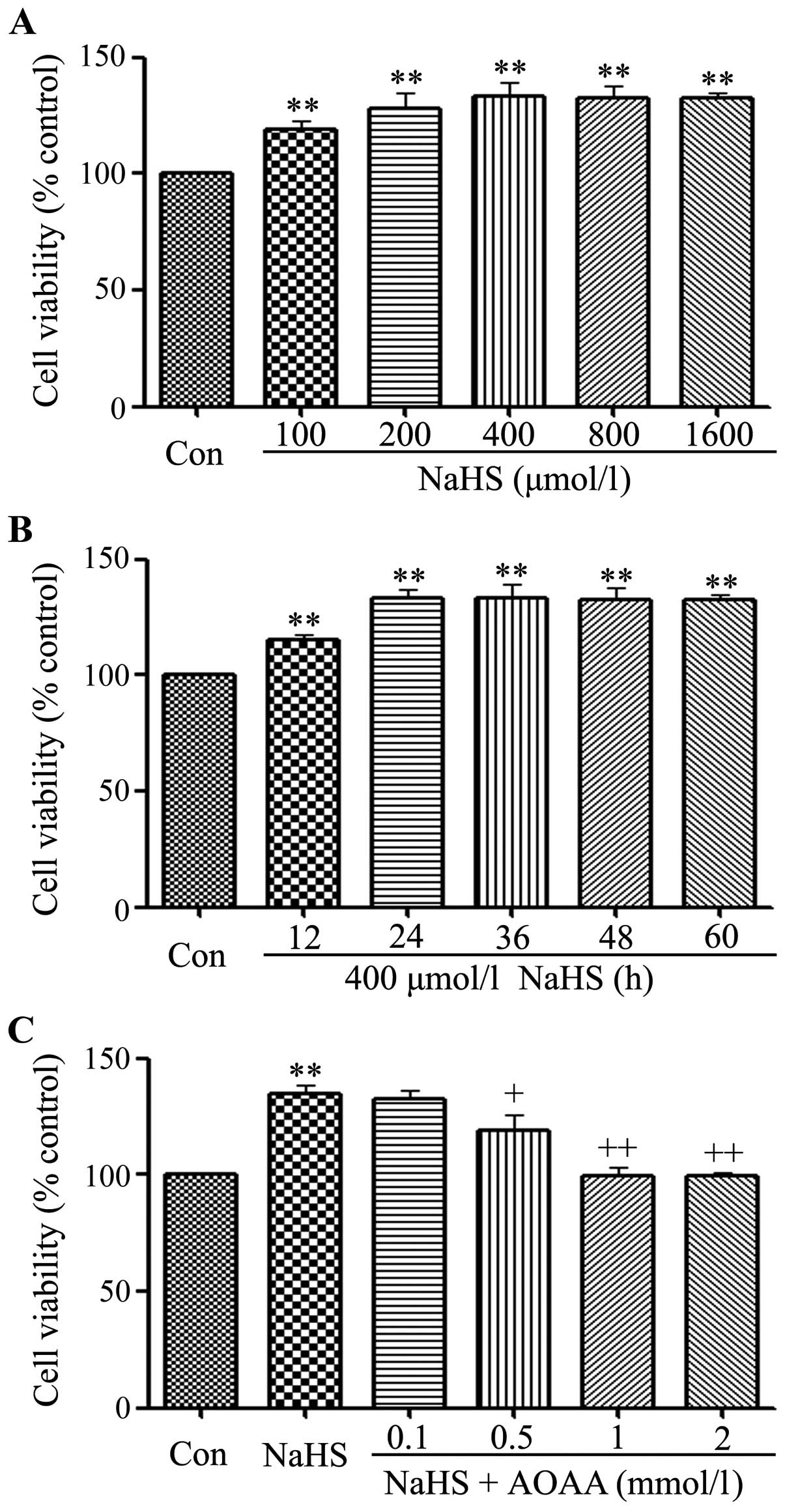
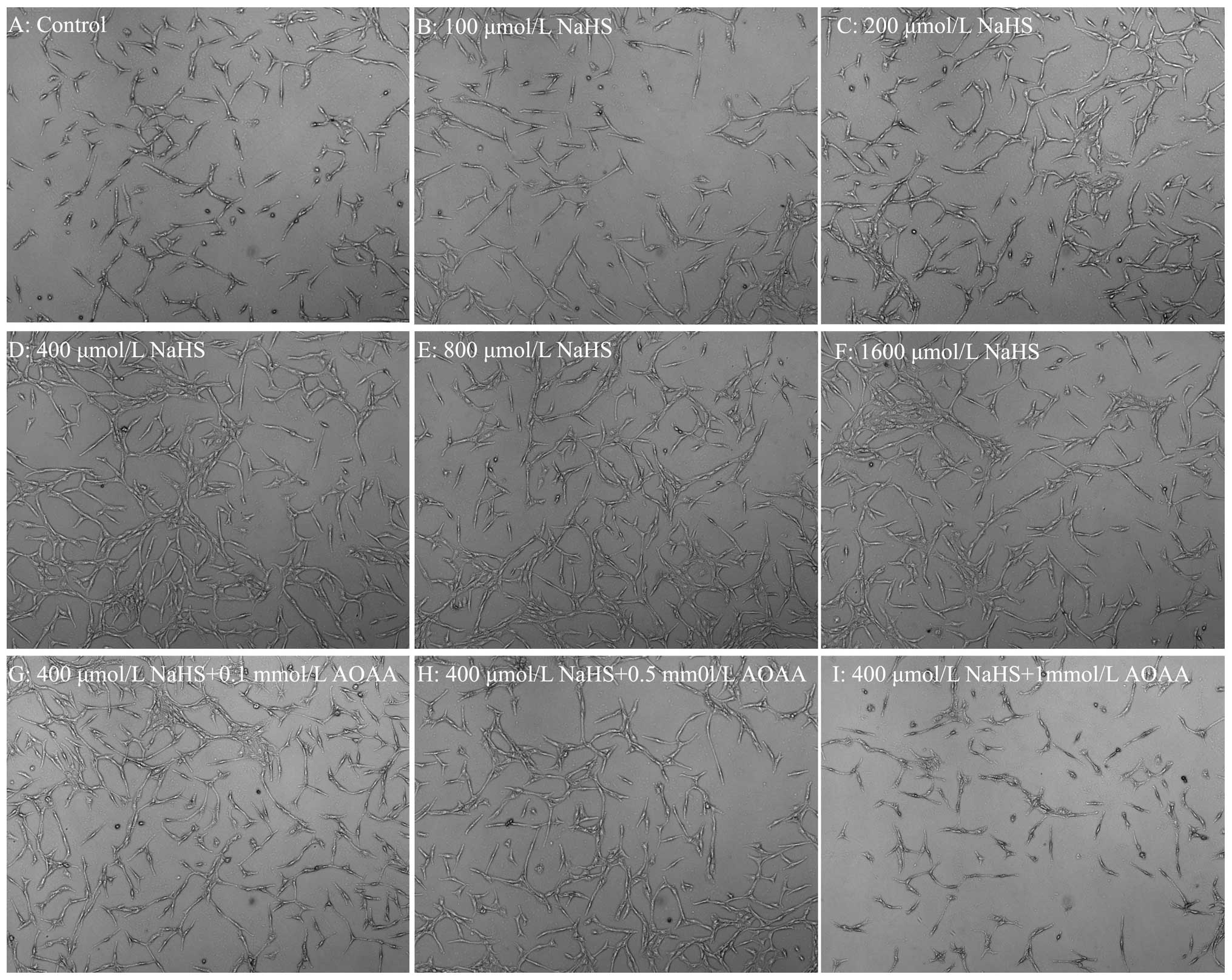
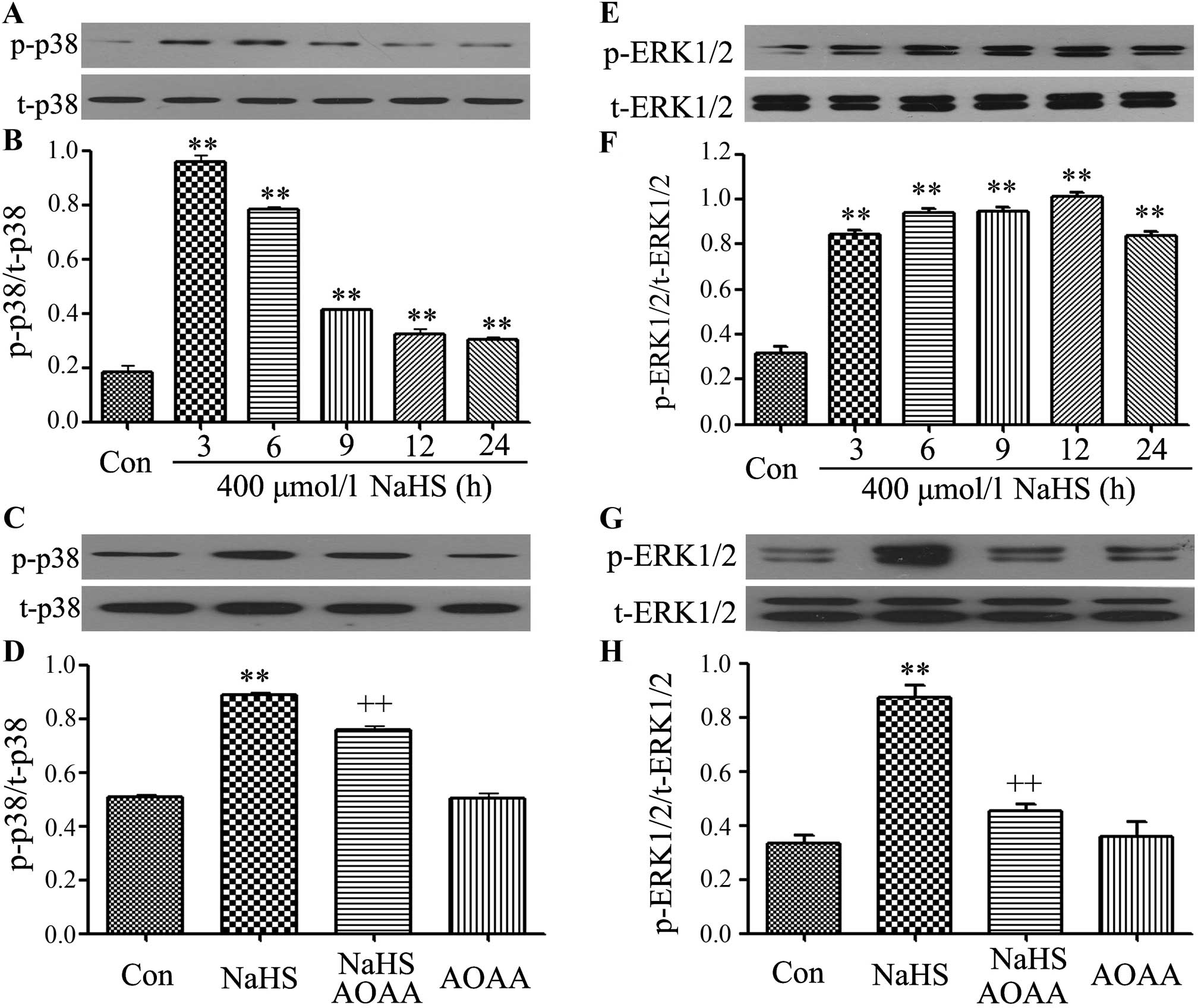
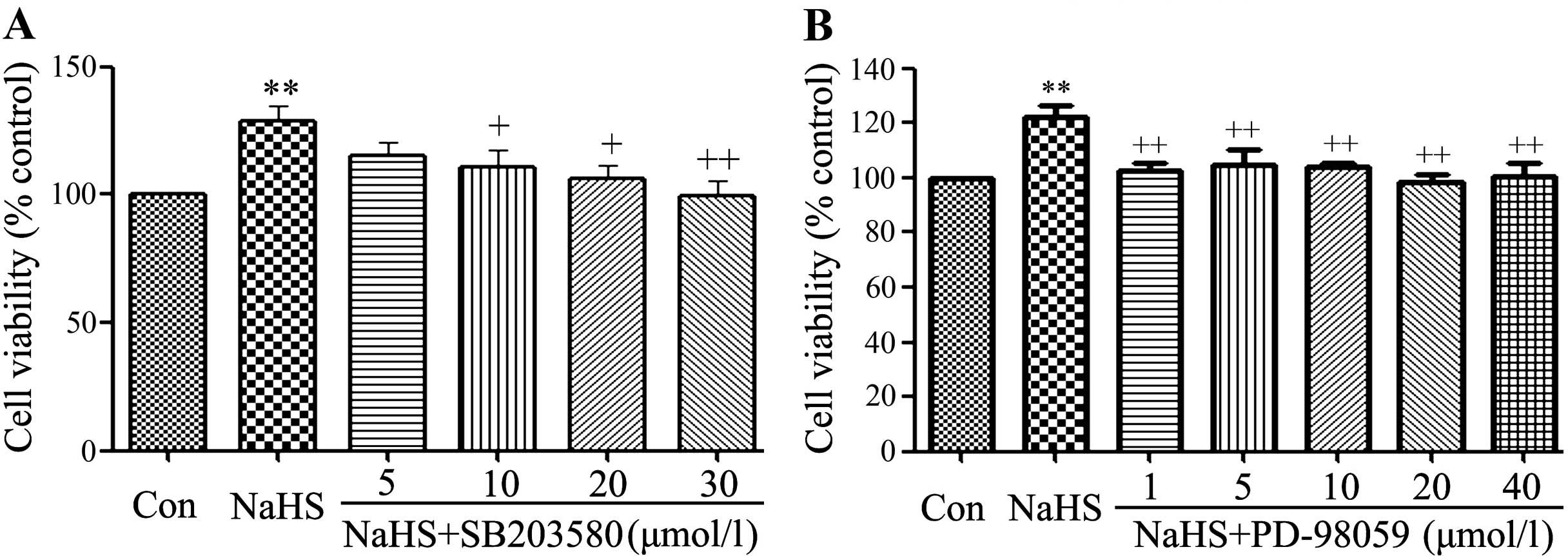
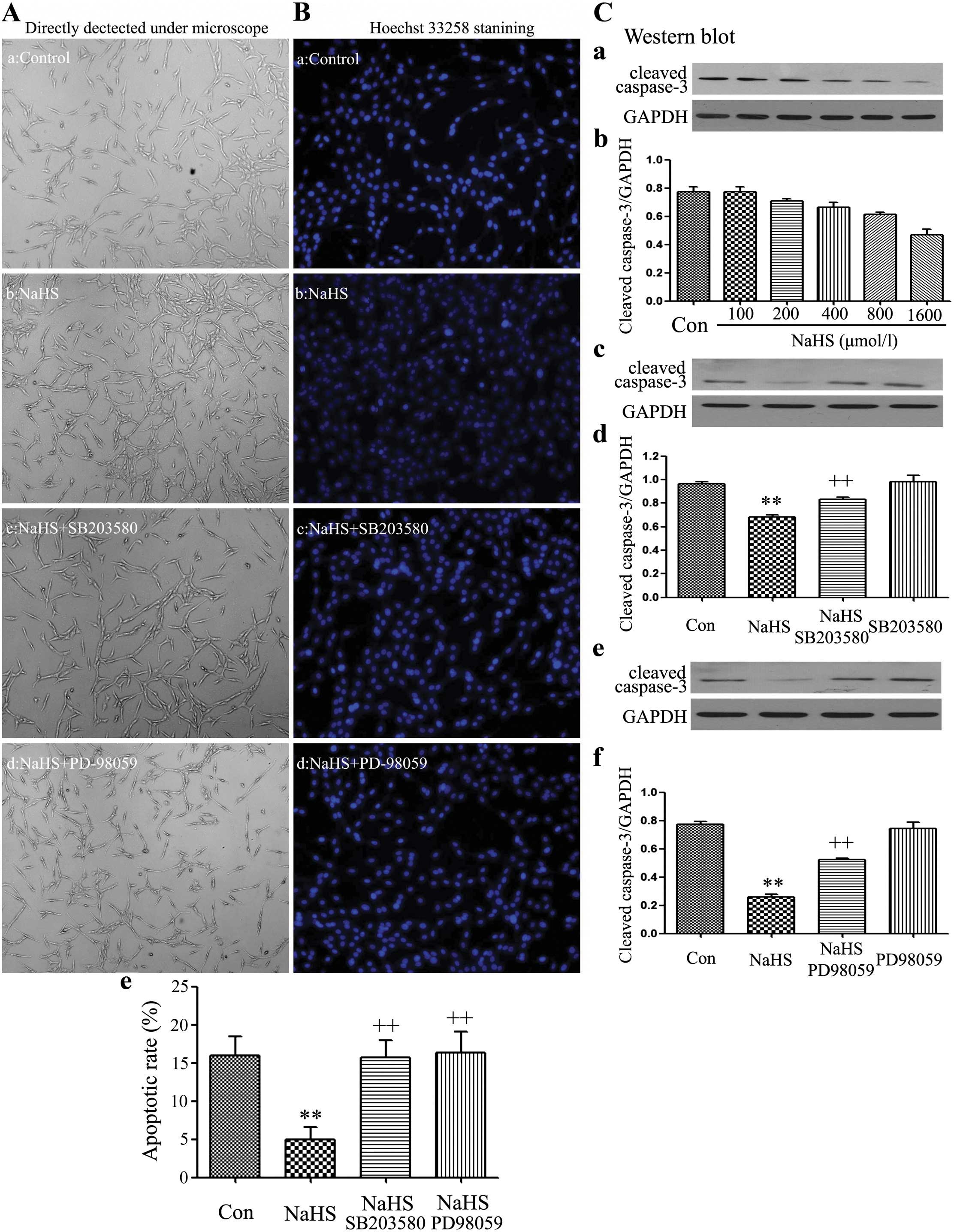
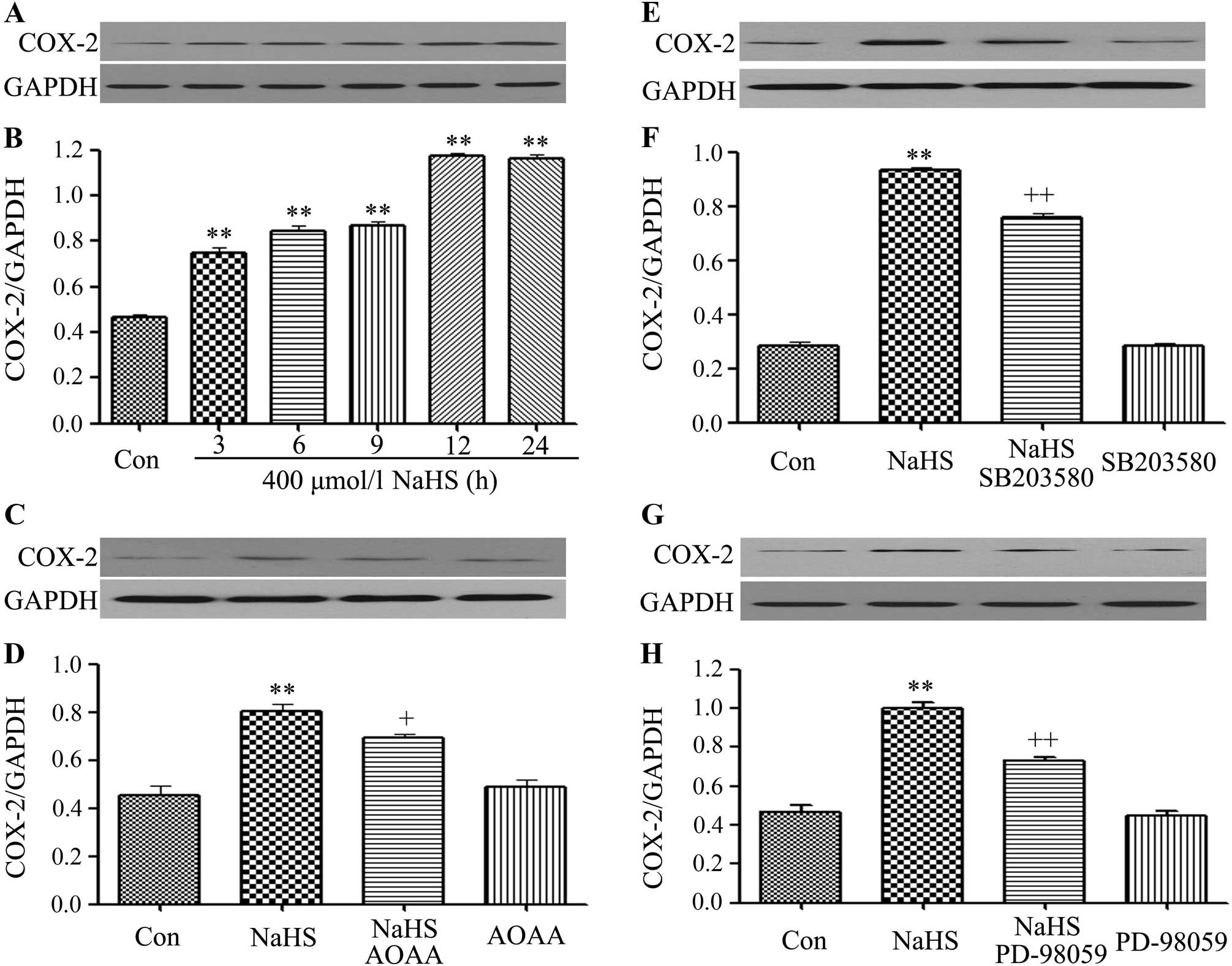
