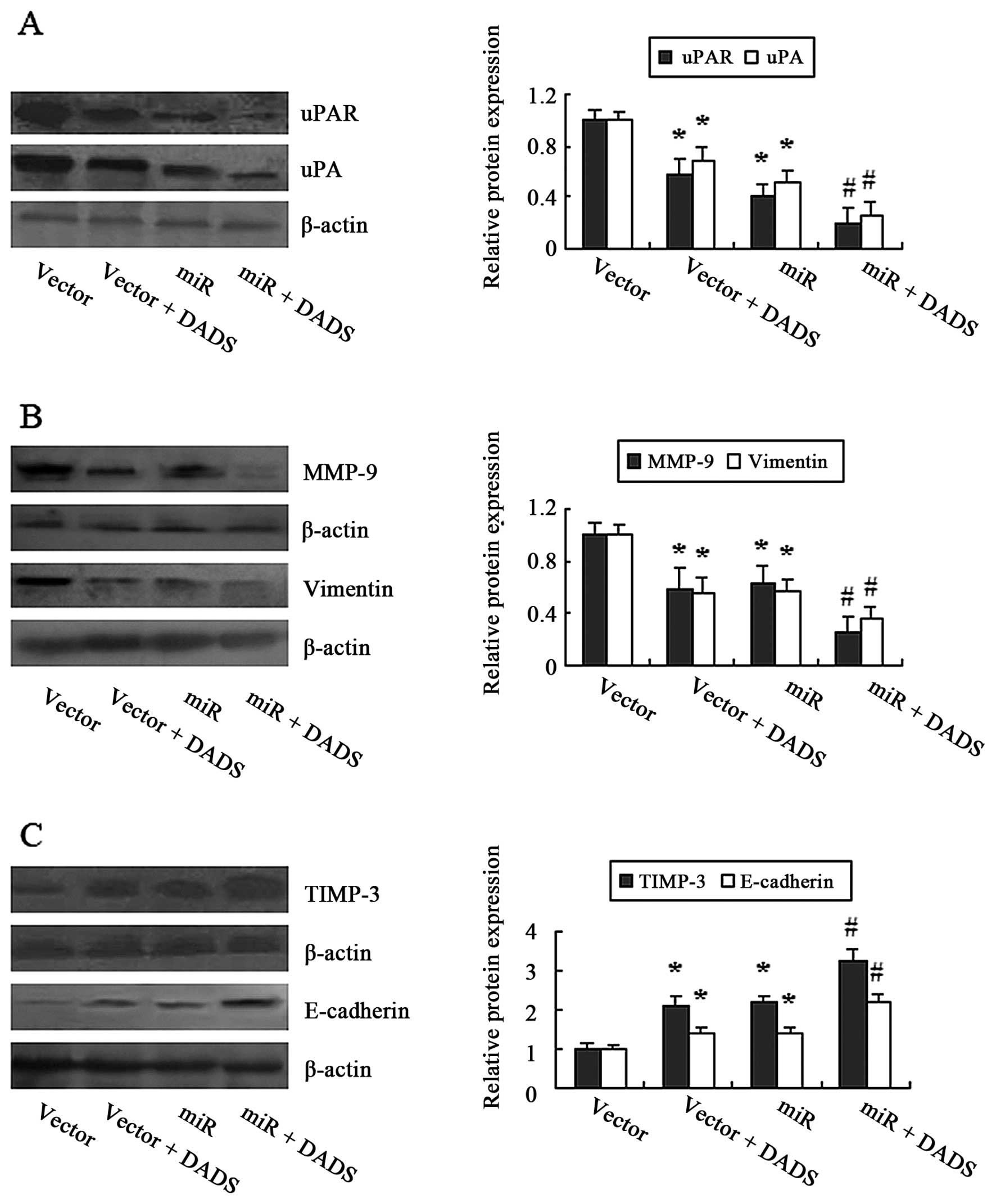
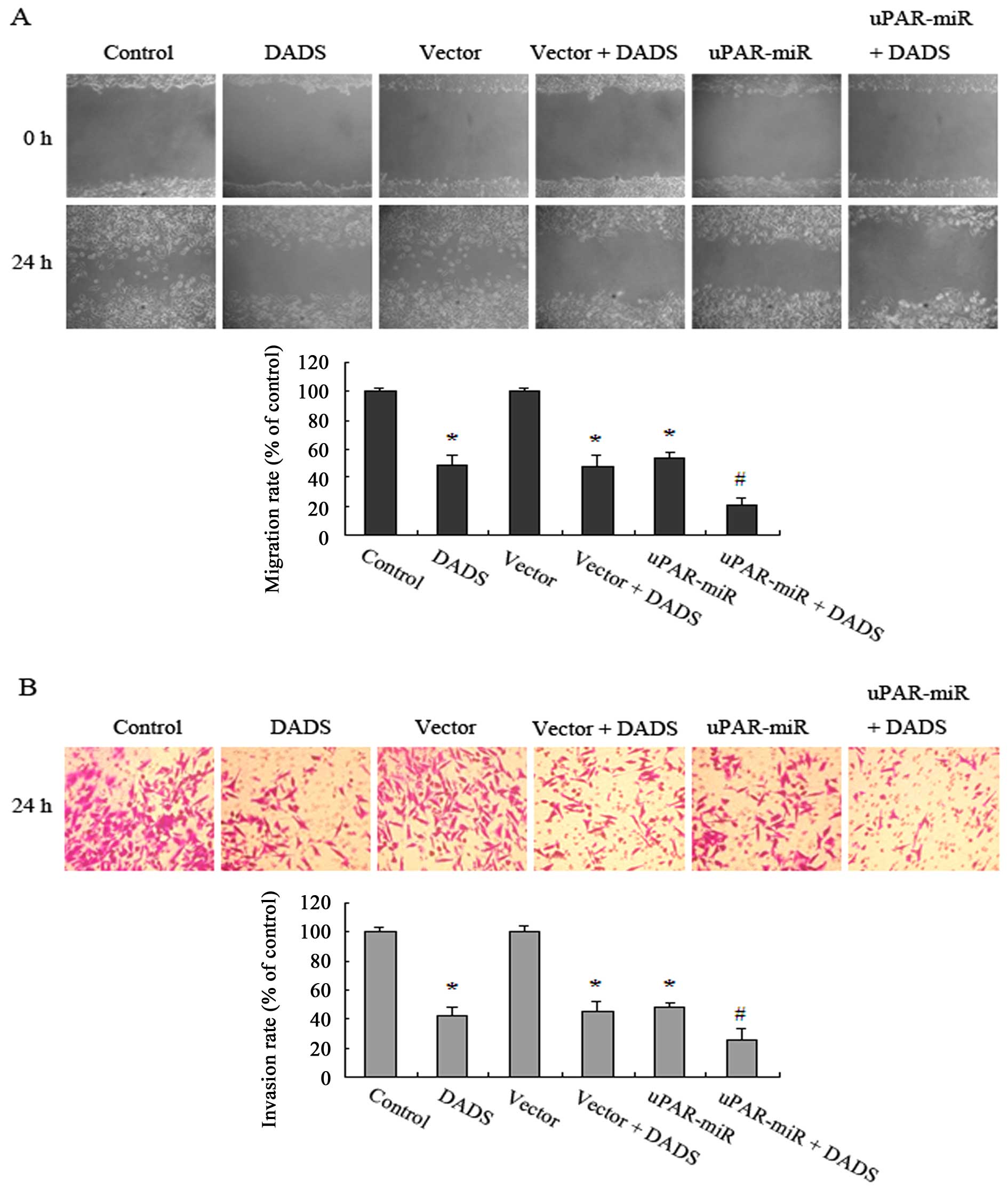
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yang L: Incidence and mortality of gastric
cancer in China. World J Gastroenterol. 12:17–20. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Patel JN, Fuchs CS, Owzar K, Chen Z and
McLeod HL: Gastric cancer pharmacogenetics: Progress or old tripe?
