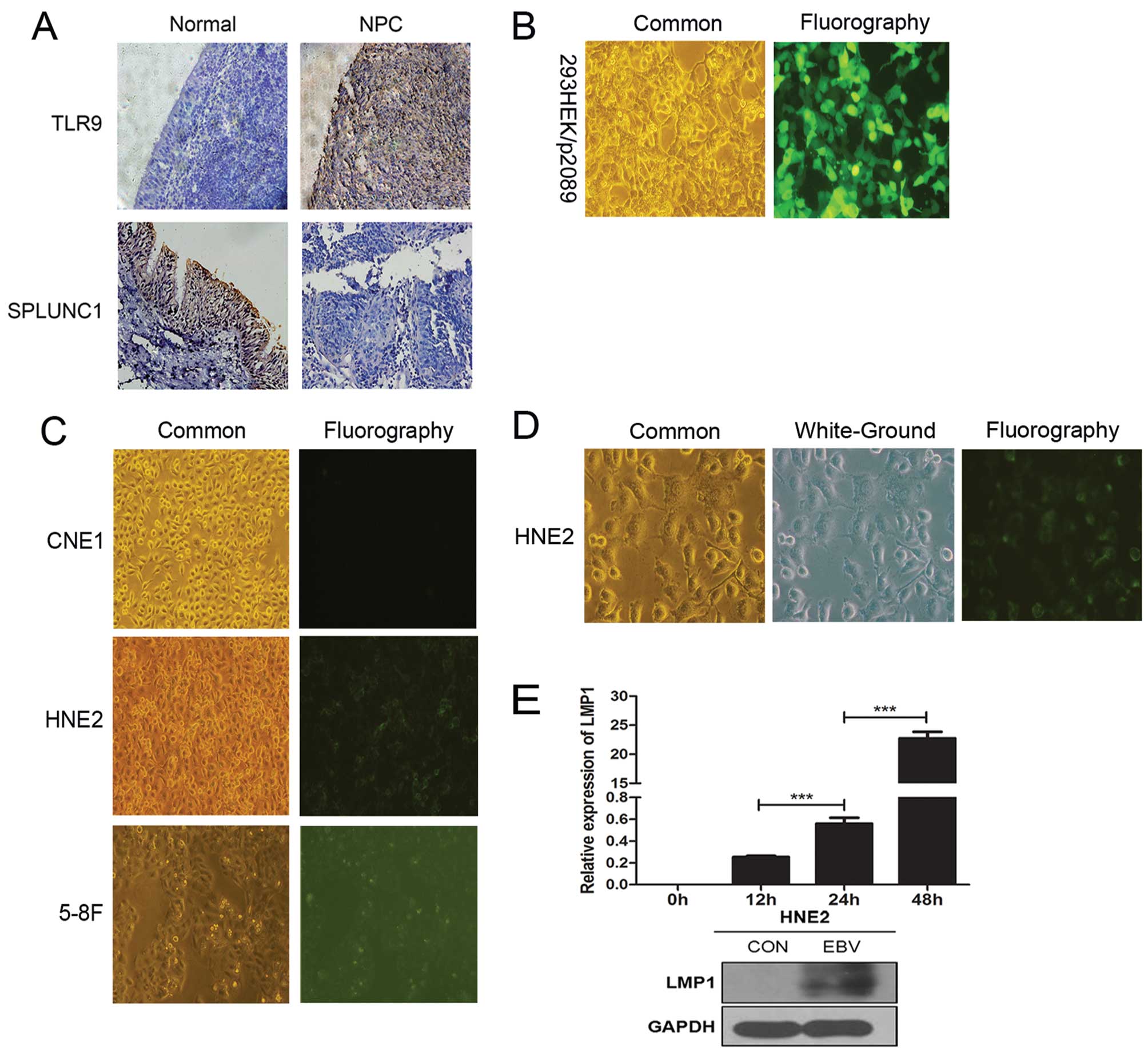
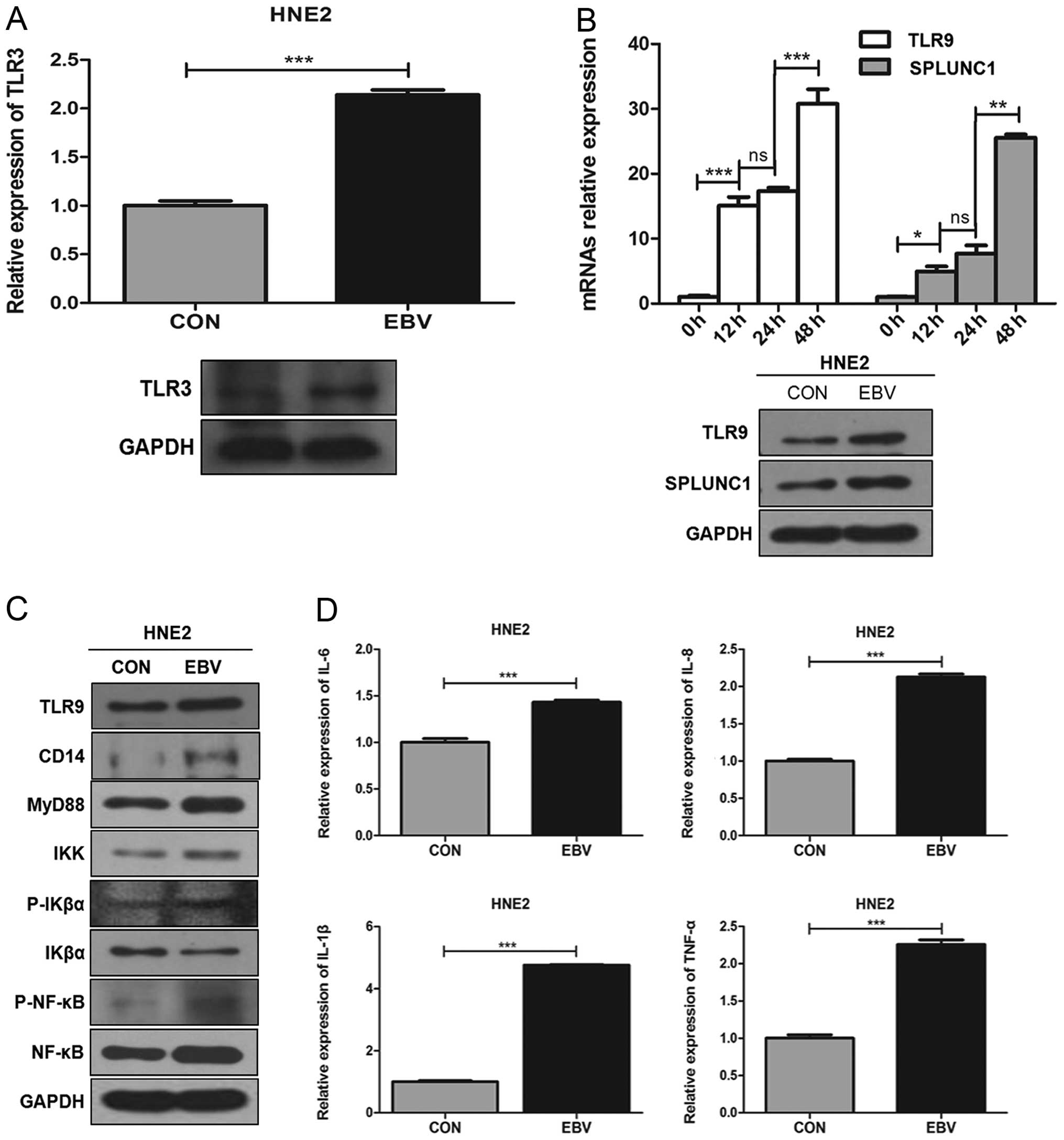
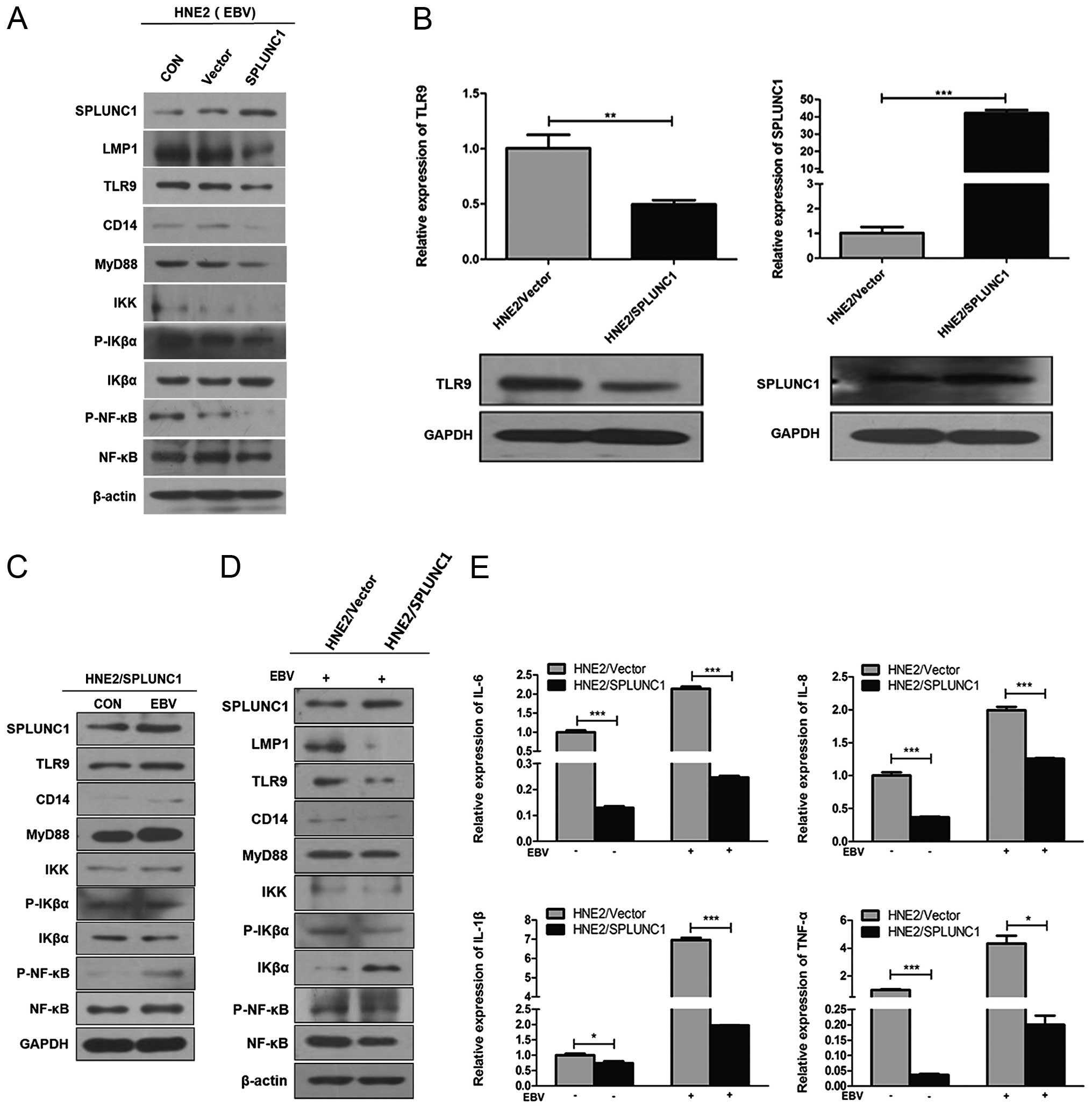
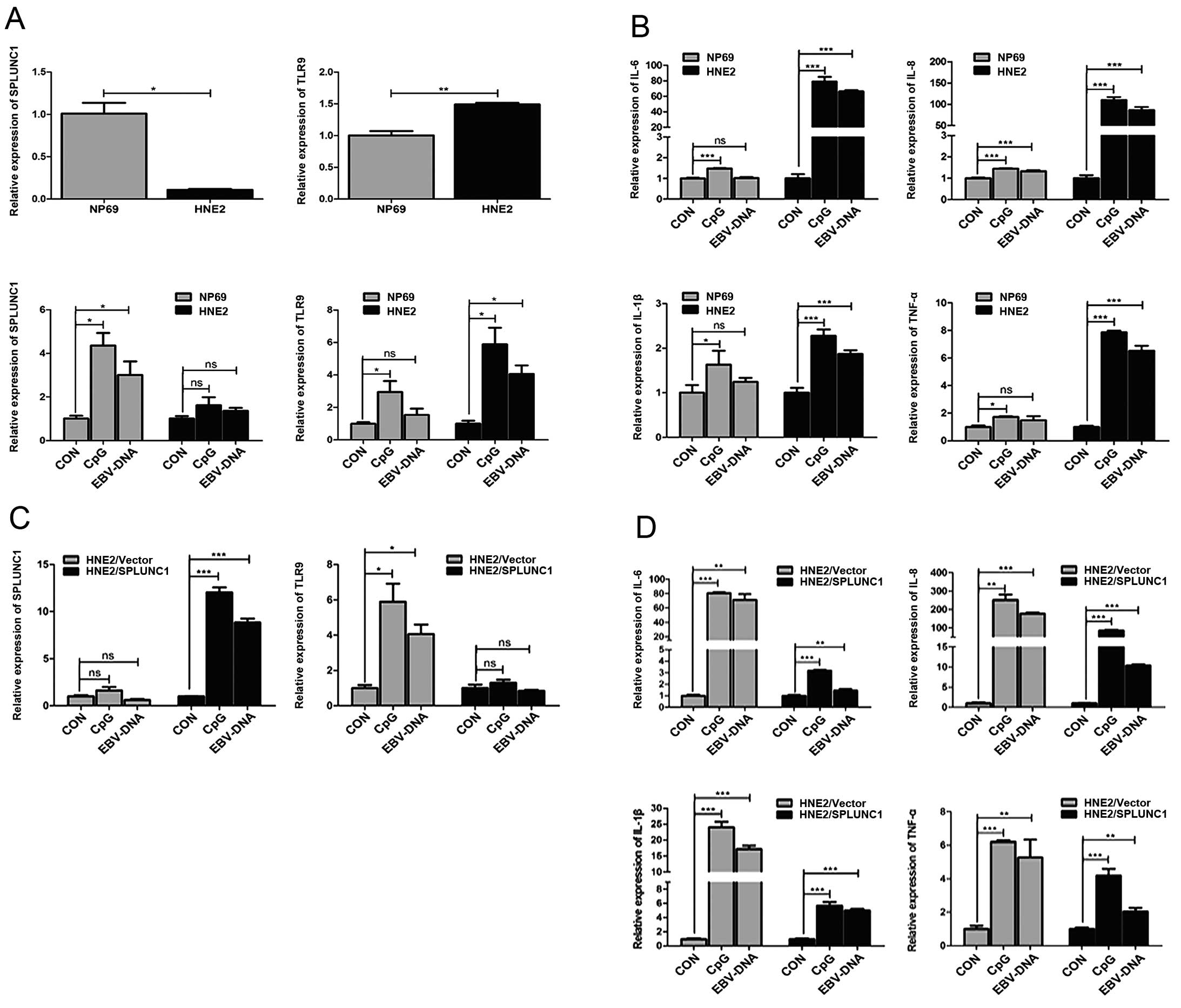
|
1
|
Gu AD, Zeng MS and Qian CN: The criteria
to confirm the role of Epstein-Barr virus in nasopharyngeal
carcinoma initiation. Int J Mol Sci. 13:13737–13747. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Odumade OA, Hogquist KA and Balfour HH Jr:
Progress and problems in understanding and managing primary
Epstein-Barr virus infections. Clin Microbiol Rev. 24:193–209.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Thompson MP and Kurzrock R: Epstein-Barr
