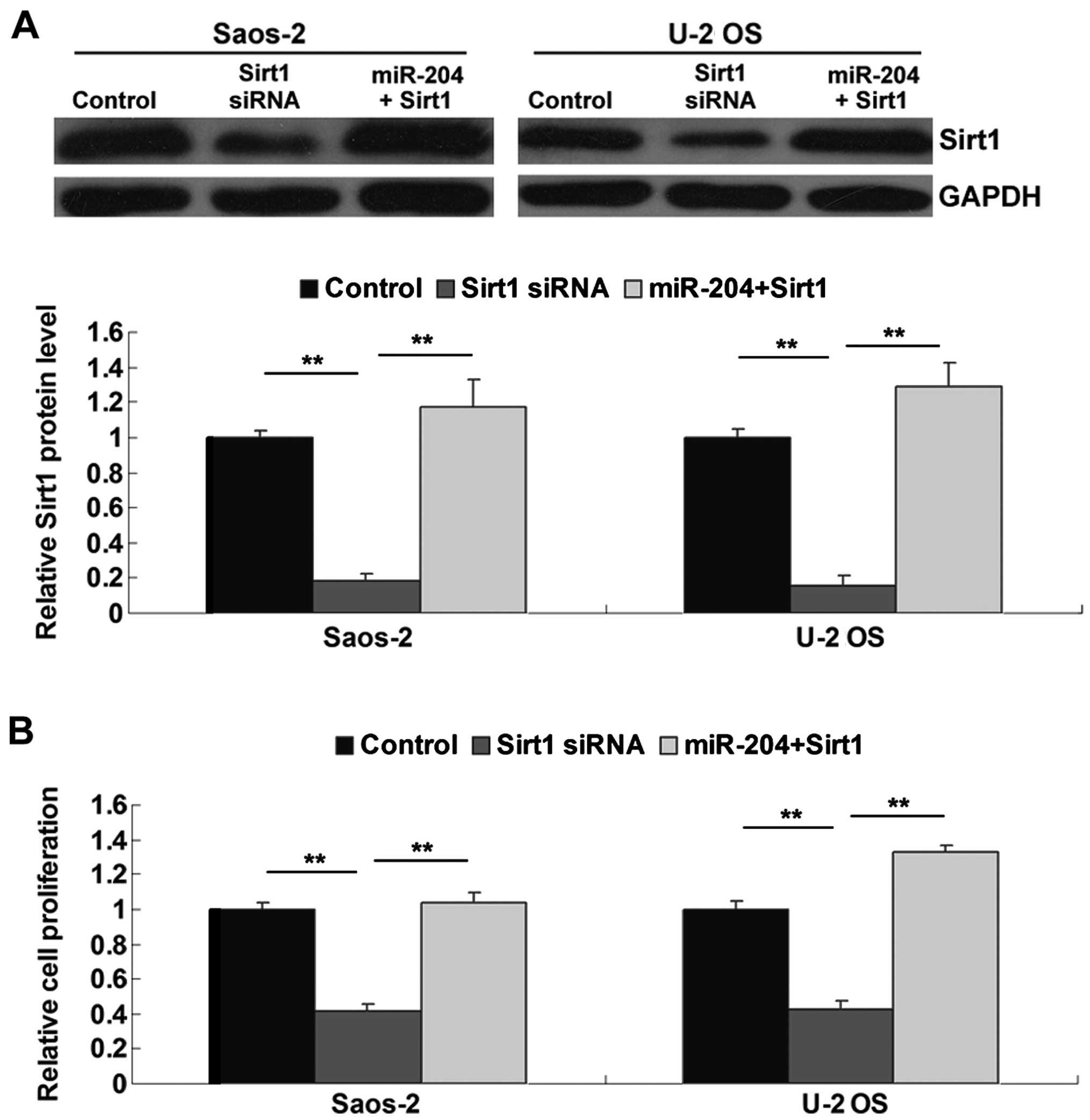
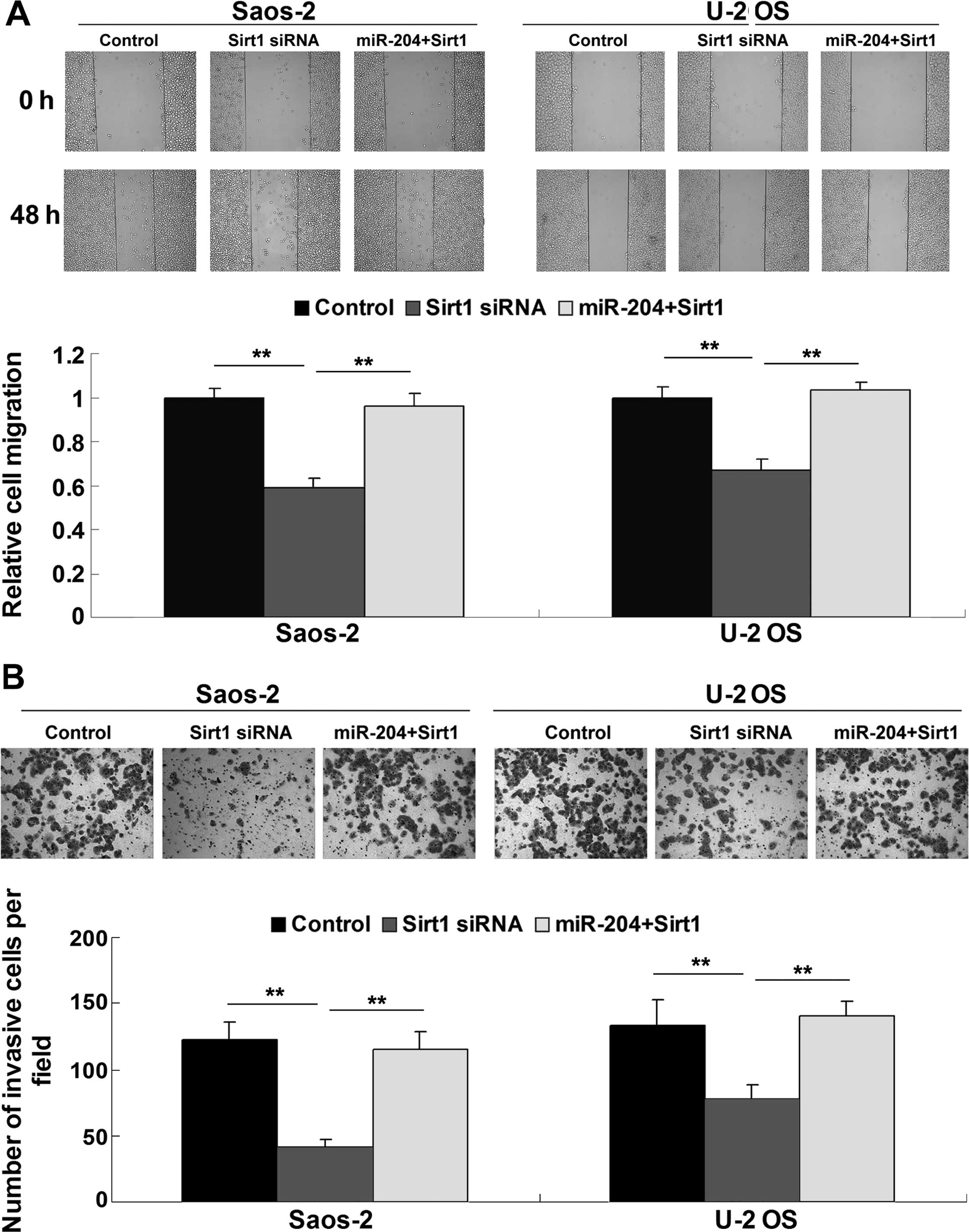
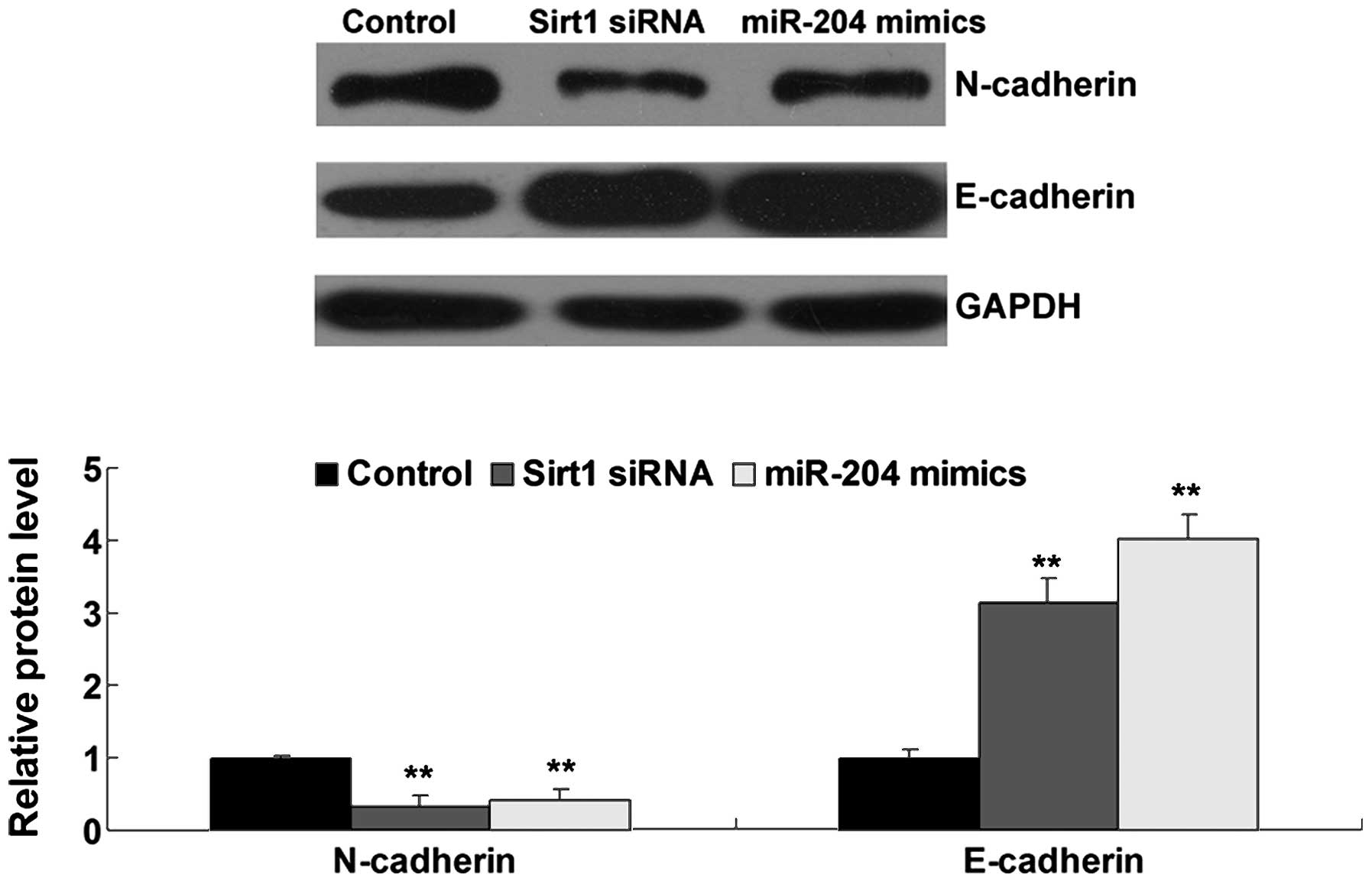
|
1
|
Thompson LD: Osteosarcoma. Ear Nose Throat
J. 92:288–290. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Liang W, Gao B, Fu P, Xu S, Qian Y and Fu
Q: The miRNAs in the pathgenesis of osteosarcoma. Front Biosci.
18:788–794. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Moss EG: MicroRNAs: Hidden in the genome.
Curr Biol. 12:R138–R140. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Choi E, Choi E and Hwang KC: MicroRNAs as
novel regulators of stem cell fate. World J Stem Cells. 5:172–187.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lujambio A, Calin GA, Villanueva A, Ropero
S, Sánchez-Céspedes M, Blanco D, Montuenga LM, Rossi S, Nicoloso
MS, Faller WJ, et al: A microRNA DNA methylation signature for
