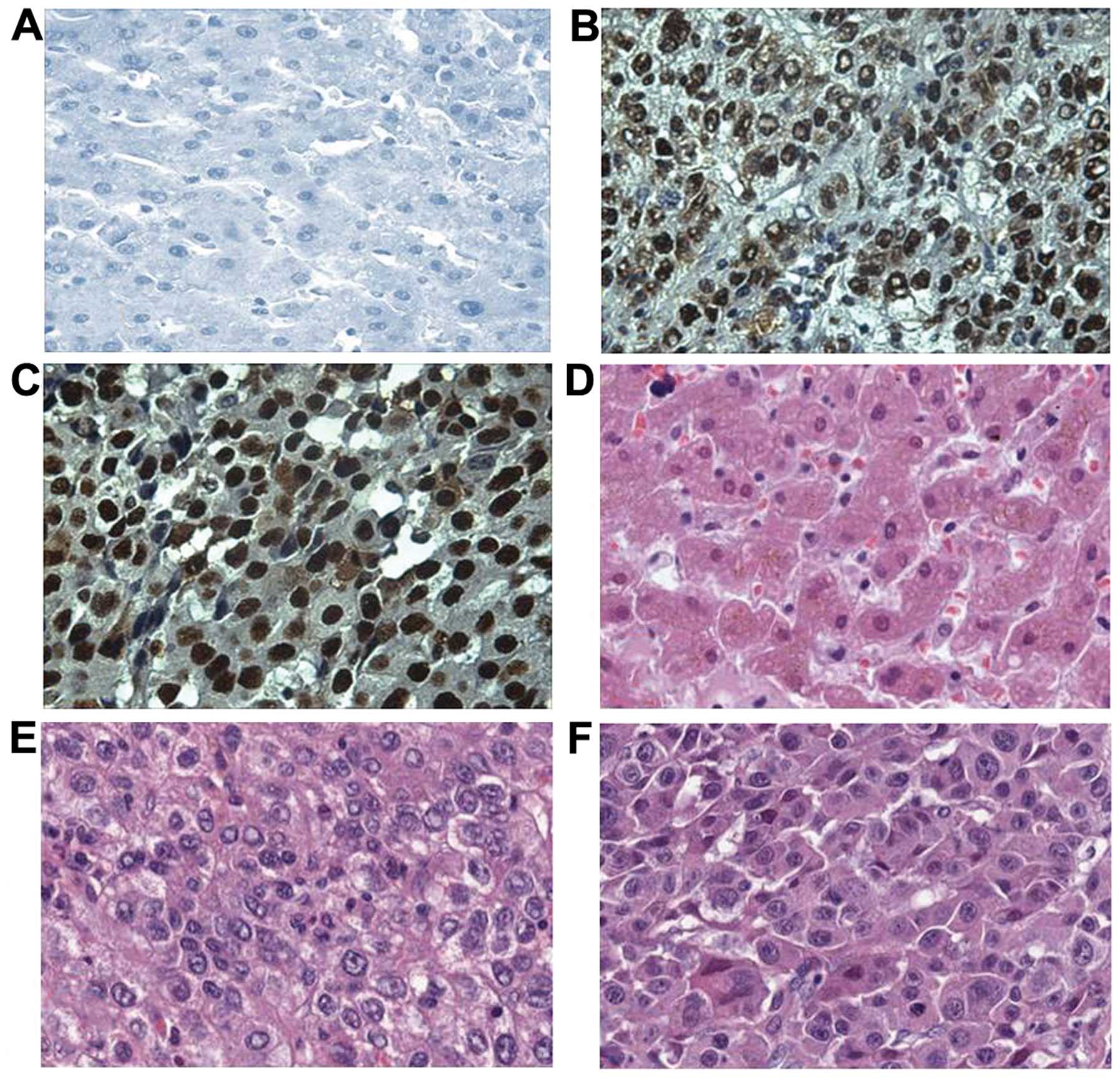
|
1
|
Borer RA, Lehner CF, Eppenberger HM and
Nigg EA: Major nucleolar proteins shuttle between nucleus and
cytoplasm. Cell. 56:379–390. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wang D, Umekawa H and Olson MO: Expression
and subcellular locations of two forms of nucleolar protein B23 in
rat tissues and cells. Cell Mol Biol Res. 39:33–42. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Grisendi S, Bernardi R, Rossi M, Cheng K,
Khandker L, Manova K and Pandolfi PP: Role of nucleophosmin in
embryonic development and tumorigenesis. Nature. 437:147–153. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wu MH and Yung BY: UV stimulation of
nucleophosmin/B23 expression is an immediate early gene response
induced by damaged DNA. J Biol Chem. 277:48234–48240. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Verheggen C, Almouzni G and
Hernandez-Verdun D: The ribosomal RNA processing machinery is
recruited to the nucleolar domain before RNA polymerase I during
Xenopus laevis sdevelopment. J Cell Biol. 149:293–306. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Huang N, Negi S, Szebeni A and Olson MO:
Protein NPM3 interacts with the multifunctional nucleolar protein
B23/nucleophosmin and inhibits ribosome biogenesis. J Biol Chem.
