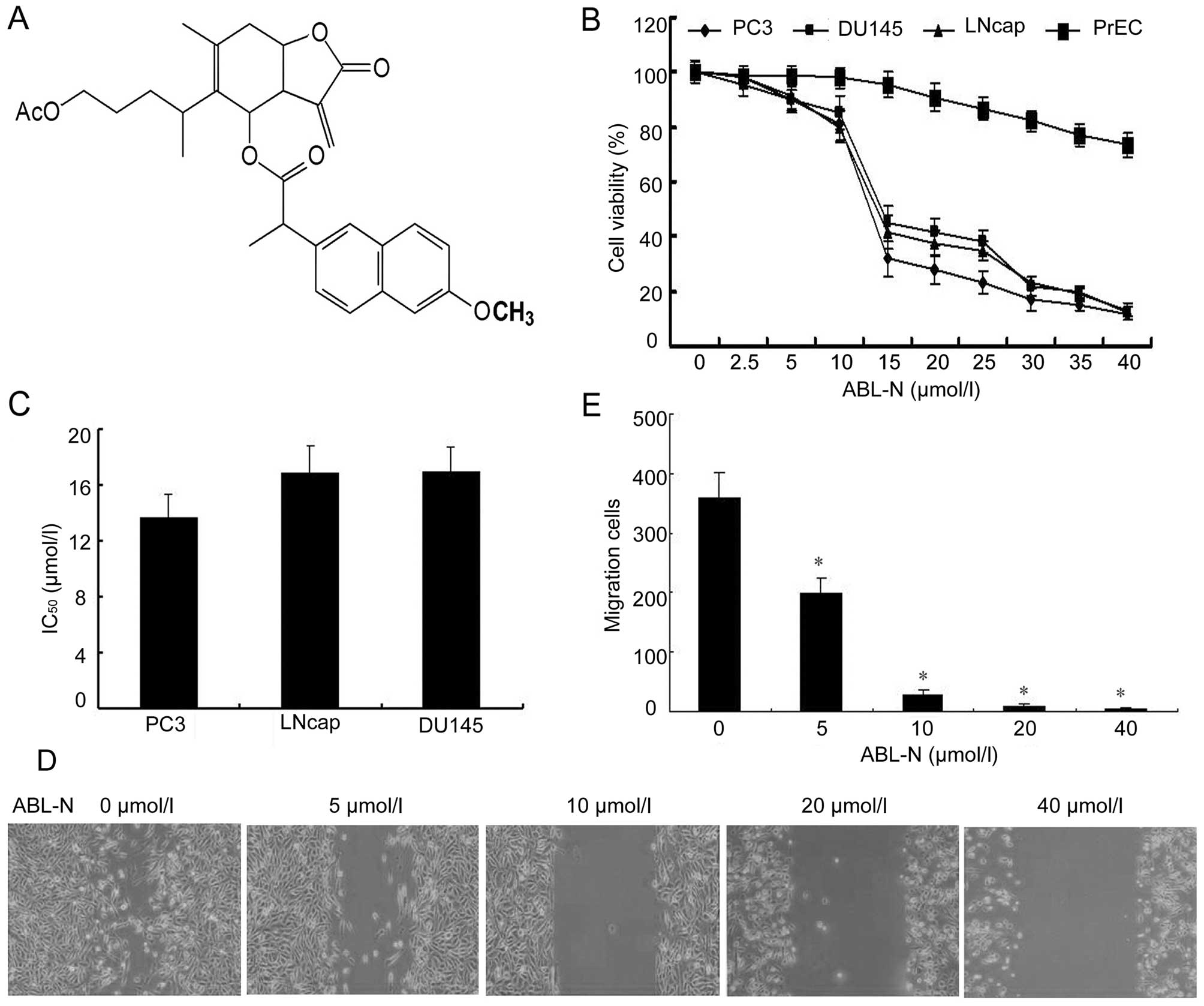
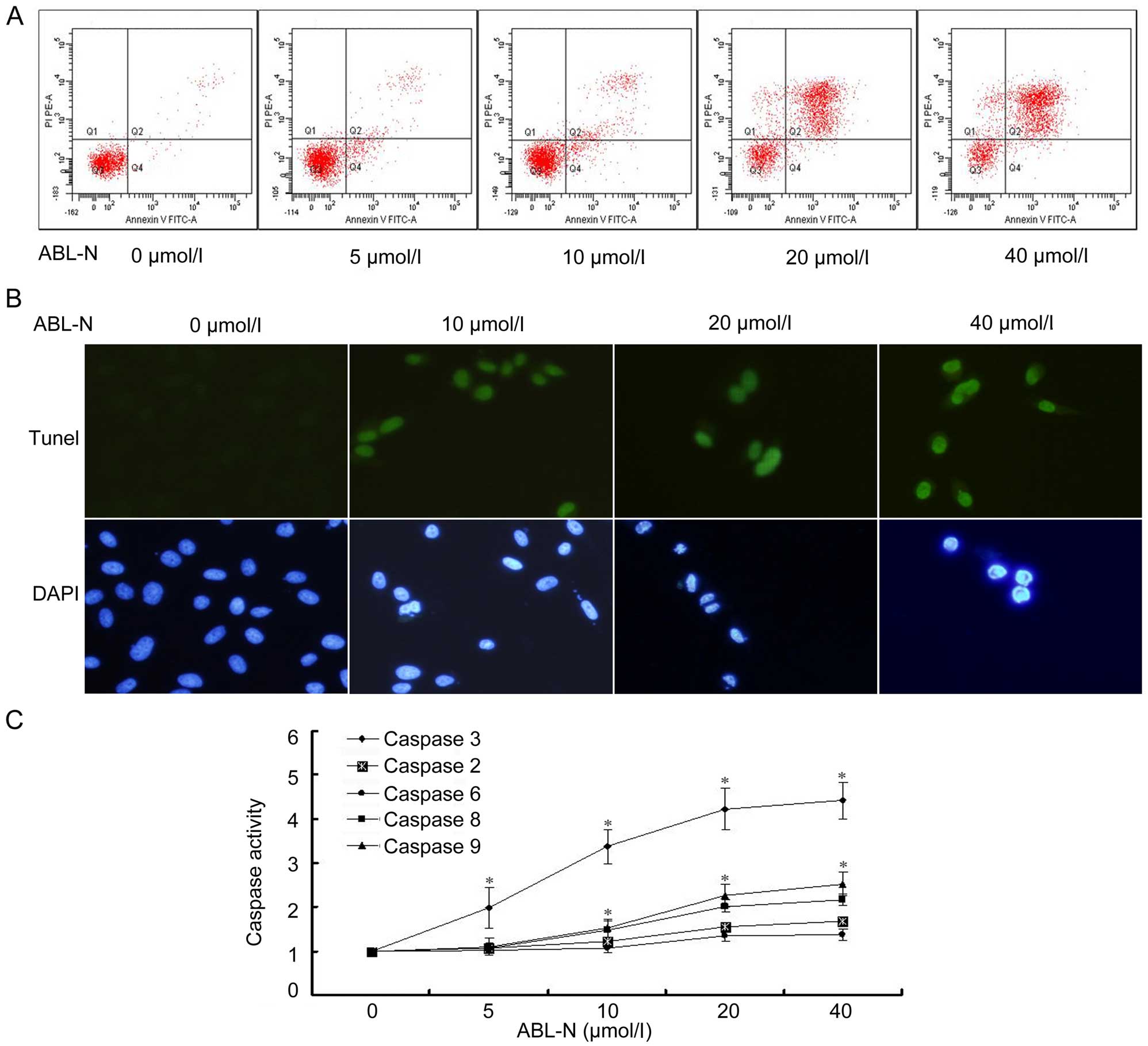
