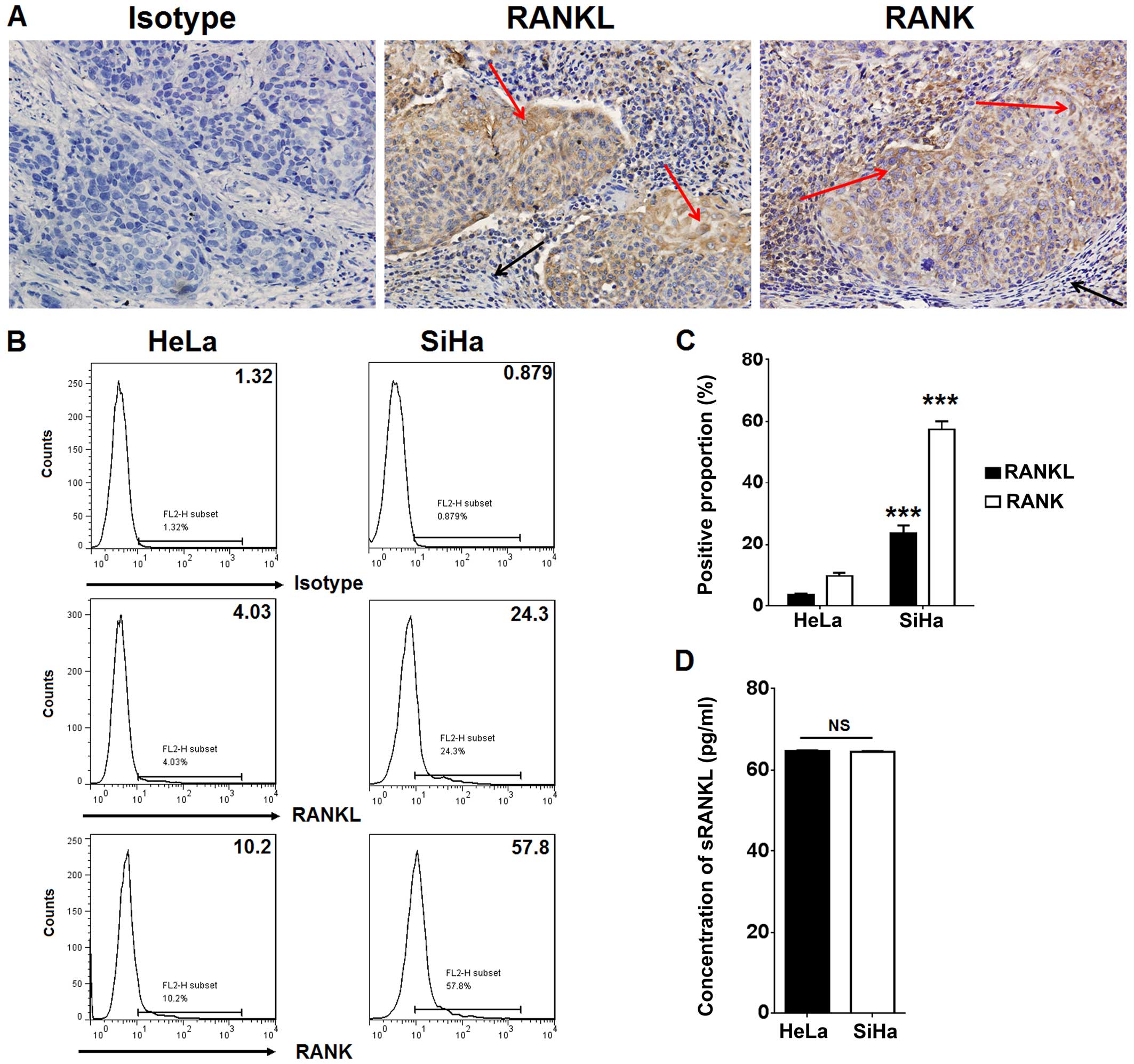
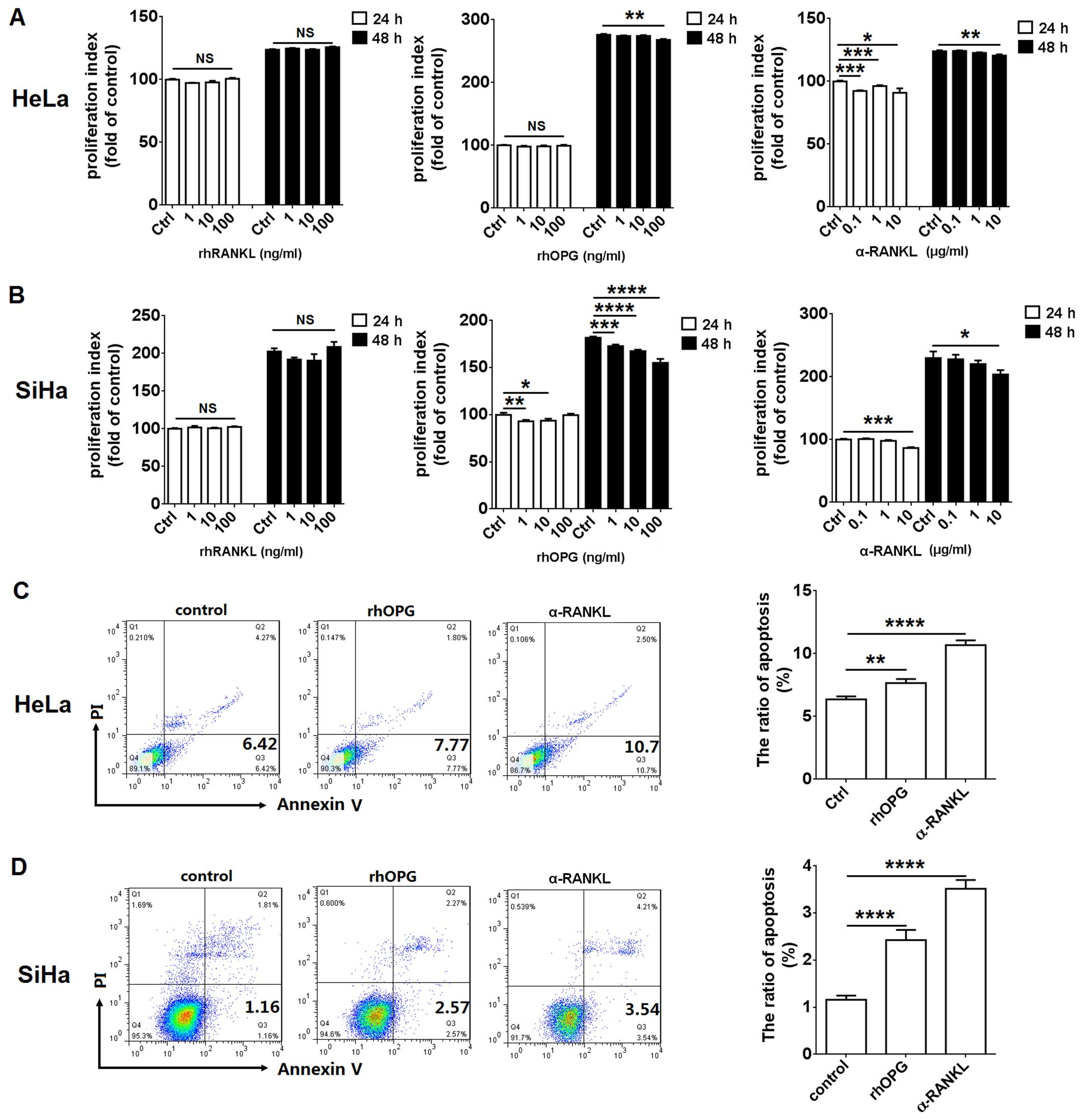
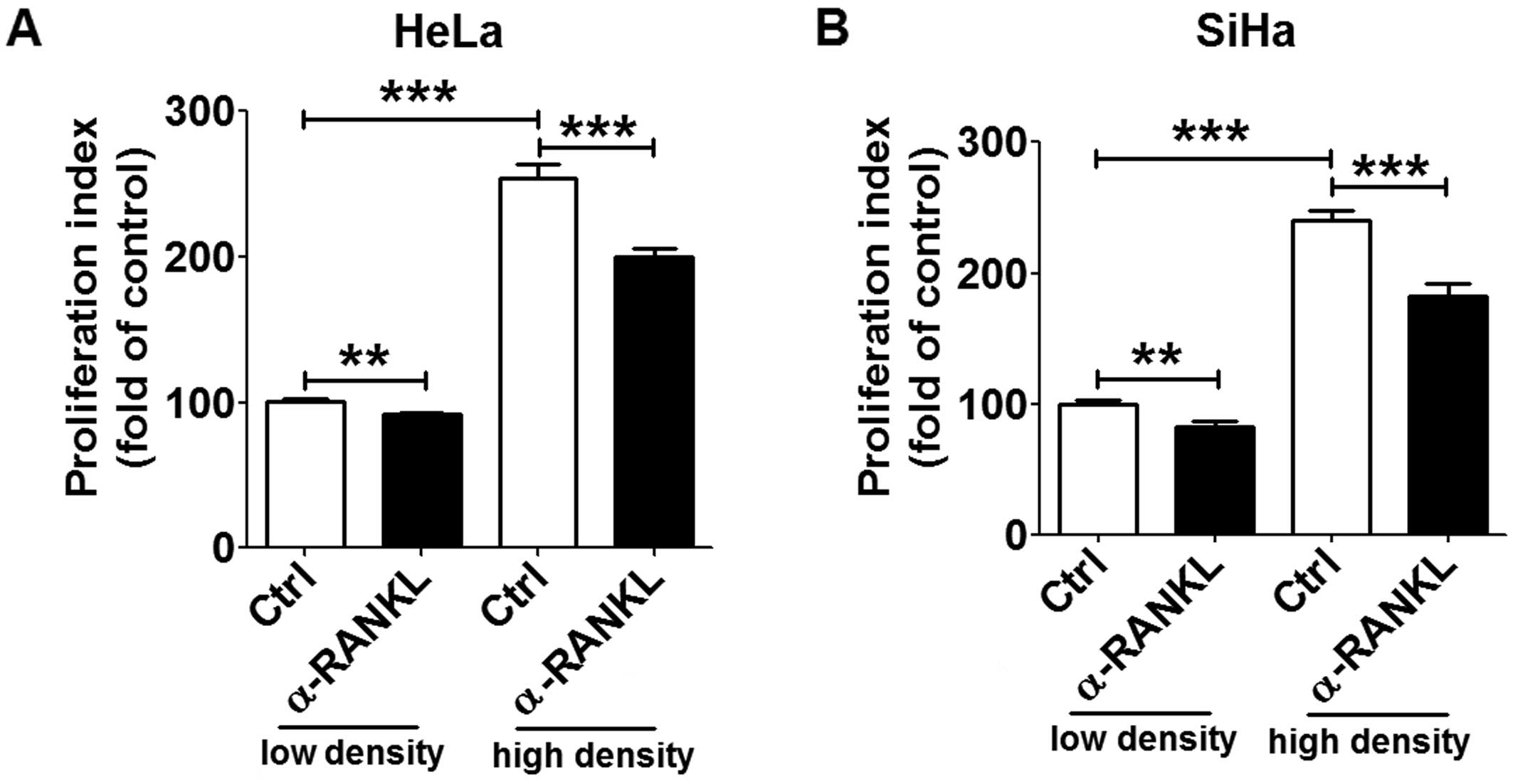