Pharmacogenomics. 14:1053–1064. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Powolny AA and Singh SV: Multitargeted
prevention and therapy of cancer by diallyl trisulfide and related
Allium vegetable-derived organosulfur compounds. Cancer Lett.
269:305–314. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yi L and Su Q: Molecular mechanisms for
the anti-cancer effects of diallyl disulfide. Food Chem Toxicol.
57:362–370. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sundaram SG and Milner JA: Diallyl
disulfide suppresses the growth of human colon tumor cell
xenografts in athymic nude mice. J Nutr. 126:1355–1361.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Nakagawa H, Tsuta K, Kiuchi K, Senzaki H,
Tanaka K, Hioki K and Tsubura A: Growth inhibitory effects of
diallyl disulfide on human breast cancer cell lines.
Carcinogenesis. 22:891–897. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Shin DY, Kim GY, Kim JI, Yoon MK, Kwon TK,
Lee SJ, Choi YW, Kang HS, Yoo YH and Choi YH: Anti-invasive
activity of diallyl disulfide through tightening of tight junctions
and inhibition of matrix metalloproteinase activities in LNCaP
prostate cancer cells. Toxicol In Vitro. 24:1569–1576. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Park HS, Kim GY, Choi IW, Kim ND, Hwang
HJ, Choi YW and Choi YH: Inhibition of matrix metalloproteinase
activities and tightening of tight junctions by diallyl disulfide
in AGS human gastric carcinoma cells. J Food Sci. 76:T105–T111.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Ling H, Wen L, Ji XX, Tang YL, He J, Tan
H, Xia H, Zhou JG and Su Q: Growth inhibitory effect and
Chk1-dependent signaling involved in G2/M arrest on
human gastric cancer cells induced by diallyl disulfide. Braz J Med
Biol Res. 43:271–278. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bo S, Hui H, Li W, Hui L, Hong X, Lin D,
Dai WX, Wu YH, Ai XH, Hao J, et al: Chk1, but not Chk2, is
responsible for G2/M phase arrest induced by diallyl disulfide in
human gastric cancer BGC823 cells. Food Chem Toxicol. 68:61–70.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yuan JP, Wang GH, Ling H, Su Q, Yang YH,
Song Y, Tang RJ, Liu Y and Huang C: Diallyl disulfide-induced G2/M
arrest of human gastric cancer MGC803 cells involves activation of
p38 MAP kinase pathways. World J Gastroenterol. 10:2731–2734.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ling H, Zhang LY, Su Q, Song Y, Luo ZY,
Zhou XT, Zeng X, He J, Tan H and Yuan JP: Erk is involved in the
differentiation induced by diallyl disulfide in the human gastric
cancer cell line MGC803. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 11:408–423. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tang H, Kong Y, Guo J, Tang Y and Xie X,
Yang L, Su Q and Xie X: Diallyl disulfide suppresses proliferation
and induces apoptosis in human gastric cancer through Wnt-1
signaling pathway by up-regulation of miR-200b and miR-22. Cancer
Lett. 340:72–81. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Gharahdaghi F, Weinberg CR, Meagher DA,
Imai BS and Mische SM: Mass spectrometric identification of
proteins from silver-stained polyacrylamide gel: A method for the
removal of silver ions to enhance sensitivity. Electrophoresis.
20:601–605. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Su B, Xiang B, Wang L, Cao L, Xiao L, Li
X, Li X, Wu M and Li G: Profiling and comparing transcription
factors activated in non-metastatic and metastatic nasopharyngeal
carcinoma cells. J Cell Biochem. 109:173–183. 2010.
|
|
17
|
Zhang LY, Ling H, Su Q, Song Y and Liang
XQ: Inhibitory effect of diallyl disulfide on human gastric cancer
cell line MGC803 in vitro. Shijie Huaren Xiaohua Zazhi.