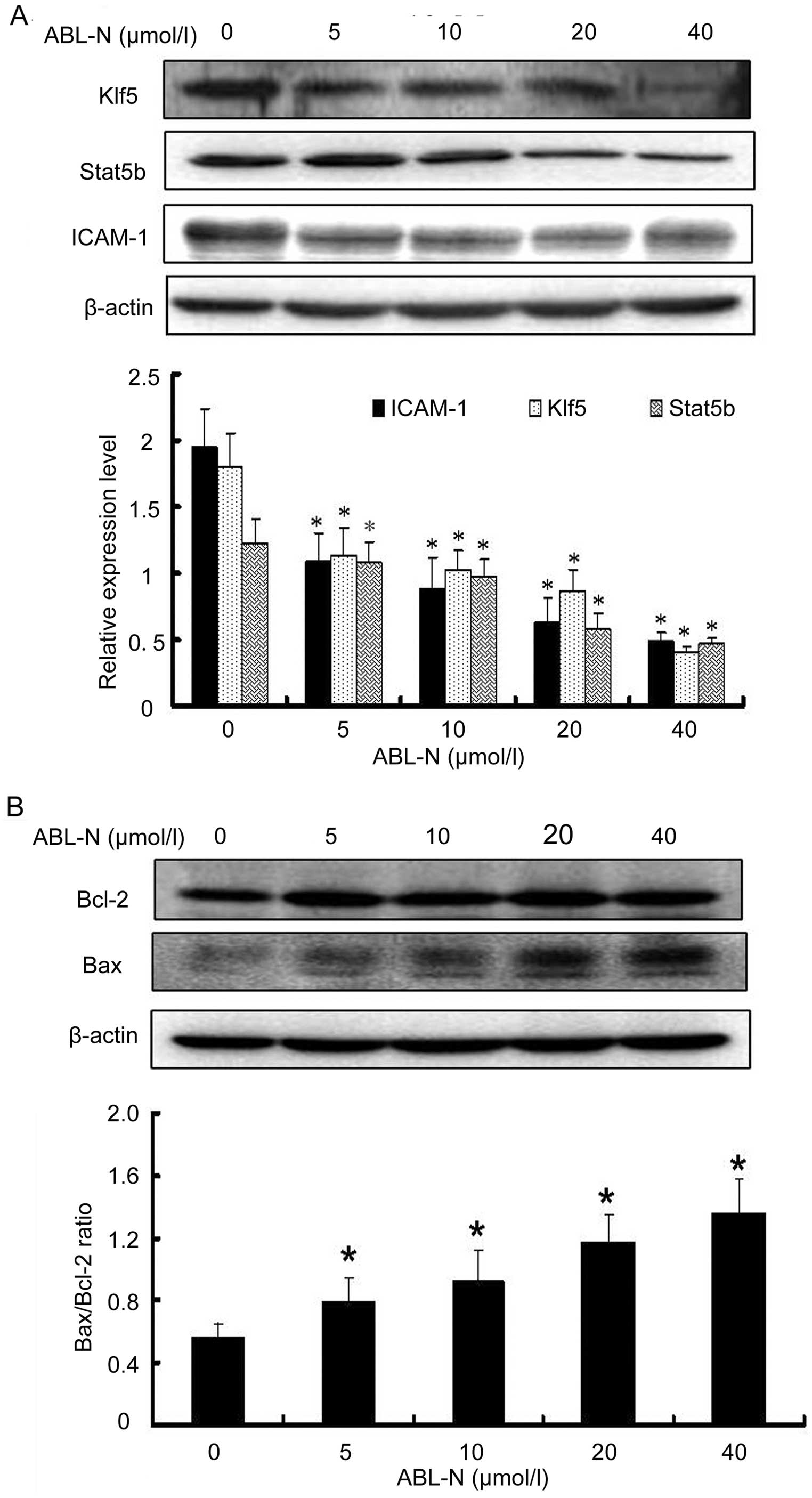
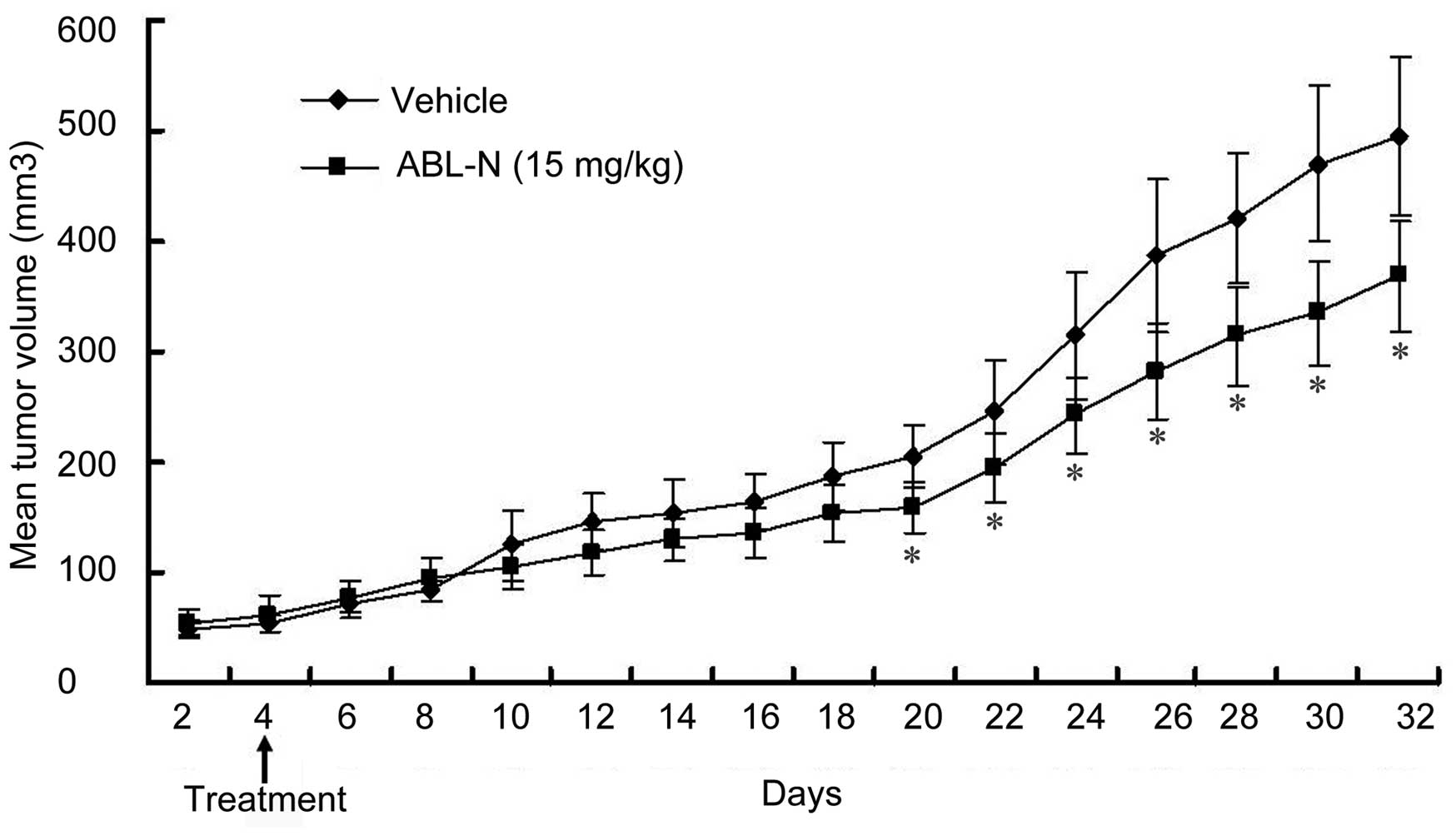
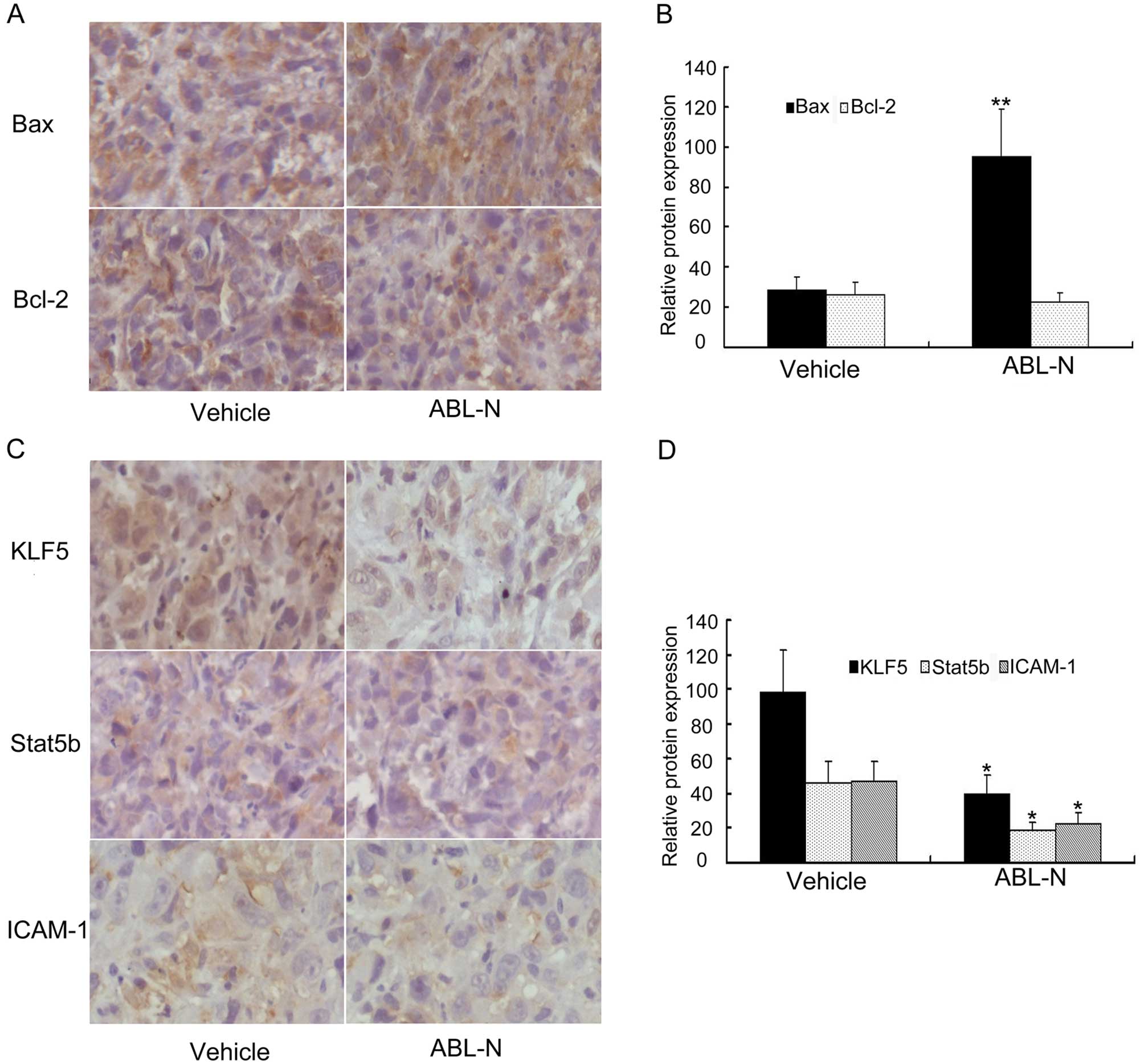
|
1
|
Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 64:9–29. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Matsuda T and Saika K: Comparison of time
trends in prostate cancer incidence (1973–2002) in Asia, from
cancer incidence in five continents, Vols IV–IX. Jpn J Clin Oncol.
