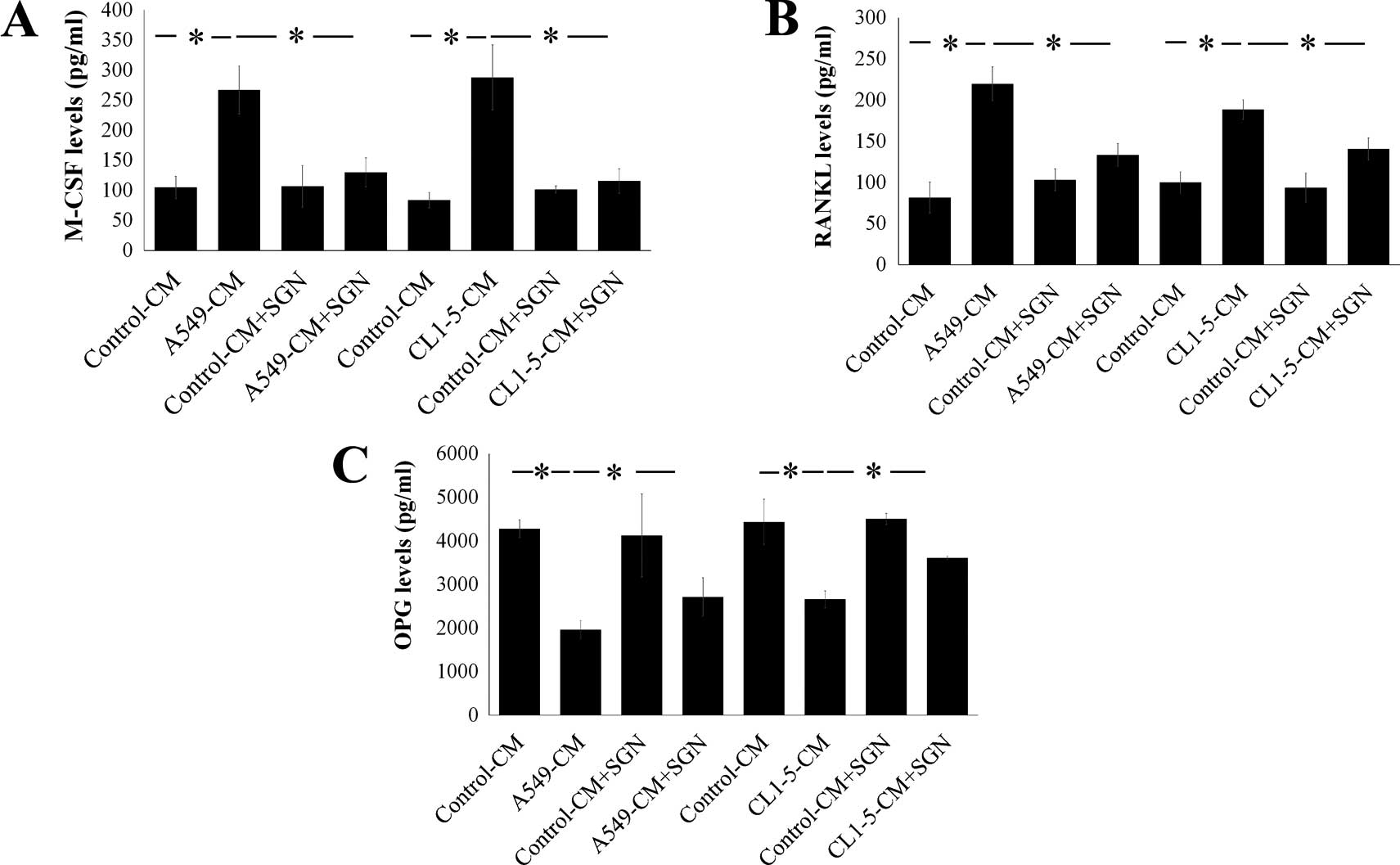
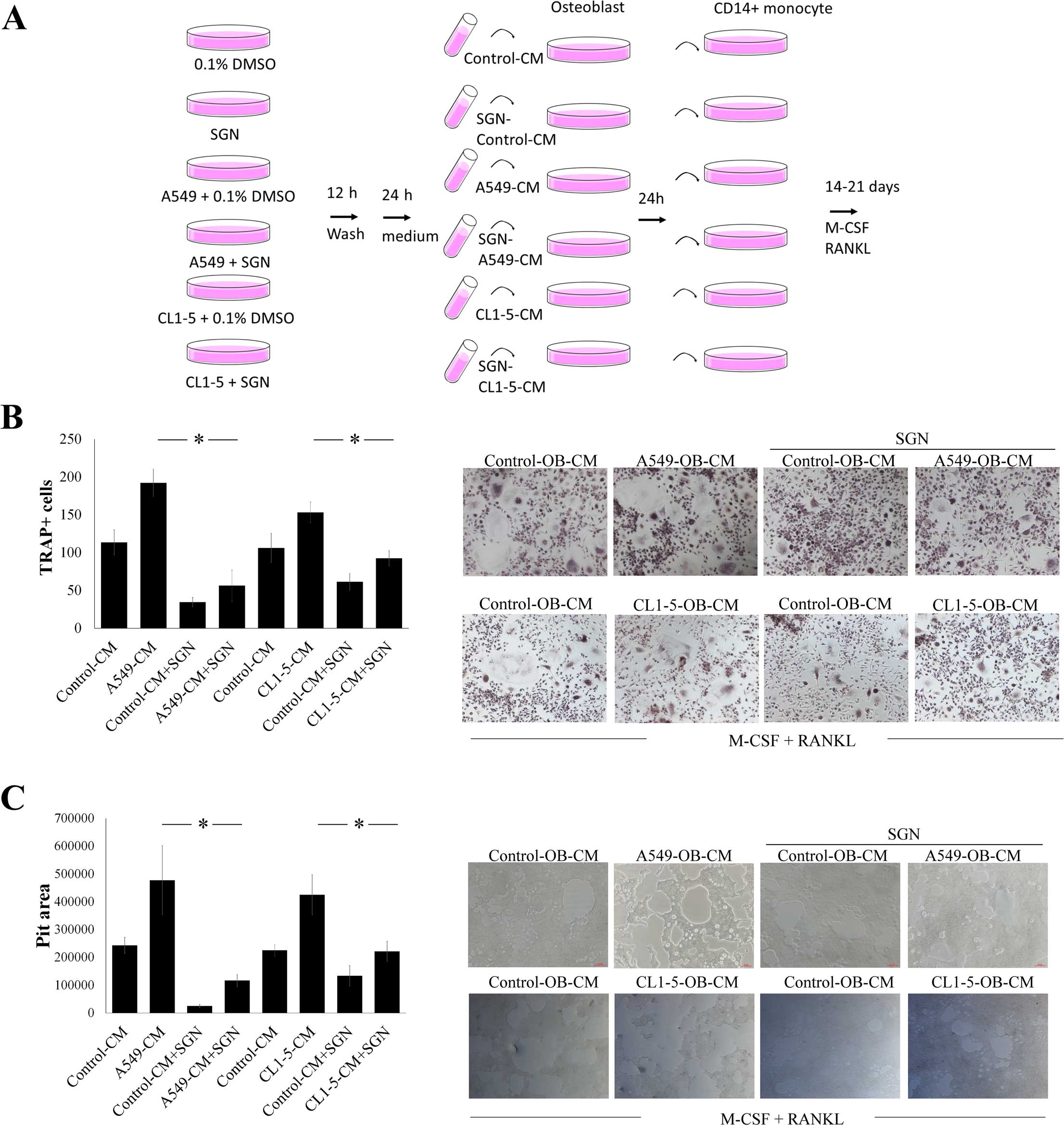
|
1
|
Siegel R, Ward E, Brawley O and Jemal A:
Cancer statistics, 2011: The impact of eliminating socioeconomic
and racial disparities on premature cancer deaths. CA Cancer J
Clin. 61:212–236. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zükin M: Epidermal growth factor receptor
inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer: Current status and future
perspectives. Rev Assoc Med Bras. 58:263–268. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kuo PL, Liao SH, Hung JY, Huang MS and Hsu
YL: MicroRNA-33a functions as a bone metastasis suppressor in lung
cancer by targeting parathyroid hormone related protein. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1830:3756–3766. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Al Husaini H, Wheatley-Price P, Clemons M
and Shepherd FA: Prevention and management of bone metastases in
lung cancer: A review. J Thorac Oncol. 4:251–259. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hirsh V, Major PP, Lipton A, Cook RJ,
Langer CJ, Smith MR, Brown JE and Coleman RE: Zoledronic acid and
survival in patients with metastatic bone disease from lung cancer
and elevated markers of osteoclast activity. J Thorac Oncol.