11:1290–1293. 2003.In Chinese.
|
|
18
|
Zhu Y, McAvoy S, Kuhn R and Smith DI:
RORA, a large common fragile site gene, is involved in cellular
stress response. Oncogene. 25:2901–2908. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lee JM, Kim IS, Kim H, Lee JS, Kim K, Yim
HY, Jeong J, Kim JH, Kim JY, Lee H, et al: RORalpha attenuates
Wnt/beta-catenin signaling by PKCalpha-dependent phosphorylation in
colon cancer. Mol Cell. 37:183–195. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Xiong G, Wang C, Evers BM, Zhou BP and Xu
R: RORα suppresses breast tumor invasion by inducing SEMA3F
expression. Cancer Res. 72:1728–1739. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yamashita S, Tsujino Y, Moriguchi K,
Tatematsu M and Ushijima T: Chemical genomic screening for
methylation-silenced genes in gastric cancer cell lines using
5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine treatment and oligonucleotide microarray.
Cancer Sci. 97:64–71. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Su B, Xiang SL, Su J, Tang HL, Liao QJ,
Zhou YJ and Su Q: Diallyl disulfide increased histone acetylation
and p21WAF1 expression in human gastric cancer cells in
vivo and in vitro. Biochem Pharmacol. 1:1–10. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Marino N, Nakayama J, Collins JW and Steeg
PS: Insights into the biology and prevention of tumor metastasis
provided by the Nm23 metastasis suppressor gene. Cancer Metastasis
Rev. 31:593–603. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Boissan M, De Wever O, Lizarraga F, Wendum
D, Poincloux R, Chignard N, Desbois-Mouthon C, Dufour S,
Nawrocki-Raby B, Birembaut P, et al: Implication of metastasis
suppressor NM23-H1 in maintaining adherens junctions and limiting
the invasive potential of human cancer cells. Cancer Res.
70:7710–7722. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Che G, Chen J, Liu L, Wang Y, Li L, Qin Y
and Zhou Q: Transfection of nm23-H1 increased expression of
beta-catenin, E-cadherin and TIMP-1 and decreased the expression of
MMP-2, CD44v6 and VEGF and inhibited the metastatic potential of
human non-small cell lung cancer cell line L9981. Neoplasma.
53:530–537. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Horak CE, Mendoza A, Vega-Valle E, Albaugh
M, Graff-Cherry C, McDermott WG, Hua E, Merino MJ, Steinberg SM,
Khanna C, et al: Nm23-H1 suppresses metastasis by inhibiting
expression of the lysophosphatidic acid receptor EDG2. Cancer Res.
67:11751–11759. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Huang CS, Liao JW and Hu ML: Lycopene
inhibits experimental metastasis of human hepatoma SK-Hep-1 cells
in athymic nude mice. J Nutr. 138:538–543. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Guan-Zhen Y, Ying C, Can-Rong N, Guo-Dong
W, Jian-Xin Q and Jie-Jun W: Reduced protein expression of
metastasis-related genes (nm23, KISS1, KAI1 and p53) in lymph node
and liver metastases of gastric cancer. Int J Exp Pathol.
88:175–183. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Bernard O: Lim kinases, regulators of
actin dynamics. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 39:1071–1076. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Wang W, Mouneimne G, Sidani M, Wyckoff J,
Chen X, Makris A, Goswami S, Bresnick AR and Condeelis JS: The
activity status of cofilin is directly related to invasion,
intravasation, and metastasis of mammary tumors. J Cell Biol.
173:395–404. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Scott RW, Hooper S, Crighton D, Li A,
König I, Munro J, Trivier E, Wickman G, Morin P, Croft DR, et al:
LIM kinases are required for invasive path generation by tumor and
tumor-associated stromal cells. J Cell Biol. 191:169–185. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhou Y, Su J, Shi L, Liao Q and Su Q: DADS
downregulates the Rac1-ROCK1/PAK1-LIMK1-ADF/cofilin signaling
pathway, inhibiting cell migration and invasion. Oncol Rep.