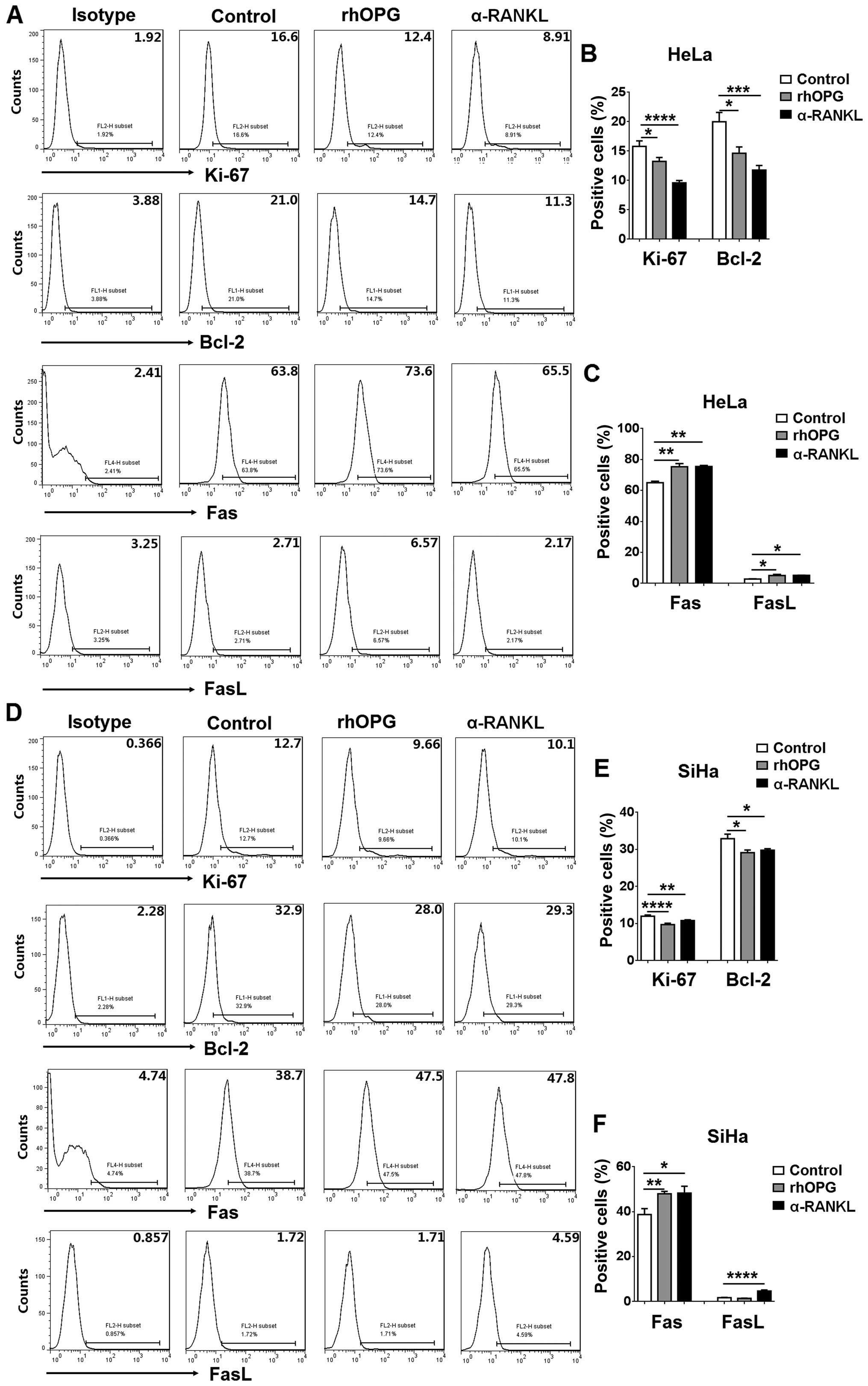
|
1
|
Stewart BW and Wild CP: World Cancer
Report 2014. World Health Organization. Chapter 5.12. IARC
Nonserial Publication; 2014
|
|
2
|
Fu Z, Chen D, Cheng H and Wang F:
Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α protects cervical carcinoma cells from
apoptosis induced by radiation via modulation of vascular
endothelial growth factor and p53 under hypoxia. Med Sci Monit.
