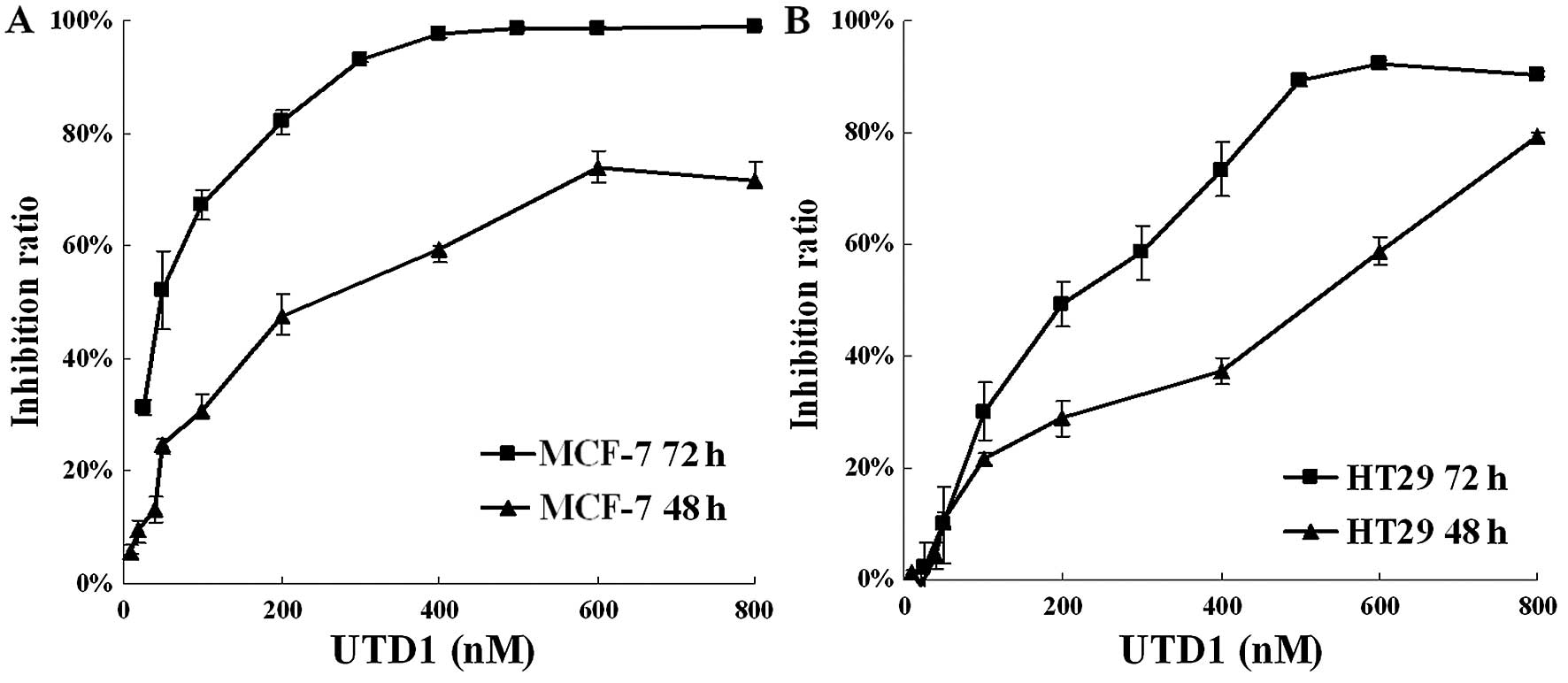
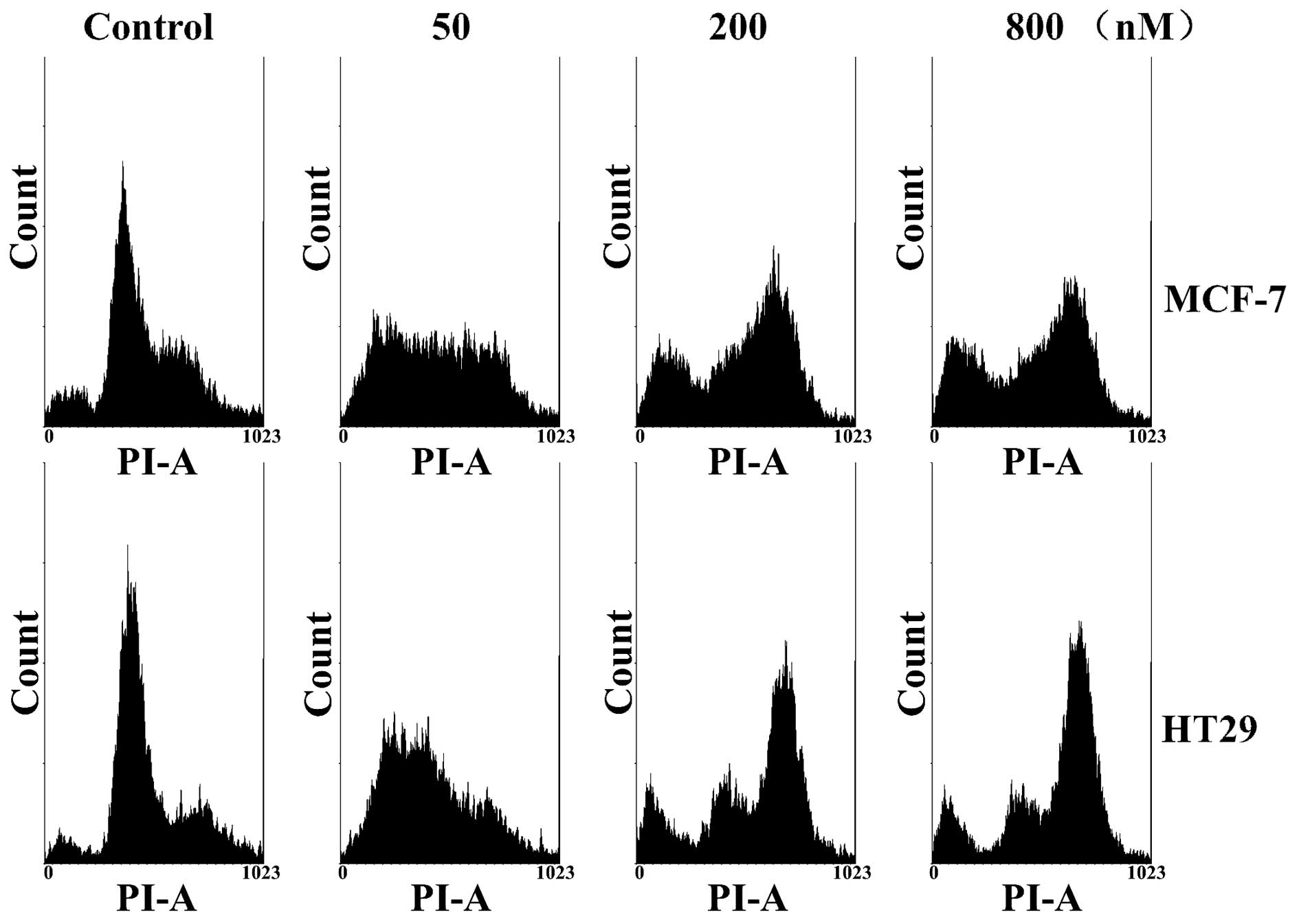
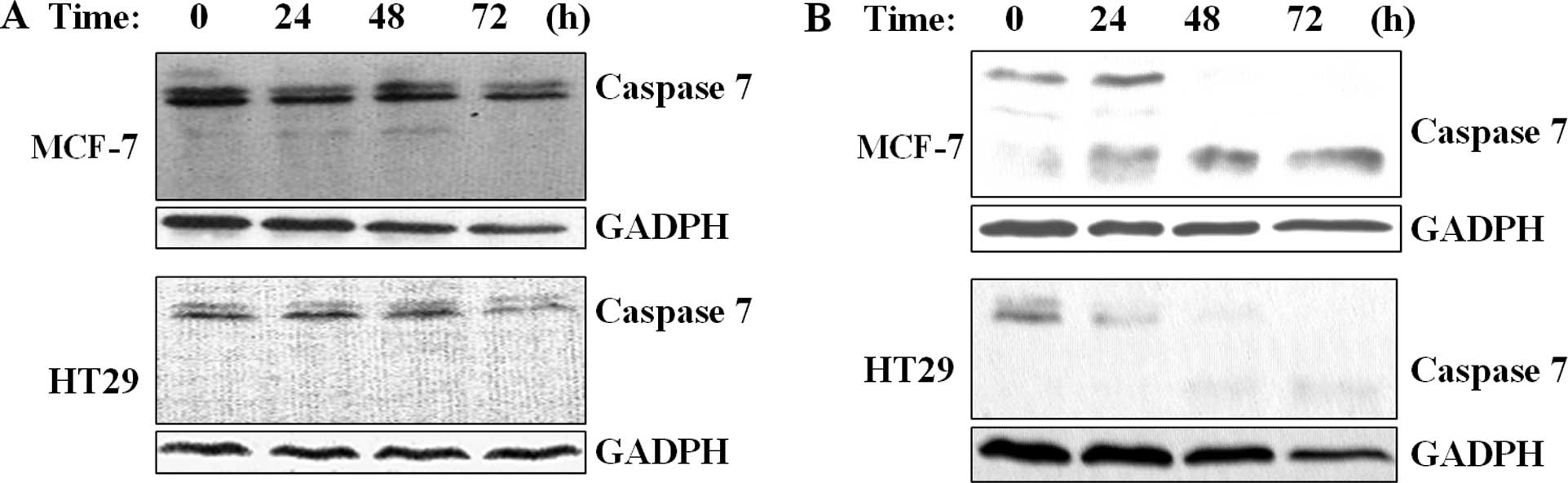
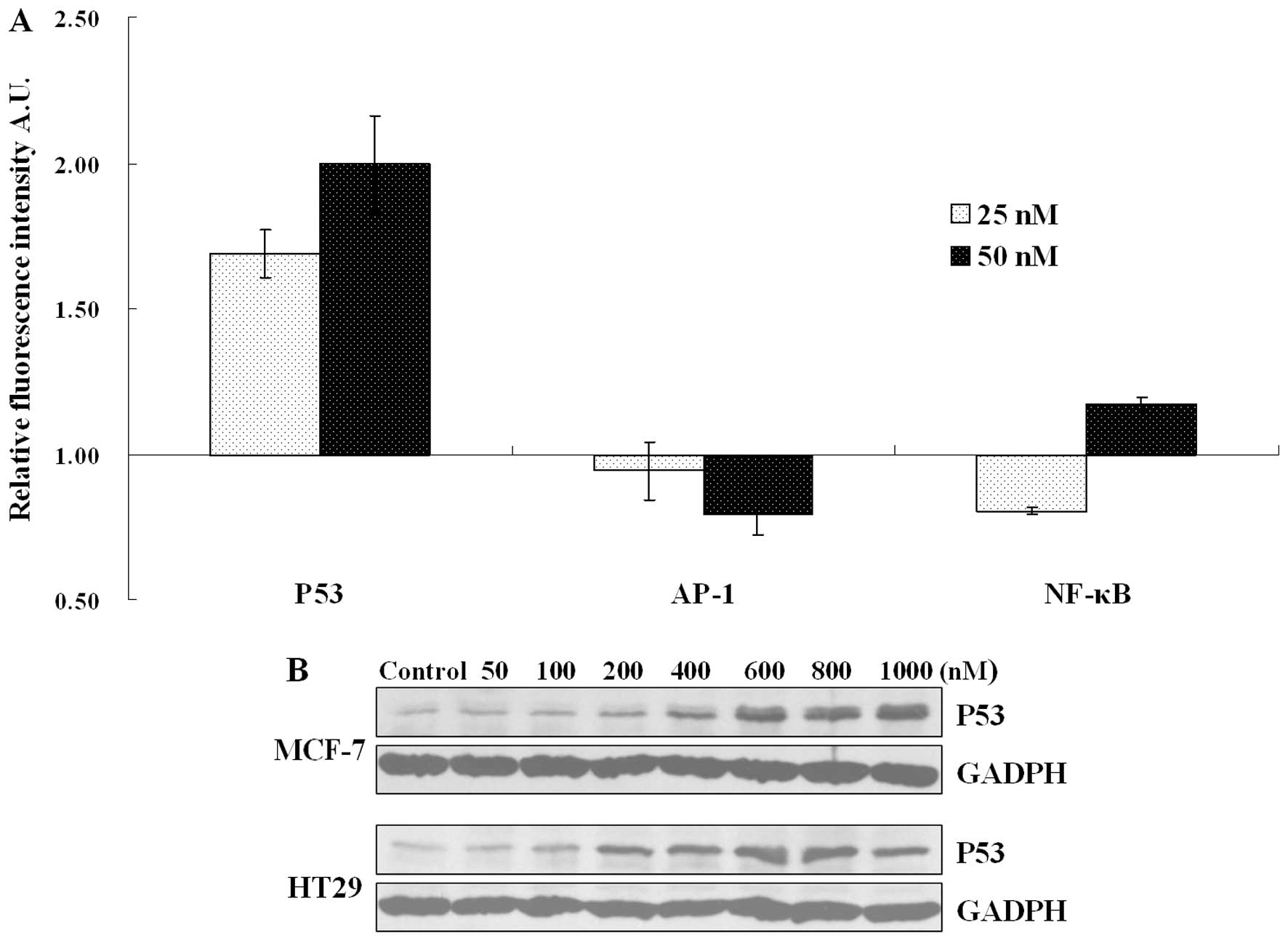
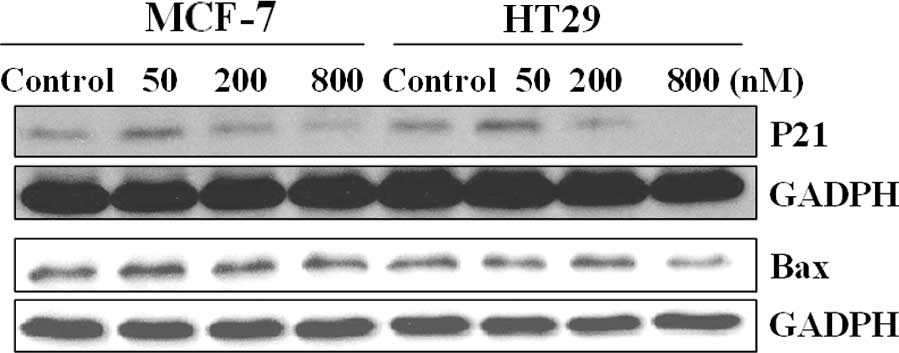
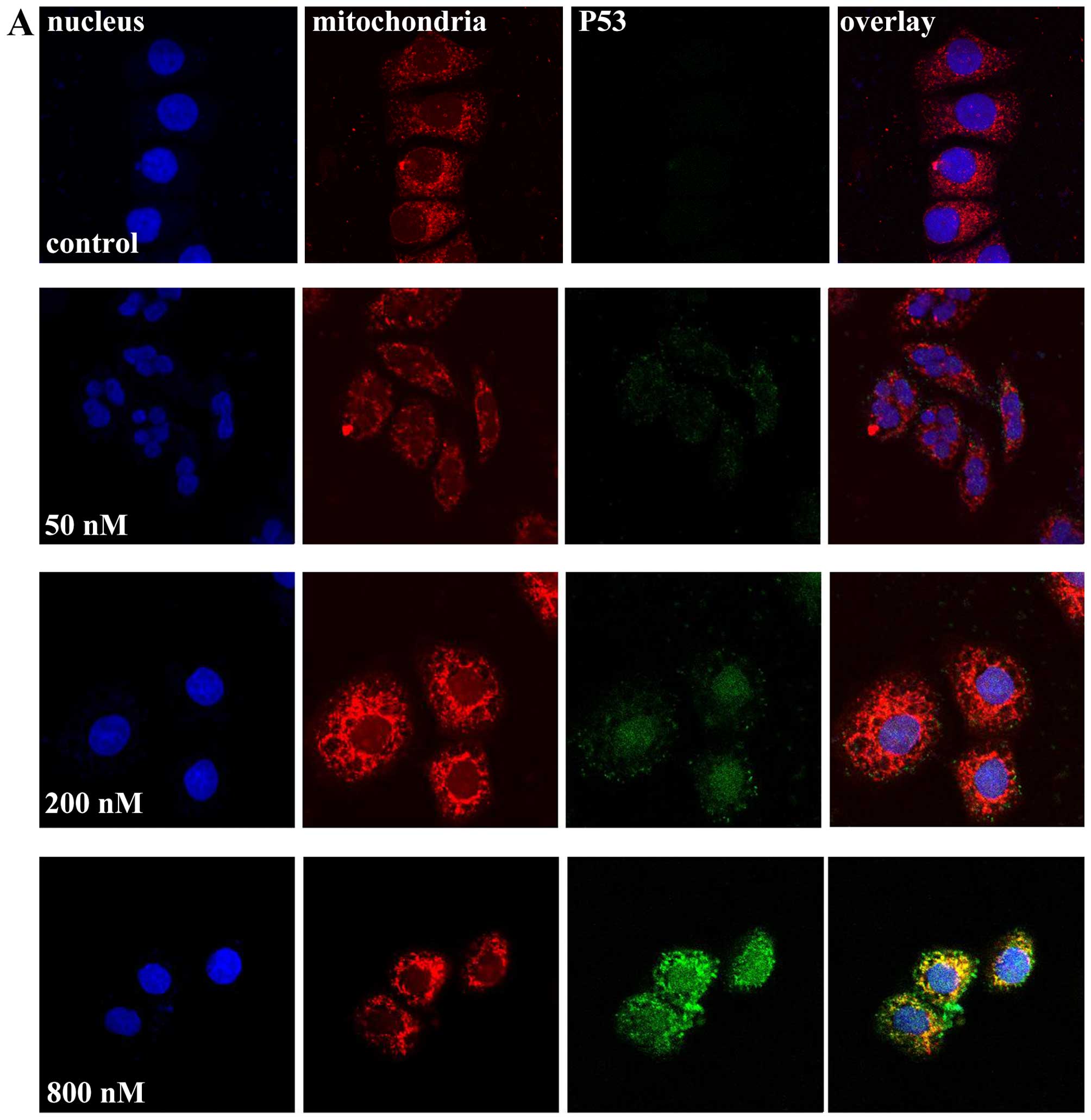
|
1
|
Gerth K, Bedorf N, Höfle G, Irschik H and
Reichenbach H: Epothilons A and B: Antifungal and cytotoxic
compounds from Sorangium cellulosum (Myxobacteria). Production,
physicochemical and biological properties. J Antibiot. 49:560–563.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Goodin S, Kane MP and Rubin EH:
Epothilones: Mechanism of action and biologic activity. J Clin
Oncol. 22:2015–2025. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lee JJ and Swain SM: Development of novel
chemotherapeutic agents to evade the mechanisms of multidrug
resistance (MDR). Semin Oncol. 32(Suppl 7): S22–S26. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lee FY, Borzilleri R, Fairchild CR, Kim
SH, Long BH, Reventos-Suarez C, Vite GD, Rose WC and Kramer RA:
BMS-247550: A novel epothilone analog with a mode of action similar
to paclitaxel but possessing superior antitumor efficacy. Clin
Cancer Res. 7:1429–1437. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Fojo AT and Menefee M: Microtubule
targeting agents: Basic mechanisms of multidrug resistance (MDR).
