|
1
|
Berger AH, Knudson AG and Pandolfi PP: A
continuum model for tumour suppression. Nature. 476:163–169. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
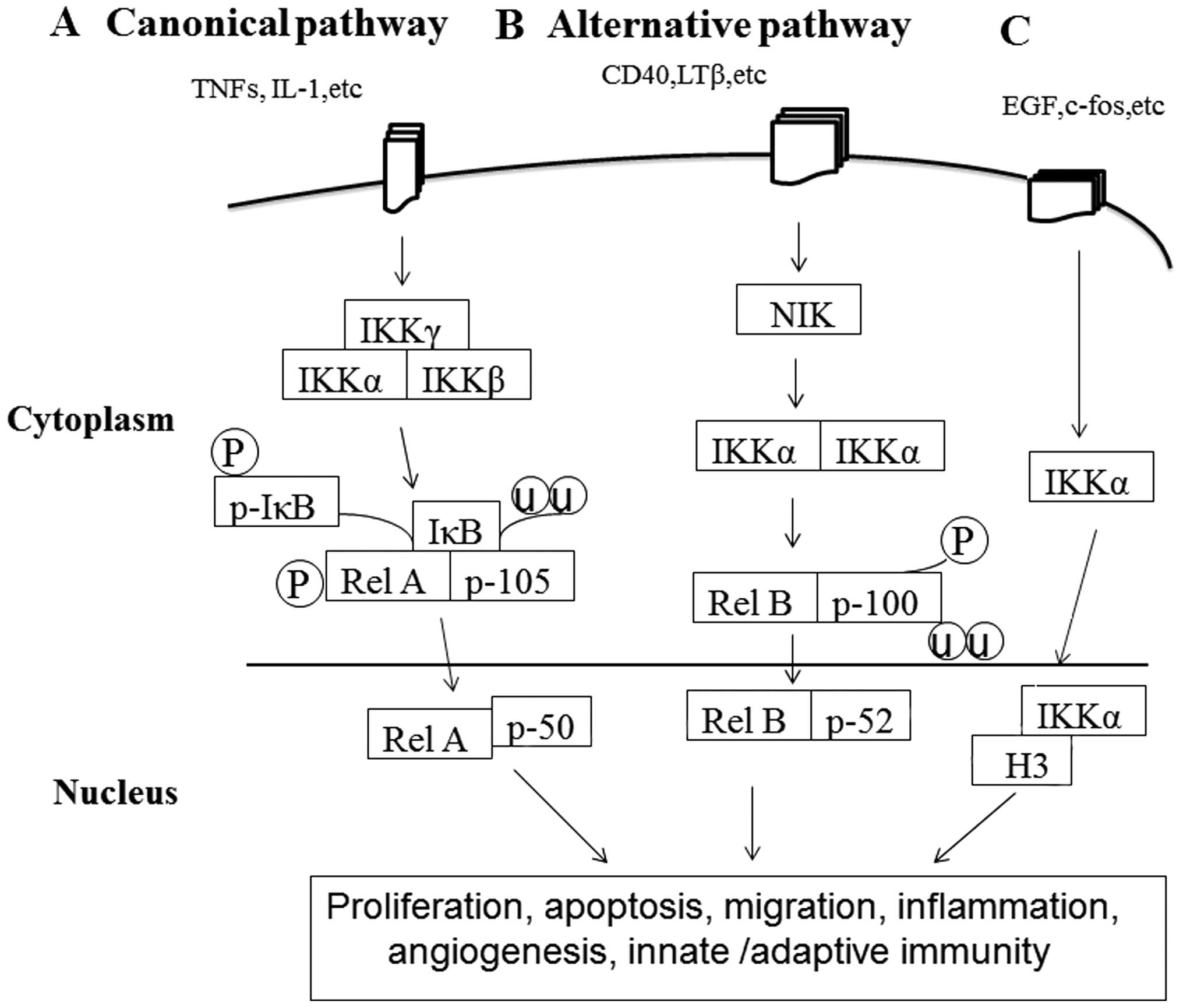
|
Stovall DB, Cao P and Sui G: SOX7: From a
developmental regulator to an emerging tumor suppressor. Histol
Histopathol. 29:439–445. 2014.