3:228–236. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sterling JA, Edwards JR, Martin TJ and
Mundy GR: Advances in the biology of bone metastasis: How the
skeleton affects tumor behavior. Bone. 48:6–15. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Sims NA and Gooi JH: Bone remodeling:
Multiple cellular interactions required for coupling of bone
formation and resorption. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 19:444–451. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Miller RE, Jones JC, Tometsko M, Blake ML
and Dougall WC: RANKL inhibition blocks osteolytic lesions and
reduces skeletal tumor burden in models of non-small-cell lung
cancer bone metastases. J Thorac Oncol. 9:345–354. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Pawelek JM and Chakraborty AK: The cancer
cell - leukocyte fusion theory of metastasis. Adv Cancer Res.
101:397–444. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Roato I: Interaction among cells of bone,
immune system, and solid tumors leads to bone metastases. Clin Dev
Immunol. 2013:3150242013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Burger JA and Stewart DJ: CXCR4 chemokine
receptor antagonists: Perspectives in SCLC. Expert Opin Investig
Drugs. 18:481–490. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hsieh CJ, Kuo PL, Hou MF, Hung JY, Chang
FR, Hsu YC, Huang YF, Tsai EM and Hsu YL: Wedelolactone inhibits
breast cancer-induced osteoclastogenesis by decreasing Akt/mTOR
signaling. Int J Oncol. 46:555–562. 2015.
|
|
13
|
Cai Z, Chen Q, Chen J, Lu Y, Xiao G, Wu Z,
Zhou Q and Zhang J: Monocyte chemotactic protein 1 promotes lung
cancer-induced bone resorptive lesions in vivo. Neoplasia.
11:228–236. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Takiguchi S, Korenaga N, Inoue K, Sugi E,
Kataoka Y, Matsusue K, Futagami K, Li YJ, Kukita T, Teramoto N, et
al: Involvement of CXCL14 in osteolytic bone metastasis from lung
cancer. Int J Oncol. 44:1316–1324. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hsu YL, Hung JY, Ko YC, Hung CH, Huang MS
and Kuo PL: Phospholipase D signaling pathway is involved in lung
cancer-derived IL-8 increased osteoclastogenesis. Carcinogenesis.
31:587–596. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Flamini R, Mattivi F, De Rosso M,
Arapitsas P and Bavaresco L: Advanced knowledge of three important
classes of grape phenolics: Anthocyanins, stilbenes and flavonols.