Semin Oncol. 32(Suppl 7): S3–S8. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Orr GA, Verdier-Pinard P, McDaid H and
Horwitz SB: Mechanisms of Taxol resistance related to microtubules.
Oncogene. 22:7280–7295. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bhandari MS and Hussain M: Epothilones and
the next generation of phase III trials for prostate cancer. BJU
Int. 96:296–302. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lee JJ and Swain SM: The epothilones:
Translating from the laboratory to the clinic. Clin Cancer Res.
14:1618–1624. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bergstralh DT and Ting JP: Microtubule
stabilizing agents: Their molecular signaling consequences and the
potential for enhancement by drug combination. Cancer Treat Rev.
32:166–179. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Larkin JM and Kaye SB: Epothilones in the
treatment of cancer. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 15:691–702. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Cortes J and Baselga J: Targeting the
microtubules in breast cancer beyond taxanes: The epothilones.
Oncologist. 12:271–280. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Low JA, Wedam SB, Lee JJ, Berman AW,
Brufsky A, Yang SX, Poruchynsky MS, Steinberg SM, Mannan N, Fojo T,
et al: Phase II clinical trial of ixabepilone (BMS-247550), an
epothilone B analog, in metastatic and locally advanced breast
cancer. J Clin Oncol. 23:2726–2734. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Thomas E, Tabernero J, Fornier M, Conté P,
Fumoleau P, Lluch A, Vahdat LT, Bunnell CA, Burris HA, Viens P, et
al: Phase II clinical trial of ixabepilone (BMS-247550), an
epothilone B analog, in patients with taxane-resistant metastatic
breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 25:3399–3406. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Perez EA, Lerzo G, Pivot X, Thomas E,
Vahdat L, Bosserman L, Viens P, Cai C, Mullaney B, Peck R, et al:
Efficacy and safety of ixabepilone (BMS-247550) in a phase II study
of patients with advanced breast cancer resistant to an
anthracycline, a taxane, and capecitabine. J Clin Oncol.
25:3407–3414. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Roché H, Yelle L, Cognetti F, Mauriac L,
Bunnell C, Sparano J, Kerbrat P, Delord JP, Vahdat L, Peck R, et
al: Phase II clinical trial of ixabepilone (BMS-247550), an
epothilone B analog, as first-line therapy in patients with
metastatic breast cancer previously treated with anthracycline
chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol. 25:3415–3420. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Denduluri N, Low JA, Lee JJ, Berman AW,
Walshe JM, Vatas U, Chow CK, Steinberg SM, Yang SX and Swain SM:
Phase II trial of ixabepilone, an epothilone B analog, in patients
with metastatic breast cancer previously untreated with taxanes. J
Clin Oncol. 25:3421–3427. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Vahdat LT, Thomas E, Li R, et al: Phase
III trial of ixabepilone plus capecitabine compared to capecitabine
alone in patients withmetastatic breast cancer (MBC) previously
treated or resistant to an anthracycline and resistant to taxanes.
Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol. 25:10062007.
|
|
18
|
Denduluri N, Lee JJ, Walshe J, Berman AW,
Vatas U, Chow CK, Steinberg SM, Cox MC, Low JA and Swain SM: Phase
II trial of ixabepilone, an epothilone B analog, given daily for
three days every three weeks, in metastatic breast cancer. Invest
New Drugs. 25:63–67. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Lee JJ, Low JA, Croarkin E, Parks R,
Berman AW, Mannan N, Steinberg SM and Swain SM: Changes in
neurologic function tests may predict neurotoxicity caused by
ixabepilone. J Clin Oncol. 24:2084–2091. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Winer E, Gralow J, Diller L, Karlan B,
Loehrer P, Pierce L, Demetri G, Ganz P, Kramer B, Kris M, et al:
Clinical cancer advances 2008: Major research advances in cancer
treatment, prevention, and screening - a report from the American
Society of Clinical Oncology. J Clin Oncol. 27:812–826. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
21
|
Zhang P, Sun M, Qiu R, Tang L, Dou G and
Xu B: Phase I clinical and pharmacokinetic study of UTD1, a
genetically engineered epothilone analog in patients with advanced
solid tumors. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 68:971–978. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Vousden KH and Lane DP: p53 in health and
disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 8:275–283. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Puca R, Nardinocchi L, Givol D and D'Orazi
G: Regulation of p53 activity by HIPK2: Molecular mechanisms and
therapeutical implications in human cancer cells. Oncogene.
29:4378–4387. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Vazquez A, Bond EE, Levine AJ and Bond GL:
The genetics of the p53 pathway, apoptosis and cancer therapy. Nat
Rev Drug Discov. 7:979–987. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chen JG, Yang CP, Cammer M and Horwitz SB:
Gene expression and mitotic exit induced by microtubule-stabilizing
drugs. Cancer Res. 63:7891–7899. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Blagosklonny MV: Prolonged mitosis versus
tetraploid checkpoint: How p53 measures the duration of mitosis.
Cell Cycle. 5:971–975. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Blagosklonny MV: Mitotic arrest and cell
fate: Why and how mitotic inhibition of transcription drives
mutually exclusive events. Cell Cycle. 6:70–74. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Marchenko ND, Wolff S, Erster S, Becker K
and Moll UM: Monoubiquitylation promotes mitochondrial p53
translocation. EMBO J. 26:923–934. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Moll UM, Marchenko N and Zhang XK: p53 and
Nur77/TR3 - transcription factors that directly target mitochondria
for cell death induction. Oncogene. 25:4725–4743. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Tomita Y, Marchenko N, Erster S,
Nemajerova A, Dehner A, Klein C, Pan H, Kessler H, Pancoska P and
Moll UM: WT p53, but not tumor-derived mutants, bind to Bcl2 via
the DNA binding domain and induce mitochondrial permeabilization. J
Biol Chem. 281:8600–8606. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Leu JI, Dumont P, Hafey M, Murphy ME and
George DL: Mitochondrial p53 activates Bak and causes disruption of
a Bak-Mcl1 complex. Nat Cell Biol. 6:443–450. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Bacus SS, Gudkov AV, Lowe M, Lyass L, Yung
Y, Komarov AP, Keyomarsi K, Yarden Y and Seger R: Taxol-induced
apoptosis depends on MAP kinase pathways (ERK and p38) and is
independent of p53. Oncogene. 20:147–155. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Woods CM, Zhu J, McQueney PA, Bollag D and
Lazarides E: Taxol-induced mitotic block triggers rapid onset of a
p53-independent apoptotic pathway. Mol Med. 1:506–526.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Giannakakou P, Robey R, Fojo T and
Blagosklonny MV: Low concentrations of paclitaxel induce cell
type-dependent p53, p21 and G1/G2 arrest instead of mitotic arrest:
Molecular determinants of paclitaxel-induced cytotoxicity.
Oncogene. 20:3806–3813. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lanni JS, Lowe SW, Licitra EJ, Liu JO and
Jacks T: p53-independent apoptosis induced by paclitaxel through an
indirect mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 94:9679–9683. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|