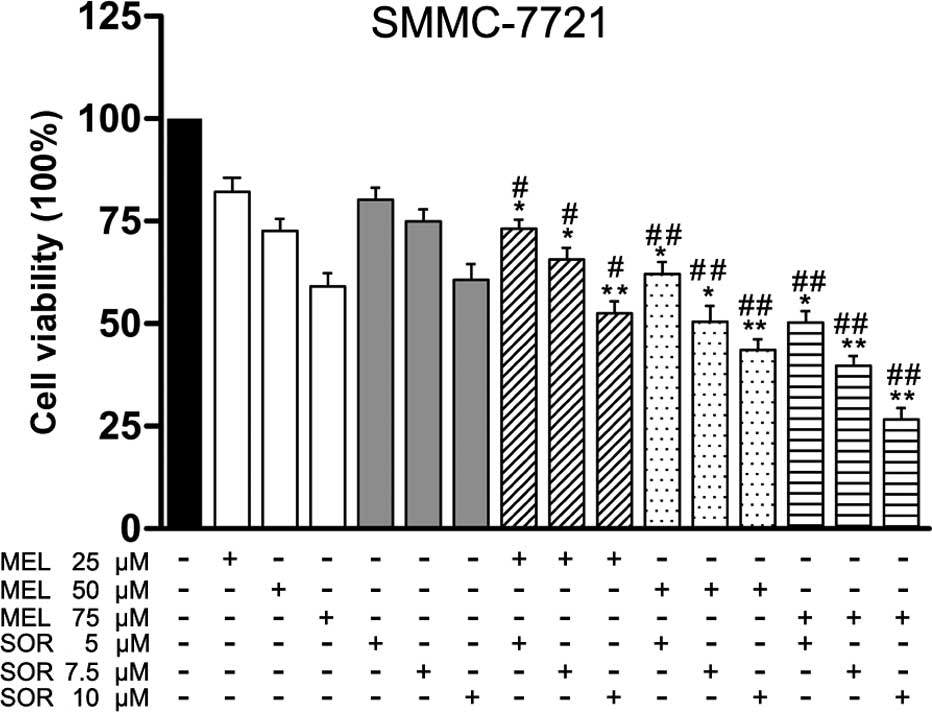
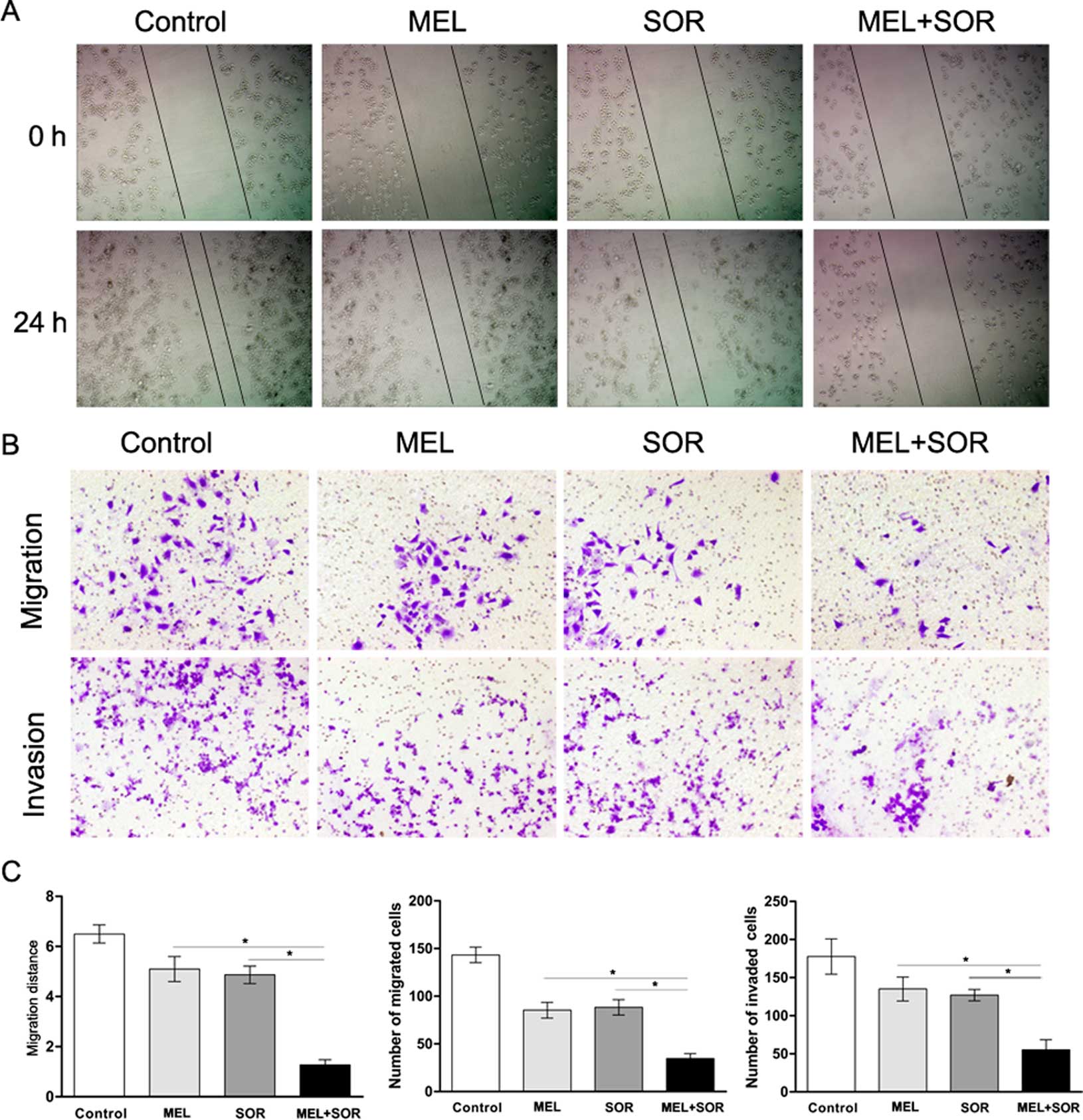
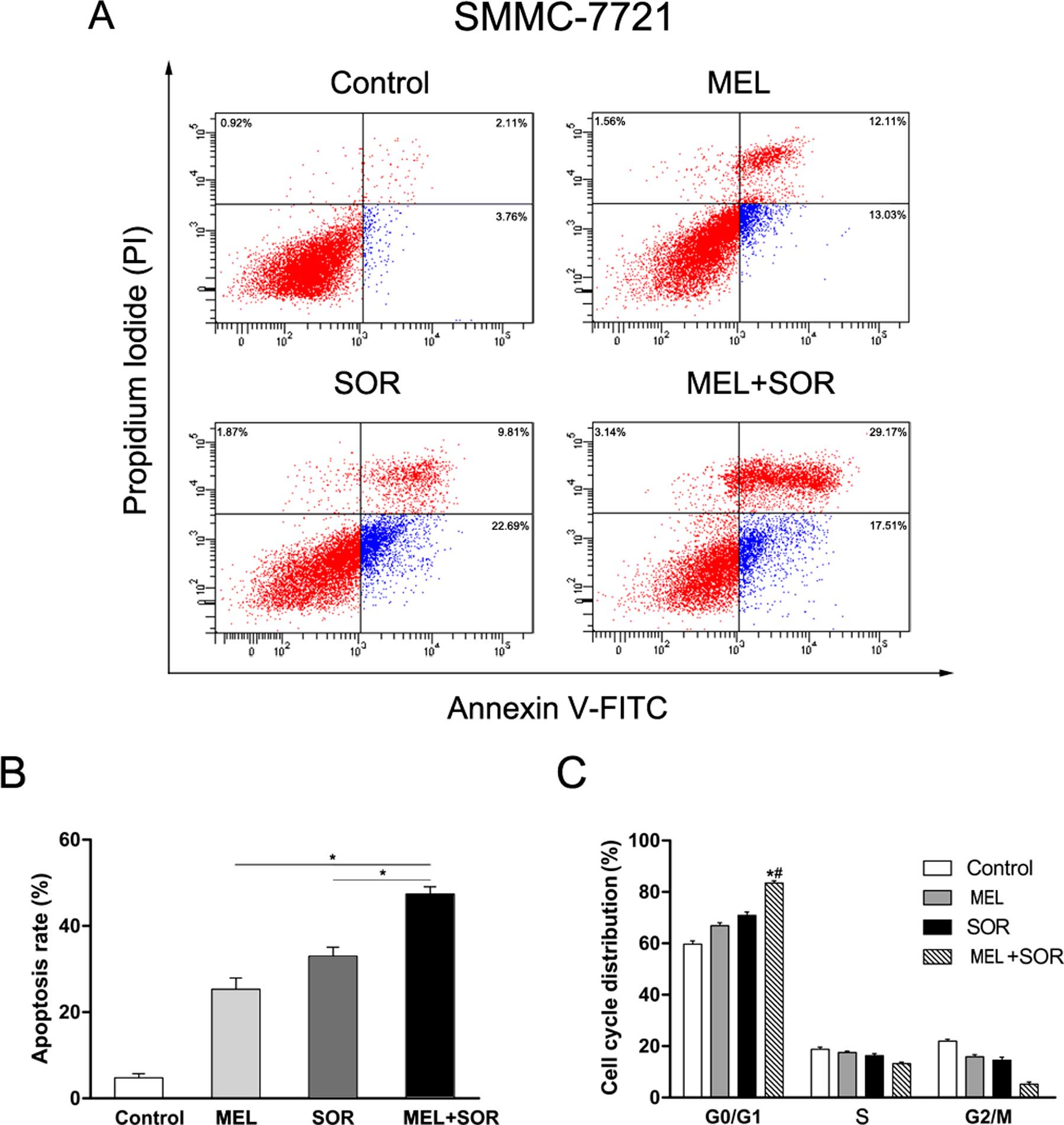
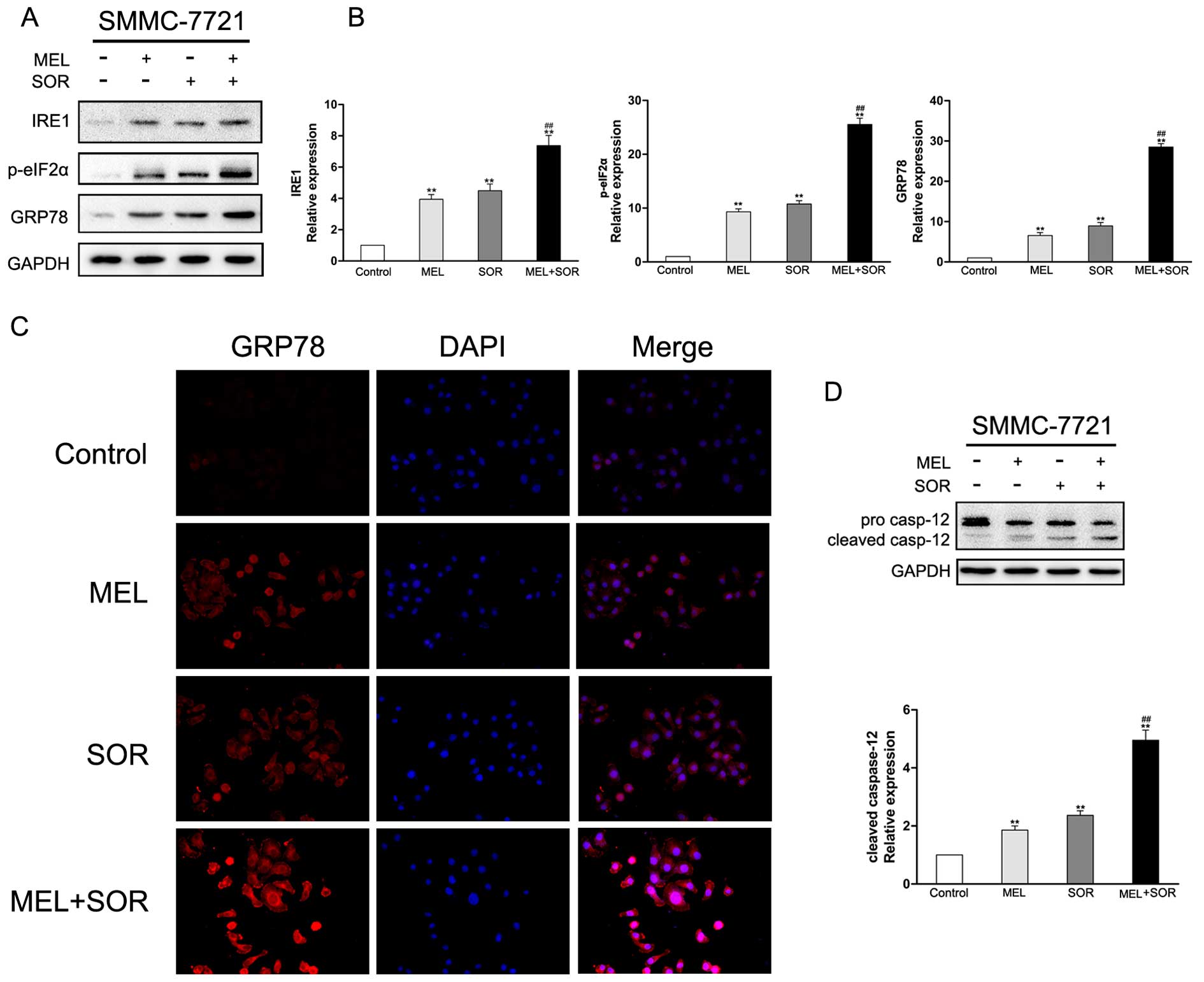
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Asghar U and Meyer T: Are there
opportunities for chemotherapy in the treatment of hepatocellular
cancer? J Hepatol. 56:686–695. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Wilhelm SM, Carter C, Tang L, Wilkie D,
McNabola A, Rong H, Chen C, Zhang X, Vincent P, McHugh M, et al:
BAY 43-9006 exhibits broad spectrum oral antitumor activity and
targets the RAF/MEK/ERK pathway and receptor tyrosine kinases
involved in tumor progression and angiogenesis. Cancer Res.
