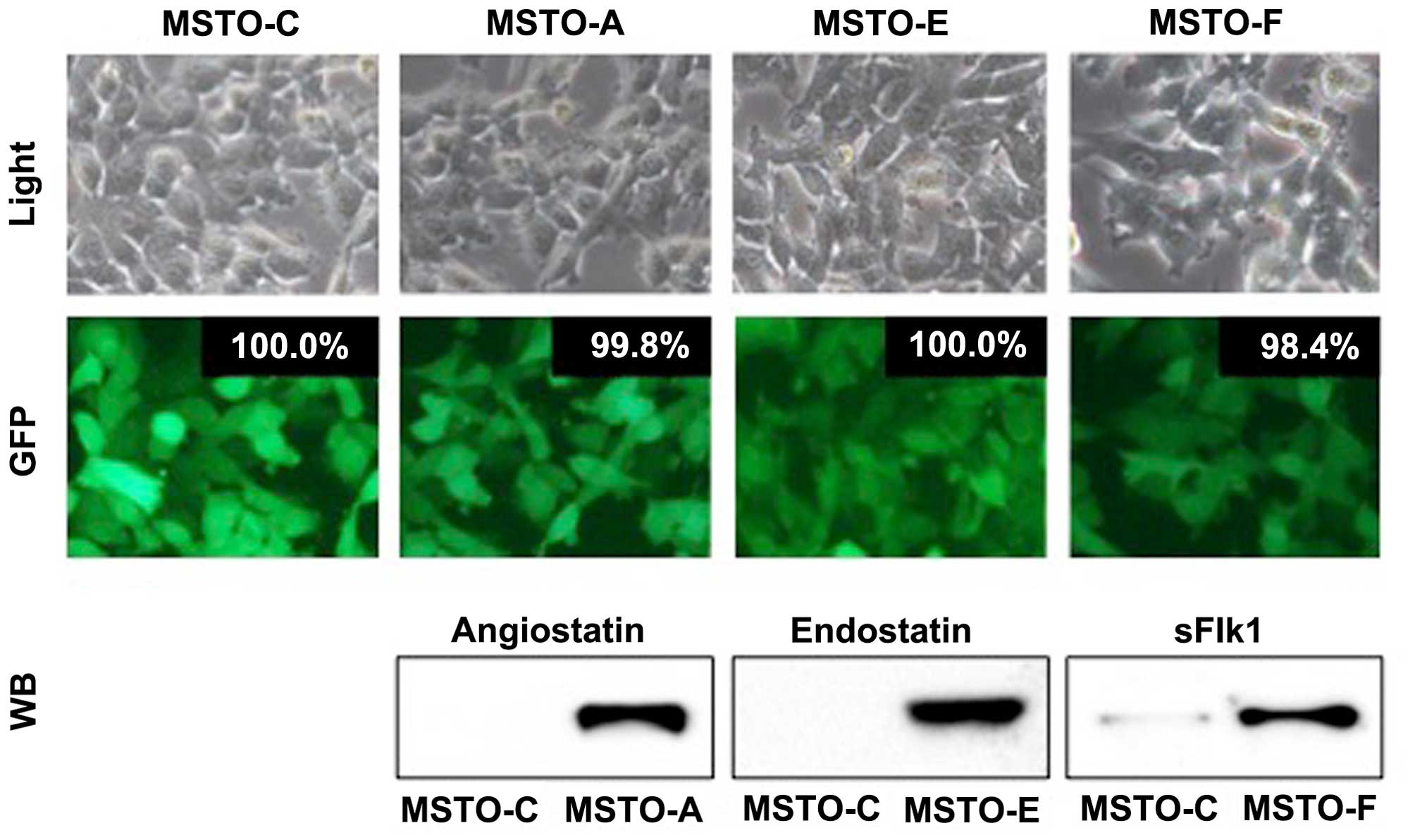
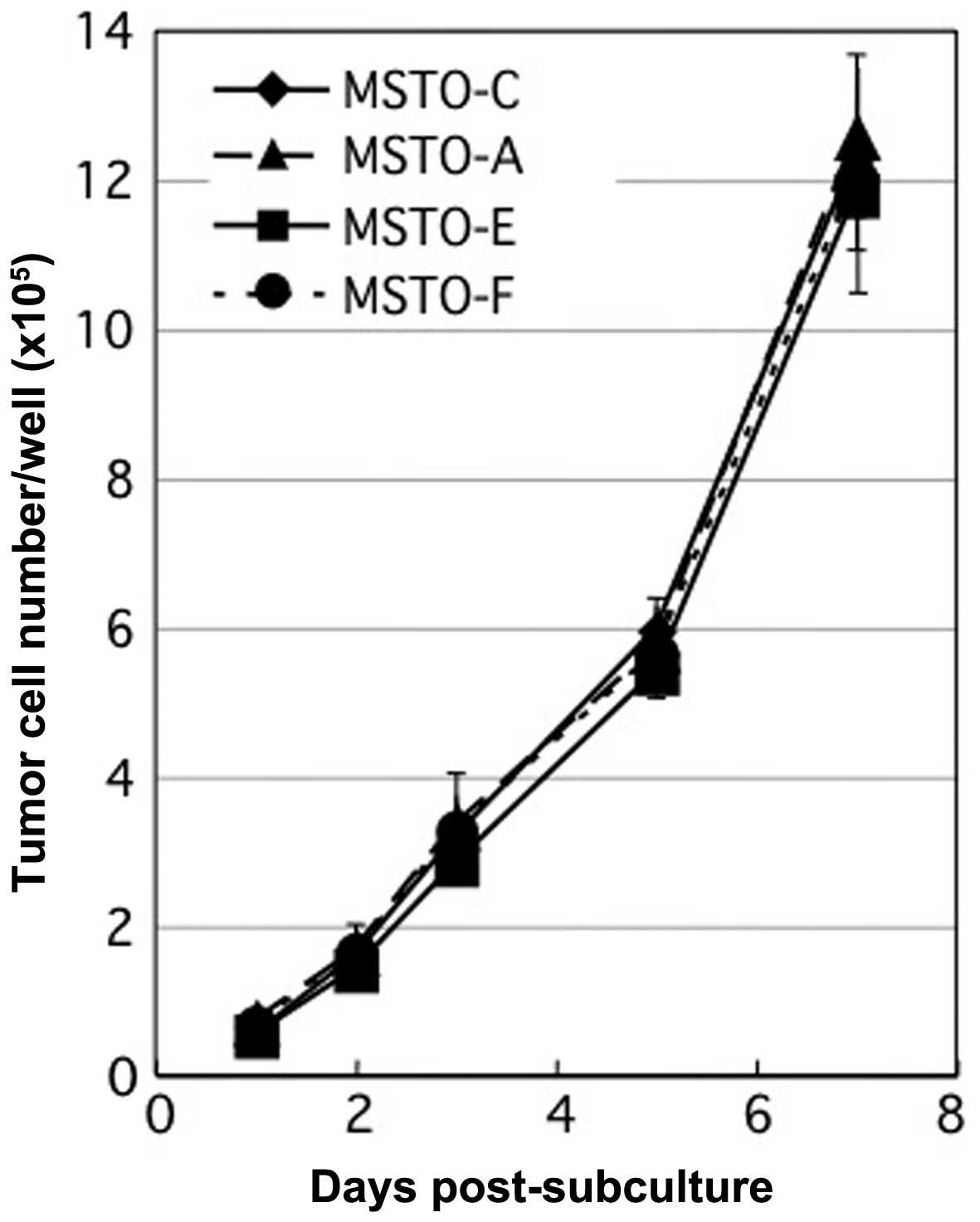
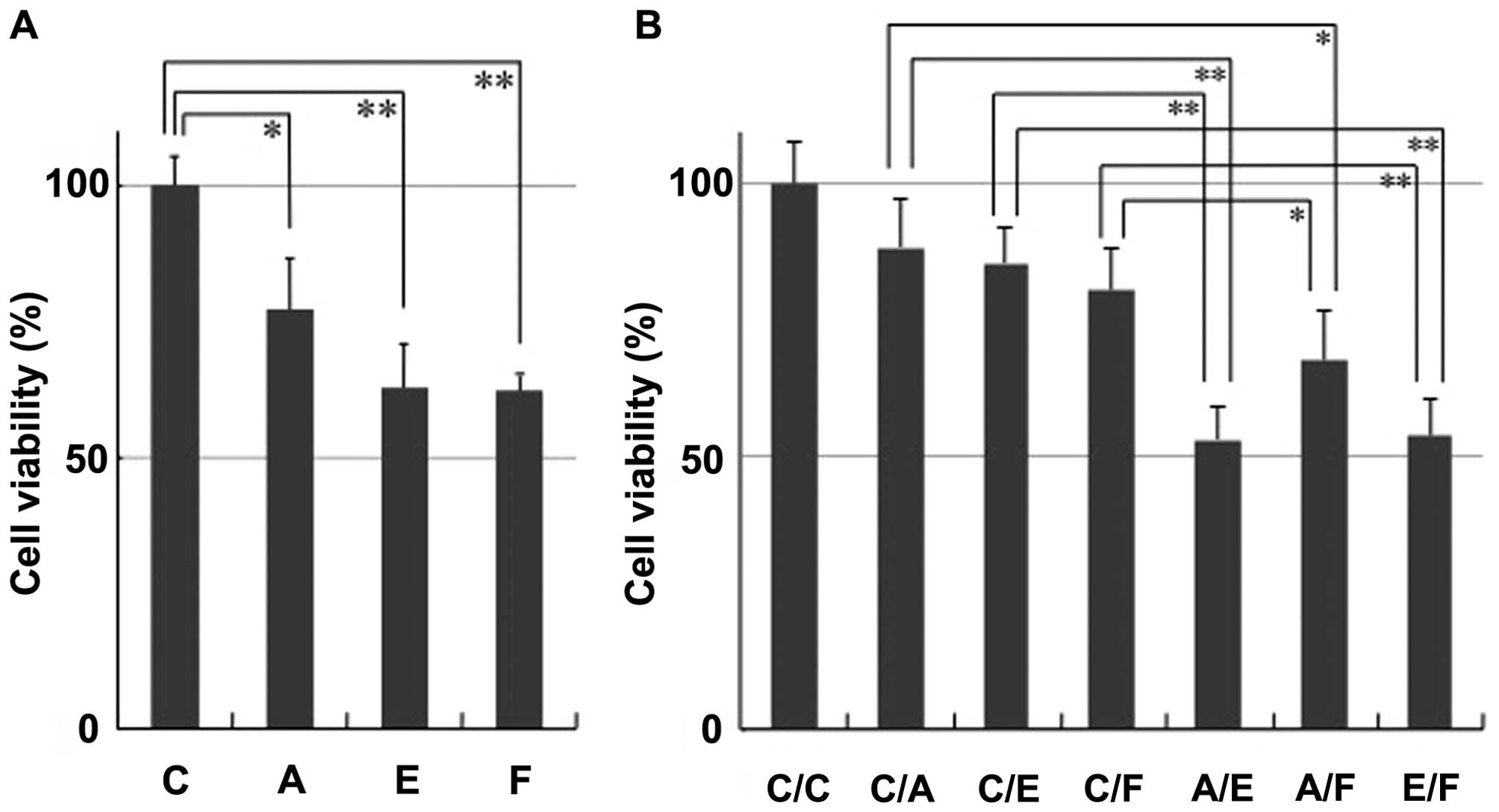
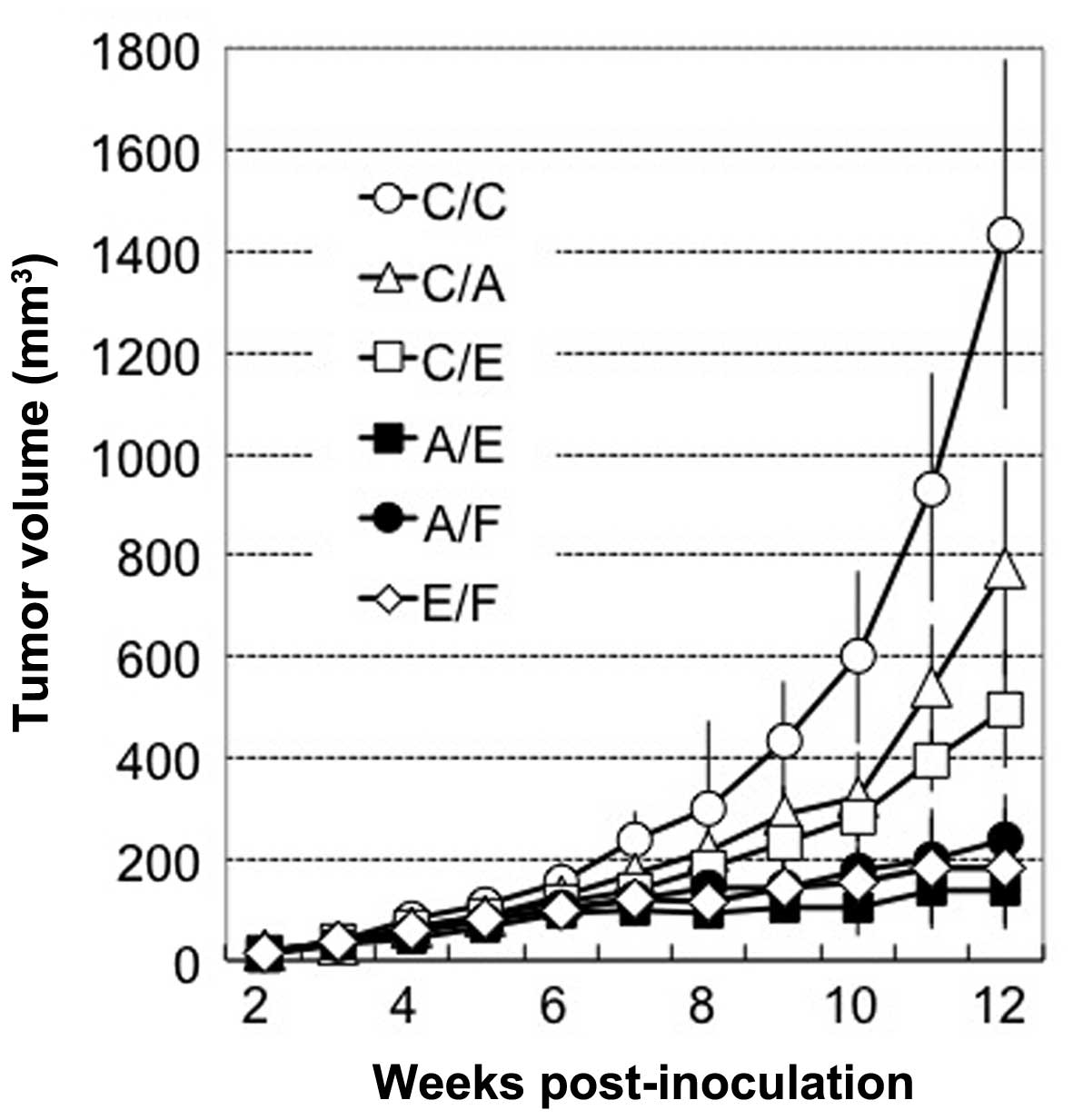
|
1
|
Ismail-Khan R, Robinson LA, Williams CC
Jr, Garrett CR, Bepler G and Simon GR: Malignant pleural
mesothelioma: A comprehensive review. Cancer Control. 13:255–263.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Tsao AS, Wistuba I, Roth JA and Kindler
HL: Malignant pleural mesothelioma. J Clin Oncol. 27:2081–2090.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
van der Most RG, Robinson BW and Nelson
DJ: Gene therapy for malignant mesothelioma: Beyond the infant
years. Cancer Gene Ther. 13:897–904. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kotova S, Wong RM and Cameron RB: New and
emerging therapeutic options for malignant pleural mesothelioma:
Review of early clinical trials. Cancer Manag Res. 7:51–63.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Weis SM and Cheresh DA: Tumor
angiogenesis: Molecular pathways and therapeutic targets. Nat Med.