39:468–469. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Peng P, Gong Y, Bao P, Ke JZ, Xiang YM,
Zhang ML and Zheng Y: Estimates and prediction of prostate cancer
incidence, mortality and prevalence in China, 2008. Zhonghua Liu
Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi. 33:1056–1059. 2012.In Chinese.
|
|
4
|
Yin PH, Liu X, Qiu YY, Cai JF, Qin JM, Zhu
HR and Li Q: Anti-tumor activity and apoptosis-regulation
mechanisms of bufalin in various cancers: New hope for cancer
patients. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 13:5339–5343. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Bilbro J, Mart M and Kyprianou N:
Therapeutic value of quinazoline-based compounds in prostate
cancer. Anticancer Res. 33:4695–4700. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Schmitz-Dräger BJ, Lümmen G, Bismarck E
and Fischer C: Prevention strategies for prostate cancer. Minerva
Urol Nefrol. 64:225–231. 2012.
|
|
7
|
Samarghandian S, Samini F and Taghavi M:
Antiproliferative and cytotoxic properties of honey in human
prostate cancer cell line (PC-3): Possible mechanism of cell growth
inhibition and apoptosis induction. Afr J Pharm Pharmacol. 8:9–15.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Hafeez BB, Siddiqui IA, Asim M, Malik A,
Afaq F, Adhami VM, Saleem M, Din M and Mukhtar H: A dietary
anthocyanidin delphinidin induces apoptosis of human prostate
cancer PC3 cells in vitro and in vivo: Involvement of nuclear
factor-kappaB signaling. Cancer Res. 68:8564–8572. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yun JM, Kweon MH, Kwon H, Hwang JK and
Mukhtar H: Induction of apoptosis and cell cycle arrest by a
chalcone panduratin A isolated from Kaempferia pandurata in
androgen-independent human prostate cancer cells PC3 and DU145.
Carcinogenesis. 27:1454–1464. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Fang XM, Liu B, Liu YB, Wang JJ, Wen JK,
Li BH and Han M: Acetylbritannilactone suppresses growth via
upregulation of krüppel-like transcription factor 4 expression in
HT-29 colorectal cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 26:1181–1187.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Rafi MM, Bai NS, Chi-Tang-Ho, Rosen RT,
White E, Perez D and Dipaola RS: A sesquiterpenelactone from Inula
britannica induces anti-tumor effects dependent on Bcl-2
phosphorylation. Anticancer Res. 25:313–318. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liu B, Han M, Sun RH, Wang JJ, Zhang YP,
Zhang DQ and Wen JK: ABL-N-induced apoptosis in human breast cancer
cells is partially mediated by c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase
activation. Breast Cancer Res. 12:R92010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Dong L-H, Wen J-K, Liu G, McNutt MA, Miao
SB, Gao R, Zheng B, Zhang H and Han M: Blockade of the
Ras-extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 pathway is involved
in smooth muscle 22 α-mediated suppression of vascular smooth
muscle cell proliferation and neointima hyperplasia. Arterioscler
Thromb Vasc Biol. 30:683–691. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Rao L and White E: Bcl-2 and the ICE
family of apoptotic regulators: Making a connection. Curr Opin
genet Dev. 7:52–58. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yi T, Yi Z, Cho SG, Luo J, Pandey MK,
Aggarwal BB and Liu M: Gambogic acid inhibits angiogenesis and
prostate tumor growth by suppressing vascular endothelial growth
factor receptor 2 signaling. Cancer Res. 68:1843–1850. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bai N, Lai CS, He K, Zhou Z, Zhang L, Quan
Z, Zhu N, Zheng QY, Pan MH and Ho CT: Sesquiterpene lactones from
Inula britannica and their cytotoxic and apoptotic effects on human
cancer cell lines. J Nat Prod. 69:531–535. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wolf BB and Green DR: Suicidal tendencies:
Apoptotic cell death by caspase family proteinases. J Biol Chem.
