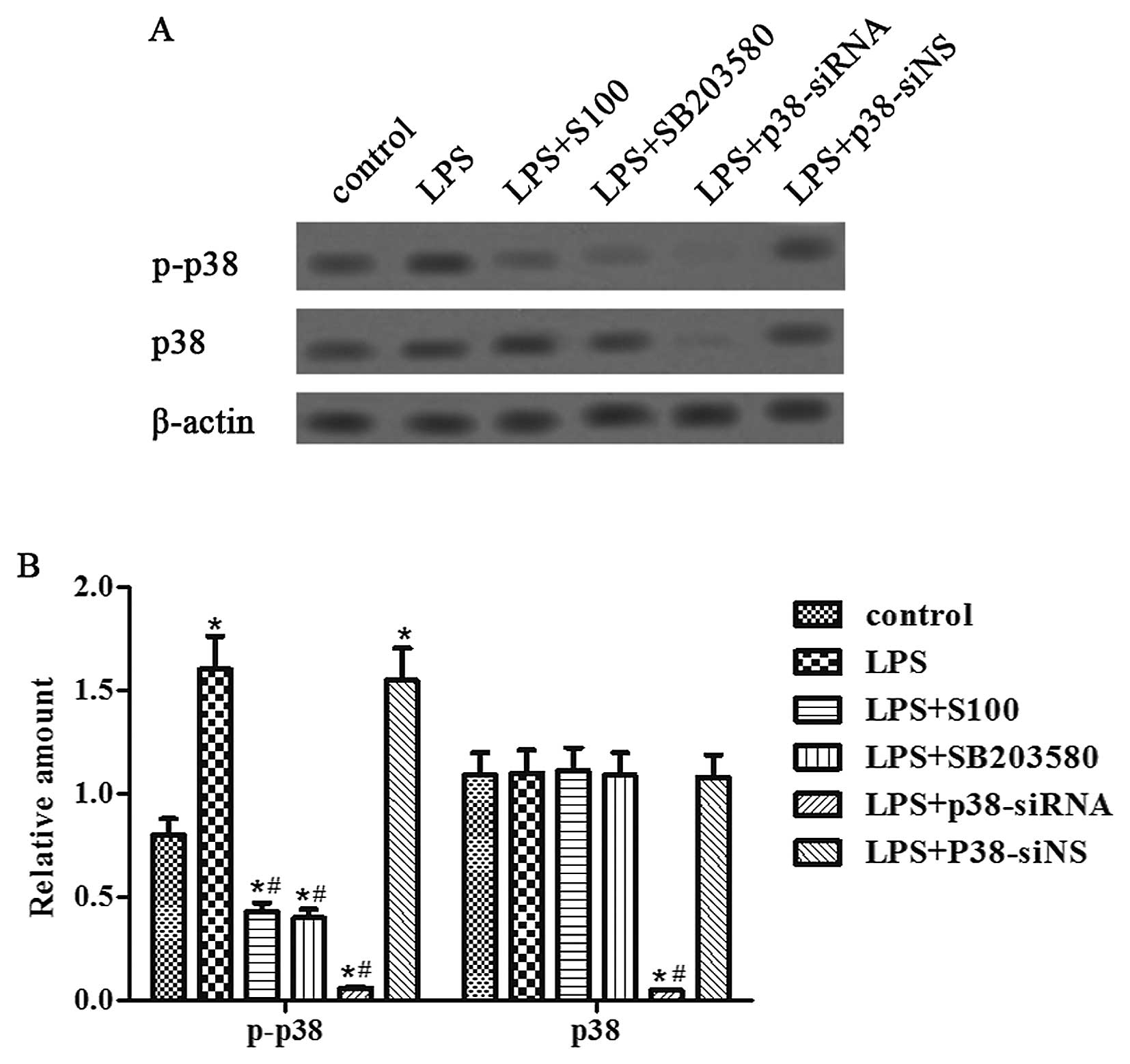
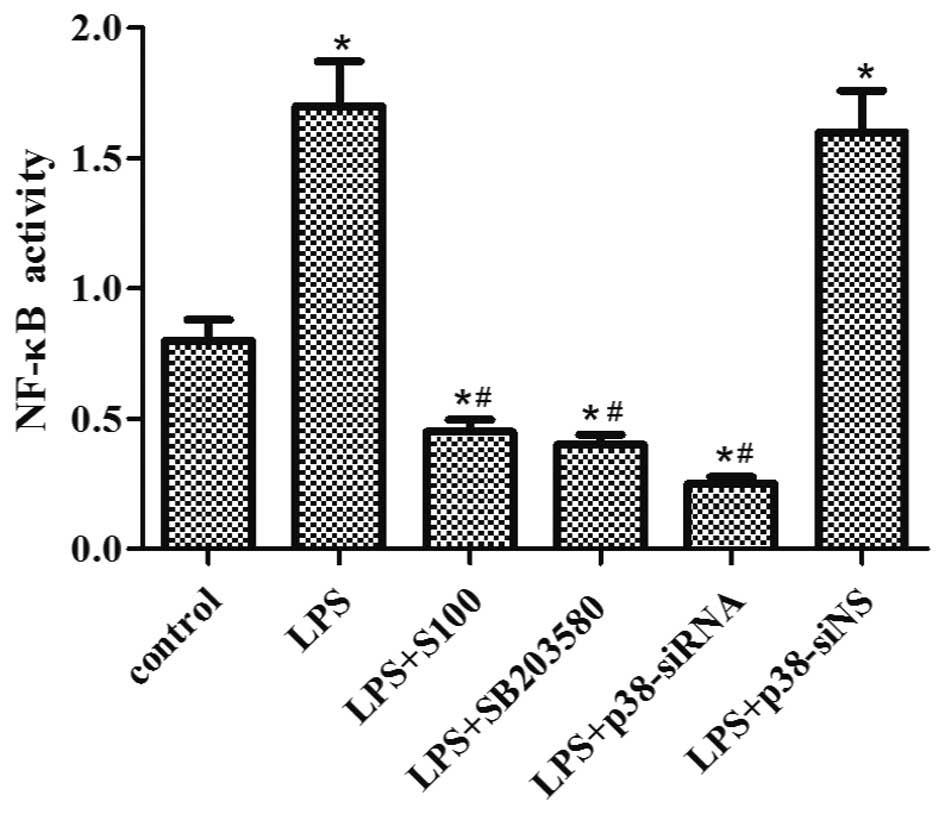
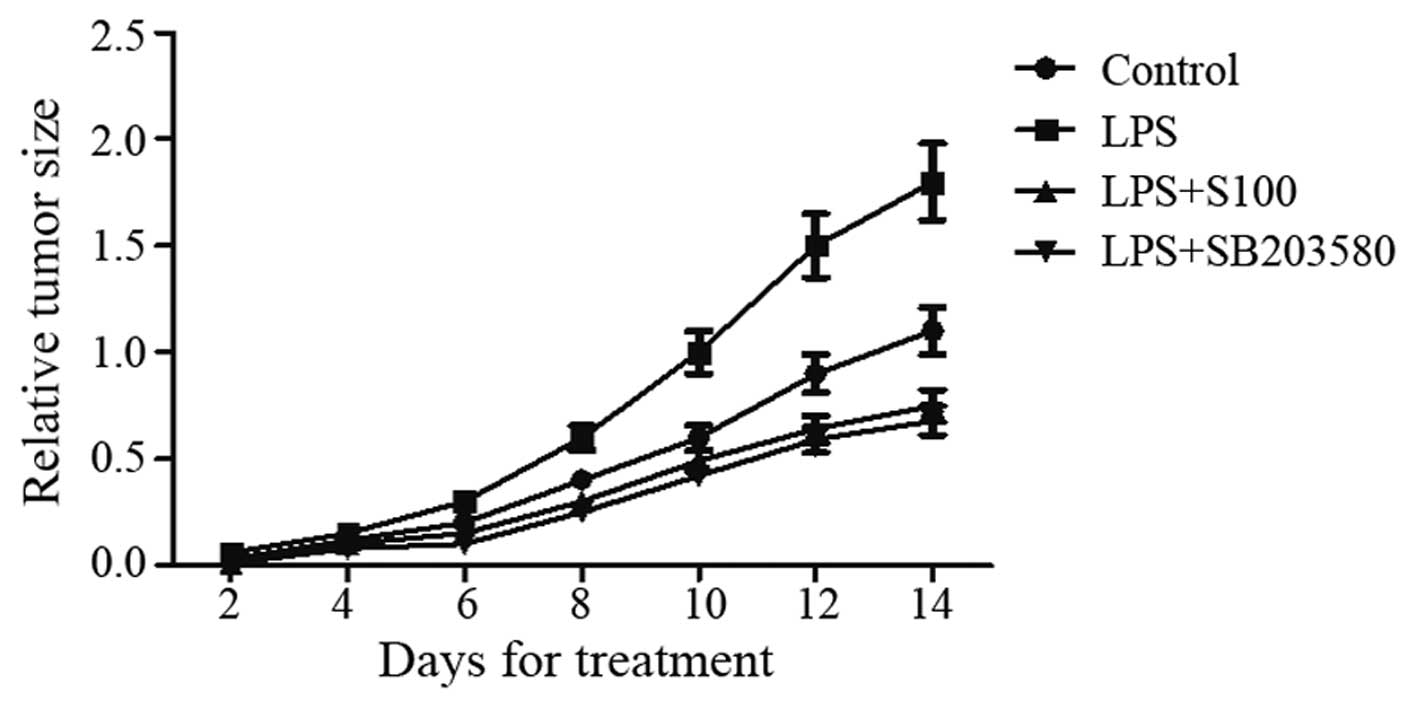
|
1
|
Lin SS, Clarke CA, Prehn AW, Glaser SL,
West DW and O’Malley CD: Survival differences among Asian
subpopulations in the United States after prostate, colorectal,
breast, and cervical carcinomas. Cancer. 94:1175–1182. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hsing AW, Tsao L and Devesa SS:
International trends and patterns of prostate cancer incidence and
mortality. Int J Cancer. 85:60–67. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Hsing AW and Devesa SS: Trends and
patterns of prostate cancer: what do they suggest? Epidemiol Rev.