human cancer metastasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:13556–13561.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Calin GA and Croce CM: MicroRNA signatures
in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:857–866. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Li W, Jin X, Zhang Q, Zhang G, Deng X and
Ma L: Decreased expression of miR-204 is associated with poor
prognosis in patients with breast cancer. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
7:3287–3292. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Xia Y, Zhu Y, Ma T, Pan C, Wang J, He Z,
Li Z, Qi X and Chen Y: miR-204 functions as a tumor suppressor by
regulating SIX1 in NSCLC. FEBS Lett. 588:3703–3712. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhang F, Huang W, Sheng M and Liu T:
MiR-451 inhibits cell growth and invasion by targeting CXCL16 and
is associated with prognosis of osteosarcoma patients. Tumour Biol.
Nov 13–2014.Epub ahead of print.
|
|
10
|
Xu M, Jin H, Xu CX, Sun B, Mao Z, Bi WZ
and Wang Y: miR-382 inhibits tumor growth and enhance
chemosensitivity in osteosarcoma. Oncotarget. 5:9472–9483.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
He Y, Meng C, Shao Z, Wang H and Yang S:
MiR-23a functions as a tumor suppressor in osteosarcoma. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 34:1485–1496. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Shen L, Wang P, Yang J and Li X:
MicroRNA-217 regulates WASF3 expression and suppresses tumor growth
and metastasis in osteosarcoma. PLoS One. 9:e1091382014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang Q, Cai J, Wang J, Xiong C and Zhao J:
MiR-143 inhibits EGFR-signaling-dependent osteosarcoma invasion.
