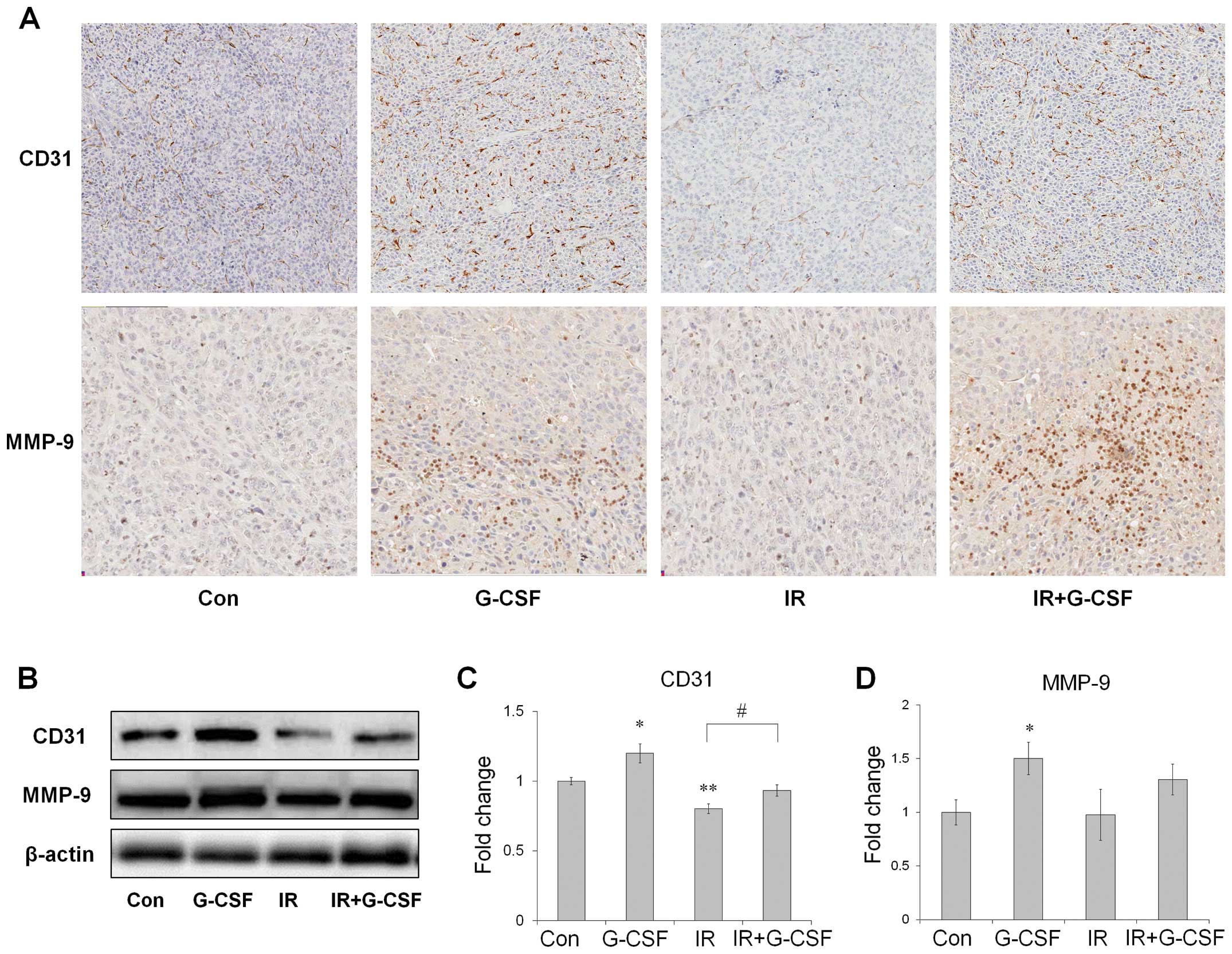
|
1
|
Mauch P, Constine L, Greenberger J, Knospe
W, Sullivan J, Liesveld JL and Deeg HJ: Hematopoietic stem cell
compartment: Acute and late effects of radiation therapy and
chemotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 31:1319–1339. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Friberg LE, Henningsson A, Maas H, Nguyen
L and Karlsson MO: Model of chemotherapy-induced myelosuppression
with parameter consistency across drugs. J Clin Oncol.
