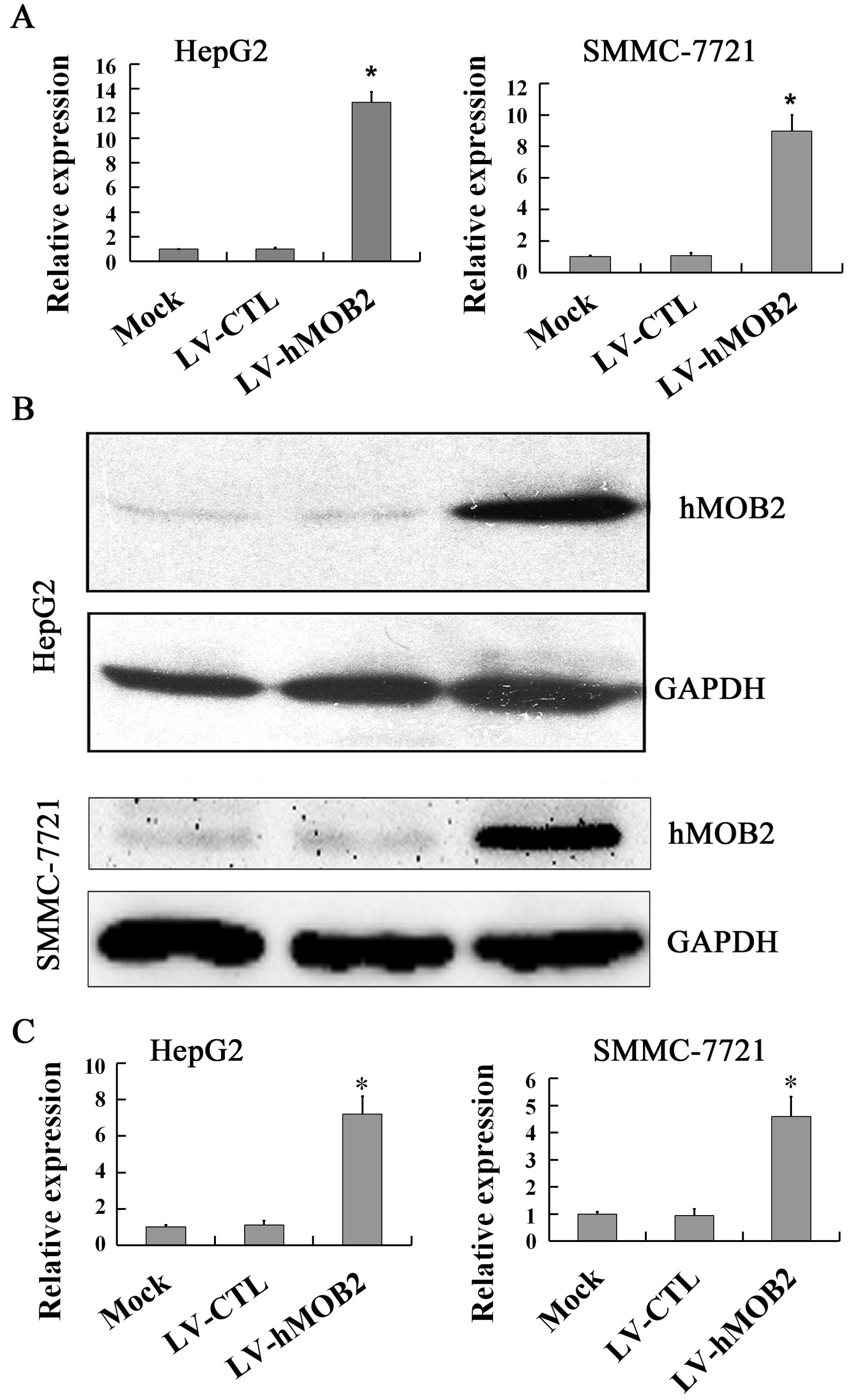
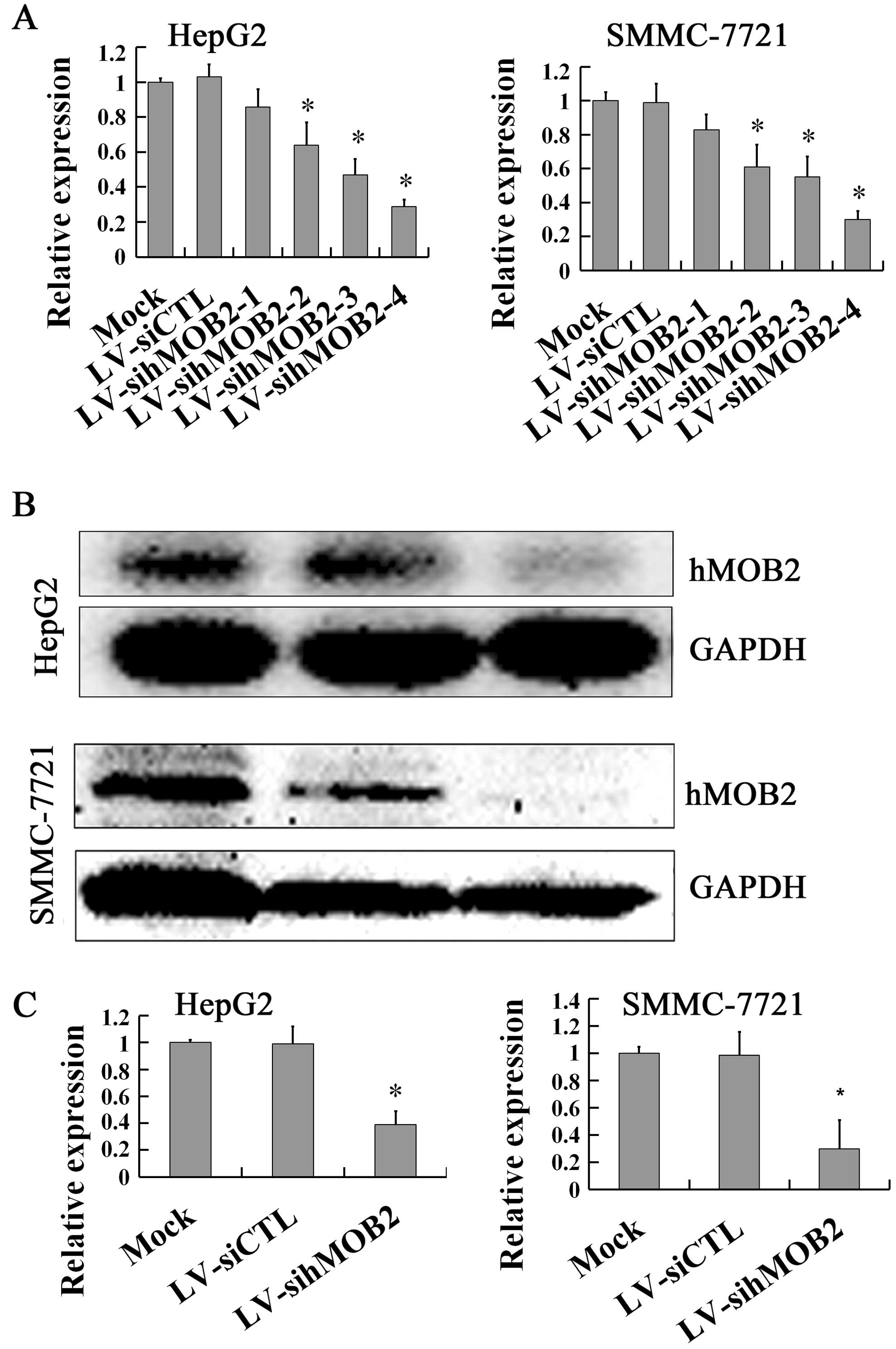
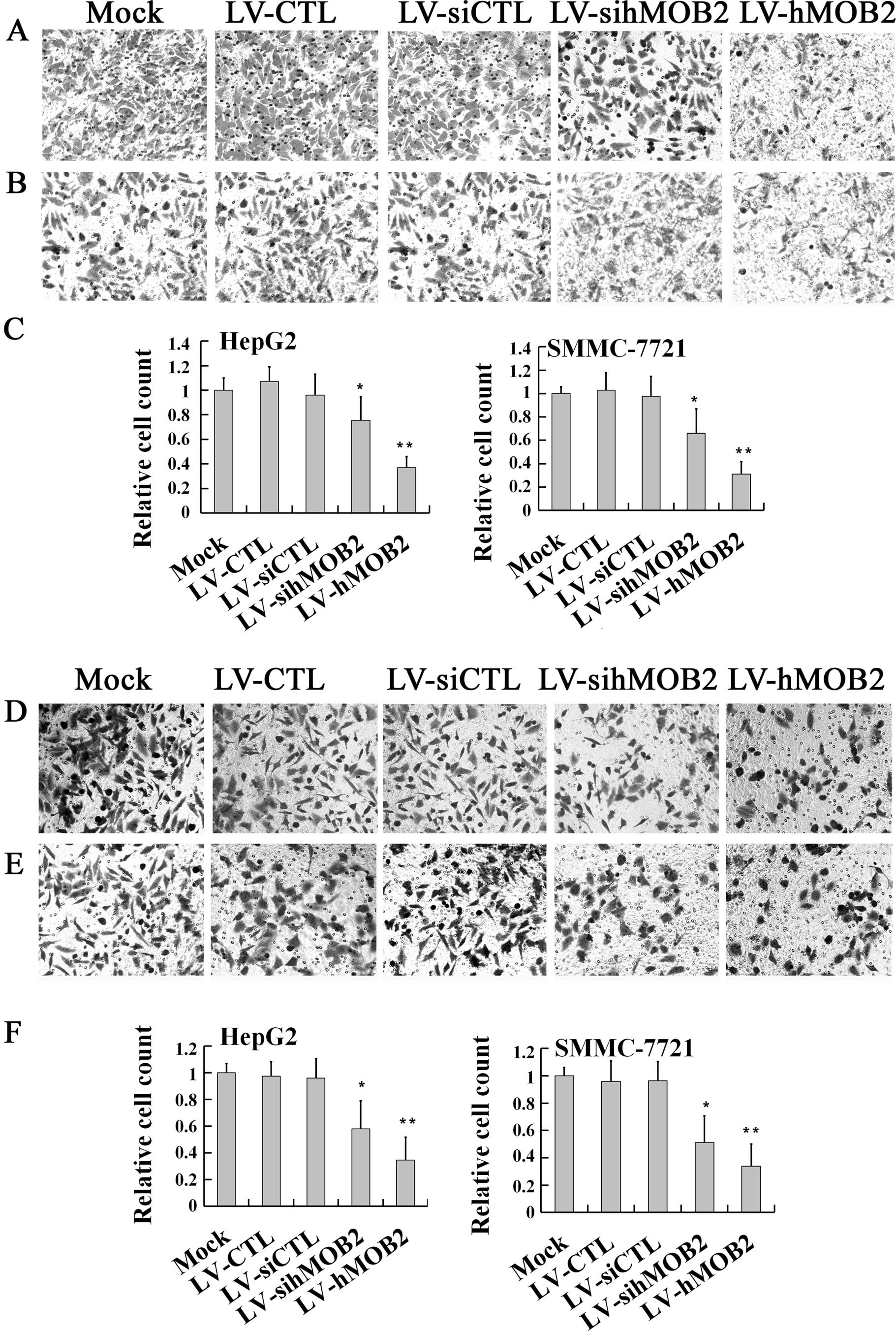
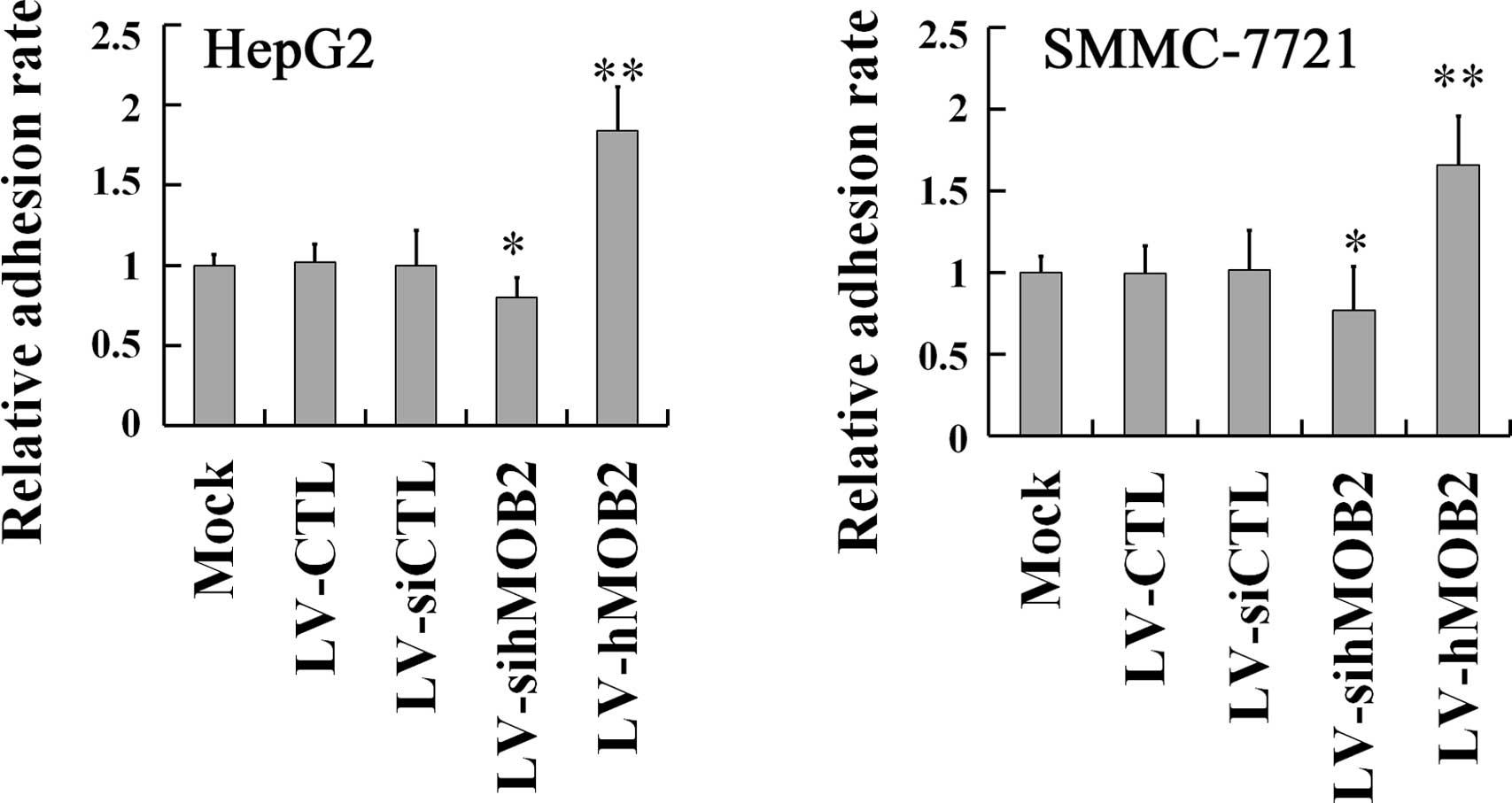
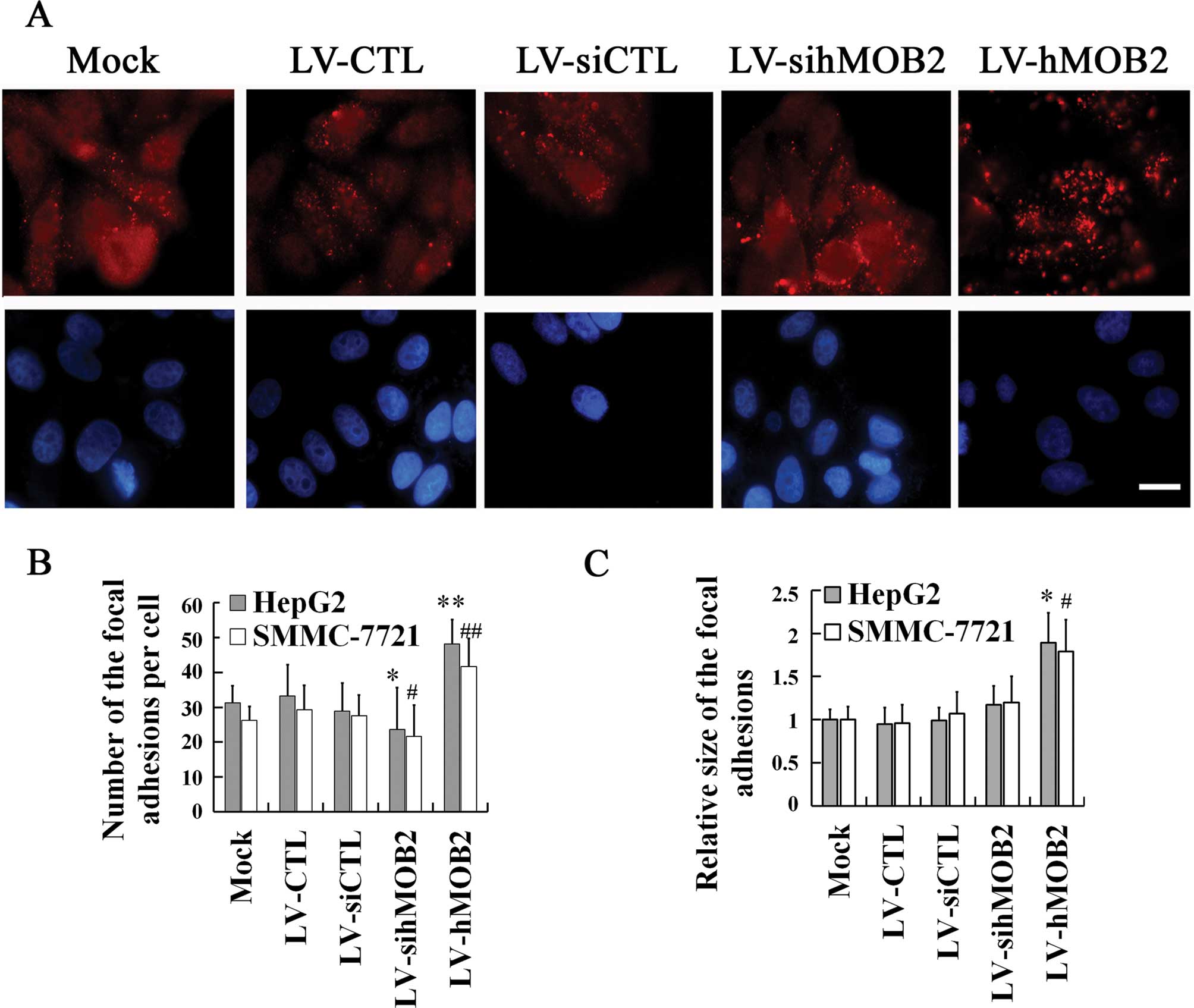
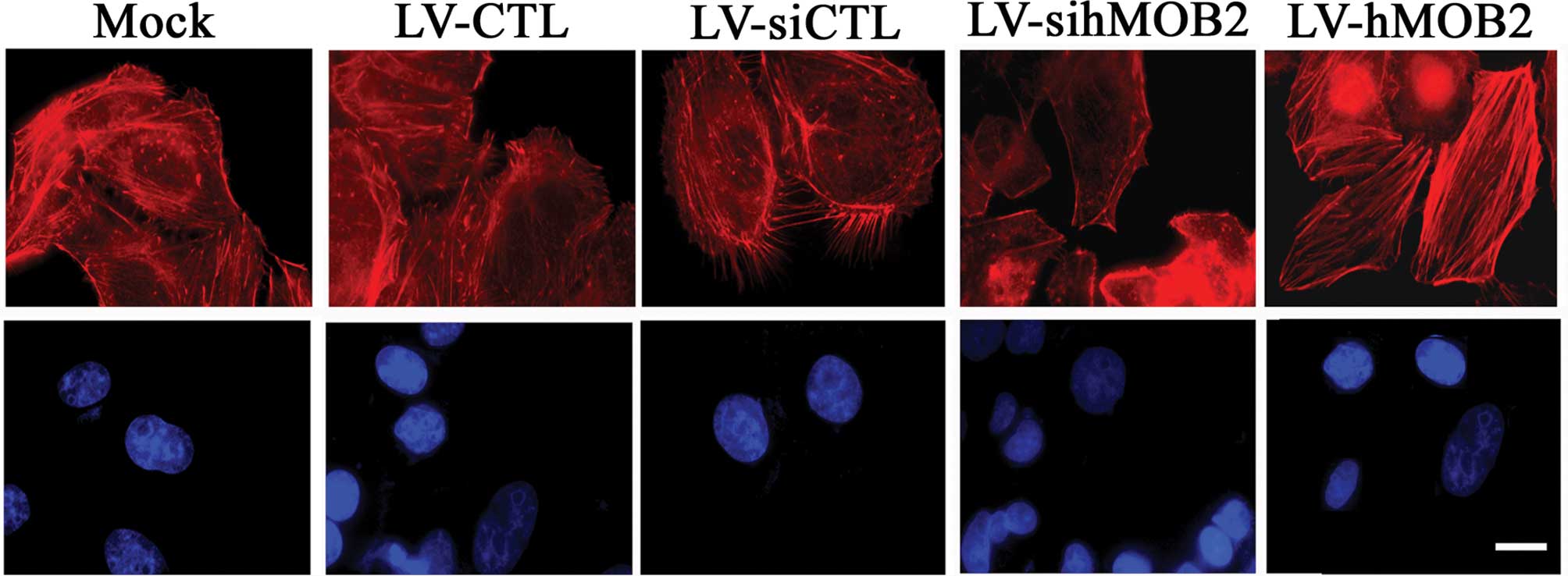
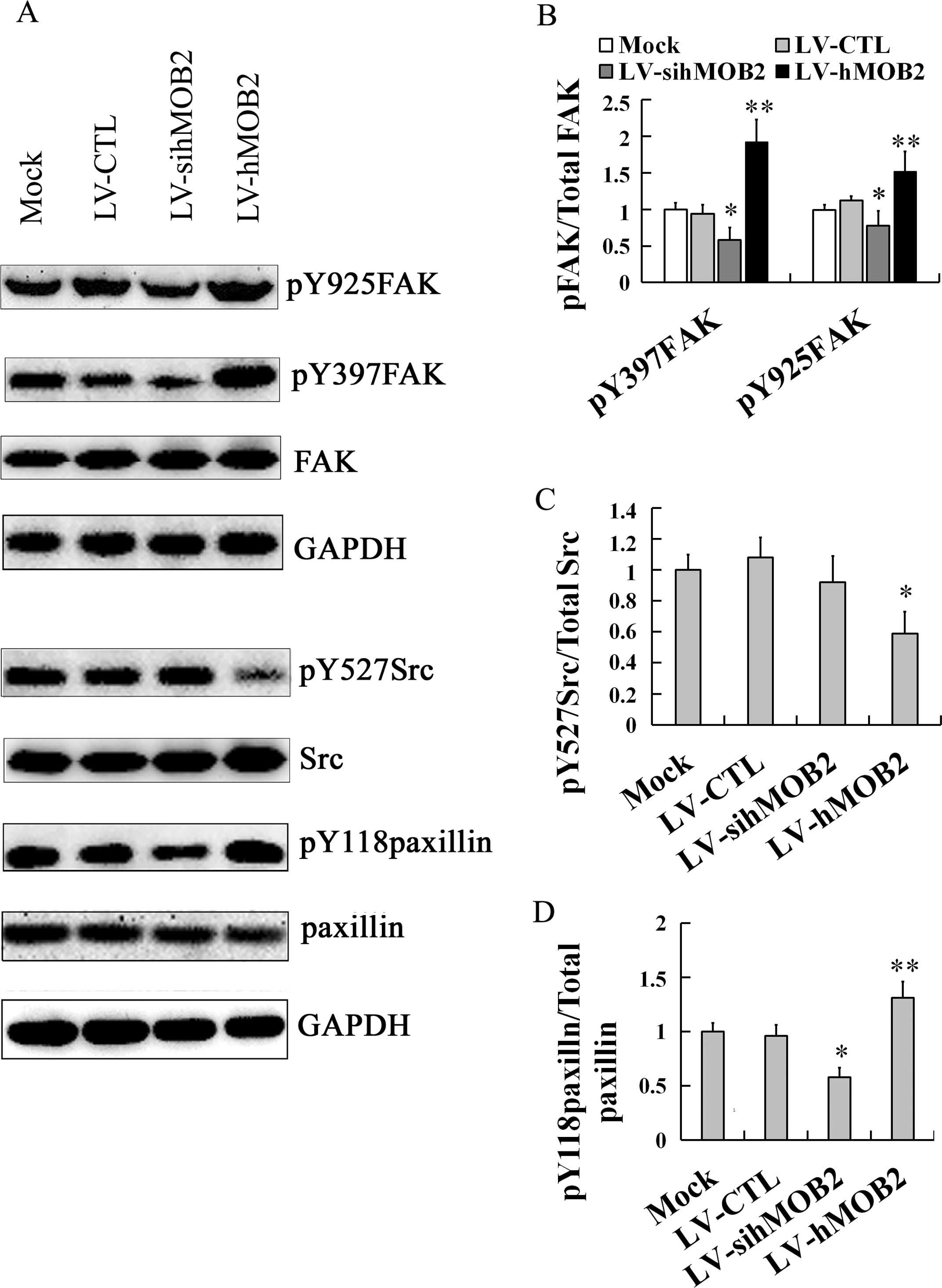
|
1
|
Hergovich A, Kohler RS, Schmitz D,
Vichalkovski A, Cornils H and Hemmings BA: The MST1 and hMOB1 tumor
suppressors control human centrosome duplication by regulating NDR
kinase phosphorylation. Curr Biol. 19:1692–1702. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hergovich A: MOB control: Reviewing a
