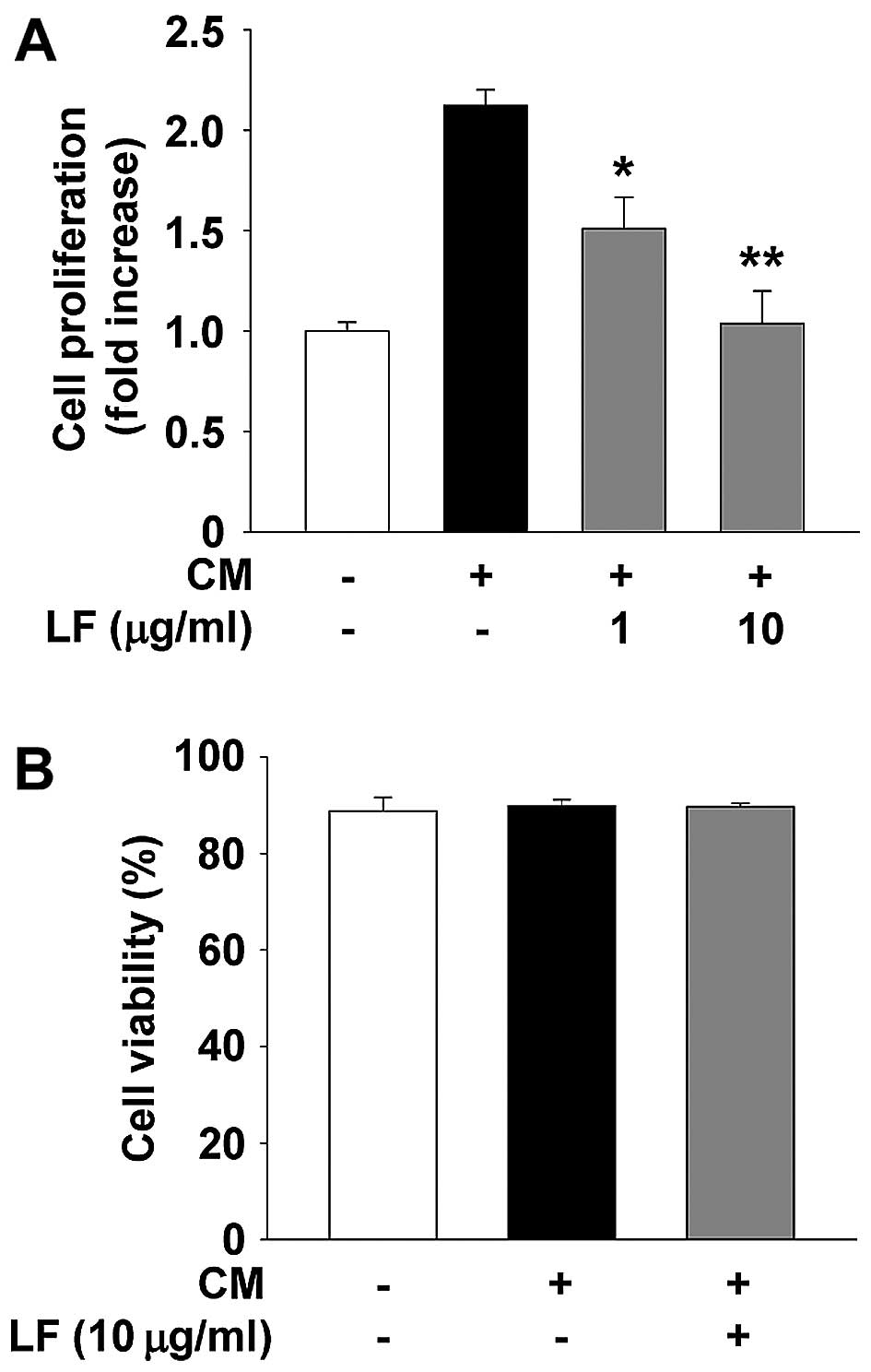
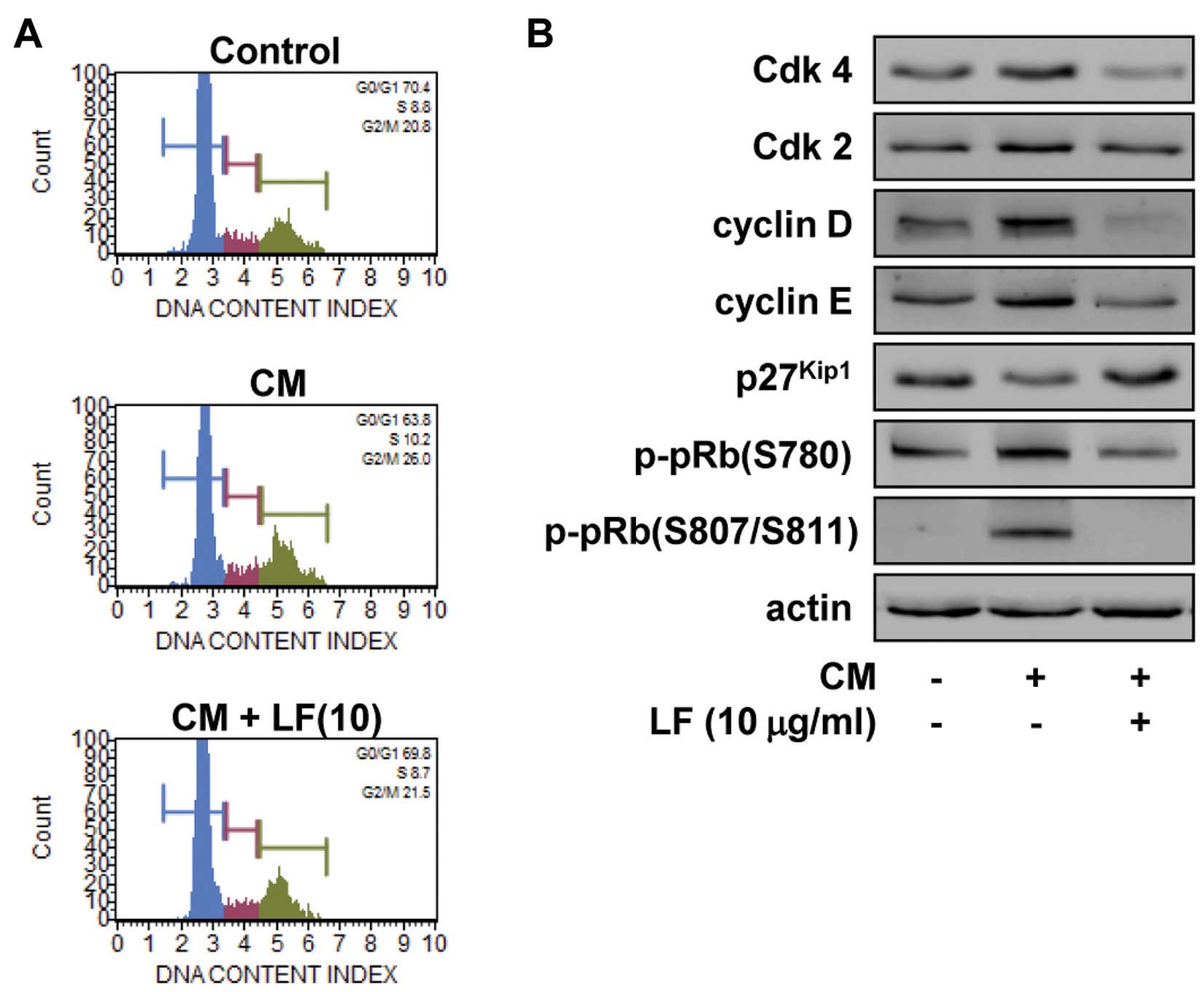
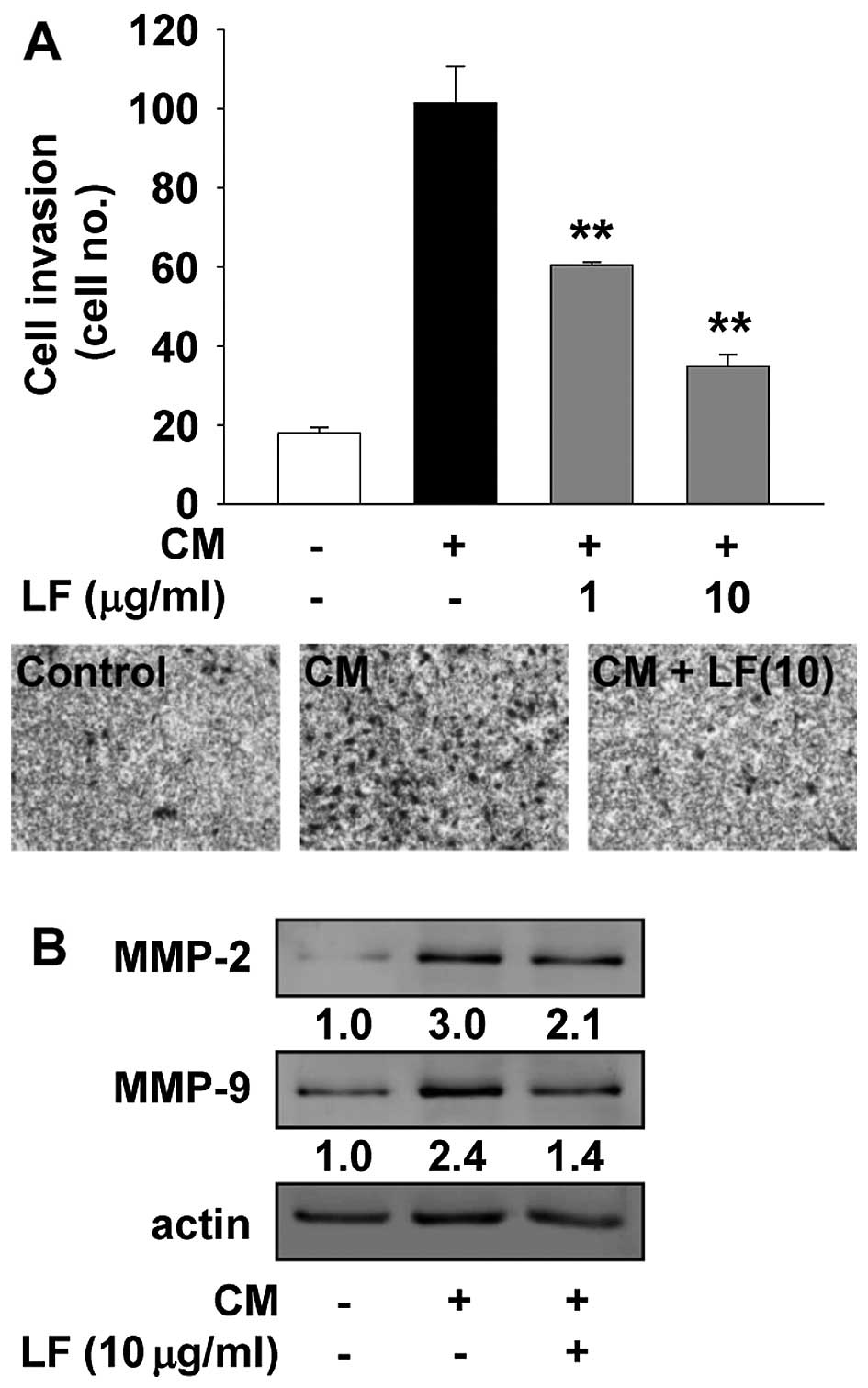
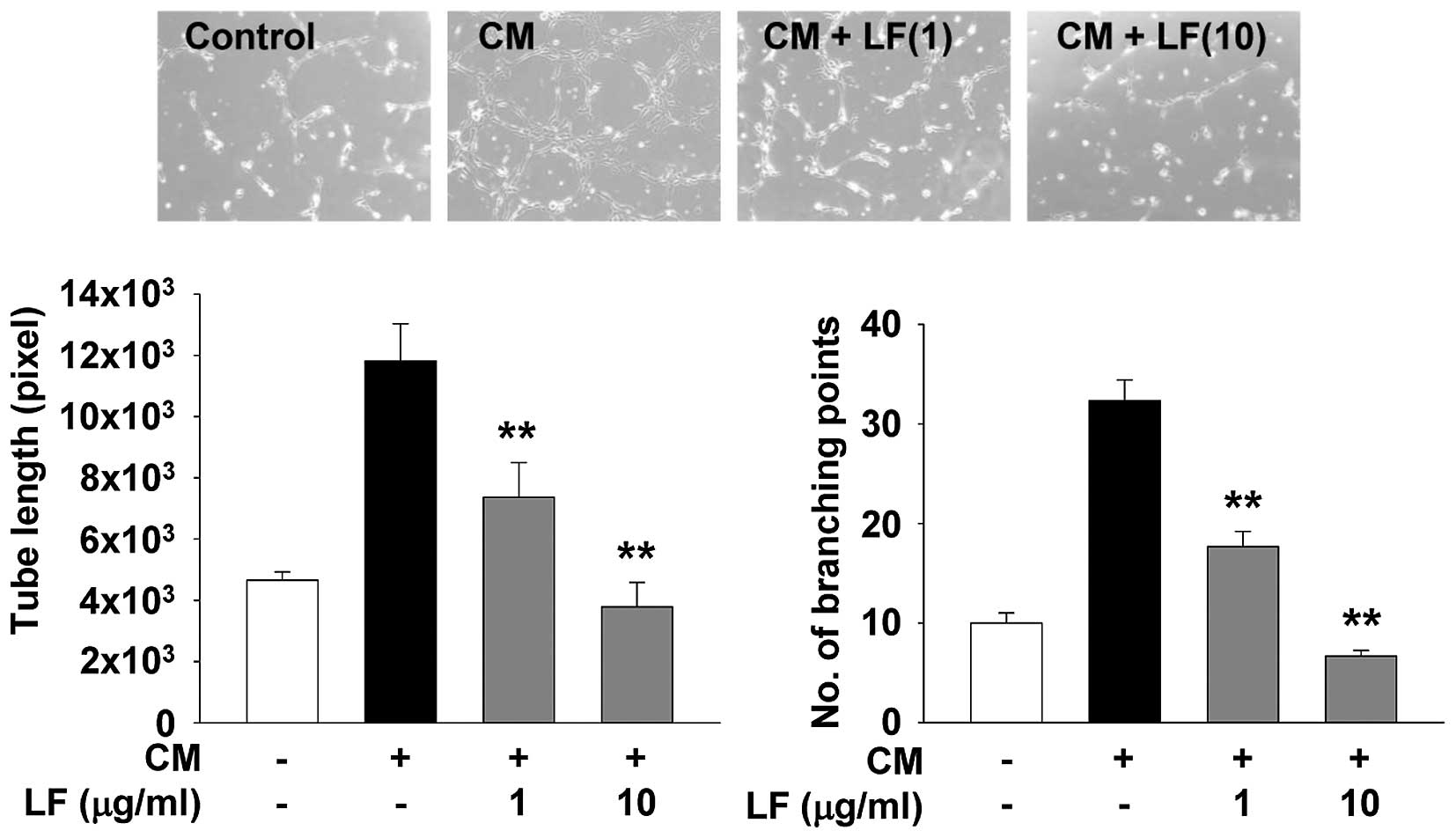
|
1
|
Cristofanilli M, Charnsangavej C and
Hortobagyi GN: Angiogenesis modulation in cancer research: novel
clinical approaches. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 1:415–426. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Folkman J: Angiogenesis: an organizing
principle for drug discovery? Nat Rev Drug Discov. 6:273–286. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Carmeliet P and Jain RK: Principles and
mechanisms of vessel normalization for cancer and other angiogenic
diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 10:417–427. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cook KM and Figg WD: Angiogenesis
inhibitors: current strategies and future prospects. CA Cancer J
Clin. 60:222–243. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Nyberg P, Xie L and Kalluri R: Endogenous
inhibitors of angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 65:3967–3979. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Stetler-Stevenson WG: Matrix
metalloproteinases in angiogenesis: a moving target for therapeutic
intervention. J Clin Invest. 103:1237–1241. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kessenbrock K, Plaks V and Werb Z: Matrix
metalloproteinases: regulators of the tumor microenvironment. Cell.