virus and cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 10:803–821. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Teramoto N, Gogolák P, Nagy N, Maeda A,
Kvarnung K, Björkholm T and Klein E: Epstein-Barr virus-infected
B-chronic lymphocyte leukemia cells express the virally encoded
nuclear proteins but they do not enter the cell cycle. J Hum Virol.
3:125–136. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Imai S, Nishikawa J and Takada K:
Cell-to-cell contact as an efficient mode of Epstein-Barr virus
infection of diverse human epithelial cells. J Virol. 72:4371–4378.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Li QX, Young LS, Niedobitek G, Dawson CW,
Birkenbach M, Wang F and Rickinson AB: Epstein-Barr virus infection
and replication in a human epithelial cell system. Nature.
356:347–350. 1992. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhang B, Nie X, Xiao B, Xiang J, Shen S,
Gong J, Zhou M, Zhu S, Zhou J, Qian J, et al: Identification of
tissue-specific genes in nasopharyngeal epithelial tissue and
differentially expressed genes in nasopharyngeal carcinoma by
suppression subtractive hybridization and cDNA microarray. Genes
Chromosomes Cancer. 38:80–90. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bingle CD and Craven CJ: Comparative
analysis of the PLUNC (palate, lung and nasal epithelium clone)
protein families. Biochem Soc Trans. 31:806–809. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Jiang D, Persinger R, Wu Q, Gross A and
Chu HW: α1-antitrypsin promotes SPLUNC1-mediated lung defense
against Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection in mice. Respir Res.
