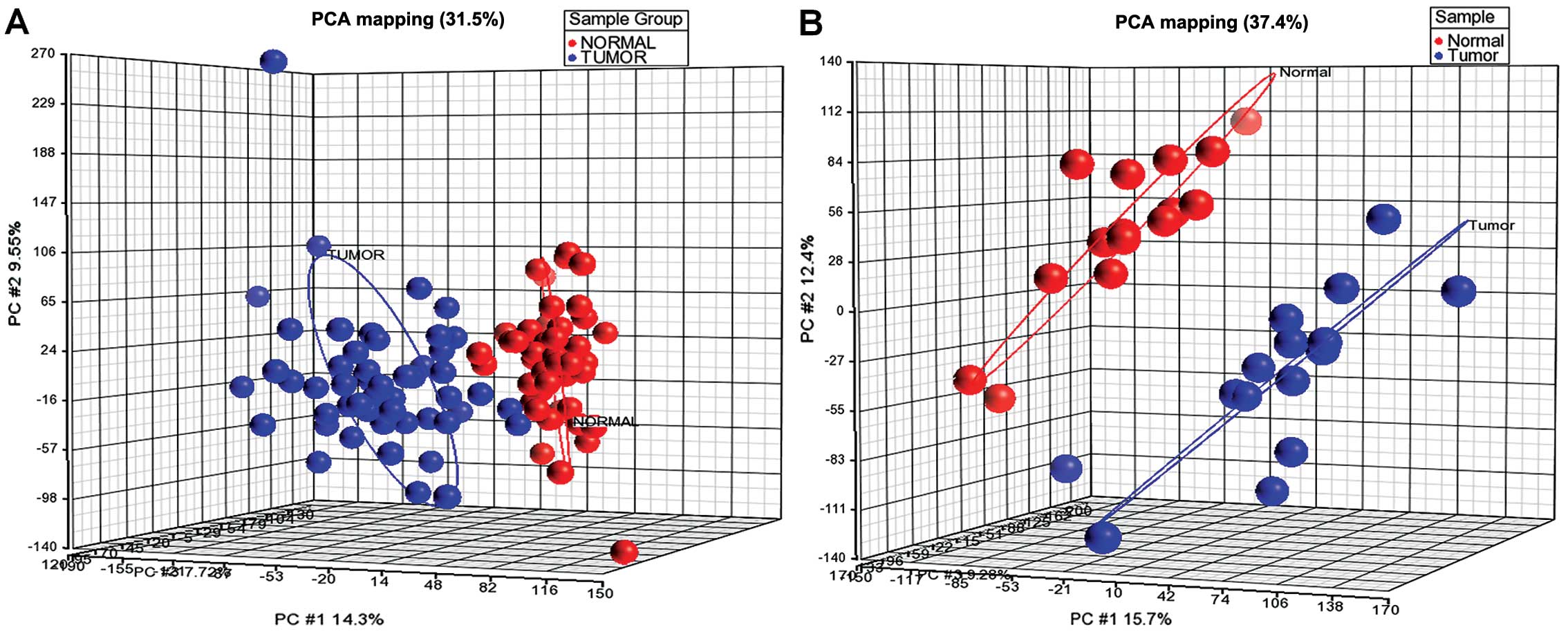
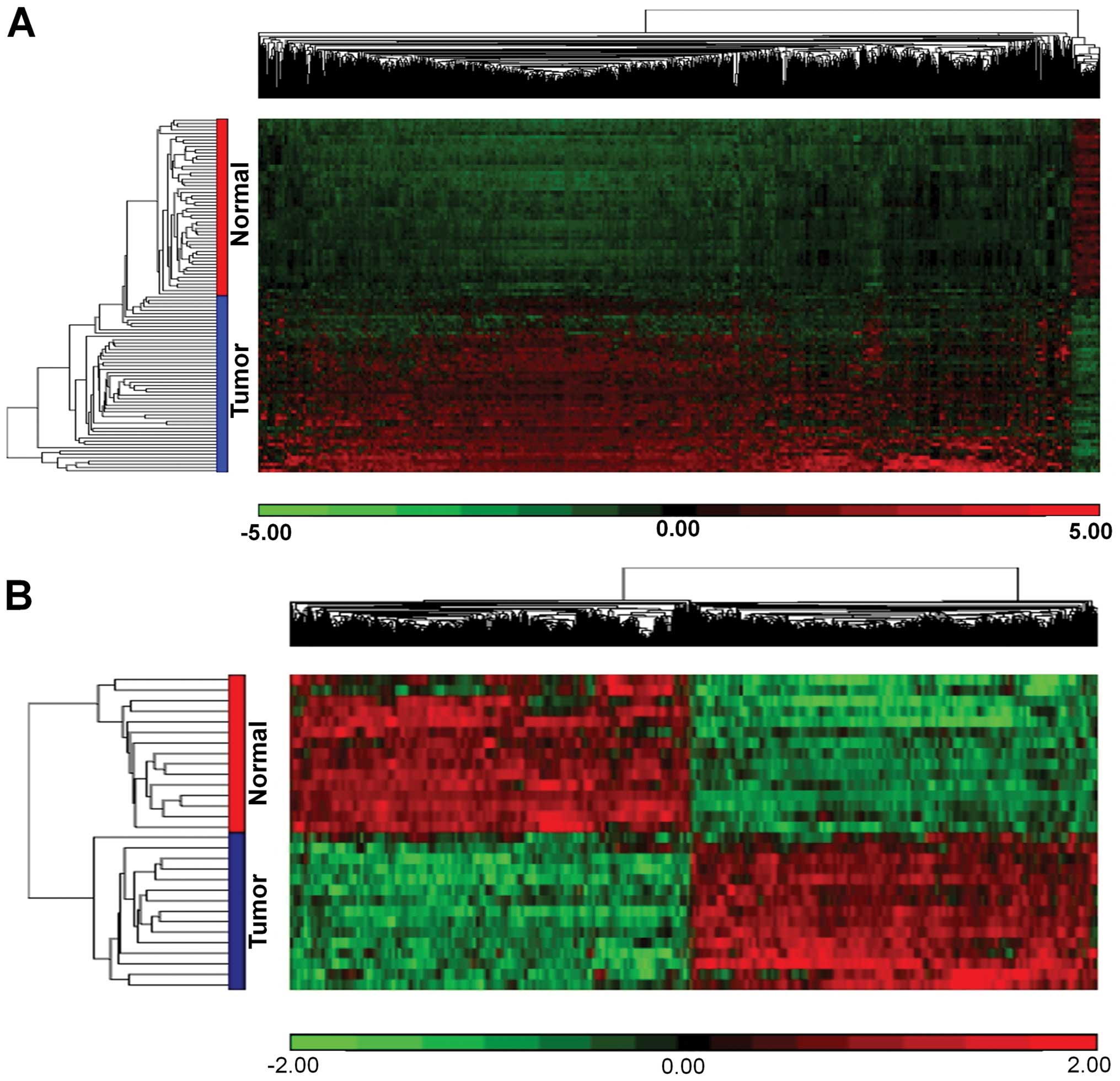