141:52–67. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bourboulia D and Stetler-Stevenson WG:
Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and tissue inhibitors of
metalloproteinases (TIMPs): positive and negative regulators in
tumor cell adhesion. Semin Cancer Biol. 20:161–168. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Dejana E, Orsenigo F and Lampugnani MG:
The role of adherens junctions and VE-cadherin in the control of
vascular permeability. J Cell Sci. 121:2115–2122. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kim SH, Cho YR, Kim HJ, Oh JS, Ahn EK, Ko
HJ, Hwang BJ, Lee SJ, Cho Y, Kim YK, et al: Antagonism of
VEGF-A-induced increase in vascular per meability by an integrin
α3β1-Shp-1-cAMP/PKA pathway. Blood. 120:4892–4902. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Herren B, Levkau B, Raines EW and Ross R:
Cleavage of beta-catenin and plakoglobin and shedding of
VE-cadherin during endothelial apoptosis: evidence for a role for
caspases and metalloproteinases. Mol Biol Cell. 9:1589–1601. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Grazia Lampugnani M, Zanetti A, Corada M,
Takahashi T, Balconi G, Breviario F, Orsenigo F, Cattelino A,
Kemler R, Daniel TO, et al: Contact inhibition of VEGF-induced
proliferation requires vascular endothelial cadherin, beta-catenin,
and the phosphatase DEP-1/CD148. J Cell Biol. 161:793–804. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
George SJ and Dwivedi A: MMPs, cadherins,
and cell proliferation. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 14:100–105. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Spring K, Chabot C, Langlois S, Lapointe
L, Trinh NT, Caron C, Hebda JK, Gavard J, Elchebly M and Royal I:
Tyrosine phosphorylation of DEP-1/CD148 as a mechanism controlling
Src kinase activation, endothelial cell permeability, invasion, and
capillary formation. Blood. 120:2745–2756. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Brew K and Nagase H: The tissue inhibitors
of metalloproteinases (TIMPs): an ancient family with structural
and functional diversity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1803:55–71. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Seo D-W, Li H, Guedez L, Wingfield PT,
Diaz T, Salloum R, Wei BY and Stetler-Stevenson WG: TIMP-2 mediated
inhibition of angiogenesis: an MMP-independent mechanism. Cell.
114:171–180. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Qi JH, Ebrahem Q, Moore N, Murphy G,
Claesson-Welsh L, Bond M, Baker A and Anand-Apte B: A novel
function for tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-3 (TIMP3):
inhibition of angiogenesis by blockage of VEGF binding to VEGF
receptor-2. Nat Med. 9:407–415. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Jung KK, Liu XW, Chirco R, Fridman R and
Kim HR: Identification of CD63 as a tissue inhibitor of
metalloproteinase-1 interacting cell surface protein. EMBO J.
25:3934–3942. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Seo DW, Li H, Qu CK, Oh J, Kim YS, Diaz T,
Wei B, Han JW and Stetler-Stevenson WG: Shp-1 mediates the
antiproliferative activity of tissue inhibitor of
metalloproteinase-2 in human microvascular endothelial cells. J
Biol Chem. 281:3711–3721. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
20
|
Seo DW, Kim SH, Eom SH, Yoon HJ, Cho YR,
Kim PH, Kim YK, Han JW, Diaz T, Wei BY, et al: TIMP-2 disrupts
FGF-2-induced downstream signaling pathways. Microvasc Res.
76:145–151. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Stetler-Stevenson WG: Tissue inhibitors of
metalloproteinases in cell signaling: metalloproteinase-independent
biological activities. Sci Signal. 1:re62008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Coussens LM, Fingleton B and Matrisian LM:
Matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors and cancer: trials and
tribulations. Science. 295:2387–2392. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Vandenbroucke RE and Libert C: Is there
new hope for therapeutic matrix metalloproteinase inhibition? Nat
Rev Drug Discov. 13:904–927. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hwang BY, Lee JH, Koo TH, Kim HS, Hong YS,
Ro JS, Lee KS and Lee JJ: Furanoligularenone, an eremophilane from
Ligularia fischeri, inhibits the LPS-induced production of nitric
oxide and prostaglandin E2 in macrophage RAW2647 cells. Planta Med.