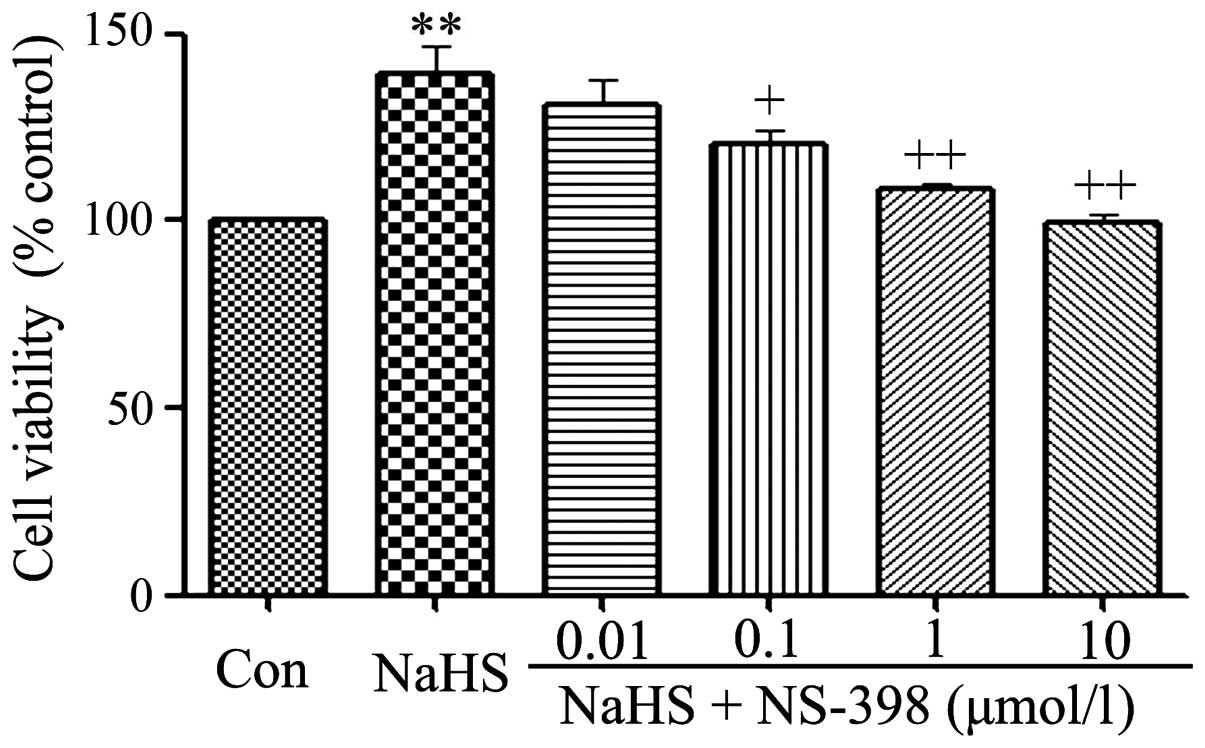
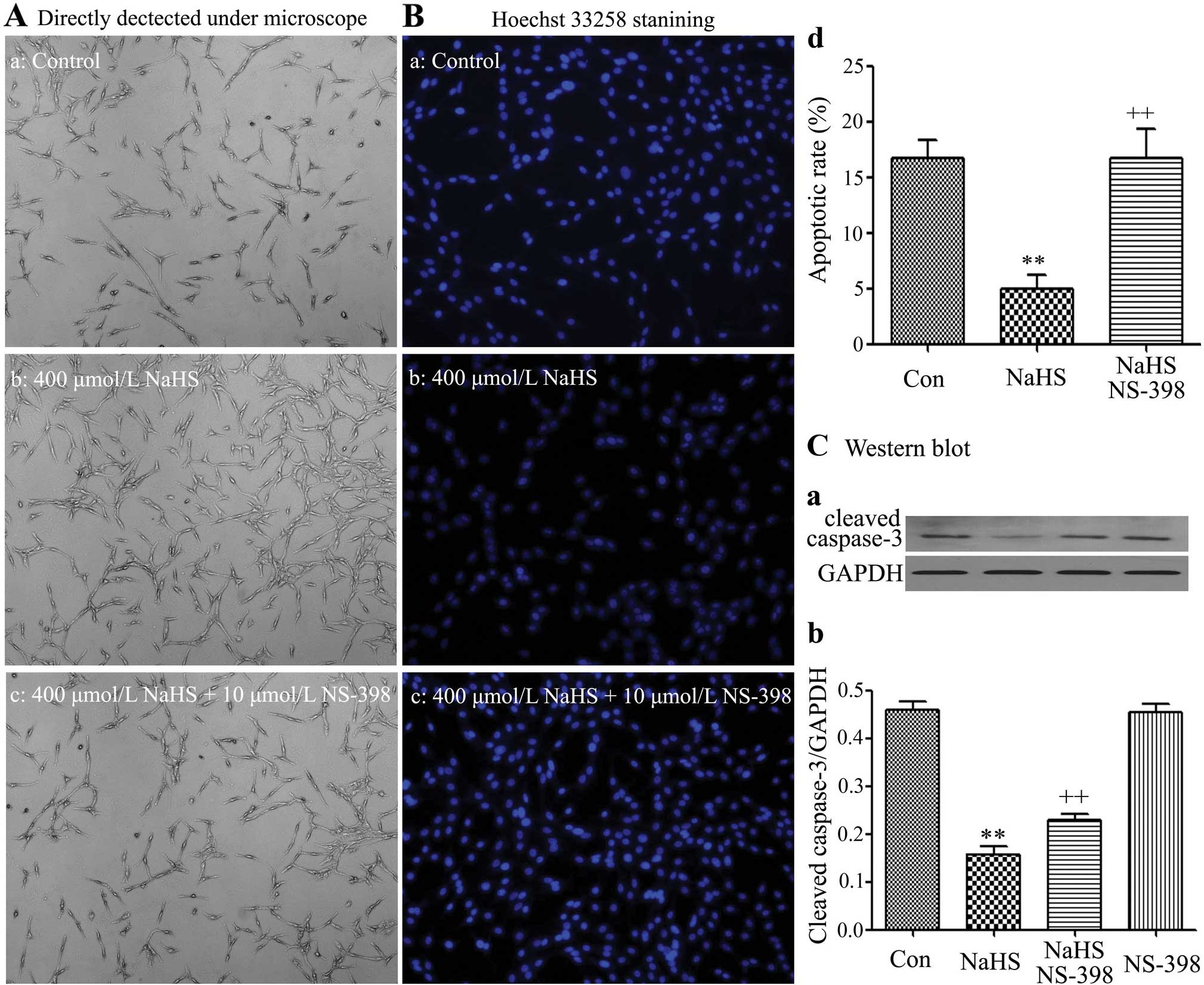
|
1
|
Louis DN, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD, Cavenee
WK, Burger PC, Jouvet A, Scheithauer BW and Kleihues P: The 2007
WHO classification of tumours of the central nervous system. Acta
Neuropathol. 114:97–109. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wei J, Gabrusiewicz K and Heimberger A:
The controversial role of microglia in malignant gliomas. Clin Dev
Immunol. 2013:2852462013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Goodenberger ML and Jenkins RB: Genetics
of adult glioma. Cancer Genet. 205:613–621. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jansen M, Yip S and Louis DN: Molecular
pathology in adult gliomas: Diagnostic, prognostic, and predictive
markers. Lancet Neurol. 9:717–726. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Schaeffer HJ and Weber MJ:
Mitogen-activated protein kinases: Specific messages from
ubiquitous messengers. Mol Cell Biol. 19:2435–2444. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Pearson G, Robinson F, Beers Gibson T, Xu
BE, Karandikar M, Berman K and Cobb MH: Mitogen-activated protein
(MAP) kinase pathways: Regulation and physiological functions.
