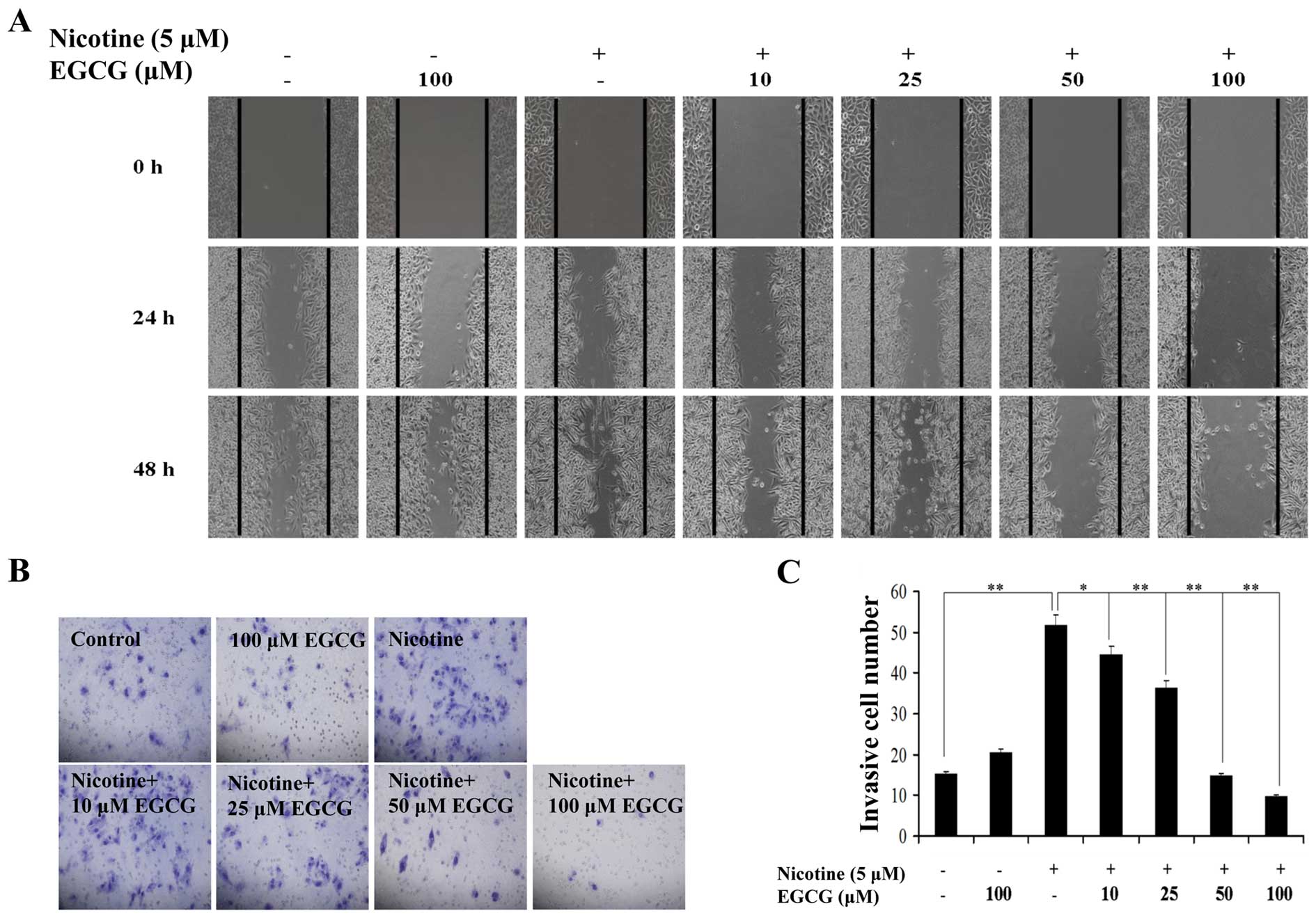
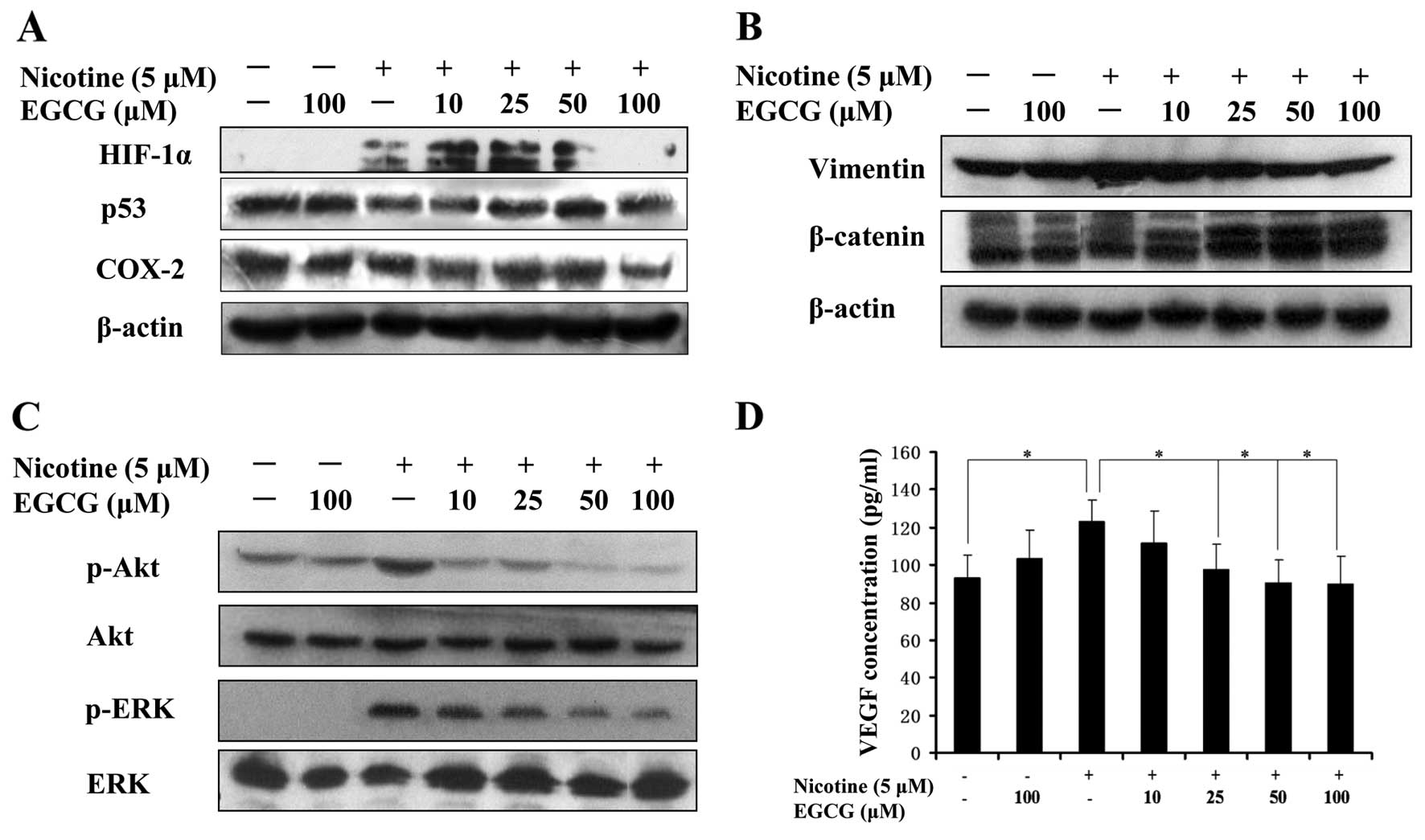
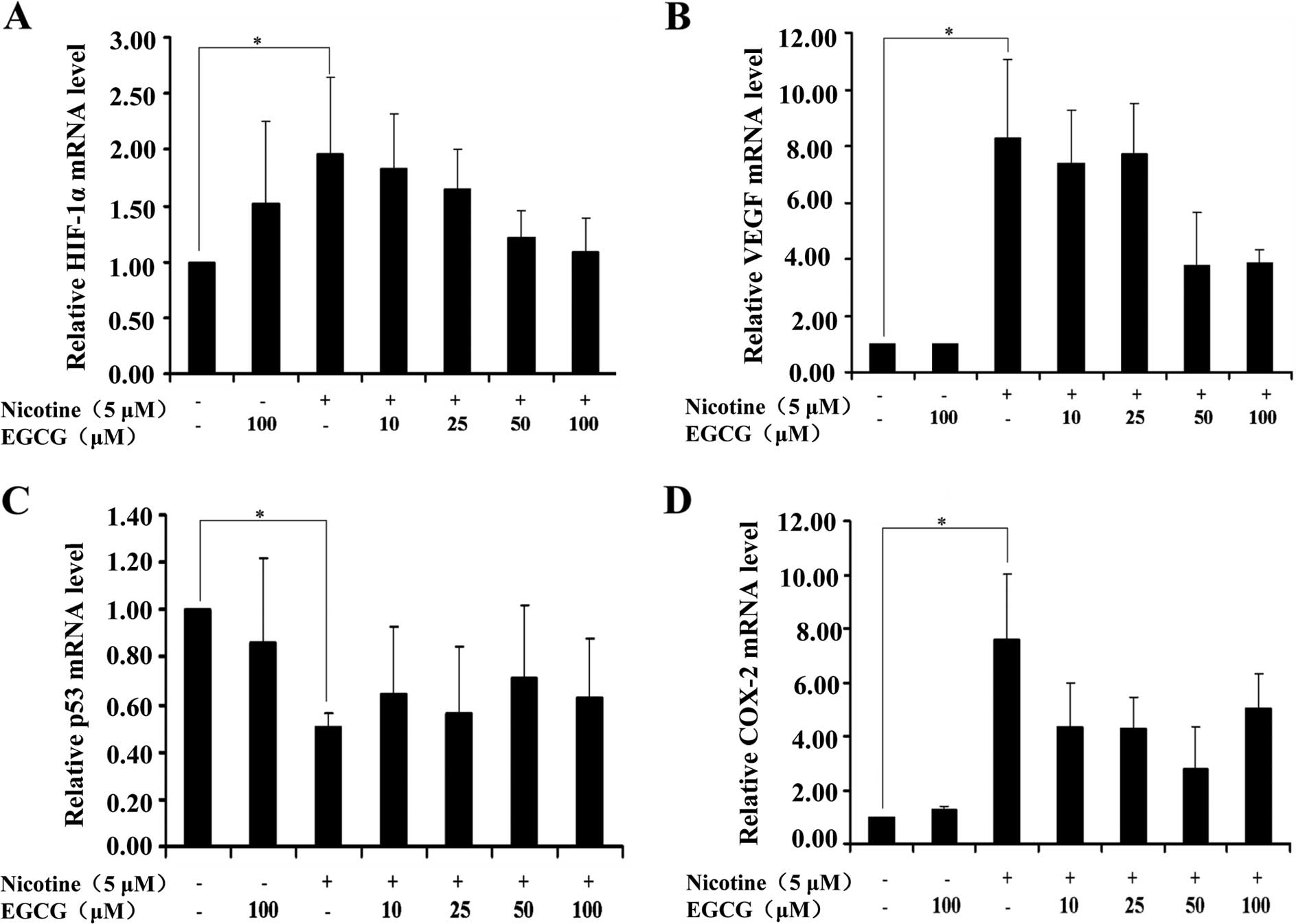
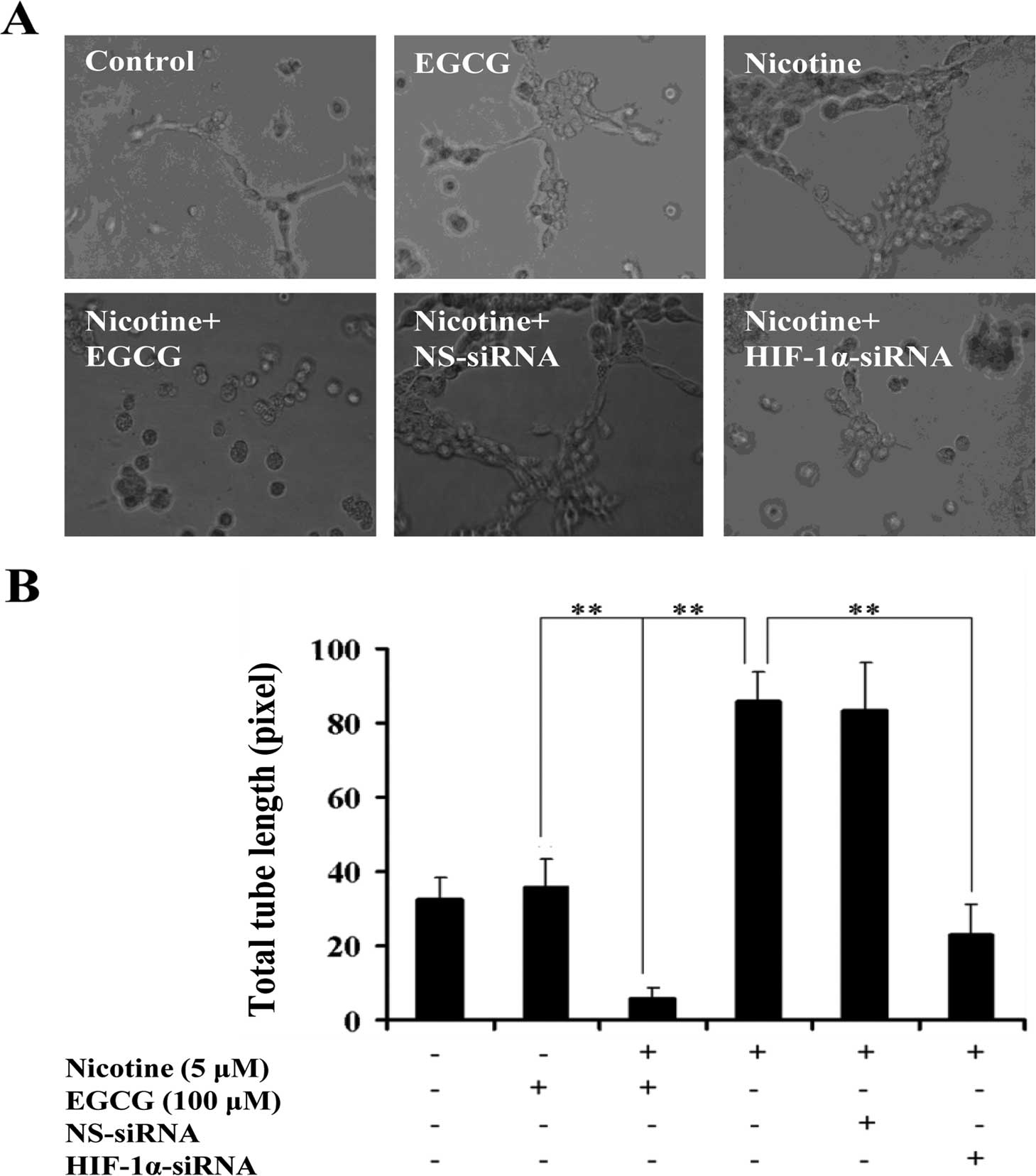
|
1
|
Pesch B, Kendzia B, Gustavsson P, Jöckel
KH, Johnen G, Pohlabeln H, Olsson A, Ahrens W, Gross IM, Brüske I,
et al: Cigarette smoking and lung cancer - relative risk estimates
for the major histological types from a pooled analysis of
case-control studies. Int J Cancer. 131:1210–1219. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
2
|
Schaal C and Chellappan SP:
Nicotine-mediated cell proliferation and tumor progression in
smoking-related cancers. Mol Cancer Res. 12:14–23. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Nair S, Bora-Singhal N, Perumal D and
Chellappan S: Nicotine-mediated invasion and migration of non-small
cell lung carcinoma cells by modulating STMN3 and GSPT1 genes in an
ID1-dependent manner. Mol Cancer. 13:1732014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Dasgupta P, Rizwani W, Pillai S, Kinkade
R, Kovacs M, Rastogi S, Banerjee S, Carless M, Kim E, Coppola D, et
al: Nicotine induces cell proliferation, invasion and
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in a variety of human cancer cell
lines. Int J Cancer. 124:36–45. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Wu SQ, Lv YE, Lin BH, Luo LM, Lv SL, Bi AH
and Jia YS: Silencing of periostin inhibits nicotine-mediated tumor
cell growth and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in lung cancer
cells. Mol Med Rep. 7:875–880. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Jackson AL, Zhou B and Kim WY: HIF,
hypoxia and the role of angiogenesis in non-small cell lung cancer.