conserved family of kinase regulators. Cell Signal. 23:1433–1440.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Stavridi ES, Harris KG, Huyen Y, Bothos J,
Verwoerd PM, Stayrook SE, Pavletich NP, Jeffrey PD and Luca FC:
Crystal structure of a human Mob1 protein: Toward understanding
Mob-regulated cell cycle pathways. Structure. 11:1163–1170. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ponchon L, Dumas C, Kajava AV, Fesquet D
and Padilla A: NMR solution structure of Mob1, a mitotic exit
network protein and its interaction with an NDR kinase peptide. J
Mol Biol. 337:167–182. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lai ZC, Wei X, Shimizu T, Ramos E,
Rohrbaugh M, Nikolaidis N, Ho LL and Li Y: Control of cell
proliferation and apoptosis by mob as tumor suppressor, mats. Cell.
120:675–685. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Mrkobrada S, Boucher L, Ceccarelli DF,
Tyers M and Sicheri F: Structural and functional analysis of
Saccharomyces cerevisiae Mob1. J Mol Biol. 362:430–440. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ho LL, Wei X, Shimizu T and Lai ZC: Mob as
tumor suppressor is activated at the cell membrane to control
tissue growth and organ size in Drosophila. Dev Biol. 337:274–283.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Kohler RS, Schmitz D, Cornils H, Hemmings
BA and Hergovich A: Differential NDR/LATS interactions with the
human MOB family reveal a negative role for human MOB2 in the
regulation of human NDR kinases. Mol Cell Biol. 30:4507–4520. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tavares A, Gonçalves J, Florindo C,
Tavares AA and Soares H: Mob1: Defining cell polarity for proper
cell division. J Cell Sci. 125:516–527. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chow A, Hao Y and Yang X: Molecular