274:20049–20052. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hu W and Kavanagh JJ: Anticancer therapy
targeting the apoptotic pathway. Lancet Oncol. 4:721–729. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang X: The expanding role of mitochondria
in apoptosis. Genes Dev. 15:2922–2933. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wolter KG, Hsu YT, Smith CL, Nechushtan A,
Xi XG and Youle RJ: Movement of Bax from the cytosol to
mitochondria during apoptosis. J Cell Biol. 139:1281–1292. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Adams JM and Cory S: The Bcl-2 protein
family: Arbiters of cell survival. Science. 281:1322–1326. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tafani M, Schneider TG, Pastorino JG and
Farber JL: Cytochrome c-dependent activation of caspase-3 by tumor
necrosis factor requires induction of the mitochondrial
permeability transition. Am J Pathol. 156:2111–2121. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ahonen TJ, Xie J, LeBaron MJ, Zhu J, Nurmi
M, Alanen K, Rui H and Nevalainen MT: Inhibition of transcription
factor Stat5 induces cell death of human prostate cancer cells. J
Biol Chem. 278:27287–27292. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Li H, Zhang Y, Glass A, Zellweger T, Gehan
E, Bubendorf L, Gelmann EP and Nevalainen MT: Activation of signal
transducer and activator of transcription-5 in prostate cancer
predicts early recurrence. Clin Cancer Res. 11:5863–5868. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gu L, Vogiatzi P, Puhr M, Dagvadorj A,
Lutz J, Ryder A, Addya S, Fortina P, Cooper C, Leiby B, et al:
Stat5 promotes metastatic behavior of human prostate cancer cells
in vitro and in vivo. Endocr Relat Cancer. 17:481–493. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Gu L, Dagvadorj A, Lutz J, Leiby B,
Bonuccelli G, Lisanti MP, Addya S, Fortina P, Dasgupta A, Hyslop T,
et al: Transcription factor Stat3 stimulates metastatic behavior of
human prostate cancer cells in vivo, whereas Stat5b has a
preferential role in the promotion of prostate cancer cell
viability and tumor growth. Am J Pathol. 176:1959–1972. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yoo NC, Chung HC, Chung HC, Park JO, Rha
SY, Kim JH, Roh JK, Min JS, Kim BS and Noh SH: Synchronous
elevation of soluble intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) and
vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) correlates with gastric
cancer progression. Yonsei Med J. 39:27–36. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Li X, Zhang B, Wu Q, Ci X, Zhao R, Zhang
Z, Xia S, Su D, Chen J, Ma G, et al: Interruption of KLF5
acetylation converts its function from tumor suppressor to tumor
promoter in prostate cancer cells. Int J Cancer. 136:536–546.
2015.
|
|
29
|
Chen C, Bhalala HV, Vessella RL and Dong
JT: KLF5 is frequently deleted and down-regulated but rarely
mutated in prostate cancer. Prostate. 55:81–88. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chen C, Sun X, Ran Q, Wilkinson KD, Murphy
TJ, Simons JW and Dong JT: Ubiquitin-proteasome degradation of KLF5
transcription factor in cancer and untransformed epithelial cells.
Oncogene. 24:3319–3327. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Tong D, Czerwenka K, Heinze G, Ryffel M,
Schuster E, Witt A, Leodolter S and Zeillinger R: Expression of
KLF5 is a prognostic factor for disease-free survival and overall
survival in patients with breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
12:2442–2448. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kwak MK, Lee H-J, Hur K, Park J, Lee HS,
Kim WH, Lee KU, Choe KJ, Guilford P and Yang HK: Expression of
Krüppel-like factor 5 in human gastric carcinomas. J Cancer Res
Clin Oncol. 134:163–167. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
McConnell BB, Bialkowska AB, Nandan MO,
Ghaleb AM, Gordon FJ and Yang VW: Haploinsufficiency of
Krüppel-like factor 5 rescues the tumor-initiating effect of the
ApcMin mutation in the intestine. Cancer Res.
69:4125–4133. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|