20:4713–4721. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sung L and Dror Y: Clinical applications
of granulocyte-colony stimulating factor. Front Biosci.
12:1988–2002. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
MacVittie TJ and Farese AM: Cytokine-based
treatment of radiation injury: Potential benefits after low-level
radiation exposure. Mil Med. 167(Suppl): 68–70. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Uckun FM, Souza L, Waddick KG, Wick M and
Song CW: In vivo radioprotective effects of recombinant human
granulocyte colony-stimulating factor in lethally irradiated mice.
Blood. 75:638–645. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hou XW, Jiang Y, Wang LF, Xu HY, Lin HM,
He XY, He JJ and Zhang S: Protective role of granulocyte
colony-stimulating factor against adriamycin induced cardiac, renal
and hepatic toxicities. Toxicol Lett. 187:40–44. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kim JS, Yang M, Jang H, Oui H, Kim SH,
Shin T, Jang WS, Lee SS and Moon C: Granulocyte-colony stimulating
factor ameliorates irradiation-induced suppression of hippocampal
neurogenesis in adult mice. Neurosci Lett. 486:43–46. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kudo T, Matsumoto T, Nakamichi I, Yada S,
Esaki M, Jo Y, Ohji Y, Yao T and Iida M: Recombinant human
granulocyte colony-stimulating factor reduces colonic epithelial
cell apoptosis and ameliorates murine dextran sulfate
sodium-induced colitis. Scand J Gastroenterol. 43:689–697. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kim JS, Ryoo SB, Heo K, Kim JG, Son TG,
Moon C and Yang K: Attenuating effects of granulocyte-colony
stimulating factor (G-CSF) in radiation induced intestinal injury
in mice. Food Chem Toxicol. 50:3174–3180. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kim JS, Yang M, Lee CG, Kim SD, Kim JK and
Yang K: In vitro and in vivo protective effects of granulocyte
colony-stimulating factor against radiation-induced intestinal
injury. Arch Pharm Res. 36:1252–1261. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lopez-Lazaro M: Granulocyte
colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF): A novel anticancer therapy based
on the ‘universal dynamics of tumor growth’? Exp Oncol. 28:249–251.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Maeda H, Uozumi T, Kurisu K, Matsuoka T,
Kawamoto K, Kiya K, Ogasawara H, Sugiyama K, Mikami T, Monden S, et
al: Combined antitumor effects of TNF and G-CSF on a human
medulloblastoma xenograft line. J Neurooncol. 21:203–213. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Natori T, Sata M, Washida M, Hirata Y,
Nagai R and Makuuchi M: G-CSF stimulates angiogenesis and promotes
tumor growth: Potential contribution of bone marrow-derived
endothelial progenitor cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
297:1058–1061. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Voloshin T, Gingis-Velitski S, Bril R,
Benayoun L, Munster M, Milsom C, Man S, Kerbel RS and Shaked Y:
G-CSF supplementation with chemotherapy can promote
revascularization and subsequent tumor regrowth: Prevention by a
CXCR4 antagonist. Blood. 118:3426–3435. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Roberts AW: G-CSF: A key regulator of
neutrophil production, but that’s not all! Growth Factors.
23:33–41. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hérodin F and Drouet M: Cytokine-based
treatment of accidentally irradiated victims and new approaches.
Exp Hematol. 33:1071–1080. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Singh VK, Fatanmi OO, Singh PK and
Whitnall MH: Role of radiation-induced granulocyte
colony-stimulating factor in recovery from whole body
gamma-irradiation. Cytokine. 58:406–414. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Garcia-Barros M, Paris F, Cordon-Cardo C,
Lyden D, Rafii S, Haimovitz-Friedman A, Fuks Z and Kolesnick R:
Tumor response to radiotherapy regulated by endothelial cell
apoptosis. Science. 300:1155–1159. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Romero-Weaver AL, Wan XS, Diffenderfer ES,
Lin L and Kennedy AR: Kinetics of neutrophils in mice exposed to
radiation and/or granulocyte colony-stimulating factor treatment.