Endocr Rev. 22:153–183. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Turjanski AG, Vaqué JP and Gutkind JS: MAP
kinases and the control of nuclear events. Oncogene. 26:3240–3253.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chang L and Karin M: Mammalian MAP kinase
signalling cascades. Nature. 410:37–40. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Roux PP and Blenis J: ERK and p38
MAPK-activated protein kinases: A family of protein kinases with
diverse biological functions. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 68:320–344.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ding D, Wei S, Song Y, Li L, Du G, Zhan H
and Cao Y: Osthole exhibits anti-cancer property in rat glioma
cells through inhibiting PI3K/Akt and MAPK signaling pathways. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 32:1751–1760. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang B, Wu T, Wang Z, Zhang Y, Wang J,
Yang B, Zhao Y, Rao Z and Gao J: p38MAPK activation mediates tumor
necrosis factor-α-induced apoptosis in glioma cells. Mol Med Rep.
11:3101–3107. 2015.
|
|
12
|
Li F, Chen T, Hu S, Lin J, Hu R and Feng
H: Superoxide mediates direct current electric field-induced
directional migration of glioma cells through the activation of AKT
and ERK. PLoS One. 8:e611952013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Subbaramaiah K, Chung WJ and Dannenberg
AJ: Ceramide regulates the transcription of cyclooxygenase-2.
Evidence for involvement of extracellular signal-regulated
kinase/c-Jun N-terminal kinase and p38 mitogen-activated protein
kinase pathways. J Biol Chem. 273:32943–32949. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Limami Y, Pinon A, Leger DY, Pinault E,
Delage C, Beneytout JL, Simon A and Liagre B: The
P2Y2/Src/p38/COX-2 pathway is involved in the resistance
to ursolic acid-induced apoptosis in colorectal and prostate cancer
cells. Biochimie. 94:1754–1763. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kim JY, Chung SW, Kim SY and Byun Y:
Enhanced anti-angiogenic effect of low molecular weight heparinbile
acid conjugates by co-administration of a selective COX-2
inhibitor. Pharm Res. 32:2318–2327. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Tegeder I, Niederberger E, Israr E,
Gühring H, Brune K, Euchenhofer C, Grösch S and Geisslinger G:
Inhibition of NF-kappaB and AP-1 activation by R- and
S-flurbiprofen. FASEB J. 15:2–4. 2001.
|
|
17
|
Seo KW, Coh YR, Rebhun RB, Ahn JO, Han SM,
Lee HW and Youn HY: Antitumor effects of celecoxib in COX-2
expressing and non-expressing canine melanoma cell lines. Res Vet
Sci. 96:482–486. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wu X, Cai M, Ji F and Lou LM: The impact
of COX-2 on invasion of osteosarcoma cell and its mechanism of
regulation. Cancer Cell Int. 14:272014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wu T, Han C, Lunz JG III, Michalopoulos G,
Shelhamer JH and Demetris AJ: Involvement of 85-kd cytosolic
phospholipase A and cyclooxygenase-2 in the proliferation of human
cholangio-2 carcinoma cells. Hepatology. 36:363–373. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chiu WT, Shen SC, Chow JM, Lin CW, Shia LT
and Chen YC: Contribution of reactive oxygen species to
migration/invasion of human glioblastoma cells U87 via
ERK-dependent COX-2/PGE2 activation. Neurobiol Dis.
37:118–129. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Wang R: Two's company, three's a crowd:
Can H2S be the third endogenous gaseous transmitter?
FASEB J. 16:1792–1798. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Guidotti TL: Hydrogen sulfide: Advances in
understanding human toxicity. Int J Toxicol. 29:569–581. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kilburn KH, Thrasher JD and Gray MR:
Low-level hydrogen sulfide and central nervous system dysfunction.