Int J Mol Sci. 14:19651–19669. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Rimando AM, Kalt W, Magee JB, Dewey J and
Ballington JR: Resveratrol, pterostilbene, and piceatannol in
vaccinium berries. J Agric Food Chem. 52:4713–4719. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Pan MH, Chang YH, Tsai ML, Lai CS, Ho SY,
Badmaev V and Ho CT: Pterostilbene suppressed
lipopolysaccharide-induced up-expression of iNOS and COX-2 in
murine macrophages. J Agric Food Chem. 56:7502–7509. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Pan MH, Chang YH, Badmaev V, Nagabhushanam
K and Ho CT: Pterostilbene induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest
in human gastric carcinoma cells. J Agric Food Chem. 55:7777–7785.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Pan MH, Chiou YS, Chen WJ, Wang JM,
Badmaev V and Ho CT: Pterostilbene inhibited tumor invasion via
suppressing multiple signal transduction pathways in human
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Carcinogenesis. 30:1234–1242. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Pan MH, Lin YT, Lin CL, Wei CS, Ho CT and
Chen WJ: Suppression of heregulin-β1/HER2-modulated invasive and
aggressive phenotype of breast carcinoma by pterostilbene via
inhibition of matrix metalloproteinase-9, p38 kinase cascade and
Akt activation. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2011:5621872011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Chiou YS, Tsai ML, Wang YJ, Cheng AC, Lai
WM, Badmaev V, Ho CT and Pan MH: Pterostilbene inhibits colorectal
aberrant crypt foci (ACF) and colon carcinogenesis via suppression
of multiple signal transduction pathways in azoxymethane-treated
mice. J Agric Food Chem. 58:8833–8841. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chiou YS, Tsai ML, Nagabhushanam K, Wang
YJ, Wu CH, Ho CT and Pan MH: Pterostilbene is more potent than
resveratrol in preventing azoxymethane (AOM)-induced colon
tumorigenesis via activation of the NF-E2-related factor 2
(Nrf2)-mediated antioxidant signaling pathway. J Agric Food Chem.
59:2725–2733. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chen RJ, Tsai SJ, Ho CT, Pan MH, Ho YS, Wu
CH and Wang YJ: Chemopreventive effects of pterostilbene on
urethane-induced lung carcinogenesis in mice via the inhibition of
EGFR-mediated pathways and the induction of apoptosis and
autophagy. J Agric Food Chem. 60:11533–11541. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Mühlbauer RC, Lozano A, Reinli A and Wetli
H: Various selected vegetables, fruits, mushrooms and red wine
residue inhibit bone resorption in rats. J Nutr. 133:3592–3597.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Singh H, Dixit S, Verma PC and Singh PK:
Evaluation of total phenolic compounds and insecticidal and
antioxidant activities of tomato hairy root extract. J Agric Food
Chem. 62:2588–2594. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Mattivi F, Guzzon R, Vrhovsek U, Stefanini
M and Velasco R: Metabolite profiling of grape: Flavonols and
anthocyanins. J Agric Food Chem. 54:7692–7702. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang H, Race EJ and Shrikhande AJ:
Anthocyanin transformation in Cabernet Sauvignon wine during aging.
J Agric Food Chem. 51:7989–7994. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Castillo-Muñoz N, Gómez-Alonso S,
García-Romero E and Hermosín-Gutiérrez I: Flavonol profiles of
Vitis vinifera red grapes and their single-cultivar wines. J Agric
Food Chem. 55:992–1002. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Castillo-Muñoz N, Gómez-Alonso S,
García-Romero E, Gómez MV, Velders AH and Hermosín-Gutiérrez I:
Flavonol 3-O-glycosides series of Vitis vinifera Cv. Petit Verdot
red wine grapes. J Agric Food Chem. 57:209–219. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Gómez-Alonso S, Collins VJ, Vauzour D,
Rodríguez-Mateos A, Corona G and Spencer JPE: Inhibition of colon
adenocarcinoma cell proliferation by flavonols is linked to a G2/M
cell cycle block and reduction in cyclin D1 expression. Food Chem.