Radiat Res. 180:177–188. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Shojaei F, Wu X, Qu X, Kowanetz M, Yu L,
Tan M, Meng YG and Ferrara N: G-CSF-initiated myeloid cell
mobilization and angiogenesis mediate tumor refractoriness to
anti-VEGF therapy in mouse models. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
106:6742–6747. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chen FH, Fu SY, Yang YC, Wang CC, Chiang
CS and Hong JH: Combination of vessel-targeting agents and
fractionated radiation therapy: The role of the SDF-1/CXCR4
pathway. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 86:777–784. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bottoni U, Bonaccorsi P, Devirgiliis V,
Panasiti V, Borroni RG, Trasimeni G, Clerico R and Calvieri S:
Complete remission of brain metastases in three patients with stage
IV melanoma treated with BOLD and G-CSF. Jpn J Clin Oncol.
35:507–513. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Löwenberg B, van Putten W, Theobald M,
Gmür J, Verdonck L, Sonneveld P, Fey M, Schouten H, de Greef G,
Ferrant A, et al: Effect of priming with granulocyte
colony-stimulating factor on the outcome of chemotherapy for acute
myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 349:743–752. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Di Carlo E, Forni G, Lollini P, Colombo
MP, Modesti A and Musiani P: The intriguing role of
polymorphonuclear neutrophils in antitumor reactions. Blood.
97:339–345. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Koga Y, Matsuzaki A, Suminoe A, Hattori H
and Hara T: Neutrophil-derived TNF-related apoptosis-inducing
ligand (TRAIL): A novel mechanism of antitumor effect by
neutrophils. Cancer Res. 64:1037–1043. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Gabrilovich DI and Nagaraj S:
Myeloid-derived suppressor cells as regulators of the immune
system. Nat Rev Immunol. 9:162–174. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ohki Y, Heissig B, Sato Y, Akiyama H, Zhu
Z, Hicklin DJ, Shimada K, Ogawa H, Daida H, Hattori K, et al:
Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor promotes neovascularization
by releasing vascular endothelial growth factor from neutrophils.
FASEB J. 19:2005–2007. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Roskoski R Jr: Vascular endothelial growth
factor (VEGF) signaling in tumor progression. Crit Rev Oncol
Hematol. 62:179–213. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Heissig B, Hattori K, Dias S, Friedrich M,
Ferris B, Hackett NR, Crystal RG, Besmer P, Lyden D, Moore MA, et
al: Recruitment of stem and progenitor cells from the bone marrow
niche requires MMP-9 mediated release of kit-ligand. Cell.
109:625–637. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hattori K, Heissig B, Tashiro K, Honjo T,
Tateno M, Shieh JH, Hackett NR, Quitoriano MS, Crystal RG, Rafii S,
et al: Plasma elevation of stromal cell-derived factor-1 induces
mobilization of mature and immature hematopoietic progenitor and
stem cells. Blood. 97:3354–3360. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kioi M, Vogel H, Schultz G, Hoffman RM,
Harsh GR and Brown JM: Inhibition of vasculogenesis, but not
angiogenesis, prevents the recurrence of glioblastoma after
irradiation in mice. J Clin Invest. 120:694–705. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Prionas SD, Kowalski J, Fajardo LF, Kaplan
I, Kwan HH and Allison AC: Effects of X irradiation on
angiogenesis. Radiat Res. 124:43–49. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Heissig B, Hattori K, Friedrich M, Rafii S
and Werb Z: Angiogenesis: Vascular remodeling of the extracellular
matrix involves metalloproteinases. Curr Opin Hematol. 10:136–141.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Bergers G, Brekken R, McMahon G, Vu TH,
Itoh T, Tamaki K, Tanzawa K, Thorpe P, Itohara S, Werb Z, et al:
Matrix metallopro-teinase-9 triggers the angiogenic switch during
carcinogenesis. Nat Cell Biol. 2:737–744. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ahn GO and Brown JM: Matrix
metalloproteinase-9 is required for tumor vasculogenesis but not
for angiogenesis: Role of bone marrow-derived myelomonocytic cells.
Cancer Cell. 13:193–205. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|