64:7099–7109. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Liu L, Cao Y, Chen C, Zhang X, McNabola A,
Wilkie D, Wilhelm S, Lynch M and Carter C: Sorafenib blocks the
RAF/MEK/ERK pathway, inhibits tumor angiogenesis, and induces tumor
cell apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma model PLC/PRF/5. Cancer
Res. 66:11851–11858. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, Hilgard
P, Gane E, Blanc JF, de Oliveira AC, Santoro A, Raoul JL, Forner A,
et al SHARP Investigators Study Group: Sorafenib in advanced
hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 359:378–390. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Thun MJ, Henley SJ and Patrono C:
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs as anticancer agents:
Mechanistic, pharmacologic, and clinical issues. J Natl Cancer
Inst. 94:252–266. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lönnroth C, Andersson M, Asting AG,
Nordgren S and Lundholm K: Preoperative low dose NSAID treatment
influences the genes for stemness, growth, invasion and metastasis
in colorectal cancer. Int J Oncol. 45:2208–2220. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ding N, Cui XX, Gao Z, Huang H, Wei X, Du
Z, Lin Y, Shih WJ, Rabson AB, Conney AH, et al: A triple
combination of atorvastatin, celecoxib and tipifarnib strongly
inhibits pancreatic cancer cells and xenograft pancreatic tumors.
Int J Oncol. 44:2139–2145. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhivkova T, Alexandrova R, Dyakova L,
Georgieva M, Miloshev G, Culita DC, Marinescu G, Patron L and
Alexandrov M: P7.05. Metal complexes of meloxicam and isoxicam
decrease viability and proliferation of virus-transformed cancer
cells. Ann Oncol. 26(Suppl 2): ii322015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Hassan MH, El-Beshbishy HA, Aly H, Attia
SM, Bahashwan SA and Ghobara MM: Modulatory effects of meloxicam on
cardiotoxicity and antitumor activity of doxorubicin in mice.
Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 74:559–569. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Arantes-Rodrigues R, Pinto-Leite R,
Ferreira R, Neuparth MJ, Pires MJ, Gaivão I, Palmeira C, Santos L,
Colaço A and Oliveira P: Meloxicam in the treatment of in vitro and
in vivo models of urinary bladder cancer. Biomed Pharmacother.
67:277–284. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Li J, Chen X, Dong X, Xu Z, Jiang H and
Sun X: Specific COX-2 inhibitor, meloxicam, suppresses
proliferation and induces apoptosis in human HepG2 hepatocellular
carcinoma cells. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 21:1814–1820. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Dong X, Li R, Xiu P, Dong X, Xu Z, Zhai B,
Liu F, Jiang H, Sun X, Li J, et al: Meloxicam executes its
antitumor effects against hepatocellular carcinoma in
COX-2-dependent and -independent pathways. PLoS One. 9:e928642014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Tabas I and Ron D: Integrating the
mechanisms of apoptosis induced by endoplasmic reticulum stress.
Nat Cell Biol. 13:184–190. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhu J, Chen M, Chen N, Ma A, Zhu C, Zhao
R, Jiang M, Zhou J, Ye L, Fu H, et al: Glycyrrhetinic acid induces
G1-phase cell cycle arrest in human non-small cell lung cancer
cells through endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway. Int J Oncol.
46:981–988. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Xu C, Bailly-Maitre B and Reed JC:
Endoplasmic reticulum stress: Cell life and death decisions. J Clin
Invest. 115:2656–2664. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Meusser B, Hirsch C, Jarosch E and Sommer
T: ERAD: The long road to destruction. Nat Cell Biol. 7:766–772.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cao SS and Zhen YS: Potentiation of
antimetabolite antitumor activity in vivo by dipyridamole and
amphotericin B. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 24:181–186. 1989.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Inamoto T and Azuma H: Sorafenib increases
endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress in concert with vorinostat.