Expert Opin Ther Targets. 14:1047–1057. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Creighton CJ, Gibbons DL and Kurie JM: The
role of epithelial-mesenchymal transition programming in invasion
and metastasis: A clinical perspective. Cancer Manag Res.
5:187–195. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhang Q, Tang X, Zhang ZF, Velikina R, Shi
S and Le AD: Nicotine induces hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha
expression in human lung cancer cells via nicotinic acetylcholine
receptor-mediated signaling pathways. Clin Cancer Res.
13:4686–4694. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ma X, Jia Y, Zu S, Li R, Jia Y, Zhao Y,
Xiao D, Dang N and Wang Y: α5 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor
mediates nicotineinduced HIF-1α and VEGF expression in non-small
cell lung cancer. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 278:172–179. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Nurwidya F, Takahashi F, Murakami A and
Takahashi K: Epithelial mesenchymal transition in drug resistance
and metastasis of lung cancer. Cancer Res Treat. 44:151–156. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang L, Zhang X, Liu J, Shen L and Li Z:
Tea consumption and lung cancer risk: A meta-analysis of
case-control and cohort studies. Nutrition. 30:1122–1127. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lin IH, Ho ML, Chen HY, Lee HS, Huang CC,
Chu YH, Lin SY, Deng YR, He YH, Lien YH, et al: Smoking, green tea
consumption, genetic polymorphisms in the insulin-like growth
factors and lung cancer risk. PLoS One. 7:e309512012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ravindranath MH, Ramasamy V, Moon S, Ruiz
C and Muthugounder S: differential growth suppression of human
melanoma cells by tea (Camellia sinensis) epicatechins (ECG, EGC
and EGCG). Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 6:523–530. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
14
|
Du GJ, Zhang Z, Wen XD, Yu C, Calway T,
Yuan CS and Wang CZ: Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) is the most
effective cancer chemopreventive polyphenol in green tea.