29:605–612. 2013.
|
|
33
|
Laufs S, Schumacher J and Allgayer H:
Urokinase-receptor (u-PAR): An essential player in multiple games
of cancer: A review on its role in tumor progression, invasion,
metastasis, proliferation/dormancy, clinical outcome and minimal
residual disease. Cell Cycle. 5:1760–1771. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Smith HW and Marshall CJ: Regulation of
cell signalling by uPAR. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 11:23–36. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Lester RD, Jo M, Montel V, Takimoto S and
Gonias SL: uPAR induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition in
hypoxic breast cancer cells. J Cell Biol. 178:425–436. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Jo M, Lester RD, Montel V, Eastman B,
Takimoto S and Gonias SL: Reversibility of epithelial-mesenchymal
transition (EMT) induced in breast cancer cells by activation of
urokinase receptor-dependent cell signaling. J Biol Chem.
284:22825–22833. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ma YY and Tao HQ: Role of urokinase
plasminogen activator receptor in gastric cancer: A potential
therapeutic target. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 27:285–290. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Belguise K, Kersual N, Galtier F and
Chalbos D: FRA-1 expression level regulates proliferation and
invasiveness of breast cancer cells. Oncogene. 24:1434–1444. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Diesch J, Sanij E, Gilan O, Love C, Tran
H, Fleming NI, Ellul J, Amalia M, Haviv I, Pearson RB, et al:
Widespread FRA1-dependent control of mesenchymal
transdifferentiation programs in colorectal cancer cells. PLoS One.
9:e889502014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Huang XY, Ke AW, Shi GM, Zhang X, Zhang C,
Shi YH, Wang XY, Ding ZB, Xiao YS, Yan J, et al: αB-crystallin
complexes with 14–3–3ζ to induce epithelial-mesenchymal transition
and resistance to sorafenib in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Hepatology. 57:2235–2247. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Andreolas C, Kalogeropoulou M, Voulgari A
and Pintzas A: Fra-1 regulates vimentin during Ha-RAS-induced
epithelial mesenchymal transition in human colon carcinoma cells.
Int J Cancer. 122:1745–1756. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Andersen H, Mejlvang J, Mahmood S, Gromova
I, Gromov P, Lukanidin E, Kriajevska M, Mellon JK and Tulchinsky E:
Immediate and delayed effects of E-cadherin inhibition on gene
regulation and cell motility in human epidermoid carcinoma cells.
Mol Cell Biol. 25:9138–9150. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Mayes PA, Dolloff NG, Daniel CJ, Liu JJ,
Hart LS, Kuribayashi K, Allen JE, Jee DI, Dorsey JF, Liu YY, et al:
Overcoming hypoxia- induced apoptotic resistance through
combinatorial inhibition of GSK-3β and CDK1. Cancer Res.
71:5265–5275. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Wu W, Ye H, Wan L, Han X, Wang G, Hu J,
Tang M, Duan X, Fan Y, He S, et al: Millepachine, a novel chalcone,
induces G2/M arrest by inhibiting CDK1 activity and
causing apoptosis via ROS-mitochondrial apoptotic pathway in human
hepatocarcinoma cells in vitro and in vivo. Carcinogenesis.
34:1636–1643. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Yi L, Ji XX, Tan H, Feng MY, Tang Y, Wen L
and Su Q: Involvement of Mcl1 in diallyl disulfide-induced G2/M
cell cycle arrest in HL-60 cells. Oncol Rep. 27:1911–1917.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Yasui W, Ayhan A, Kitadai Y, Nishimura K,
Yokozaki H, Ito H and Tahara E: Increased expression of p34cdc2 and
its kinase activity in human gastric and colonic carcinomas. Int J
Cancer. 53:36–41. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|