17:1359–1370. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Redlitz A, Daum G and Sage EH: Angiostatin
diminishes activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinases
ERK-1 and ERK-2 in human dermal microvascular endothelial cells. J
Vasc Res. 36:28–34. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
O’reilly MS, Holmgren L, Shing Y, Chen C,
Rosenthal RA, Moses M, Lane WS, Cao Y, Sage EH and Folkman J:
Angiostatin: A novel angiogenesis inhibitor that mediates the
suppression of metastases by a Lewis lung carcinoma. Cell.
79:315–328. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Shichinohe T, Bochner BH, Mizutani K,
Nishida M, Hegerich-Gilliam S, Naldini L and Kasahara N:
Development of lentiviral vectors for antiangiogenic gene delivery.
Cancer Gene Ther. 8:879–889. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
O’reilly MS, Boehm T, Shing Y, Fukai N,
Vasios G, Lane WS, Flynn E, Birkhead JR, Olsen BR and Folkman J:
Endostatin: An endogenous inhibitor of angiogenesis and tumor
growth. Cell. 88:277–285. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Kuo CJ, Farnebo F, Yu EY, Christofferson
R, Swearingen RA, Carter R, von Recum HA, Yuan J, Kamihara J, Flynn
E, et al: Comparative evaluation of the antitumor activity of
antiangiogenic proteins delivered by gene transfer. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 98:4605–4610. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Szentirmai O, Baker CH, Bullain SS, Lin N,
Takahashi M, Folkman J, Mulligan RC and Carter BS: Successful
inhibition of intracranial human glioblastoma multiforme xenograft
growth via systemic adenoviral delivery of soluble endostatin and
soluble vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2: Laboratory
investigation. J Neurosurg. 108:979–988. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wu Y, Li ZY, Zhao X, Kan B and Wei YQ:
Inhibition of ovarian tumor growth by gene therapy with recombinant
soluble vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2. Hum Gene
Ther. 17:941–948. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zucali PA, Ceresoli GL, De Vincenzo F,
Simonelli M, Lorenzi E, Gianoncelli L and Santoro A: Advances in
the biology of malignant pleural mesothelioma. Cancer Treat Rev.
37:543–558. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Remon J, Lianes P, Martínez S, Velasco M,
Querol R and Zanui M: Malignant mesothelioma: New insights into a
rare disease. Cancer Treat Rev. 39:584–591. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Strizzi L, Catalano A, Vianale G, Orecchia
S, Casalini A, Tassi G, Puntoni R, Mutti L and Procopio A: Vascular
endothelial growth factor is an autocrine growth factor in human
malignant mesothelioma. J Pathol. 193:468–475. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kumar-Singh S, Weyler J, Martin MJ,
Vermeulen PB and Van Marck E: Angiogenic cytokines in mesothelioma:
A study of VEGF, FGF-1 and -2, and TGF beta expression. J Pathol.
189:72–78. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yasumitsu A, Tabata C, Tabata R, Hirayama
N, Murakami A, Yamada S, Terada T, Iida S, Tamura K, Fukuoka K, et
al: Clinical significance of serum vascular endothelial growth
factor in malignant pleural mesothelioma. J Thorac Oncol.