Nutrients. 4:1679–1691. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang F, Chang Z, Fan Q and Wang L:
Epigallocatechin-3-gallate inhibits the proliferation and migration
of human ovarian carcinoma cells by modulating p38 kinase and
matrix metallo-proteinase-2. Mol Med Rep. 9:1085–1089.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhang W, Yang P, Gao F, Yang J and Yao K:
Effects of epigallocatechin gallate on the proliferation and
apoptosis of the nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell line CNE2. Exp Ther
Med. 8:1783–1788. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Li H, Li Z, Xu YM, Wu Y, Yu KK, Zhang C,
Ji YH, Ding G and Chen FX: Epigallocatechin-3-gallate induces
apoptosis, inhibits proliferation and decreases invasion of glioma
cell. Neurosci Bull. 30:67–73. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Li X, Feng Y, Liu J, Feng X, Zhou K and
Tang X: Epigallocatechin-3-gallate inhibits IGF-I-stimulated lung
cancer angiogenesis through downregulation of HIF-1α and VEGF
expression. J Nutrigenet Nutrigenomics. 6:169–178. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Zhang Q, Tang X, Lu Q, Zhang Z, Rao J and
Le AD: Green tea extract and (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate inhibit
hypoxia- and serum-induced HIF-1alpha protein accumulation and VEGF
expression in human cervical carcinoma and hepatoma cells. Mol
Cancer Ther. 5:1227–1238. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
He L, Zhang E, Shi J, Li X, Zhou K, Zhang
Q, Le AD and Tang X: (−)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate inhibits human
papillomavirus (HPV)-16 oncoprotein-induced angiogenesis in
non-small cell lung cancer cells by targeting HIF-1α. Cancer
Chemother Pharmacol. 71:713–725. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Liu LC, Tsao TC, Hsu SR, Wang HC, Tsai TC,
Kao JY and Way TD: EGCG inhibits transforming growth
factor-β-mediated epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition via the
inhibition of Smad2 and Erk1/2 signaling pathways in nonsmall cell
lung cancer cells. J Agric Food Chem. 60:9863–9873. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ko H, So Y, Jeon H, Jeong MH, Choi HK, Ryu
SH, Lee SW, Yoon HG and Choi KC: TGF-β1-induced
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and acetylation of Smad2 and
Smad3 are negatively regulated by EGCG in human A549 lung cancer
cells. Cancer Lett. 335:205–213. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Takahashi A, Watanabe T, Mondal A, Suzuki
K, Kurusu-Kanno M, Li Z, Yamazaki T, Fujiki H and Suganuma M:
Mechanism-based inhibition of cancer metastasis with
(−)-epigal-locatechin gallate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 443:1–6.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Nilsson I, Shibuya M and Wennström S:
differential activation of vascular genes by hypoxia in primary
endothelial cells. Exp Cell Res. 299:476–485. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Li G, He L, Zhang E, Shi J, Zhang Q, Le
AD, Zhou K and Tang X: Overexpression of human papillomavirus (HPV)
type 16 oncoproteins promotes angiogenesis via enhancing HIF-1α and
VEGF expression in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Cancer Lett.
311:160–170. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Skinner HD, Zheng JZ, Fang J, Agani F and
Jiang BH: Vascular endothelial growth factor transcriptional
activation is mediated by hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha, HDM2,
and p70S6K1 in response to phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/AKT
signaling. J Biol Chem. 279:45643–45651. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wang L, Gu F, Ma N, Zhang L, Bian JM and
Cao HY: CIP2A expression is associated with altered expression of
epithelial-mesenchymal transition markers and predictive of poor
prognosis in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Tumour Biol.
34:2309–2313. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhao D, Yang K, Tang XF, Lin NN and Liu
JY: Expression of integrin-linked kinase in adenoid cystic
carcinoma of salivary glands correlates with epithelial-mesenchymal
transition markers and tumor progression. Med Oncol. 30:6192013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Balanis N, Wendt MK, Schiemann BJ, Wang Z,
Schiemann WP and Carlin CR: Epithelial to mesenchymal transition
promotes breast cancer progression via a fibronectin-dependent
STAT3 signaling pathway. J Biol Chem. 288:17954–17967. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Xing Y, Qi J, Deng S, Wang C, Zhang L and
Chen J: Small interfering RNA targeting ILK inhibits metastasis in
human tongue cancer cells through repression of
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Exp Cell Res. 319:2058–2072.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
López-Novoa JM and Nieto MA: Inflammation
and EMT: An alliance towards organ fibrosis and cancer progression.
EMBO Mol Med. 1:303–314. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Pirozzi G, Tirino V, Camerlingo R, Franco
R, La Rocca A, Liguori E, Martucci N, Paino F, Normanno N and Rocco
G: Epithelial to mesenchymal transition by TGFβ-1 induction
increases stemness characteristics in primary non small cell lung
cancer cell line. PLoS One. 6:e215482011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Kim H, Yoo SB, Sun P, Jin Y, Jheon S, Lee
CT and Chung JH: Alteration of the E-cadherin/β-catenin complex is
an independent poor prognostic factor in lung adenocarcinoma.