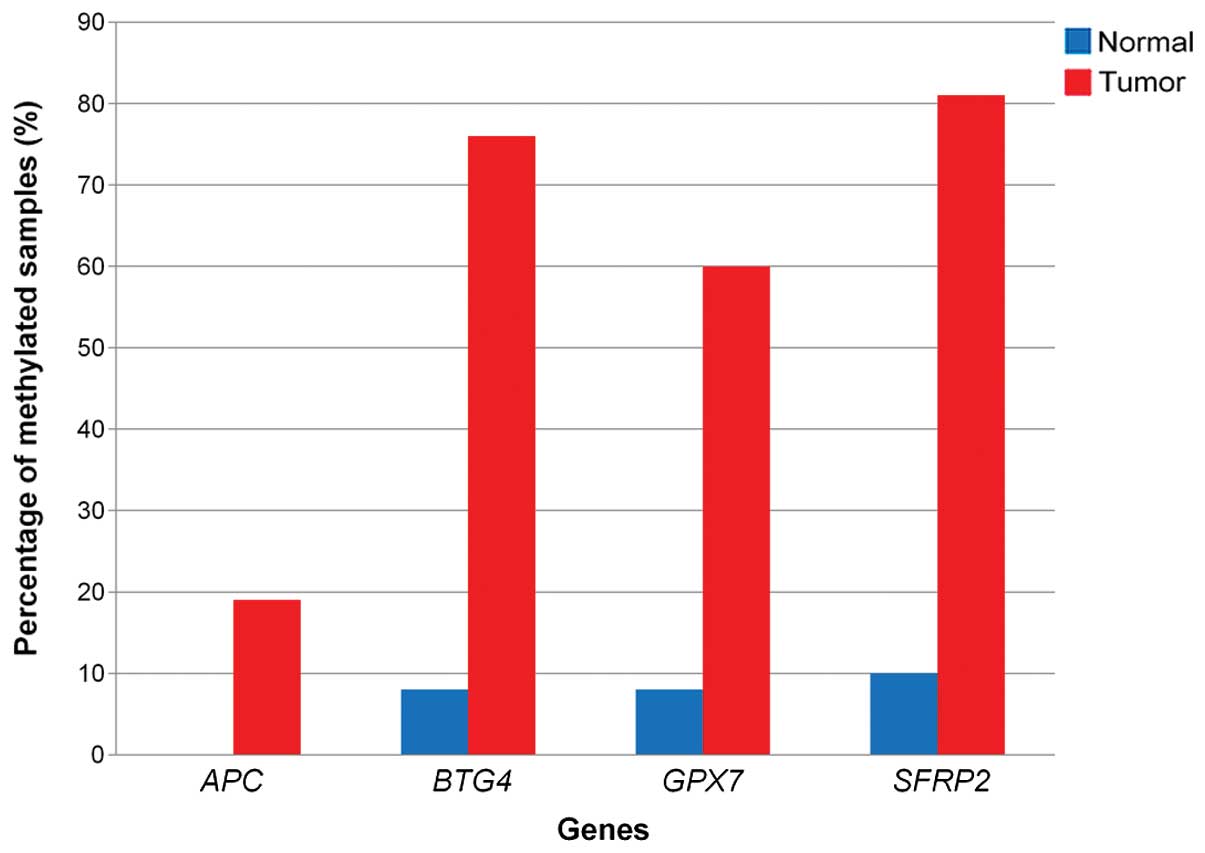
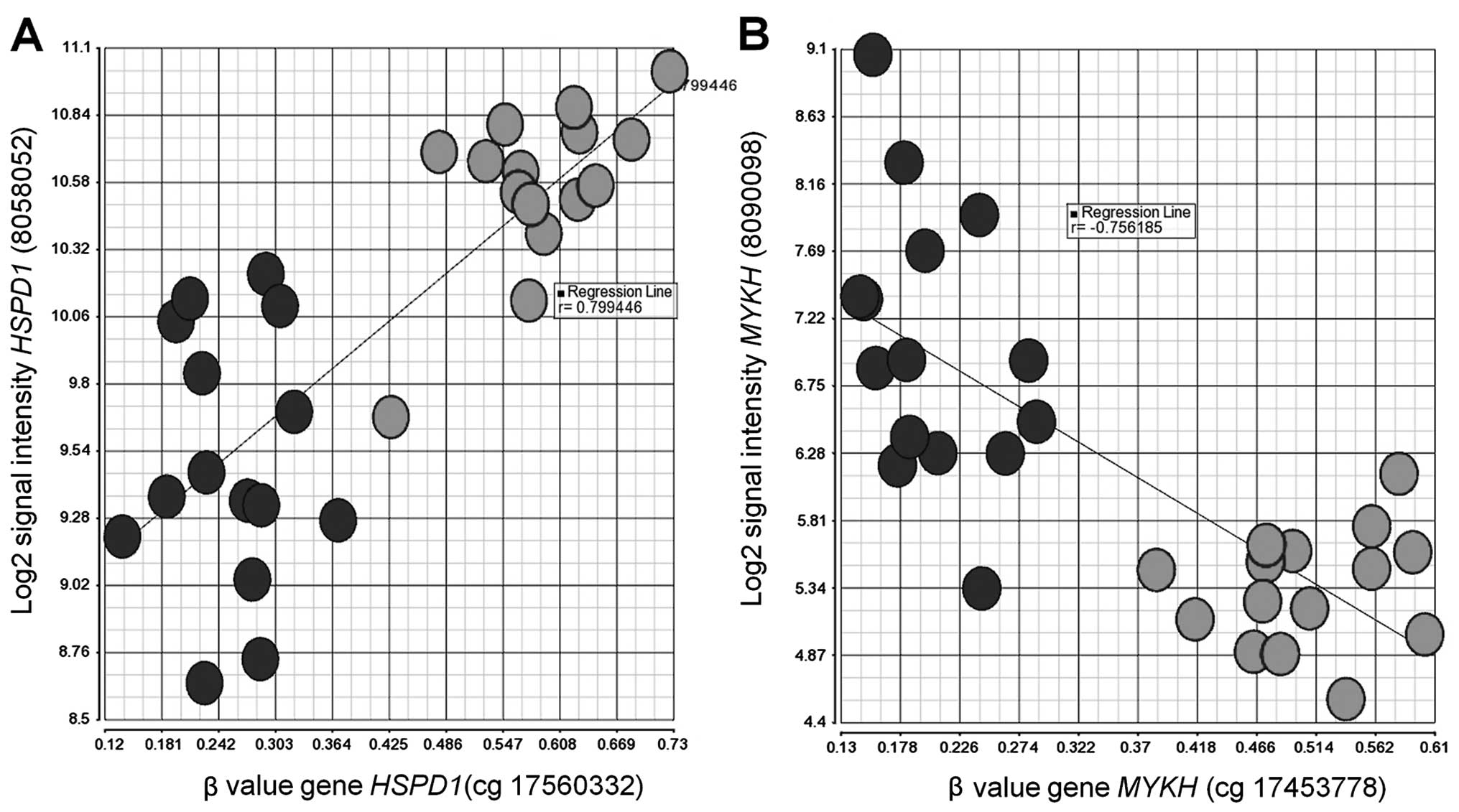
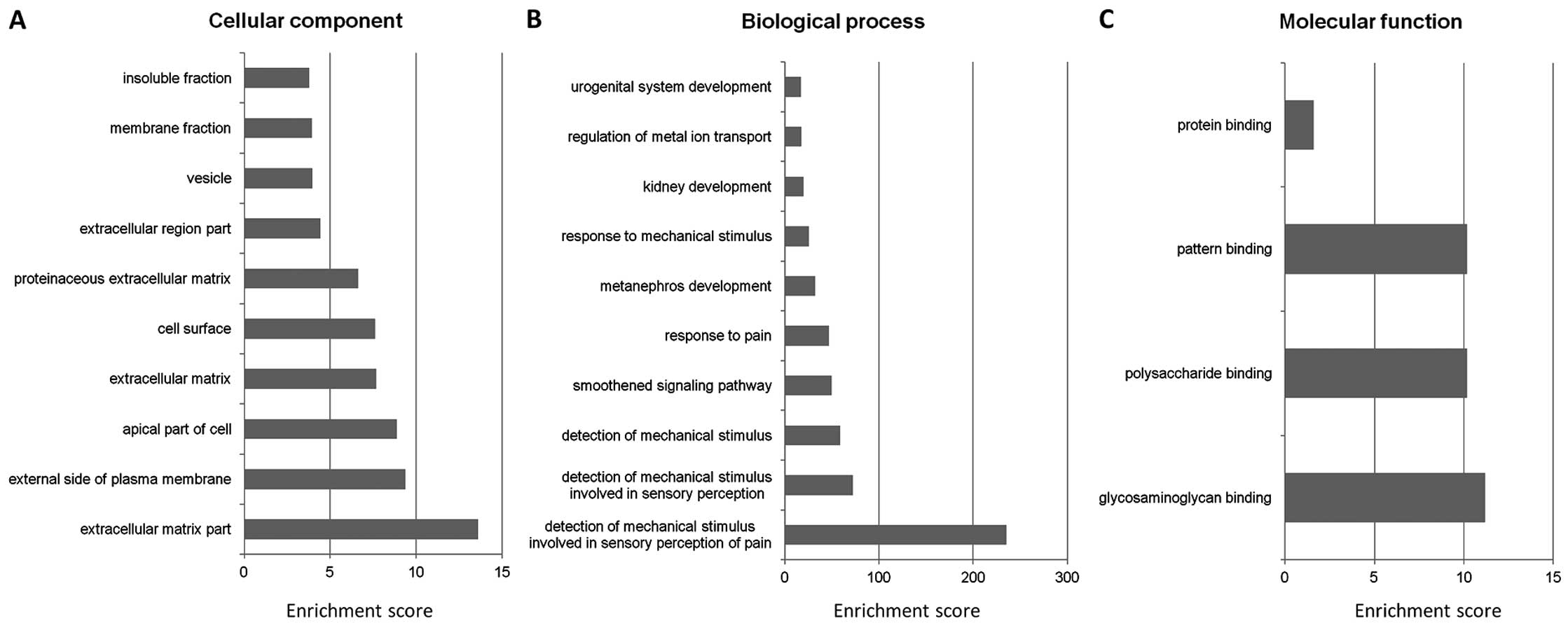