|
|
3
|
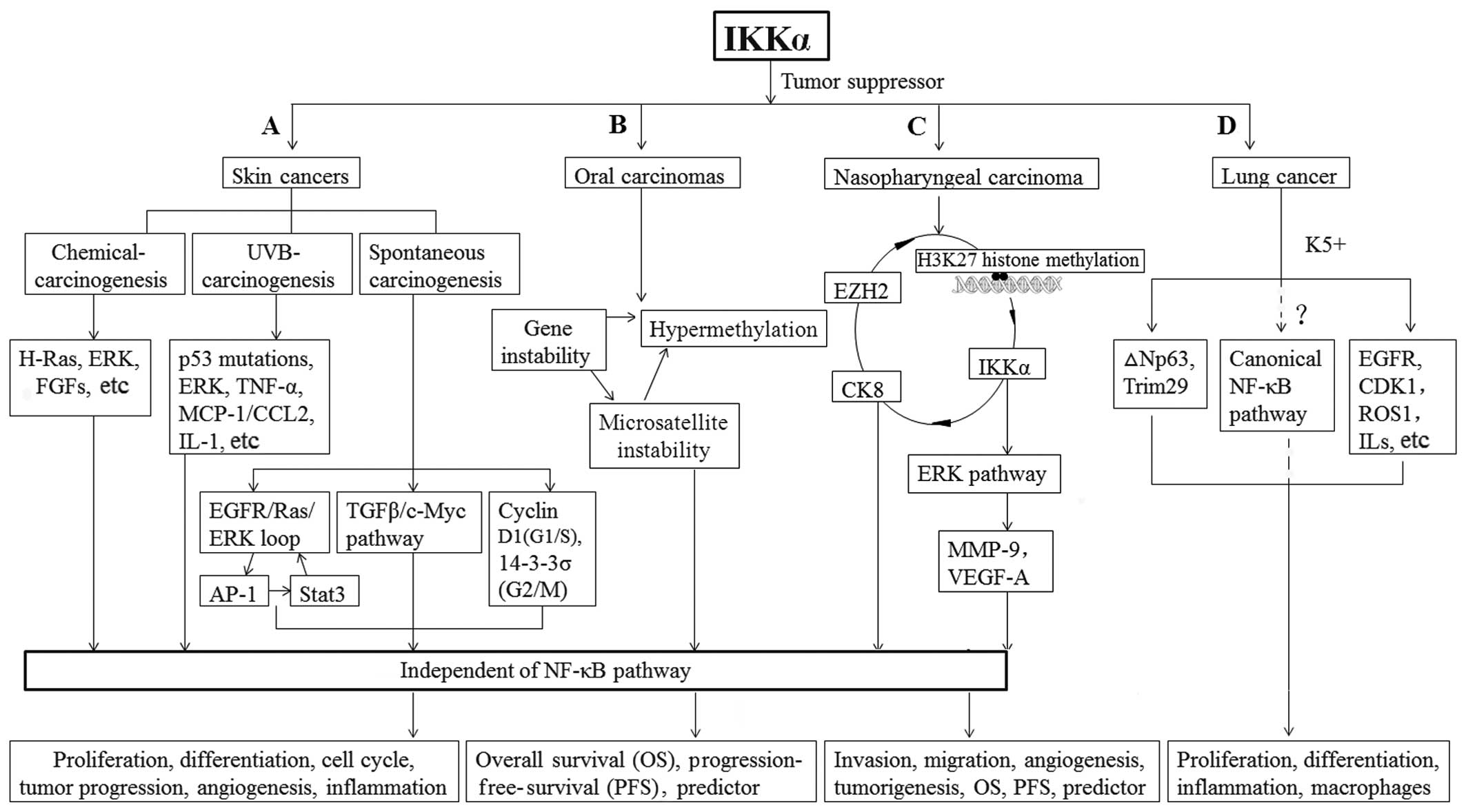
Liu B, Xia X, Zhu F, Park E, Carbajal S,
Kiguchi K, DiGiovanni J, Fischer SM and Hu Y: IKKalpha is required
to maintain skin homeostasis and prevent skin cancer. Cancer Cell.