Tumour Biol. 35:12743–12748. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jiang L, He A, Zhang Q and Tao C: miR-126
inhibits cell growth, invasion, and migration of osteosarcoma cells
by downregulating ADAM-9. Tumour Biol. 35:12645–12654. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhang K, Zhang Y, Ren K, Zhao G, Yan K and
Ma B: MicroRNA-101 inhibits the metastasis of osteosarcoma cells by
downregulation of EZH2 expression. Oncol Rep. 32:2143–2149.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Han K, Zhao T, Chen X, Bian N, Yang T, Ma
Q, Cai C, Fan Q, Zhou Y and Ma B: microRNA-194 suppresses
osteosarcoma cell proliferation and metastasis in vitro and in vivo
by targeting CDH2 and IGF1R. Int J Oncol. 45:1437–1449.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yang J and Zhang W: New molecular insights
into osteosarcoma targeted therapy. Curr Opin Oncol. 25:398–406.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Shi L, Zhang B, Sun X, Lu S, Liu Z, Liu Y,
Li H, Wang L, Wang X and Zhao C: MiR-204 inhibits human NSCLC
metastasis through suppression of NUAK1. Br J Cancer.
111:2316–2327. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhou X, Li L, Su J and Zhang G: Decreased
miR-204 in H. pyloriassociated gastric cancer promotes cancer cell
proliferation and invasion by targeting SOX4. PLoS One.
9:e1014572014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Ying Z, Li Y, Wu J, Zhu X, Yang Y, Tian H,
Li W, Hu B, Cheng SY and Li M: Loss of miR-204 expression enhances
glioma migration and stem cell-like phenotype. Cancer Res.
73:990–999. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
21
|
Yoshitaka T, Kawai A, Miyaki S, Numoto K,
Kikuta K, Ozaki T, Lotz M and Asahara H: Analysis of microRNAs
expressions in chondrosarcoma. J Orthop Res. 31:1992–1998. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang L, Wang X and Chen P: MiR-204 down
regulates SIRT1 and reverts SIRT1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal
transition, anoikis resistance and invasion in gastric cancer
cells. BMC Cancer. 13:2902013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Li D, Bi FF, Chen NN, Cao JM, Sun WP, Zhou
YM, Li CY and Yang Q: A novel crosstalk between BRCA1 and sirtuin 1
in ovarian cancer. Sci Rep. 4:66662014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lin L, Zheng X, Qiu C, Dongol S, Lv Q,
Jiang J, Kong B and Wang C: SIRT1 promotes endometrial tumor growth
by targeting SREBP1 and lipogenesis. Oncol Rep. 32:2831–2835.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Xu JQ, Liu P, Si MJ and Ding XY:
MicroRNA-126 inhibits osteosarcoma cells proliferation by targeting
Sirt1. Tumour Biol. 34:3871–3877. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chu F, Chou PM, Zheng X, Mirkin BL and
Rebbaa A: Control of multidrug resistance gene mdr1 and cancer
resistance to chemotherapy by the longevity gene sirt1. Cancer Res.
65:10183–10187. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Li Y, Bäckesjö CM, Haldosén LA and
Lindgren U: Resveratrol inhibits proliferation and promotes
apoptosis of osteosarcoma cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 609:13–18. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Moustakas A and Heldin CH: Signaling
networks guiding epithelial-mesenchymal transitions during
embryogenesis and cancer progression. Cancer Sci. 98:1512–1520.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Thiery JP and Sleeman JP: Complex networks
orchestrate epithelial-mesenchymal transitions. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 7:131–142. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Mikhaylova O, Stratton Y, Hall D, Kellner
E, Ehmer B, Drew AF, Gallo CA, Plas DR, Biesiada J, Meller J, et
al: VHL-regulated miR-204 suppresses tumor growth through
inhibition of LC3B-mediated autophagy in renal clear cell
carcinoma. Cancer Cell. 21:532–546. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sacconi A, Biagioni F, Canu V, Mori F, Di
Benedetto A, Lorenzon L, Ercolani C, Di Agostino S, Cambria AM,
Germoni S, et al: miR-204 targets Bcl-2 expression and enhances
responsiveness of gastric cancer. Cell Death Dis. 3:e4232012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chen Z, Sangwan V, Banerjee S, Mackenzie
T, Dudeja V, Li X, Wang H, Vickers SM and Saluja AK: miR-204
mediated loss of Myeloid cell leukemia-1 results in pancreatic
cancer cell death. Mol Cancer. 12:1052013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yin Y, Zhang B, Wang W, Fei B, Quan C,
Zhang J, Song M, Bian Z, Wang Q, Ni S, et al: miR-204-5p inhibits
proliferation and invasion and enhances chemotherapeutic
sensitivity of colorectal cancer cells by downregulating RAB22A.
Clin Cancer Res. 20:6187–6199. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|