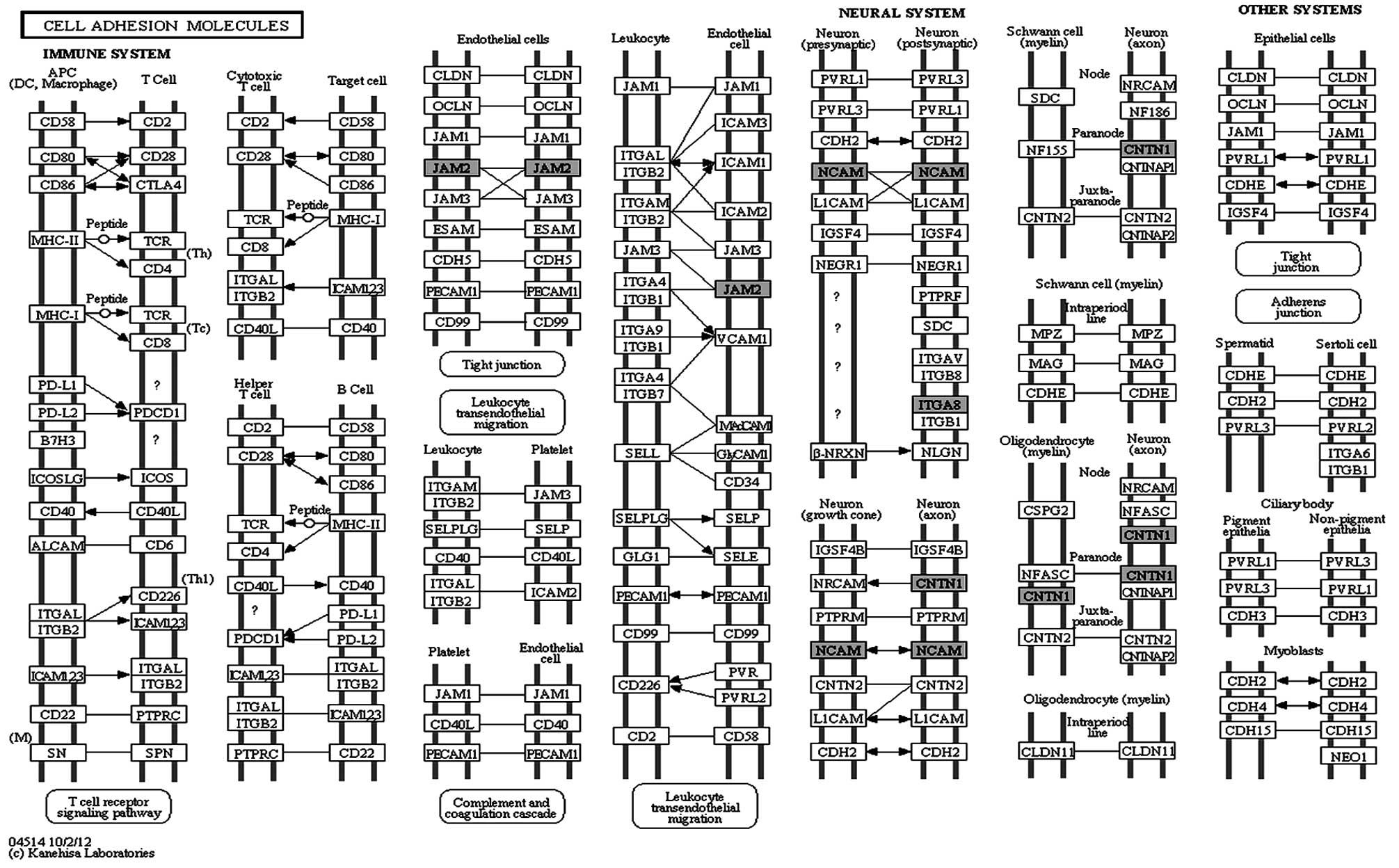
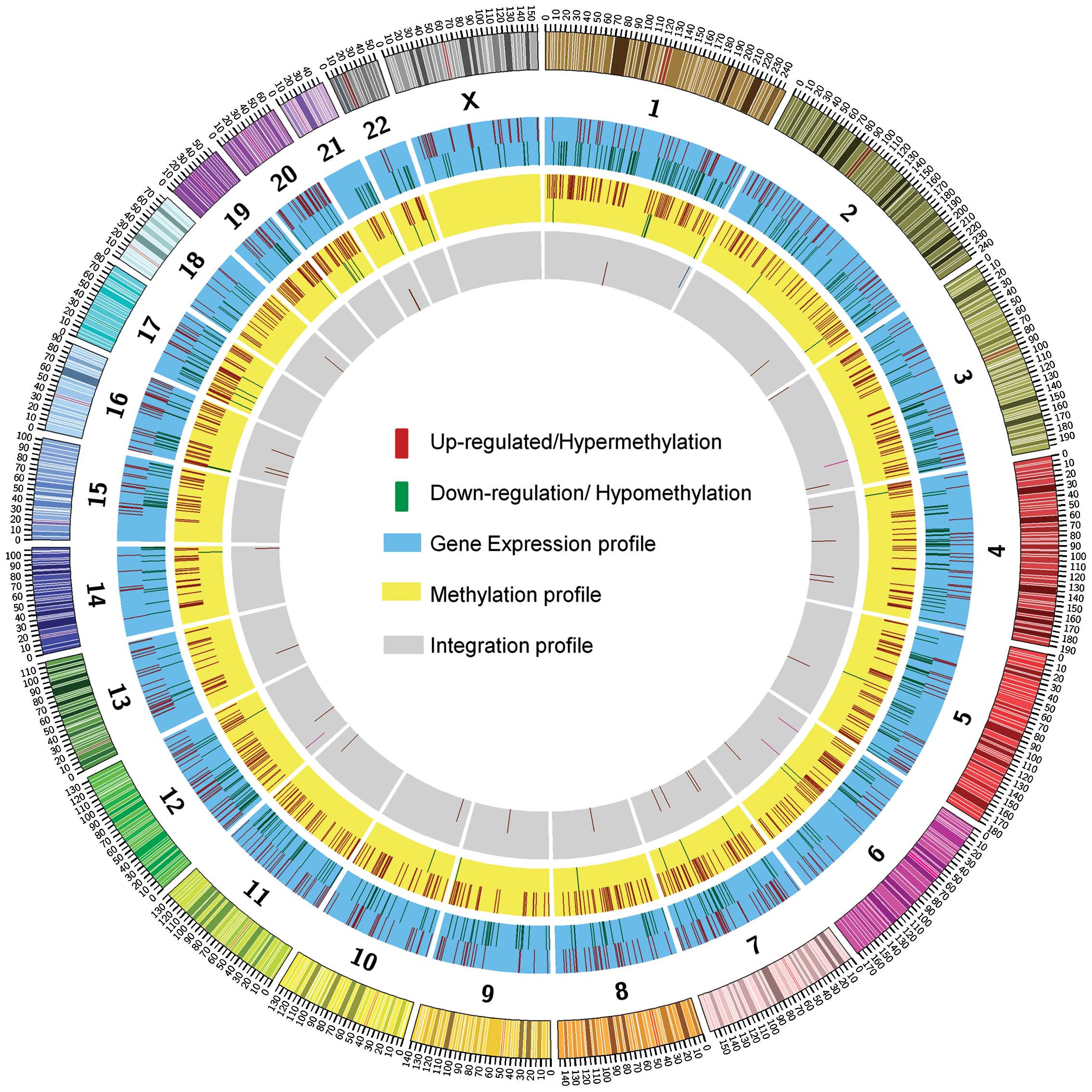
|
1
|
Soon MS, Soon A, Lin TY and Lin OS:
Distribution of colon neoplasia in Chinese patients: Implications
for endoscopic screening strategies. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol.