14:212–225. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kwak YT, Radaideh SM, Ding L, Li R,
Frenkel E, Story MD, Girard L, Minna J and Verma UN: Cells lacking
IKKalpha show nuclear cyclin D1 overexpression and a neoplastic
phenotype: Role of IKKalpha as a tumor suppressor. Mol Cancer Res.
9:341–349. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Marinari B, Ballaro C, Koster MI,
Giustizieri ML, Moretti F, Crosti F, Papoutsaki M, Karin M, Alema
S, Chimenti S, et al: IKKalpha is a p63 transcriptional target
involved in the pathogenesis of ectodermal dysplasias. J Invest
Dermatol. 129:60–69. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Marinari B, Moretti F, Botti E,
Giustizieri ML, Descargues P, Giunta A, Stolfi C, Ballaro C,
Papoutsaki M, Alemà S, et al: The tumor suppressor activity of
IKKalpha in stratified epithelia is exerted in part via the
TGF-beta antiproliferative pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
105:17091–17096. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
McKenzie FR, Connelly MA, Balzarano D,
Muller JR, Geleziunas R and Marcu KB: Functional isoforms of
IkappaB kinase alpha (IKKalpha) lacking leucine zipper and
helix-loop-helix domains reveal that IKKalpha and IKKbeta have
different activation requirements. Mol Cell Biol. 20:2635–2649.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Connelly MA and Marcu KB: CHUK, a new
member of the helix-loop-helix and leucine zipper families of
interacting proteins, contains a serine-threonine kinase catalytic
domain. Cell Mol Biol Res. 41:537–549. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ghosh S and Karin M: Missing pieces in the
NF-kappaB puzzle. Cell. 109(Suppl): S81–S96. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sakurai H, Suzuki S, Kawasaki N, Nakano H,
Okazaki T, Chino A, Doi T and Saiki I: Tumor necrosis
factor-alpha-induced IKK phosphorylation of NF-kappaB p65 on serine
536 is mediated through the TRAF2, TRAF5, and TAK1 signaling
pathway. J Biol Chem. 278:36916–36923. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Van Waes C, Yu M, Nottingham L and Karin
M: Inhibitor-kappaB kinase in tumor promotion and suppression
during progression of squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res.
13:4956–4959. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Van Waes C: Nuclear factor-kappaB in
development, prevention, and therapy of cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
13:1076–1082. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Anest V, Cogswell PC and Baldwin AS Jr:
IkappaB kinase alpha and p65/RelA contribute to optimal epidermal
growth factor-induced c-fos gene expression independent of
IkappaBalpha degradation. J Biol Chem. 279:31183–31189. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Elias PM, Ahn SK, Denda M, Brown BE,
Crumrine D, Kimutai LK, Kömüves L, Lee SH and Feingold KR:
Modulations in epidermal calcium regulate the expression of
differentiation-specific markers. J Invest Dermatol. 119:1128–1136.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu B, Zhu F, Xia X, Park E and Hu Y: A
tale of terminal differentiation: IKKalpha, the master keratinocyte
regulator. Cell Cycle. 8:527–531. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Liu B, Park E, Zhu F, Bustos T, Liu J,
Shen J, Fischer SM and Hu Y: A critical role for I kappaB kinase
alpha in the development of human and mouse squamous cell
carcinomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:17202–17207. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sil AK, Maeda S, Sano Y, Roop DR and Karin
M: IkappaB kinase-alpha acts in the epidermis to control skeletal
and craniofacial morphogenesis. Nature. 428:660–664. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Park E, Liu B, Xia X, Zhu F, Jami WB and
Hu Y: Role of IKKalpha in skin squamous cell carcinomas. Future
Oncol. 7:123–134. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Park E, Zhu F, Liu B, Xia X, Shen J,
Bustos T, Fischer SM and Hu Y: Reduction in IkappaB kinase alpha
expression promotes the development of skin papillomas and
carcinomas. Cancer Res. 67:9158–9168. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhu F, Park E, Liu B, Xia X, Fischer SM
and Hu Y: Critical role of IkappaB kinase alpha in embryonic skin
development and skin carcinogenesis. Histol Histopathol.