characterization of human homologs of yeast MOB1. Int J Cancer.
126:2079–2089. 2010.
|
|
11
|
Florindo C, Perdigão J, Fesquet D,
Schiebel E, Pines J and Tavares AA: Human Mob1 proteins are
required for cytokinesis by controlling microtubule stability. J
Cell Sci. 125:3085–3090. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang ZX, Wang HY and Wu MC: Identification
and characterization of a novel human hepatocellular
carcinoma-associated gene. Br J Cancer. 85:1162–1167. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
He Y, Emoto K, Fang X, Ren N, Tian X, Jan
YN and Adler PN: Drosophila Mob family proteins interact with the
related tricor-nered (Trc) and warts (Wts) kinases. Mol Biol Cell.
16:4139–4152. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Emoto K, He Y, Ye B, Grueber WB, Adler PN,
Jan LY and Jan YN: Control of dendritic branching and tiling by the
Tricornered-kinase/Furry signaling pathway in Drosophila sensory
neurons. Cell. 119:245–256. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu LY, Lin CH and Fan SS: Function of
Drosophila mob2 in photoreceptor morphogenesis. Cell Tissue Res.
338:377–389. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lin CH, Hsieh M and Fan SS: The promotion
of neurite formation in Neuro2A cells by mouse Mob2 protein. FEBS
Lett. 585:523–530. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Stork O, Zhdanov A, Kudersky A, Yoshikawa
T, Obata K and Pape HC: Neuronal functions of the novel
serine/threonine kinase Ndr2. J Biol Chem. 279:45773–45781. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Akakura S and Gelman IH: Pivotal role of
AKAP12 in the regulation of cellular adhesion dynamics: Control of
cytoskeletal architecture, cell migration, and mitogenic signaling.