20:642–647. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sung JJ, Lau JY, Goh KL and Leung WK; Asia
Pacific Working Group on Colorectal Cancer: Increasing incidence of
colorectal cancer in Asia: Implications for screening. Lancet
Oncol. 6:871–876. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yeh CC, Hsieh LL, Tang R, Chang-Chieh CR
and Sung FC: Risk factors for colorectal cancer in Taiwan: A
hospital-based case-control study. J Formos Med Assoc. 102:305–312.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Flamen P, Hoekstra OS, Homans F, Van
Cutsem E, Maes A, Stroobants S, Peeters M, Penninckx F, Filez L,
Bleichrodt RP, et al: Unexplained rising carcinoembryonic antigen
(CEA) in the postoperative surveillance of colorectal cancer: The
utility of positron emission tomography (PET). Eur J Cancer.
37:862–869. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Steele N, Haigh R, Knowles G and Mackean
M: Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) testing in colorectal cancer
follow up: What do patients think? Postgrad Med J. 83:612–614.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Duffy MJ: Carcinoembryonic antigen as a
marker for colo rectal cancer: Is it clinically useful? Clin Chem.
47:624–630. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Leung WK, To KF, Man EP, Chan MW, Bai AH,
Hui AJ, Chan FK, Lee JF and Sung JJ: Detection of epigenetic
changes in fecal DNA as a molecular screening test for colorectal
cancer: A feasibility study. Clin Chem. 50:2179–2182. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Esteller M: Epigenetics in cancer. N Engl
J Med. 358:1148–1159. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Jones PA and Baylin SB: The epigenomics of
cancer. Cell. 128:683–692. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Illingworth RS and Bird AP: CpG islands -
‘a rough guide’. FEBS Lett. 583:1713–1720. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Saxonov S, Berg P and Brutlag DL: A
genome-wide analysis of CpG dinucleotides in the human genome
distinguishes two distinct classes of promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 103:1412–1417. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Baylin SB and Jones PA: A decade of
exploring the cancer epigenome - biological and translational
implications. Nat Rev Cancer. 11:726–734. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lao VV and Grady WM: Epigenetics and
colorectal cancer. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 8:686–700. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hinoue T, Weisenberger DJ, Lange CP, Shen
H, Byun HM, Van Den Berg D, Malik S, Pan F, Noushmehr H, van Dijk
CM, et al: Genome-scale analysis of aberrant DNA methylation in
colorectal cancer. Genome Res. 22:271–282. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
15
|
Bird A: DNA methylation patterns and
epigenetic memory. Genes Dev. 16:6–21. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ballestar E and Esteller M:
Methyl-CpG-binding proteins in cancer: Blaming the DNA methylation
messenger. Biochem Cell Biol. 83:374–384. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Coppede F: Epigenetic biomarkers of
colorectal cancer: Focus on DNA methylation. Cancer Lett.
342:238–247. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Eckhardt F, Lewin J, Cortese R, Rakyan VK,
Attwood J, Burger M, Burton J, Cox TV, Davies R, Down TA, et al:
DNA methylation profiling of human chromosomes 6, 20 and 22. Nat
Genet. 38:1378–1385. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lofton-Day C, Model F, Devos T, Tetzner R,
Distler J, Schuster M, Song X, Lesche R, Liebenberg V, Ebert M, et
al: DNA methylation biomarkers for blood-based colorectal cancer
screening. Clin Chem. 54:414–423. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Ahlquist T, Lind GE, Costa VL, Meling GI,
Vatn M, Hoff GS, Rognum TO, Skotheim RI, Thiis-Evensen E and Lothe
RA: Gene methylation profiles of normal mucosa, and benign and
malignant colorectal tumors identify early onset markers. Mol
Cancer. 7:942008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Ang PW, Loh M, Liem N, Lim PL, Grieu F,
Vaithilingam A, Platell C, Yong WP, Iacopetta B and Soong R:
Comprehensive profiling of DNA methylation in colorectal cancer
reveals subgroups with distinct clinicopathological and molecular
features. BMC Cancer. 10:2272010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang H, Song YC and Dang CX: Detection of
hypermethylated spastic paraplegia-20 in stool samples of patients
with colorectal cancer. Int J Med Sci. 10:230–234. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kibriya MG, Raza M, Jasmine F, Roy S,
Paul-Brutus R, Rahaman R, Dodsworth C, Rakibuz-Zaman M, Kamal M and
Ahsan H: A genome-wide DNA methylation study in colorectal
carcinoma. BMC Med Genomics. 4:502011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Derks S, Postma C, Carvalho B, van den
Bosch SM, Moerkerk PT, Herman JG, Weijenberg MP, de Bruïne AP,
Meijer GA and van Engeland M: Integrated analysis of chromosomal,
micro-satellite and epigenetic instability in colorectal cancer
identifies specific associations between promoter methylation of
pivotal tumour suppressor and DNA repair genes and specific
chromosomal alterations. Carcinogenesis. 29:434–439. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Mo Q, Wang S, Seshan VE, Olshen AB,
Schultz N, Sander C, Powers RS, Ladanyi M and Shen R: Pattern
discovery and cancer gene identification in integrated cancer
genomic data. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 110:4245–4250. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Cancer Genome Atlas Network: Comprehensive
molecular characterization of human colon and rectal cancer.