24:265–271. 2009.
|
|
21
|
Xia X, Park E, Liu B, Willette-Brown J,
Gong W, Wang J, Mitchell D, Fischer SM and Hu Y: Reduction of
IKKalpha expression promotes chronic ultraviolet B exposure-induced
skin inflammation and carcinogenesis. Am J Pathol. 176:2500–2508.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Peinado C, Kang X, Hardamon C, Arora S,
Mah S, Zhang H, Ngolab J and Bui JD: The nuclear factor-kappaB
pathway down-regulates expression of the NKG2D ligand H60a in
vitro: Implications for use of nuclear factor-kappaB inhibitors in
cancer therapy. Immunology. 139:265–274. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Fujimoto H, Sangai T, Ishii G, Ikehara A,
Nagashima T, Miyazaki M and Ochiai A: Stromal MCP-1 in mammary
tumors induces tumor-associated macrophage infiltration and
contributes to tumor progression. Int J Cancer. 125:1276–1284.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Huovila AP, Turner AJ, Pelto-Huikko M,
Karkkainen I and Ortiz RM: Shedding light on ADAM
metalloproteinases. Trends Biochemical Sci. 30:413–422. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Liu S, Chen Z, Zhu F and Hu Y: IkappaB
kinase alpha and cancer. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 32:152–158.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
26
|
Liu B, Willette-Brown J, Liu S, Chen X,
Fischer SM and Hu Y: IKKalpha represses a network of inflammation
and proliferation pathways and elevates c-Myc antagonists and
differentiation in a dose-dependent manner in the skin. Cell Death
Differ. 18:1854–1864. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zenz R, Eferl R, Scheinecker C, Redlich K,
Smolen J, Schonthaler HB, Kenner L, Tschachler E and Wagner EF:
Activator protein 1 (Fos/Jun) functions in inflammatory bone and
skin disease. Arthritis Res Ther. 10:2012008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sano S, Chan KS and DiGiovanni J: Impact
of Stat3 activation upon skin biology: A dichotomy of its role
between homeostasis and diseases. J Dermatol Sci. 50:1–14. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Descargues P, Sil AK, Sano Y, Korchynskyi
O, Han G, Owens P, Wang XJ and Karin M: IKKalpha is a critical
coregulator of a Smad4-independent TGFbeta-Smad2/3 signaling
pathway that controls keratinocyte differentiation. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 105:2487–2492. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Gandarillas A: The mysterious human
epidermal cell cycle, or an oncogene-induced differentiation
checkpoint. Cell Cycle. 11:4507–4516. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Pulverer B, Sommer A, McArthur GA,
Eisenman RN and Luscher B: Analysis of Myc/Max/Mad network members
in adipogenesis: Inhibition of the proliferative burst and
differentiation by ectopically expressed Mad1. J Cell Physiol.
183:399–410. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Drabsch Y and ten Dijke P: TGF-β
signalling and its role in cancer progression and metastasis.
Cancer Metastasis Rev. 31:553–568. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Mordasky Markell L, Perez-Lorenzo R,
Masiuk KE, Kennett MJ and Glick AB: Use of a TGFbeta type I
receptor inhibitor in mouse skin carcinogenesis reveals a dual role
for TGFbeta signaling in tumor promotion and progression.
Carcinogenesis. 31:2127–2135. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ikushima H and Miyazono K: TGFbeta
signalling: A complex web in cancer progression. Nat Rev Cancer.