23:3–13. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sonn GA, Aronson W and Litwin MS: Impact
of diet on prostate cancer: a review. Prostate Cancer Prostatic
Dis. 8:304–310. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Schetter AJ, Heegaard NH and Harris CC:
Inflammation and cancer: interweaving microRNA, free radical,
cytokine and p53 pathways. Carcinogenesis. 31:37–49. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
6
|
Coussens LM and Werb Z: Inflammation and
cancer. Nature. 420:860–867. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Mantovani A: Cancer: inflammation by
remote control. Nature. 435:752–753. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hsu RY, Chan CH, Spicer JD, Rousseau MC,
Giannias B, Rousseau S and Ferri LE: LPS-induced TLR4 signaling in
human colorectal cancer cells increases beta1 integrin-mediated
cell adhesion and liver metastasis. Cancer Res. 71:1989–1998. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Li J, Chong T, Wang Z, Chen H and Li H,
Cao J, Zhang P and Li H: A novel anti-cancer effect of resveratrol:
reversal of epithelial mesenchymal transition in prostate cancer
cells. Mol Med Rep. 10:1717–1724. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Im HJ, Park NH, Kwon YJ, Shin S, Kim D and
Chun YJ: Bacterial lipopolysaccharides induce steroid sulfatase
expression and cell migration through IL-6 pathway in human
prostate cancer cells. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 20:556–561. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Michalaki V, Syrigos K, Charles P and
Waxman J: Serum levels of IL-6 and TNF-alpha correlate with
clinicopathological features and patient survival in patients with
prostate cancer. Br J Cancer. 90:2312–2316. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Balkwill F: Tumor necrosis factor or tumor
promoting factor? Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 13:135–141. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Szlosarek PW and Balkwill FR: Tumour
necrosis factor alpha: a potential target for the therapy of solid
tumours. Lancet Oncol. 4:565–573. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ayre JE: Cervical cancer: chronic
inflammation, stress and adaptation factors. Acta Unio Int Contra
Cancrum. 12:20–27. 1956.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Dalgleish AG and O’Byrne KJ: Chronic
immune activation and inflammation in the pathogenesis of AIDS and
cancer. Adv Cancer Res. 84:231–276. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Farrow B and Evers BM: Inflammation and
the development of pancreatic cancer. Surg Oncol. 10:153–169. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Nelson WG, De Marzo AM, DeWeese TL and
Isaacs WB: The role of inflammation in the pathogenesis of prostate
cancer. J Urol. 172:S6–S12. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Schwartsburd PM: Chronic inflammation as
inductor of pro-cancer microenvironment: pathogenesis of
dysregulated feedback control. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 22:95–102.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tiwari N, Gheldof A, Tatari M and
Christofori G: EMT as the ultimate survival mechanism of cancer
cells. Semin Cancer Biol. 22:194–207. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chen MC, Chang WW, Kuan YD, Lin ST, Hsu HC
and Lee CH: Resveratrol inhibits LPS-induced epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in mouse melanoma model. Innate Immun. 18:685–693. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lu JN, Lee WS, Kim MJ, Yun JW, Jung JH, Yi
SM, Jeong JH, Kim HJ, Choi YH, Kim GS, et al: The inhibitory effect
of anthocyanins on Akt on invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal
transition is not associated with the anti-EGFR effect of the
anthocyanins. Int J Oncol. 44:1756–1766. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yang CS and Wang X: Green tea and cancer
prevention. Nutr Cancer. 62:931–937. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Gloria NF, Soares N, Brand C, Oliveira FL,
Borojevic R and Teodoro AJ: Lycopene and beta-carotene induce
cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis in human breast cancer cell lines.