14:1222013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Seshadri S, Lin DC, Rosati M, Carter RG,
Norton JE, Suh L, Kato A, Chandra RK, Harris KE, Chu HW, et al:
Reduced expression of antimicrobial PLUNC proteins in nasal polyp
tissues of patients with chronic rhinosinusitis. Allergy.
67:920–928. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Di YP, Tkach AV, Yanamala N, Stanley S,
Gao S, Shurin MR, Kisin ER, Kagan VE and Shvedova A: Dual acute
proinflam-matory and antifibrotic pulmonary effects of short
palate, lung, and nasal epithelium clone-1 after exposure to carbon
nanotubes. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 49:759–767. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lu JH, Tang YL, Yu HB, Zhou JH, Fu CY,
Zeng X, Yu ZY, Yin HL, Wu MH, Zhang JY, et al: Epstein-Barr virus
facilitates the malignant potential of immortalized epithelial
cells: from latent genome to viral production and maintenance. Lab
Invest. 90:196–209. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Tsao SW, Wang X, Liu Y, Cheung YC, Feng H,
Zheng Z, Wong N, Yuen PW, Lo AK, Wong YC, et al: Establishment of
two immor-talized nasopharyngeal epithelial cell lines using SV40
large T and HPV16E6/E7 viral oncogenes. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1590:150–158. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhou HD, Fan SQ, Zhao J, Huang DH, Zhou M,
Liu HY, Zeng ZY, Yang YX, Huang H, Li XL, et al: Tissue
distribution of the secretory protein, SPLUNC1, in the human fetus.
Histochem Cell Biol. 125:315–324. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Tang YL, Lu JH, Cao L, Wu MH, Peng SP,
Zhou HD, Huang C, Yang YX, Zhou YH, Chen Q, et al: Genetic
variations of EBV-LMP1 from nasopharyngeal carcinoma biopsies:
Potential loss of T cell epitopes. Braz J Med Biol Res. 41:110–116.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lu J, Tang Y, Zhou M, Wu M, Ouyang J, Gao
J, Zhang L, Li D, Chen Q, Xiong W, et al: Gene modification in the
genome of Epstein-Barr virus cloned as a bacterial artificial
chromosome. Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao. 48:385–390. 2008.In Chinese.
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chen L, Yin J, Chen Y and Zhong J:
Induction of Epstein-Barr virus lytic replication by recombinant
adenoviruses expressing the zebra gene with EBV specific promoters.
Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 37:215–220. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Yu H, Lu J, Zuo L, Yan Q, Yu Z, Li X,
Huang J, Zhao L, Tang H, Luo Z, et al: Epstein-Barr virus
downregulates microRNA 203 through the oncoprotein latent membrane
protein 1: a contribution to increased tumor incidence in
epithelial cells. J Virol. 86:3088–3099. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
19
|
Wang WY, Chien YC, Jan JS, Chueh CM and
Lin JC: Consistent sequence variation of Epstein-Barr virus nuclear
antigen 1 in primary tumor and peripheral blood cells of patients
with naso-pharyngeal carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 8:2586–2590.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Omerović J, Lev L and Longnecker R: The
amino terminus of Epstein-Barr virus glycoprotein gH is important
for fusion with epithelial and B cells. J Virol. 79:12408–12415.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Karin M: Nuclear factor-kappaB in cancer
development and progression. Nature. 441:431–436. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Cavallo F, De Giovanni C, Nanni P, Forni G
and Lollini PL: 2011: the immune hallmarks of cancer. Cancer
Immunol Immunother. 60:319–326. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Oeckinghaus A, Hayden MS and Ghosh S:
Crosstalk in NF-κB signaling pathways. Nat Immunol. 12:695–708.
2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mantovani A, Allavena P, Sica A and
Balkwill F: Cancer-related inflammation. Nature. 454:436–444. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Colotta F, Allavena P, Sica A, Garlanda C
and Mantovani A: Cancer-related inflammation, the seventh hallmark
of cancer: links to genetic instability. Carcinogenesis.