280:5496–5502. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Okuda M: The role of nucleophosmin in
centrosome duplication. Oncogene. 21:6170–6174. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Okuda M, Horn HF, Tarapore P, Tokuyama Y,
Smulian AG, Chan PK, Knudsen ES, et al: Nucleophosmin/B23 is a
target of CDK2/cyclin E in centrosome duplication. Cell.
103:127–140. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Okuwaki M, Matsumoto K, Tsujimoto M and
Nagata K: Function of nucleophosmin/B23, a nucleolar acidic
protein, as a histone chaperone. FEBS Lett. 506:272–276. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lindström MS and Zhang Y: Ribosomal
protein S9 is a novel B23/NPM-binding protein required for normal
cell proliferation. J Biol Chem. 283:15568–15576. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Maggi LB Jr, Kuchenruether M, Dadey DY,
Schwope RM, Grisendi S, Townsend RR, Pandolfi PP and Weber JD:
Nucleophosmin serves as a rate-limiting nuclear export chaperone
for the mammalian ribosome. Mol Cell Biol. 28:7050–7065. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Avitabile D, Bailey B, Cottage CT,
Sundararaman B, Joyo A, McGregor M, Gude N, et al: Nucleolar stress
is an early response to myocardial damage involving nucleolar
proteins nucleostemin and nucleophosmin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
108:6145–6150. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Khandelwal N, Simpson J, Taylor G, Rafique
S, Whitehouse A, Hiscox J and Stark LA: Nucleolar NF-κB/RelA
mediates apoptosis by causing cytoplasmic relocalization of
nucleophosmin. Cell Death Differ. 18:1889–1903. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Li J, Zhang X, Sejas DP, Bagby GC and Pang
Q: Hypoxia-induced nucleophosmin protects cell death through
inhibition of p53. J Biol Chem. 279:41275–41279. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Colombo E, Alcalay M and Pelicci PG:
Nucleophosmin and its complex network: a possible therapeutic
target in hematological diseases. Oncogene. 30:2595–2609. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Colombo E, Marine JC, Danovi D, Falini B
and Pelicci PG: Nucleophosmin regulates the stability and
transcriptional activity of p53. Nat Cell Biol. 4:529–533. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kurki S, Peltonen K, Latonen L, Kiviharju
TM, Ojala PM, Meek D and Laiho M: Nucleolar protein NPM interacts
with HDM2 and protects tumor suppressor protein p53 from
HDM2-mediated degradation. Cancer Cell. 5:465–475. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Maiguel DA, Jones L, Chakravarty D, Yang C
and Carrier F: Nucleophosmin sets a threshold for p53 response to
UV radiation. Mol Cell Biol. 24:3703–3711. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Bertwistle D, Sugimoto M and Sherr CJ:
Physical and functional interactions of the Arf tumor suppressor
protein with nucleophosmin/B23. Mol Cell Biol. 24:985–996. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Falini B, Nicoletti I, Martelli MF and
Mecucci C: Acute myeloid leukemia carrying cytoplasmic/mutated
nucleophosmin (NPMc+ AML): biologic and clinical
features. Blood. 109:874–885. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Meani N and Alcalay M: Role of
nucleophosmin in acute myeloid leukemia. Expert Rev Anticancer
Ther. 9:1283–1294. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Grisendi S, Mecucci C, Falini B and
Pandolfi PP: Nucleophosmin and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:493–505.
2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Liu X, Liu D, Qian D, Dai J, An Y, Jiang
S, Stanley B, et al: Nucleophosmin (NPM1/B23) interacts with
activating transcription factor 5 (ATF5) protein and promotes
proteasome- and caspase-dependent ATF5 degradation in
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. J Biol Chem. 287:19599–19609. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Johnson PJ, Leung N, Cheng P, Welby C,
Leung WT, Lau WY, Yu S and Ho S: ‘Hepatoma-specific’
alphafetoprotein may permit preclinical diagnosis of malignant
change in patients with chronic liver disease. Br J Cancer.
75:236–240. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Zhang JY, Casiano CA, Peng XX, Koziol JA,
Chan EK and Tan EM: Enhancement of antibody detection in cancer
using panel of recombinant tumor-associated antigens. Cancer
Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 12:136–143. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhang JY, Megliorino R, Peng XX, Tan EM,
Chen Y and Chan EK: Antibody detection using tumor-associated
antigen mini-array in diagnosing human hepatocellular carcinoma. J
Hepatol. 46:107–114. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Looi KS, Nakayasu ES, Diaz RA, Tan EM,
Almeida IC and Zhang JY: Using proteomic approach to identify
tumor-associated antigens as markers in hepatocellular carcinoma. J
Proteome Res. 7:4004–4012. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhang J, Wang K, Zhang J, Liu SS, Dai L
and Zhang JY: Using proteomic approach to identify tumor-associated
proteins as biomarkers in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
J Proteome Res. 10:2863–2872. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ersvaer E, Zhang JY, McCormack E, Olsnes
A, Anensen N, Tan EM, Gjertsen BT and Bruserud O: Cyclin B1 is
commonly expressed in the cytoplasm of primary human acute
myelogenous leukemia cells and serves as a leukemia-associated
antigen associated with autoantibody response in a subset of
patients. Eur J Haematol. 79:210–225. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Looi K, Megliorino R, Shi FD, Peng XX,
Chen Y and Zhang JY: Humoral immune response to p16, a
cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor in human malignancies. Oncol Rep.