Nature. 487:330–337. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ramalho-Carvalho J, Pires M, Lisboa S,
Graça I, Rocha P, Barros-Silva JD, Savva-Bordalo J, Maurício J,
Resende M, Teixeira MR, et al: Altered expression of MGMT in
high-grade gliomas results from the combined effect of epigenetic
and genetic aberrations. PLoS One. 8:e582062013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ali Hassan NZ, Mokhtar NM, Kok Sin T,
Mohamed Rose I, Sagap I, Harun R and Jamal R: Integrated analysis
of copy number variation and genome-wide expression profiling in
colorectal cancer tissues. PLoS One. 9:e925532014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kim YH, Lee HC, Kim SY, Yeom YI, Ryu KJ,
Min BH, Kim DH, Son HJ, Rhee PL, Kim JJ, et al: Epigenomic analysis
of aberrantly methylated genes in colorectal cancer identifies
genes commonly affected by epigenetic alterations. Ann Surg Oncol.
18:2338–2347. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lin SY, Yeh KT, Chen WT, Chen HC, Chen ST
and Chang JG: Promoter CpG methylation of caveolin-1 in sporadic
colorectal cancer. Anticancer Res. 24(3a): 1645–1650.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wang DR and Tang D: Hypermethylated SFRP2
gene in fecal DNA is a high potential biomarker for colorectal
cancer noninvasive screening. World J Gastroenterol. 14:524–531.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Oster B, Thorsen K, Lamy P, Wojdacz TK,
Hansen LL, Birkenkamp-Demtröder K, Sørensen KD, Laurberg S, Orntoft
TF and Andersen CL: Identification and validation of highly
frequent CpG island hypermethylation in colorectal adenomas and
carcinomas. Int J Cancer. 129:2855–2866. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lind GE, Raiborg C, Danielsen SA, Rognum
TO, Thiis-Evensen E, Hoff G, Nesbakken A, Stenmark H and Lothe RA:
SPG20, a novel biomarker for early detection of colorectal cancer,
encodes a regulator of cytokinesis. Oncogene. 30:3967–3978. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Mori Y, Cai K, Cheng Y, Wang S, Paun B,
Hamilton JP, Jin Z, Sato F, Berki AT, Kan T, et al: A genome-wide
search identifies epigenetic silencing of somatostatin,
tachykinin-1, and 5 other genes in colon cancer. Gastroenterology.
131:797–808. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chen WF, Gao WD, Li QL, Zhou PH, Xu MD and
Yao LQ: SLIT2 inhibits cell migration in colorectal cancer through
the AKT-GSK3β signaling pathway. Int J Colorectal Dis. 28:933–940.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Jacinto FV, Ballestar E, Ropero S and
Esteller M: Discovery of epigenetically silenced genes by
methylated DNA immuno-precipitation in colon cancer cells. Cancer
Res. 67:11481–11486. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lind GE, Kleivi K, Meling GI, Teixeira MR,
Thiis-Evensen E, Rognum TO and Lothe RA: ADAMTS1, CRABP1, and NR3C1
identified as epigenetically deregulated genes in colorectal
tumorigenesis. Cell Oncol. 28:259–272. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zou H, Harrington JJ, Shire AM, Rego RL,
Wang L, Campbell ME, Oberg AL and Ahlquist DA: Highly methylated
genes in colorectal neoplasia: Implications for screening. Cancer
Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 16:2686–2696. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Syeed N, Hussain F, Husain SA and Siddiqi
MA: 5′-CpG island promoter hypermethylation of the CAV-1 gene in
breast cancer patients of Kashmir. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev.
13:371–375. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Sen M, Ozdemir O, Turan M, Arici S, Yildiz
F, Koksal B and Goze F: Epigenetic inactivation of tumor suppressor
SFRP2 and point mutation in KRAS proto-oncogene in
fistula-associated mucinous type anal adenocarcinoma: Report of two
cases. Intern Med. 49:1637–1640. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Lee SM, Park JY and Kim DS: Methylation of
TMEFF2 gene in tissue and serum DNA from patients with non-small
cell lung cancer. Mol Cells. 34:171–176. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Jin Z, Mori Y, Hamilton JP, Olaru A, Sato
F, Yang J, Ito T, Kan T, Agarwal R and Meltzer SJ: Hypermethylation
of the somatostatin promoter is a common, early event in human
esophageal carcinogenesis. Cancer. 112:43–49. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Beggs AD, Jones A, Shepherd N, Arnaout A,
Finlayson C, Abulafi AM, Morton DG, Matthews GM, Hodgson SV and
Tomlinson IP: Loss of expression and promoter methylation of SLIT2
are associated with sessile serrated adenoma formation. PLoS Genet.