21:318–325. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
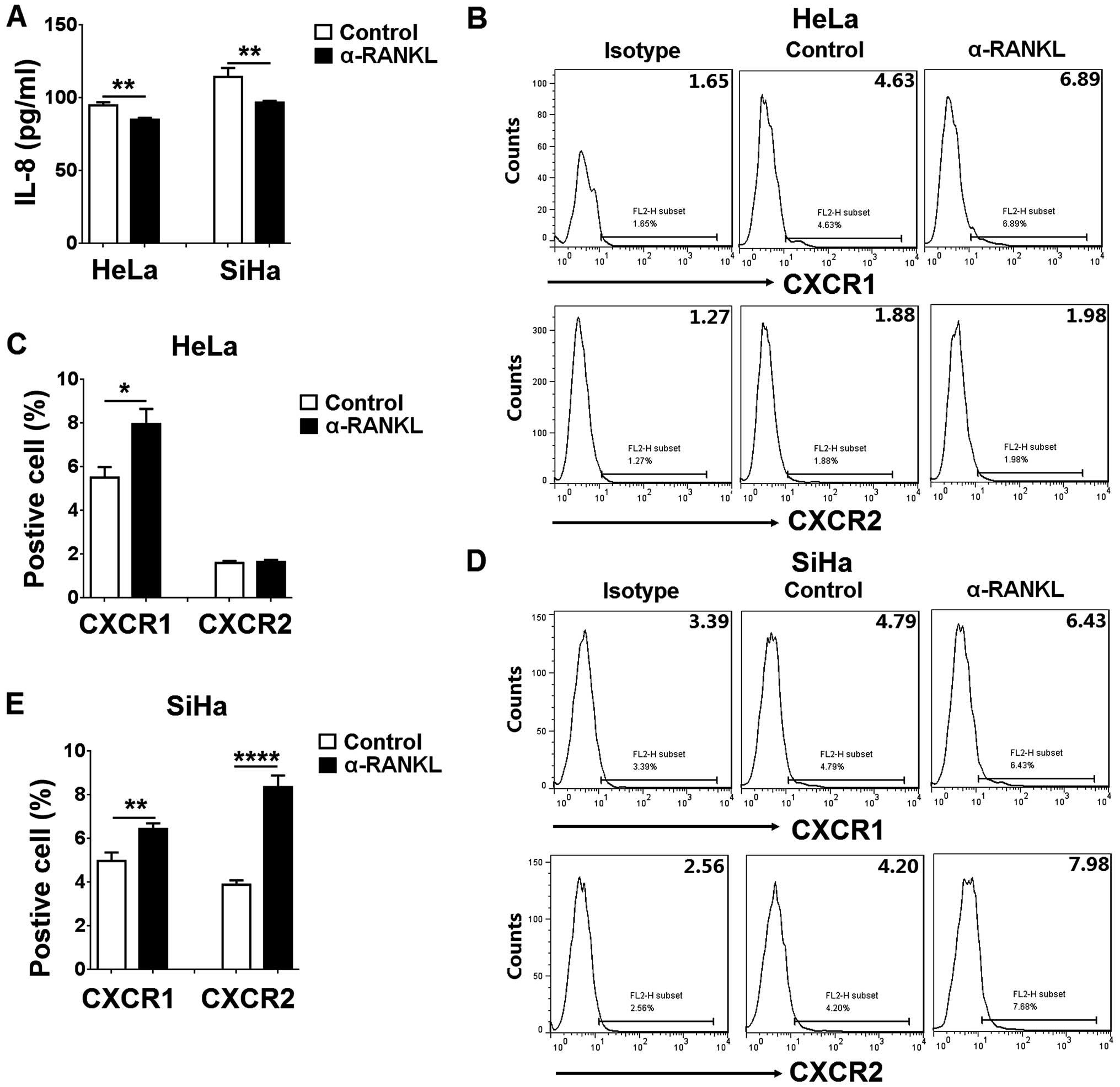
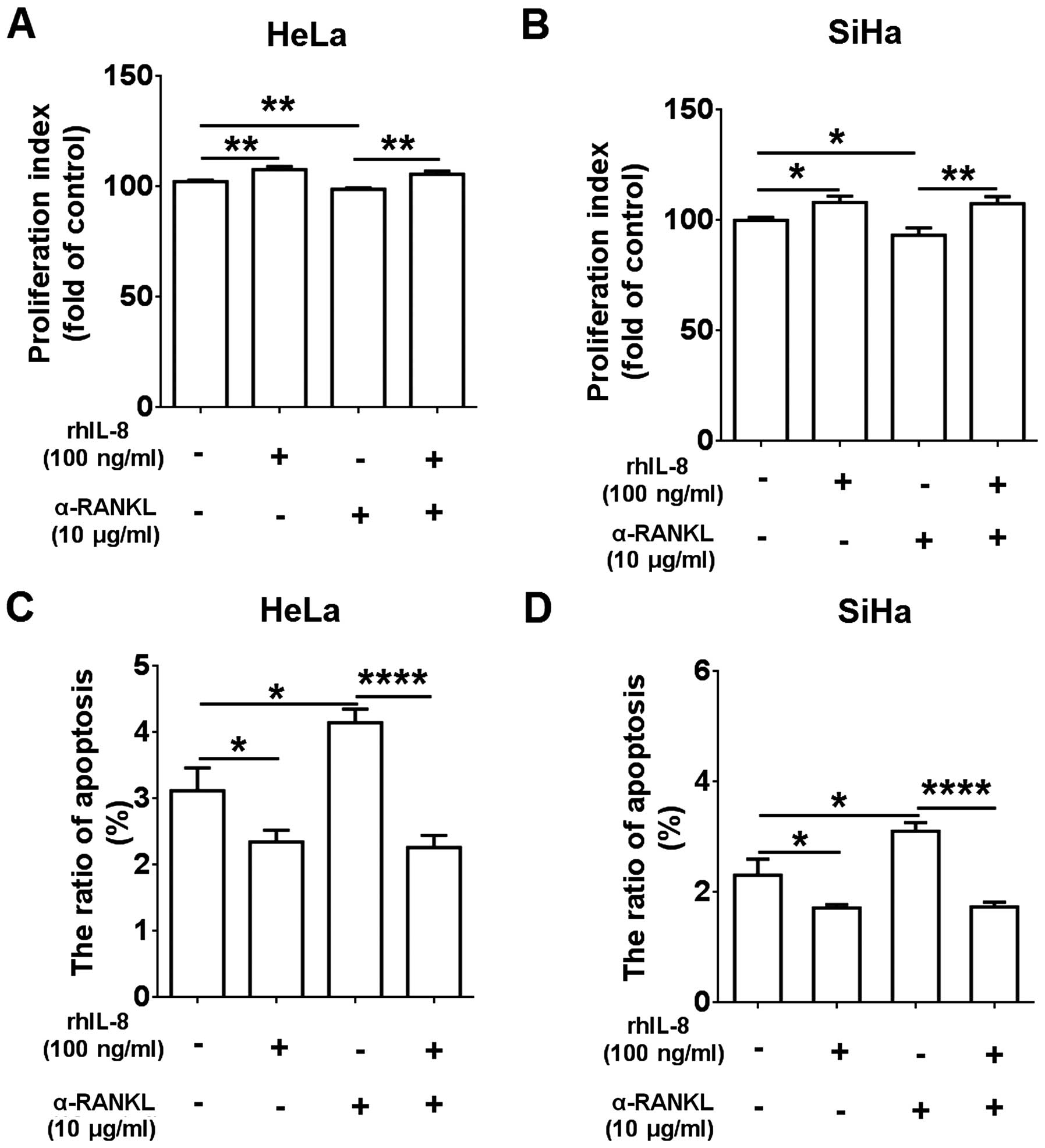