68:101–105. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lee KH and Choi EM: Analgesic and
anti-inflammatory effects of Ligularia fischeri leaves in
experimental animals. J Ethnopharmacol. 120:103–107. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Choi EM: Ligularia fischeri leaf extract
prevents the oxidative stress in DBA/1J mice with type II
collagen-induced arthritis. J Appl Toxicol. 27:176–182. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Shang YF, Kim SM, Song DG, Pan CH, Lee WJ
and Um BH: Isolation and identification of antioxidant compounds
from Ligularia fischeri. J Food Sci. 75:C530–C535. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Choi J, Park JK, Lee KT, Park KK, Kim WB,
Lee JH, Jung HJ and Park HJ: In vivo antihepatotoxic effects of
Ligularia fischeri var. spiciformis and the identification of the
active component, 3,4-dicaffeoylquinic acid. J Med Food. 8:348–352.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Cha KH, Song DG, Kim SM and Pan CH:
Inhibition of gastrointestinal lipolysis by green tea, coffee, and
gomchui (Ligularia fischeri) tea polyphenols during simulated
digestion. J Agric Food Chem. 60:7152–7157. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Jeong SH, Koo SJ, Choi JH, Park JH, Ha J,
Park HJ and Lee KT: Intermedeol isolated from the leaves of
Ligularia fischeri var. spiciformis induces the differentiation of
human acute promyeocytic leukemia HL-60 cells. Planta Med.
68:881–885. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Xie WD, Li X, Weng CW, Liu SS and Row KH:
Fischerisin A and B, cytotoxic sesquiterpenoid-geranylhydroquinones
from Ligularia fischeri. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 59:511–514. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Cho YR, Kim JK, Kim J, Oh J and Seo DW:
Ligularia fischeri regulates lung cancer cell proliferation and
migration through down-regulation of epidermal growth factor
receptor and integrin β1 expression. Genes Genom. 35:741–746. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Lee HN, Kim JK, Kim JH, Lee SJ, Ahn EK, Oh
JS and Seo DW: A mechanistic study on the anti-cancer activity of
ethyl caffeate in human ovarian cancer SKOV-3 cells. Chem Biol
Interact. 219:151–158. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kim HJ, Cho YR, Kim SH and Seo DW:
TIMP-2-derived 18-mer peptide inhibits endothelial cell
proliferation and migration through cAMP/PKA-dependent mechanism.
Cancer Lett. 343:210–216. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Kim HJ, Ko HY, Choi SW and Seo DW:
Anti-angiogenic effects of Siegesbeckia glabrescens are mediated by
suppression of the Akt and p70S6K-dependent signaling
pathways. Oncol Rep. 33:699–704. 2015.
|
|
36
|
Cho YR, Choi SW and Seo DW: The in vitro
antitumor activity of Siegesbeckia glabrescens against ovarian
cancer through suppression of receptor tyrosine kinase expression
and the signaling pathways. Oncol Rep. 30:221–226. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lee HN, Joo JH, Oh JS, Choi SW and Seo DW:
Regulatory effects of Siegesbeckia glabrescens on non-small cell
lung cancer cell proliferation and invasion. Am J Chin Med.
42:453–463. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Yoon HJ, Cho YR, Joo JH and Seo DW:
Knockdown of integrin α3β1 expression induces proliferation and
migration of non-small cell lung cancer cells. Oncol Rep.
29:662–668. 2013.
|
|
39
|
Cho YR, Kim JH, Kim JK, Ahn EK, Ko HJ, In
JK, Lee SJ, Bae GU, Kim YK, Oh JS, et al: Broussonetia kazinoki
modulates the expression of VEGFR-2 and MMP-2 through the
inhibition of ERK, Akt and p70S6K-dependent signaling
pathways: its implication in endothelial cell proliferation,
migration and tubular formation. Oncol Rep. 32:1531–1536.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Lemmon MA and Schlessinger J: Cell
signaling by receptor tyrosine kinases. Cell. 141:1117–1134. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|