Toxicol Ind Health. 26:387–405. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Szabo C, Coletta C, Chao C, Módis K,
Szczesny B, Papapetropoulos A and Hellmich MR: Tumor-derived
hydrogen sulfide, produced by cystathionine-β-synthase, stimulates
bioenergetics, cell proliferation, and angiogenesis in colon
cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 110:12474–12479. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Pupo E, Pla AF, Avanzato D, Moccia F, Cruz
JE, Tanzi F, Merlino A, Mancardi D and Munaron L: Hydrogen sulfide
promotes calcium signals and migration in tumor-derived endothelial
cells. Free Radic Biol Med. 51:1765–1773. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Du SX, Xiao J, Guan F, Sun LM, Wu WS, Tang
H, Du JB, Tang CS and Jin HF: Predictive role of cerebrospinal
fluid hydrogen sulfide in central nervous system leukemia. Chin Med
J. 124:3450–3454. 2011.
|
|
27
|
Levine J, Ellis CJ, Furne JK, Springfield
J and Levitt MD: Fecal hydrogen sulfide production in ulcerative
colitis. Am J Gastroenterol. 93:83–87. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Rose P, Moore PK, Ming SH, Nam OC,
Armstrong JS and Whiteman M: Hydrogen sulfide protects colon cancer
cells from chemopreventative agent beta-phenylethyl isothiocyanate
induced apoptosis. World J Gastroenterol. 11:3990–3997.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Cai WJ, Wang MJ, Ju LH, Wang C and Zhu YC:
Hydrogen sulfide induces human colon cancer cell proliferation:
Role of Akt, ERK and p21. Cell Biol Int. 34:565–572. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Cao Q, Zhang L, Yang G, Xu C and Wang R:
Butyrate-stimulated H2S production in colon cancer
cells. Antioxid Redox Signal. 12:1101–1109. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Zhen Y, Pan W, Hu F, Wu H, Feng J, Zhang Y
and Chen J: Exogenous hydrogen sulfide exerts
proliferation/anti-apoptosis/angiogenesis/migration effects via
amplifying the activation of NF-κB pathway in PLC/PRF/5 hepatoma
cells. Int J Oncol. 46:2194–2204. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Tan BH, Wong PT and Bian JS: Hydrogen
sulfide: A novel signaling molecule in the central nervous system.
Neurochem Int. 56:3–10. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Rong W, Kimura H and Grundy D: The
neurophysiology of hydrogen sulfide. Inflamm Allergy Drug Targets.
10:109–117. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhang X and Bian JS: Hydrogen sulfide: A
neuromodulator and neuroprotectant in the central nervous system.
ACS Chem Neurosci. 5:876–883. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chan SJ, Chai C, Lim TW, Yamamoto M, Lo
EH, Lai MK and Wong PT: Cystathionine β-synthase inhibition is a
potential therapeutic approach to treatment of ischemic injury. ASN
Neuro. 7:17590914155787112015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Chen WL, Niu YY, Jiang WZ, Tang HL, Zhang
C, Xia QM and Tang XQ: Neuroprotective effects of hydrogen sulfide
and the underlying signaling pathways. Rev Neurosci. 26:129–142.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Donatti AF, Soriano RN, Sabino JP and
Branco LG: Involvement of endogenous hydrogen sulfide
(H2S) in the rostral ventrolateral medulla (RVLM) in
hypoxia-induced hypothermia. Brain Res Bull. 108:94–99. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Jiang JM, Zhou CF, Gao SL, Tian Y, Wang
CY, Wang L, Gu HF and Tang XQ: BDNF-TrkB pathway mediates
neuroprotection of hydrogen sulfide against formaldehyde-induced
toxicity to PC12 cells. PLoS One. 10:e01194782015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Xu K, Wang L and Shu HK: COX-2
overexpression increases malignant potential of human glioma cells
through Id1. Oncotarget. 5:1241–1252. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ma K, Liu Y, Zhu Q, Liu CH, Duan JL, Tan
BK and Zhu YZ: H2S donor, S-propargylcysteine, increases
CSE in SGC-7901 and cancer-induced mice: Evidence for a novel
anti-cancer effect of endogenous H2S? PLoS One.
6:e205252011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Murata T, Sato T, Kamoda T, Moriyama H,
Kumazawa Y and Hanada N: Differential susceptibility to hydrogen
sulfide-induced apoptosis between PHLDA1-overexpressing oral cancer
cell lines and oral keratinocytes: Role of PHLDA1 as an apoptosis
suppressor. Exp Cell Res. 320:247–257. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Chattopadhyay M, Kodela R, Olson KR and
Kashfi K: NOSH-aspirin (NBS-1120), a novel nitric oxide- and
hydrogen sulfide-releasing hybrid is a potent inhibitor of colon
cancer cell growth in vitro and in a xenograft mouse model. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 419:523–528. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Lee ZW, Zhou J, Chen CS, Zhao Y, Tan CH,
Li L, Moore PK and Deng LW: The slow-releasing hydrogen sulfide
donor, GYY4137, exhibits novel anti-cancer effects in vitro and in
vivo. PLoS One. 6:e210772011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|