J Signal Transduct. 2012:5291792012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lock JG, Wehrle-Haller B and Strömblad S:
Cell-matrix adhesion complexes: Master control machinery of cell
migration. Semin Cancer Biol. 18:65–76. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Zong F, Fthenou E, Mundt F, Szatmári T,
Kovalszky I, Szilák L, Brodin D, Tzanakakis G, Hjerpe A and Dobra
K: Specific syndecan-1 domains regulate mesenchymal tumor cell
adhesion, motility and migration. PLoS One. 6:e148162011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Geiger B, Spatz JP and Bershadsky AD:
Environmental sensing through focal adhesions. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 10:21–33. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lanning NJ, Su HW, Argetsinger LS and
Carter-Su C: Identification of SH2B1β as a focal adhesion protein
that regulates focal adhesion size and number. J Cell Sci.
124:3095–3105. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Webb DJ, Donais K, Whitmore LA, Thomas SM,
Turner CE, Parsons JT and Horwitz AF: FAK-Src signalling through
paxillin, ERK and MLCK regulates adhesion disassembly. Nat Cell
Biol. 6:154–161. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Fraley SI, Feng Y, Krishnamurthy R, Kim
DH, Celedon A, Longmore GD and Wirtz D: A distinctive role for
focal adhesion proteins in three-dimensional cell motility. Nat
Cell Biol. 12:598–604. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
van Nimwegen MJ and van de Water B: Focal
adhesion kinase: A potential target in cancer therapy. Biochem
Pharmacol. 73:597–609. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Mitra SK and Schlaepfer DD:
Integrin-regulated FAK-Src signaling in normal and cancer cells.
Curr Opin Cell Biol. 18:516–523. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ishikawa T and Kramer RH: Sdc1 negatively
modulates carcinoma cell motility and invasion. Exp Cell Res.
316:951–965. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
28
|
Geiger B, Bershadsky A, Pankov R and
Yamada KM: Transmembrane crosstalk between the extracellular matrix
- cytoskeleton crosstalk. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2:793–805. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hynes RO: Integrins: Bidirectional,
allosteric signaling machines. Cell. 110:673–687. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Gupton SL and Waterman-Storer CM:
Spatiotemporal feedback between actomyosin and focal-adhesion
systems optimizes rapid cell migration. Cell. 125:1361–1374. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hotulainen P and Lappalainen P: Stress
fibers are generated by two distinct actin assembly mechanisms in
motile cells. J Cell Biol. 173:383–394. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hall A: Rho GTPases and the actin
cytoskeleton. Science. 279:509–514. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ridley AJ: Rho GTPases and cell migration.
J Cell Sci. 114:2713–2722. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Machacek M, Hodgson L, Welch C, Elliott H,
Pertz O, Nalbant P, Abell A, Johnson GL, Hahn KM and Danuser G:
Coordination of Rho GTPase activities during cell protrusion.
Nature. 461:99–103. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Liu J, Di G, Wu CT, Hu X and Duan H:
CEACAM1 inhibits cell-matrix adhesion and promotes cell migration
through regulating the expression of N-cadherin. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 430:598–603. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Luo M and Guan JL: Focal adhesion kinase:
A prominent determinant in breast cancer initiation, progression
and metastasis. Cancer Lett. 289:127–139. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
37
|
Zhao J and Guan JL: Signal transduction by
focal adhesion kinase in cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 28:35–49.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Van Slambrouck S, Jenkins AR, Romero AE
and Steelant WF: Reorganization of the integrin α2 subunit controls
cell adhesion and cancer cell invasion in prostate cancer. Int J
Oncol. 34:1717–1726. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Van Slambrouck S, Grijelmo C, De Wever O,
Bruyneel E, Emami S, Gespach C and Steelant WF: Activation of the
FAK-src molecular scaffolds and p130Cas-JNK signaling cascades by
α1-integrins during colon cancer cell invasion. Int J Oncol.
31:1501–1508. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Crosara-Alberto DP, Inoue RY and Costa CR:
FAK signalling mediates NF-kappaB activation by mechanical stress
in cardiac myocytes. Clin Chim Acta. 403:81–86. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Bjorge JD, Jakymiw A and Fujita DJ:
Selected glimpses into the activation and function of Src kinase.
Oncogene. 19:5620–5635. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|