5:479–483. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kourlas H and Abrams P: Ranibizumab for
the treatment of neovascular age-related macular degeneration: A
review. Clin Ther. 29:1850–1861. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jenab-Wolcott J and Giantonio BJ:
Bevacizumab: Current indications and future development for
management of solid tumors. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 9:507–517. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Langer C and Soria JC: The role of
anti-epidermal growth factor receptor and anti-vascular endothelial
growth factor therapies in the treatment of non-small-cell lung
cancer. Clin Lung Cancer. 11:82–90. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ceresoli GL, Zucali PA, Mencoboni M, Botta
M, Grossi F, Cortinovis D, Zilembo N, Ripa C, Tiseo M, Favaretto
AG, et al: Phase II study of pemetrexed and carboplatin plus
bevacizumab as first-line therapy in malignant pleural
mesothelioma. Br J Cancer. 109:552–558. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Dowell JE, Dunphy FR, Taub RN, Gerber DE,
Ngov L, Yan J, Xie Y and Kindler HL: A multicenter phase ii study
of cisplatin, pemetrexed, and bevacizumab in patients with advanced
malignant mesothelioma. Lung Cancer. 77:567–571. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kubo S and Mitani K: A new hybrid system
capable of efficient lentiviral vector production and stable gene
transfer mediated by a single helper-dependent adenoviral vector. J
Virol. 77:2964–2971. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kubo S, Seleme MC, Soifer HS, Perez JL,
Moran JV, Kazazian HH Jr and Kasahara N: L1 retrotransposition in
non-dividing and primary human somatic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 103:8036–8041. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Takahashi S: Vascular endothelial growth
factor (VEGF), VEGF receptors and their inhibitors for
antiangiogenic tumor therapy. Biol Pharm Bull. 34:1785–1788. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Bougatef F, Quemener C, Kellouche S, Naïmi
B, Podgorniak MP, Millot G, Gabison EE, Calvo F, Dosquet C, Lebbé
C, et al: EMMPRIN promotes angiogenesis through hypoxia-inducible
factor-2alpha-mediated regulation of soluble VEGF isoforms and
their receptor VEGFR-2. Blood. 114:5547–5556. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lee S, Chen TT, Barber CL, Jordan MC,
Murdock J, Desai S, Ferrara N, Nagy A, Roos KP and Iruela-Arispe
ML: Autocrine VEGF signaling is required for vascular homeostasis.
Cell. 130:691–703. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Robinson CJ and Stringer SE: The splice
variants of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and their
receptors. J Cell Sci. 114:853–865. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Li Q, Yano S, Ogino H, Wang W, Uehara H,
Nishioka Y and Sone S: The therapeutic efficacy of anti vascular
endothelial growth factor antibody, bevacizumab, and pemetrexed
against orthotopically implanted human pleural mesothelioma cells
in severe combined immunodeficient mice. Clin Cancer Res.
13:5918–5925. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kawasaki Y, Tamamoto A, Takagi-Kimura M,
Maeyama Y, Yamaoka N, Terada N, Okamura H, Kasahara N and Kubo S:
Replication-competent retrovirus vector-mediated prodrug activator
gene therapy in experimental models of human malignant
mesothelioma. Cancer Gene Ther. 18:571–578. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kubo S, Takagi-Kimura M, Logg CR and
Kasahara N: Highly efficient tumor transduction and antitumor
efficacy in experimental human malignant mesothelioma using
replicating gibbon ape leukemia virus. Cancer Gene Ther.
20:671–677. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kubo S, Kawasaki Y, Yamaoka N, Tagawa M,
Kasahara N, Terada N and Okamura H: Complete regression of human
malignant mesothelioma xenografts following local injection of
midkine promoter-driven oncolytic adenovirus. J Gene Med.
12:681–692. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Takagi-Kimura M, Yamano T, Tagawa M and
Kubo S: Oncolytic virotherapy for osteosarcoma using midkine
promoter-regulated adenoviruses. Cancer Gene Ther. 21:126–132.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Takagi-Kimura M, Yamano T, Tamamoto A,
Okamura N, Okamura H, Hashimoto-Tamaoki T, Tagawa M, Kasahara N and
Kubo S: Enhanced antitumor efficacy of fiber-modified, midkine
promoter-regulated oncolytic adenovirus in human malignant
mesothelioma. Cancer Sci. 104:1433–1439. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|