Anticancer Res. 34:1377–1386. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Akl MR, Ayoub NM, Abuasal BS, Kaddoumi A
and Sylvester PW: Sesamin synergistically potentiates the
anticancer effects of γ-tocotrienol in mammary cancer cell lines.
Fitoterapia. 84:347–359. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Tanabe H, Kuribayashi K, Tsuji N, Tanaka
M, Kobayashi D and Watanabe N: Sesamin induces autophagy in colon
cancer cells by reducing tyrosine phosphorylation of EphA1 and
EphB2. Int J Oncol. 39:33–40. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yokota T, Matsuzaki Y, Koyama M, Hitomi T,
Kawanaka M, Enoki-Konishi M, Okuyama Y, Takayasu J, Nishino H,
Nishikawa A, et al: Sesamin, a lignan of sesame, down-regulates
cyclin D1 protein expression in human tumor cells. Cancer Sci.
98:1447–1453. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Deng P, Wang C, Chen L, Wang C, Du Y, Yan
X, Chen M, Yang G and He G: Sesamin induces cell cycle arrest and
apoptosis through the inhibition of signal transducer and activator
of transcription 3 signalling in human hepatocellular carcinoma
cell line HepG2. Biol Pharm Bull. 36:1540–1548. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang HM, Cheng KC, Lin CJ, Hsu SW, Fang
WC, Hsu TF, Chiu CC, Chang HW, Hsu CH and Lee AY: Obtusilactone A
and (−)-sesamin induce apoptosis in human lung cancer cells by
inhibiting mitochondrial Lon protease and activating DNA damage
checkpoints. Cancer Sci. 101:2612–2620. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Harikumar KB, Sung B, Tharakan ST, Pandey
MK, Joy B, Guha S, Krishnan S and Aggarwal BB: Sesamin manifests
chemopreventive effects through the suppression of NF-kappa
B-regulated cell survival, proliferation, invasion, and angiogenic
gene products. Mol Cancer Res. 8:751–761. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Liu L, Ge D, Ma L, Mei J, Liu S, Zhang Q,
Ren F, Liao H, Pu Q, Wang T, et al: Interleukin-17 and
prostaglandin E2 are involved in formation of an M2
macrophage-dominant microenvironment in lung cancer. J Thorac
Oncol. 7:1091–1100. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Bieniek J, Childress C, Swatski MD and
Yang W: COX-2 inhibitors arrest prostate cancer cell cycle
progression by down-regulation of kinetochore/centromere proteins.
Prostate. 74:999–1011. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang L, Zhu R, Huang Z, Li H and Zhu H:
Lipopoly-saccharide-induced toll-like receptor 4 signaling in
cancer cells promotes cell survival and proliferation in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Dig Dis Sci. 58:2223–2236. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Li Y, Fan L, Sun Y, Zhang D, Yue Z, Niu Y,
Meng J, Yang T, Liu W and Mei Q: An apple oligogalactan suppresses
endotoxin-induced cyclooxygenase-2 expression by inhibition of LPS
pathways. Int J Biol Macromol. 61:75–81. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lee CC, Liu KJ, Wu YC, Lin SJ, Chang CC
and Huang TS: Sesamin inhibits macrophage-induced vascular
endothelial growth factor and matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression
and proangiogenic activity in breast cancer cells. Inflammation.
34:209–221. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Lu T and Stark GR: Cytokine overexpression
and constitutive NFkappaB in cancer. Cell Cycle. 3:1114–1117. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Rousseau MC, Hsu RY, Spicer JD, McDonald
B, Chan CH, Perera RM, Giannias B, Chow SC, Rousseau S, Law S, et
al: Lipopolysaccharide-induced toll-like receptor 4 signaling
enhances the migratory ability of human esophageal cancer cells in
a selectin-dependent manner. Surgery. 154:69–77. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhang Y, Guo Z, Du T, Chen J, Wang W, Xu
K, Lin T and Huang H: Prostate specific membrane antigen (PSMA): a
novel modulator of p38 for proliferation, migration, and survival
in prostate cancer cells. Prostate. 73:835–841. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Leelahavanichkul K, Amornphimoltham P,
Molinolo AA, Basile JR, Koontongkaew S and Gutkind JS: A role for
p38 MAPK in head and neck cancer cell growth and tumor-induced
angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis. Mol Oncol. 8:105–118. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
39
|
Sukhtankar D, Okun A, Chandramouli A,
Nelson MA, Vanderah TW, Cress AE, Porreca F and King T: Inhibition
of p38-MAPK signaling pathway attenuates breast cancer induced bone
pain and disease progression in a murine model of cancer-induced
bone pain. Mol Pain. 7:812011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|