9:e10034882013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Senchenko VN, Krasnov GS, Dmitriev AA,
Kudryavtseva AV, Anedchenko EA, Braga EA, Pronina IV, Kondratieva
TT, Ivanov SV, Zabarovsky ER, et al: Differential expression of
CHL1 gene during development of major human cancers. PLoS One.
6:e156122011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Cai LY, Abe M, Izumi S, Imura M, Yasugi T
and Ushijima T: Identification of PRTFDC1 silencing and aberrant
promoter methylation of GPR150, ITGA8 and HOXD11 in ovarian
cancers. Life Sci. 80:1458–1465. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Bovolenta P, Esteve P, Ruiz JM, Cisneros E
and Lopez-Rios J: Beyond Wnt inhibition: New functions of secreted
Frizzled-related proteins in development and disease. J Cell Sci.
121:737–746. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
MacDonald BT, Tamai K and He X:
Wnt/beta-catenin signaling: Components, mechanisms, and diseases.
Dev Cell. 17:9–26. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Qi J, Zhu YQ, Luo J and Tao WH:
Hypermethylation and expression regulation of secreted
frizzled-related protein genes in colorectal tumor. World J
Gastroenterol. 12:7113–7117. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Bakowska JC, Jupille H, Fatheddin P,
Puertollano R and Blackstone C: Troyer syndrome protein spartin is
mono-ubiquitinated and functions in EGF receptor trafficking. Mol
Biol Cell. 18:1683–1692. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Hooper C, Puttamadappa SS, Loring Z,
Shekhtman A and Bakowska JC: Spartin activates
atrophin-1-interacting protein 4 (AIP4) E3 ubiquitin ligase and
promotes ubiquitination of adipophilin on lipid droplets. BMC Biol.
8:722010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Urdinguio RG, Sanchez-Mut JV and Esteller
M: Epigenetic mechanisms in neurological diseases: Genes,
syndromes, and therapies. Lancet Neurol. 8:1056–1072. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
White WM, Brost B, Sun Z, Rose C, Craici
I, Wagner SJ, Turner ST and Garovic VD: Genome-wide methylation
profiling demonstrates hypermethylation in maternal leukocyte DNA
in preeclamptic compared to normotensive pregnancies. Hypertens
Pregnancy. 32:257–269. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Shen J, Wang S, Zhang YJ, Kappil M, Wu HC,
Kibriya MG, Wang Q, Jasmine F, Ahsan H, Lee PH, et al: Genome-wide
DNA methylation profiles in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology.
55:1799–1808. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Stahl JM, Sharma A, Cheung M, Zimmerman M,
Cheng JQ, Bosenberg MW, Kester M, Sandirasegarane L and Robertson
GP: Deregulated Akt3 activity promotes development of malignant
melanoma. Cancer Res. 64:7002–7010. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Mure H, Matsuzaki K, Kitazato KT,
Mizobuchi Y, Kuwayama K, Kageji T and Nagahiro S: Akt2 and Akt3
play a pivotal role in malignant gliomas. Neuro Oncol. 12:221–232.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Dinger ME, Amaral PP, Mercer TR, Pang KC,
Bruce SJ, Gardiner BB, Askarian-Amiri ME, Ru K, Soldà G, Simons C,
et al: Long noncoding RNAs in mouse embryonic stem cell
pluripotency and differentiation. Genome Res. 18:1433–1445. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Khalil AM, Guttman M, Huarte M, Garber M,
Raj A, Rivea Morales D, Thomas K, Presser A, Bernstein BE, van
Oudenaarden A, et al: Many human large intergenic noncoding RNAs
associate with chromatin-modifying complexes and affect gene
expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:11667–11672. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Zhao J, Ohsumi TK, Kung JT, Ogawa Y, Grau
DJ, Sarma K, Song JJ, Kingston RE, Borowsky M and Lee JT:
Genome-wide identification of polycomb-associated RNAs by RIP-seq.
Mol Cell. 40:939–953. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Amaral PP, Clark MB, Gascoigne DK, Dinger
ME and Mattick JS: lncRNAdb: A reference database for long
noncoding RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 39:D146–D151. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
60
|
Kibler K, Svetz J, Nguyen TL, Shaw C and
Shaulsky G: A cell-adhesion pathway regulates intercellular
communication during Dictyostelium development. Dev Biol.
264:506–521. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Juliano RL: Signal transduction by cell
adhesion receptors and the cytoskeleton: Functions of integrins,
cadherins, selectins, and immunoglobulin-superfamily members. Annu
Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 42:283–323. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Beckman M: CAMs are stopping cancer in its
metastatic tracks. J Natl Cancer Inst. 98:576–577. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Conacci-Sorrell ME, Ben-Yedidia T,
Shtutman M, Feinstein E, Einat P and Ben-Ze’ev A: Nr-CAM is a
target gene of the beta-catenin/LEF-1 pathway in melanoma and colon
cancer and its expression enhances motility and confers
tumorigenesis. Genes Dev. 16:2058–2072. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Li S, Jo YS, Lee JH, Min JK, Lee ES, Park
T, Kim JM and Hong HJ: L1 cell adhesion molecule is a novel
independent poor prognostic factor of extrahepatic
cholangiocarcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 15:7345–7351. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|