10:415–424. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ravindran A, Mohammed J, Gunderson AJ, Cui
X and Glick AB: Tumor-promoting role of TGFbeta1 signaling in
ultraviolet B-induced skin carcinogenesis is associated with
cutaneous inflammation and lymph node migration of dermal dendritic
cells. Carcinogenesis. 35:959–966. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
36
|
Kwak YT, Li R, Becerra CR, Tripathy D,
Frenkel EP and Verma UN: IkappaB kinase alpha regulates subcellular
distribution and turnover of cyclin D1 by phosphorylation. J Biol
Chem. 280:33945–33952. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Tashiro E, Tsuchiya A and Imoto M:
Functions of cyclin D1 as an oncogene and regulation of cyclin D1
expression. Cancer Sci. 98:629–635. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Diehl JA, Cheng M, Roussel MF and Sherr
CJ: Glycogen synthase kinase-3beta regulates cyclin D1 proteolysis
and subcellular localization. Genes Dev. 12:3499–3511. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Alt JR, Cleveland JL, Hannink M and Diehl
JA: Phosphorylation-dependent regulation of cyclin D1 nuclear
export and cyclin D1-dependent cellular transformation. Genes Dev.
14:3102–3114. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Chan TA, Hwang PM, Hermeking H, Kinzler KW
and Vogelstein B: Cooperative effects of genes controlling the
G(2)/M checkpoint. Genes Dev. 14:1584–1588. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zhu F, Xia X, Liu B, Shen J and Hu Y,
Person M and Hu Y: IKKalpha shields 14-3-3sigma, a G(2)/M cell
cycle checkpoint gene, from hypermethylation, preventing its
silencing. Mol Cell. 27:214–227. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Dellambra E, Golisano O, Bondanza S,
Siviero E, Lacal P, Molinari M, D'Atri S and De Luca M:
Downregulation of 14-3-3sigma prevents clonal evolution and leads
to immortalization of primary human keratinocytes. J Cell Biol.
149:1117–1130. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Xiao Z, Jiang Q, Willette-Brown J, Xi S,
Zhu F, Burkett S, Back T, Song NY, Datla M and Sun Z: The pivotal
role of IKKalpha in the development of spontaneous lung squamous
cell carcinomas. Cancer Cell. 23:527–540. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Hackett NR, Shaykhiev R, Walters MS, Wang
R, Zwick RK, Ferris B, Witover B, Salit J and Crystal RG: The human
airway epithelial basal cell transcriptome. PloS One. 6:e183782011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Ye S, Lee KB, Park MH, Lee JS and Kim SM:
p63 regulates growth of esophageal squamous carcinoma cells via the
Akt signaling pathway. Int J Oncol. 44:2153–2159. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Koster MI, Dai D, Marinari B, Sano Y,
Costanzo A, Karin M and Roop DR: p63 induces key target genes
required for epidermal morphogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
104:3255–3260. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Cambiaghi V, Giuliani V, Lombardi S,
Marinelli C, Toffalorio F and Pelicci PG: TRIM proteins in cancer.
Adv Exp Med Biol. 770:77–91. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Sho T, Tsukiyama T, Sato T, Kondo T, Cheng
J, Saku T, Asaka M and Hatakeyama S: TRIM29 negatively regulates
p53 via inhibition of Tip60. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1813:1245–1253.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Hayashi A, Yamauchi N, Shibahara J, Kimura
H, Morikawa T, Ishikawa S, Nagae G, Nishi A, Sakamoto Y and Kokudo
N: Concurrent activation of acetylation and tri-methylation of
H3K27 in a subset of hepatocellular carcinoma with aggressive
behavior. PloS One. 9:e913302014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Tie F, Banerjee R, Saiakhova AR, Howard B,
Monteith KE, Scacheri PC, Cosgrove MS and Harte PJ: Trithorax
monomethylates histone H3K4 and interacts directly with CBP to
promote H3K27 acetylation and antagonize Polycomb silencing.