Korean J Pathol. 47:44–51. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhan H, Liang H, Liu X, Deng J, Wang B and
Hao X: Expression of Rac1, HIF-1α, and VEGF in gastric carcinoma:
Correlation with angiogenesis and prognosis. Onkologie. 36:102–107.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Simonetti O, Lucarini G, Rubini C, Goteri
G, Zizzi A, Staibano S, Campanati A, Ganzetti G, Di Primio R and
Offidani A: Microvessel density and VEGF, HIF-1α expression in
primary oral melanoma: Correlation with prognosis. Oral dis.
19:620–627. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kang FW, Gao Y, Que L, Sun J and Wang ZL:
Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α overexpression indicates poor clinical
outcomes in tongue squamous cell carcinoma. Exp Ther Med.
5:112–118. 2013.
|
|
37
|
Zhang L, Huang G, Li X, Zhang Y, Jiang Y,
Shen J, Liu J, Wang Q, Zhu J, Feng X, et al: Hypoxia induces
epithelial-mesenchymal transition via activation of SNAI1 by
hypoxia-inducible factor -1α in hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC
Cancer. 13:108–117. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Ning Q, Liu C, Hou L, Meng M, Zhang X, Luo
M, Shao S, Zuo X and Zhao X: Vascular endothelial growth factor
receptor-1 activation promotes migration and invasion of breast
cancer cells through epithelial-mesenchymal transition. PLoS One.
8:e652172013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Semenza GL: Defining the role of
hypoxia-inducible factor 1 in cancer biology and therapeutics.
Oncogene. 29:625–634. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
40
|
Jiang Y, Cukic B, Adjeroh DA, Skinner HD,
Lin J, Shen QJ and Jiang BH: An algorithm for identifying novel
targets of transcription factor families: Application to
hypoxia-inducible factor 1 targets. Cancer Inform. 7:75–89.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kaidi A, Qualtrough D, Williams AC and
Paraskeva C: Direct transcriptional up-regulation of
cyclooxygenase-2 by hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1 promotes
colorectal tumor cell survival and enhances HIF-1 transcriptional
activity during hypoxia. Cancer Res. 66:6683–6691. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Obacz J, Pastorekova S, Vojtesek B and
Hrstka R: Cross-talk between HIF and p53 as mediators of molecular
responses to physiological and genotoxic stresses. Mol Cancer.
12:932013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zhang E, Feng X, Liu F, Zhang P, Liang J
and Tang X: Roles of PI3K/Akt and c-Jun signaling pathways in human
papillomavirus type 16 oncoprotein-induced HIF-1α, VEGF, and IL-8
expression and in vitro angiogenesis in non-small cell lung cancer
cells. PLoS One. 9:e1034402014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Yu H, Zhang L and Liu P: CXCR7 signaling
induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition by AKT and ERK pathways
in epithelial ovarian carcinomas. Tumour Biol. Oct 31–2014.Epub
ahead of print.
|
|
45
|
Wojtalla A and Arcaro A: Targeting
phosphoinositide 3-kinase signalling in lung cancer. Crit Rev Oncol
Hematol. 80:278–290. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zhang J, Cao J, Ma S, et al: Tumor hypoxia
enhances non-small cell lung cancer metastasis by selectively
promoting macrophage M2 polarization through the activation of ERK
signaling. Oncotarget Oct. 5:9664–9677. 2014.
|
|
47
|
Beck JT, Ismail A and Tolomeo C: Targeting
the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/AKT/mammalian target of
rapamycin (mTOR) pathway: An emerging treatment strategy for
squamous cell lung carcinoma. Cancer Treat Rev. 40:980–989. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Stinchcombe TE and Johnson GL: MEK
inhibition in non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 86:121–125.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|