16:1105–1110. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Liu W, Wang P, Li Z, Xu W, Dai L, Wang K
and Zhang J: Evaluation of tumour-associated antigen (TAA)
miniarray in immunodiagnosis of colon cancer. Scand J Immunol.
69:57–63. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Vogelstein B and Kinzler W: The multistep
nature of cancer. Trends Genet. 9:138–141. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: the next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chen Y, Zhou Y, Qiu S, Wang K, Liu S, Peng
XX, Li J, et al: Autoantibodies to tumor-associated antigens
combined with abnormal alpha-fetoprotein enhance immunodiagnosis of
hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 289:32–39. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
35
|
Zhang JY: Mini-array of multiple
tumor-associated antigens to enhance autoantibody detection for
immunodiagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Autoimmun Rev.
6:143–148. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Himoto T, Kuriyama S, Zhang JY, Chan EK,
Nishioka M and Tan EM: Significance of autoantibodies against
insulin-like growth factor II mRNA-binding proteins in patients
with hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 26:311–317.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhang JY and Tan EM: Autoantibodies to
tumor-associated antigens as diagnostic biomarkers in
hepatocellular carcinoma and other solid tumors. Expert Rev Mol
Diagn. 10:321–328. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Chen W, Rassidakis GZ and Medeiros LJ:
Nucleophosmin gene mutations in acute myeloid leukemia. Arch Pathol
Lab Med. 130:1687–1692. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Chou SH, Ko BS, Chiou JS, Hsu YC, Tsai MH,
Chiu YC, Yu IS, et al: A knock-in Npm1 mutation in mice results in
myeloproliferation and implies a perturbation in hematopoietic
microenvironment. PLoS One. 7:e497692012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Qin FX, Shao HY, Chen XC, Tan S, Zhang HJ,
Miao ZY, Wang L, et al: Knockdown of NPM1 by RNA interference
inhibits cells proliferation and induces apoptosis in leukemic cell
line. Int J Med Sci. 8:287–294. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Tsui KH, Juang HH, Lee TH, Chang PL, Chen
CL and Yung BY: Association of nucleophosmin/B23 with bladder
cancer recurrence based on immunohistochemical assessment in
clinical samples. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 29:364–370. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Montazeri A, Vahdaninia M, Harirchi I, et
al: Breast cancer in Iran: need for greater women awareness of
warning signs and effective screening methods. Asia Pac Fam Med.
7(6)2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Pianta A, Puppin C, Passon N, Franzoni A,
Romanello M, Tell G, Di Loreto C, et al: Nucleophosmin
delocalization in thyroid tumour cells. Endocr Pathol. 22:18–23.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Liu Y, Zhang F, Zhang XF, Qi LS, Yang L,
Guo H and Zhang N: Expression of nucleophosmin/NPM1 correlates with
migration and invasiveness of colon cancer cells. J Biomed Sci.
19(53)2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Karhemo PR, Rivinoja A, Lundin J, Hyvönen
M, Chernenko A, Lammi J, Sihto H, et al: An extensive tumor array
analysis supports tumor suppressive role for nucleophosmin in
breast cancer. Am J Pathol. 179:1004–1014. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Tsui KH, Cheng AJ, Chang Pe, Pan TL and
Yung BY: Association of nucleophosmin/B23 mRNA expression with
clinical outcome in patients with bladder carcinoma. Urology.
64:839–844. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Skaar TC, Prasad SC, Sharareh S, Lippman
ME, Brünner N and Clarke R: Two-dimensional gel electrophoresis
analyses identify nucleophosmin as an estrogen regulated protein
associated with acquired estrogen-independence in human breast
cancer cells. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 67:391–402. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Yun JP, Miao J, Chen GG, Tian QH, Zhang
CQ, Xiang J, Fu J and Lai PB: Increased expression of
nucleophosmin/B23 in hepatocellular carcinoma and correlation with
clinicopathological parameters. Br J Cancer. 96:477–484. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Falini B, Mecucci C, Tiacci E, Alcalay M,
Rosati R, Pasqualucci L, La Starza R, et al: ; GIMEMA Acute
Leukemia Working Party: Cytoplasmic nucleophosmin in acute
myelogenous leukemia with a normal karyotype. N Engl J Med.
352:254–266. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|