130:493–500. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Hsu YL, Liang HL, Hung CH and Kuo PL:
Syringetin, a flavonoid derivative in grape and wine, induces human
osteoblast differentiation through bone morphogenetic
protein-2/extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 pathway. Mol
Nutr Food Res. 53:1452–1461. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Chen HW, Lee JY, Huang JY, Wang CC, Chen
WJ, Su SF, Huang CW, Ho CC, Chen JJ, Tsai MF, et al: Curcumin
inhibits lung cancer cell invasion and metastasis through the tumor
suppressor HLJ1. Cancer Res. 68:7428–7438. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chu YW, Yang PC, Yang SC, Shyu YC, Hendrix
MJ, Wu R and Wu CW: Selection of invasive and metastatic
subpopulations from a human lung adenocarcinoma cell line. Am J
Respir Cell Mol Biol. 17:353–360. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Sambandam Y, Sundaram K, Liu A, Kirkwood
KL, Ries WL and Reddy SV: CXCL13 activation of c-Myc induces RANK
ligand expression in stromal/preosteoblast cells in the oral
squamous cell carcinoma tumor-bone microenvironment. Oncogene.
32:97–105. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Wu X, Liu T, Fang O, Leach LJ, Hu X and
Luo Z: miR-194 suppresses metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer
through regulating expression of BMP1 and p27kip1.
Oncogene. 33:1506–1514. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Hernández I, Moreno JL, Zandueta C,
Montuenga L and Lecanda F: Novel alternatively spliced ADAM8
isoforms contribute to the aggressive bone metastatic phenotype of
lung cancer. Oncogene. 29:3758–3769. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Sone S and Yano S: Molecular pathogenesis
and its therapeutic modalities of lung cancer metastasis to bone.
Cancer Metastasis Rev. 26:685–689. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Weilbaecher KN, Guise TA and McCauley LK:
Cancer to bone: A fatal attraction. Nat Rev Cancer. 11:411–425.
2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Coleman RE and McCloskey EV:
Bisphosphonates in oncology. Bone. 49:71–76. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Furugaki K, Moriya Y, Iwai T, Yorozu K,
Yanagisawa M, Kondoh K, Fujimoto-Ohuchi K and Mori K: Erlotinib
inhibits osteolytic bone invasion of human non-small-cell lung
cancer cell line NCI-H292. Clin Exp Metastasis. 28:649–659. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Hsu YL, Huang MS, Yang CJ, Hung JY, Wu LY
and Kuo PL: Lung tumor-associated osteoblast-derived bone
morphogenetic protein-2 increased epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition of cancer by Runx2/Snail signaling pathway. J Biol Chem.
286:37335–37346. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Takayanagi H: New immune connections in
osteoclast formation. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1192:117–123. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Mountzios G, Dimopoulos MA, Bamias A,
Papadopoulos G, Kastritis E, Syrigos K, Pavlakis G and Terpos E:
Abnormal bone remodeling process is due to an imbalance in the
receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappaB ligand
(RANKL)/osteoprotegerin (OPG) axis in patients with solid tumors
metastatic to the skeleton. Acta Oncol. 46:221–229. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
McGrath EE: OPG/RANKL/RANK pathway as a
therapeutic target in cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 6:1468–1473. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Skeen JE, Bhaskar PT, Chen CC, Chen WS,
Peng XD, Nogueira V, Hahn-Windgassen A, Kiyokawa H and Hay N: Akt
deficiency impairs normal cell proliferation and suppresses
oncogenesis in a p53-independent and mTORC1-dependent manner.
Cancer Cell. 10:269–280. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Moon JB, Kim JH, Kim K, Youn BU, Ko A, Lee
SY and Kim N: Akt induces osteoclast differentiation through
regulating the GSK3β/NFATc1 signaling cascade. J Immunol.
188:163–169. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Cao H, Zhu K, Qiu L, Li S, Niu H, Hao M,
Yang S, Zhao Z, Lai Y, Anderson JL, et al: Critical role of AKT
protein in myeloma-induced osteoclast formation and osteolysis. J
Biol Chem. 288:30399–30410. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Sugatani T and Hruska KA: Akt1/Akt2 and
mammalian target of rapamycin/Bim play critical roles in osteoclast
differentiation and survival, respectively, whereas Akt is
dispensable for cell survival in isolated osteoclast precursors. J
Biol Chem. 280:3583–3589. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Sanchez CP and He YZ: Bone growth during
rapamycin therapy in young rats. BMC Pediatr. 9:32009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|