Cancer Biol Ther. 12:10182011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Shi YH, Ding ZB, Zhou J, Hui B, Shi GM, Ke
AW, Wang XY, Dai Z, Peng YF, Gu CY, et al: Targeting autophagy
enhances sorafenib lethality for hepatocellular carcinoma via ER
stress-related apoptosis. Autophagy. 7:1159–1172. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Suzuki K, Gerelchuluun A, Hong Z, Sun L,
Zenkoh J, Moritake T and Tsuboi K: Celecoxib enhances
radiosensitivity of hypoxic glioblastoma cells through endoplasmic
reticulum stress. Neurooncol. 15:1186–1199. 2013.
|
|
22
|
Kim SJ, Ha GH, Bae JH, Kim GR, Son CH,
Park YS, Yang K, Oh SO, Kim SH and Kang CD: COX-2- and endoplasmic
reticulum stress-independent induction of ULBP-1 and enhancement of
sensitivity to NK cell-mediated cytotoxicity by celecoxib in colon
cancer cells. Exp Cell Res. 330:451–459. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Momoi T: Caspases involved in ER
stress-mediated cell death. J Chem Neuroanat. 28:101–105. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Virrey JJ, Dong D, Stiles C, Patterson JB,
Pen L, Ni M, Schönthal AH, Chen TC, Hofman FM and Lee AS: Stress
chaperone GRP78/BiP confers chemoresistance to tumor-associated
endothelial cells. Mol Cancer Res. 6:1268–1275. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Egger L, Madden DT, Rhême C, Rao RV and
Bredesen DE: Endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced cell death
mediated by the proteasome. Cell Death Differ. 14:1172–1180. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Komatsu S, Miyazawa K, Moriya S, Takase A,
Naito M, Inazu M, Kohno N, Itoh M and Tomoda A: Clarithromycin
enhances bortezomib-induced cytotoxicity via endoplasmic reticulum
stress-mediated CHOP (GADD153) induction and autophagy in breast
cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 40:1029–1039. 2012.
|
|
27
|
Dupuy E, Hainaud P, Villemain A,
Bodevin-Phèdre E, Brouland JP, Briand P and Tobelem G: Tumoral
angiogenesis and tissue factor expression during hepatocellular
carcinoma progression in a transgenic mouse model. J Hepatol.
38:793–802. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Geis T, Döring C, Popp R, Grossmann N,
Fleming I, Hansmann ML, Dehne N and Brüne B: HIF-2alpha-dependent
PAI-1 induction contributes to angiogenesis in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Exp Cell Res. 331:46–57. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Yusup G, Akutsu Y, Mutallip M, Qin W, Hu
X, Komatsu-Akimoto A, Hoshino I, Hanari N, Mori M, Akanuma N, et
al: A COX-2 inhibitor enhances the antitumor effects of
chemotherapy and radiotherapy for esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 44:1146–1152. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Agarwal V, Hodgkinson VC, Eagle GL, Scaife
L, Lind MJ and Cawkwell L: Proteomic (antibody microarray)
exploration of the molecular mechanism of action of the specific
COX-2 inhibitor DuP 697. Int J Oncol. 42:1088–1092. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Rutkowski DT and Kaufman RJ: A trip to the
ER: Coping with stress. Trends Cell Biol. 14:20–28. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Dolai S, Pal S, Yadav RK and Adak S:
Endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis in Leishmania
through Ca2+-dependent and caspase-independent
mechanism. J Biol Chem. 286:13638–13646. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Fribley AM, Miller JR, Brownell AL,
Garshott DM, Zeng Q, Reist TE, Narula N, Cai P, Xi Y, Callaghan MU,
et al: Celastrol induces unfolded protein response-dependent cell
death in head and neck cancer. Exp Cell Res. 330:412–422. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Li J and Lee AS: Stress induction of
GRP78/BiP and its role in cancer. Curr Mol Med. 6:45–54. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kulkarni P, Rajagopalan K, Yeater D and
Getzenberg RH: Protein folding and the order/disorder paradox. J
Cell Biochem. 112:1949–1952. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wu J and Kaufman RJ: From acute ER stress
to physiological roles of the Unfolded Protein Response. Cell Death
Differ. 13:374–384. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lee AS: GRP78 induction in cancer:
Therapeutic and prognostic implications. Cancer Res. 67:3496–3499.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ermakova SP, Kang BS, Choi BY, Choi HS,
Schuster TF, Ma WY, Bode AM and Dong Z: (−)-Epigallocatechin
gallate overcomes resistance to etoposide-induced cell death by
targeting the molecular chaperone glucose-regulated protein 78.
Cancer Res. 66:9260–9269. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|