Development. 141:1129–1139. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Ring BZ, Seitz RS, Beck RA, Shasteen WJ,
Soltermann A, Arbogast S, Robert F, Schreeder MT and Ross DT: A
novel five-antibody immunohistochemical test for subclassification
of lung carcinoma. Mod Pathol. 22:1032–1043. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Hu Y, Baud V, Oga T, Kim KI, Yoshida K and
Karin M: IKKalpha controls formation of the epidermis independently
of NF-kappaB. Nature. 410:710–714. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Maeda G, Chiba T, Kawashiri S, Satoh T and
Imai K: Epigenetic inactivation of IkappaB Kinase-alpha in oral
carcinomas and tumor progression. Clin Cancer Res. 13:5041–5047.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Choi JD and Lee JS: Interplay between
epigenetics and genetics in cancer. Genomics Inform. 11:164–173.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Ahuja N, Mohan AL, Li Q, Stolker JM,
Herman JG, Hamilton SR, Baylin SB and Issa JP: Association between
CpG island methylation and microsatellite instability in colorectal
cancer. Cancer Res. 57:3370–3374. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Bairwa NK, Saha A, Gochhait S, Pal R,
Gupta V and Bamezai RN: Microsatellite instability: an indirect
assay to detect defects in the cellular mismatch repair machinery.
Methods Mol Biol. 1105:497–509. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Gu L, Zhu N, Findley HW, Woods WG and Zhou
M: Identification and characterization of the IKKalpha promoter:
Positive and negative regulation by ETS-1 and p53, respectively. J
Biol Chem. 279:52141–52149. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Deng L, Li Y, Ai P, Xie Y, Zhu H and Chen
N: Increase in IkappaB kinase alpha expression suppresses the tumor
progression and improves the prognosis for nasopharyngeal
carcinoma. Mol Carcinog. 54:156–165. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Yan M, Zhang Y, He B, Xiang J, Wang ZF,
Zheng FM, Xu J, Chen MY, Zhu YL, Wen HJ, et al: IKKalpha
restoration via EZH2 suppression induces nasopharyngeal carcinoma
differentiation. Nat Commun. 5:36612014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
van Dorst EB, van Muijen GN, Litvinov SV
and Fleuren GJ: The limited difference between keratin patterns of
squamous cell carcinomas and adenocarcinomas is explicable by both
cell lineage and state of differentiation of tumour cells. J Clin
Pathol. 51:679–684. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Huang WG, Cheng AL, Chen ZC, Peng F, Zhang
PF, Li MY, Li F, Li JL, Li C, Yi H, et al: Targeted proteomic
analysis of 14-3-3sigma in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Int J Biochem
Cell Biol. 42:137–147. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Sullu Y, Demirag GG, Yildirim A, Karagoz F
and Kandemir B: Matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2) and MMP-9
expression in invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast. Pathol Res
Pract. 207:747–753. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Busson P, Ooka T and Corbex M:
Nasopharyngeal carcinomas and Epstein-Barr virus: From epidemiology
and detection to therapy. Med Sci (Paris). 20:453–457. 2004.In
French. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Valentine R, Dawson CW, Hu C, Shah KM,
Owen TJ, Date KL, Maia SP, Shao J, Arrand JR and Young LS:
Epstein-Barr virus-encoded EBNA1 inhibits the canonical NF-kappaB
pathway in carcinoma cells by inhibiting IKK phosphorylation. Mol
Cancer. 9:12010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Xie Y, Li Y, Peng X, Henderson F Jr, Deng
L and Chen N: Ikappa B kinase alpha involvement in the development
of nasopharyngeal carcinoma through a NF-kappaB-independent and
ERK-dependent pathway. Oral Oncol. 49:1113–1120. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Park KJ, Krishnan V, O'Malley BW, Yamamoto
Y and Gaynor RB: Formation of an IKKalpha-dependent transcription
complex is required for estrogen receptor-mediated gene activation.
Mol Cell. 18:71–82. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Luo JL, Tan W, Ricono JM, Korchynskyi O,
Zhang M, Gonias SL, Cheresh DA and Karin M: Nuclear
cytokine-activated IKKalpha controls prostate cancer metastasis by
repressing Maspin. Nature. 446:690–694. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Cao Y, Bonizzi G, Seagroves TN, Greten FR,
Johnson R, Schmidt EV and Karin M: IKKalpha provides an essential
link between RANK signaling and cyclin D1 expression during mammary
gland development. Cell. 107:763–775. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Merkhofer EC, Cogswell P and Baldwin AS:
Her2 activates NF-kappaB and induces invasion through the canonical
pathway involving IKKalpha. Oncogene. 29:1238–1248. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|