30:1073–1081. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Takeuchi O and Akira S: Pattern
recognition receptors and inflammation. Cell. 140:805–820. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Iwasaki A and Medzhitov R: Regulation of
adaptive immunity by the innate immune system. Science.
327:291–295. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Basith S, Manavalan B, Yoo TH, Kim SG and
Choi S: Roles of toll-like receptors in cancer: a double-edged
sword for defense and offense. Arch Pharm Res. 35:1297–1316. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Amirchaghmaghi E, Taghavi SA, Shapouri F,
Saeidi S, Rezaei A and Aflatoonian R: The role of toll like
receptors in pregnancy. Int J Fertil Steril. 7:147–154. 2013.
|
|
30
|
Droemann D, Albrecht D, Gerdes J, Ulmer
AJ, Branscheid D, Vollmer E, Dalhoff K, Zabel P and Goldmann T:
Human lung cancer cells express functionally active Toll-like
receptor 9. Respir Res. 6:12005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lee JW, Choi JJ, Seo ES, Kim MJ, Kim WY,
Choi CH, Kim TJ, Kim BG, Song SY and Bae DS: Increased toll-like
receptor 9 expression in cervical neoplasia. Mol Carcinog.
46:941–947. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Berger R, Fiegl H, Goebel G, Obexer P,
Ausserlechner M, Doppler W, Hauser-Kronberger C, Reitsamer R, Egle
D, Reimer D, et al: Toll-like receptor 9 expression in breast and
ovarian cancer is associated with poorly differentiated tumors.
Cancer Sci. 101:1059–1066. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ronkainen H, Hirvikoski P, Kauppila S,
Vuopala KS, Paavonen TK, Selander KS and Vaarala MH: Absent
Toll-like receptor-9 expression predicts poor prognosis in renal
cell carcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 30:842011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Woods DC, White YA, Dau C and Johnson AL:
TLR4 activates NF-κB in human ovarian granulosa tumor cells.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 409:675–680. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ben Abdelwahed R, Cosette J, Donnou S,
Crozet L, Ouakrim H, Fridman WH, Sautès-Fridman C, Mahjoub A and
Fisson S: Lymphoma B-cell responsiveness to CpG-DNA depends on the
tumor microenvironment. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 32:182013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Baumann CL, Aspalter IM, Sharif O,
Pichlmair A, Blüml S, Grebien F, Bruckner M, Pasierbek P, Aumayr K,
Planyavsky M, et al: CD14 is a coreceptor of Toll-like receptors 7
and 9. J Exp Med. 207:2689–2701. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhou HD, Li GY, Yang YX, Li XL, Sheng SR,
Zhang WL and Zhao J: Intracellular co-localization of SPLUNC1
protein with nanobacteria in nasopharyngeal carcinoma epithelia
HNE1 cells depended on the bactericidal permeability increasing
protein domain. Mol Immunol. 43:1864–1871. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Zhou HD, Li XL, Li GY, Zhou M, Liu HY,
Yang YX, Deng T, Ma J and Sheng SR: Effect of SPLUNC1 protein on
the Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Epstein-Barr virus. Mol Cell
Biochem. 309:191–197. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Chen P, Guo X, Zhou H, Zhang W, Zeng Z,
Liao Q, Li X, Xiang B, Yang J, Ma J, et al: SPLUNC1 regulates cell
progression and apoptosis through the miR-141-PTEN/p27 pathway, but
is hindered by LMP1. PLoS One. 8:e569292013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Chu HW, Gally F, Thaikoottathil J,
Janssen-Heininger YM, Wu Q, Zhang G, Reisdorph N, Case S, Minor M,
Smith S, et al: SPLUNC1 regulation in airway epithelial cells: role
of Toll-like receptor 2 signaling. Respir Res. 11:1552010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Thaikoottathil J and Chu HW: MAPK/AP-1
activation mediates TLR2 agonist-induced SPLUNC1 expression in
human lung epithelial cells. Mol Immunol. 49:415–422. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zheng Y, Qin Z, Ye Q, Chen P, Wang Z, Yan
Q, Luo Z, Liu X, Zhou Y, Xiong W, et al: Lactoferrin suppresses the
Epstein-Barr virus-induced inflammatory response by interfering
with pattern recognition of TLR2 and TLR9. Lab Invest.
94:1188–1199. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|