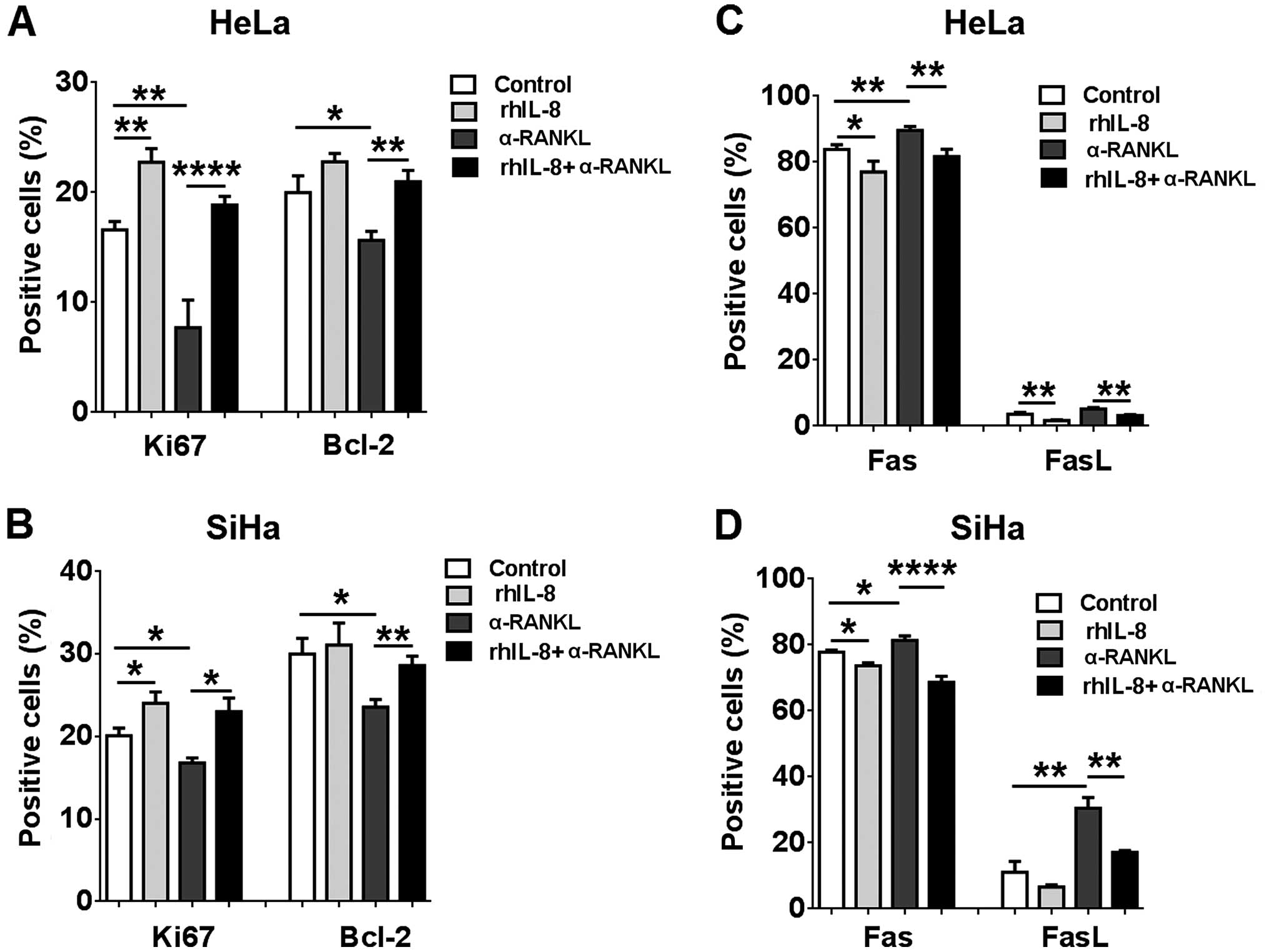
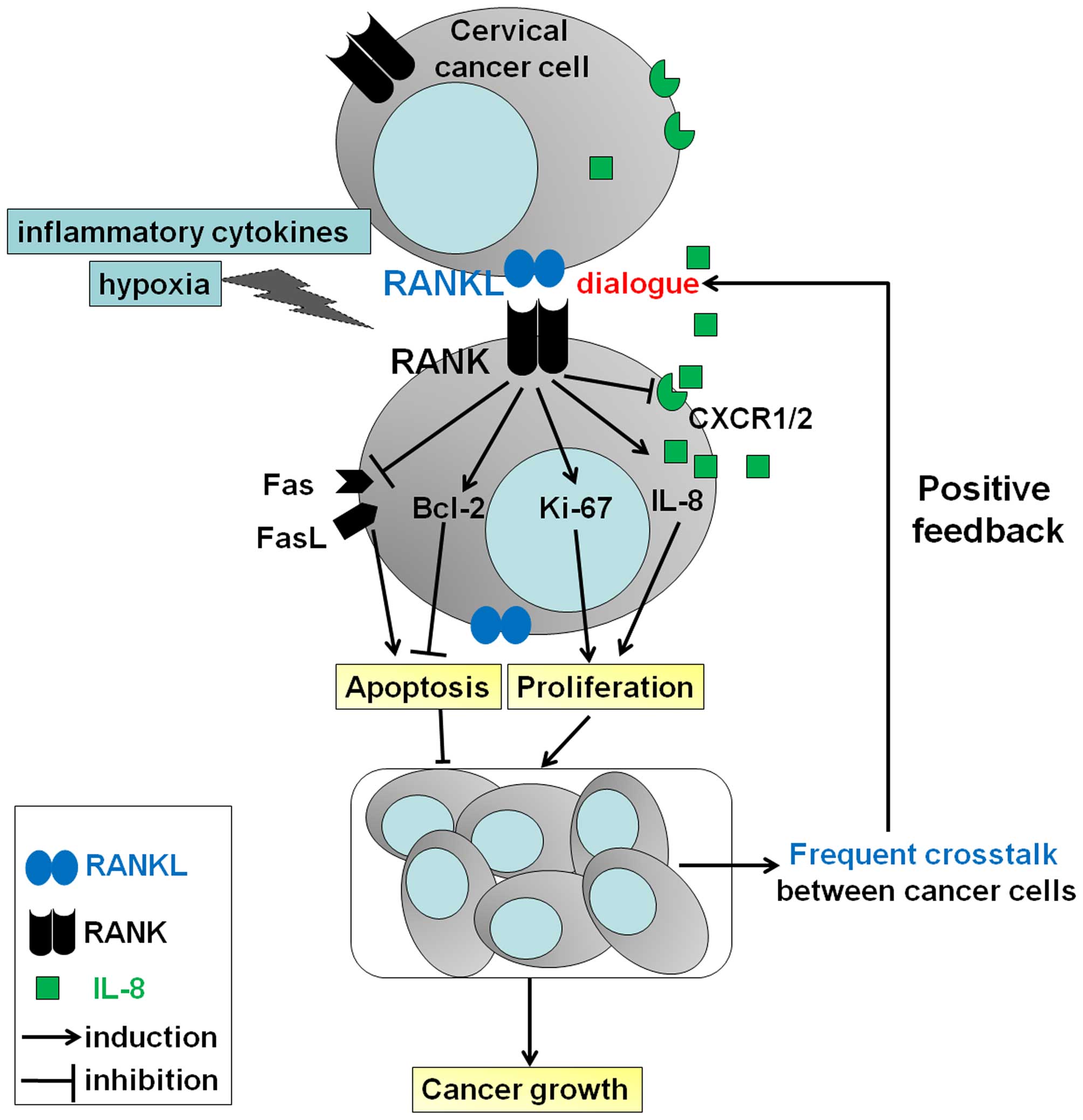
Lacey DL, Timms E, Tan HL, Kelley MJ,
Dunstan CR, Burgess T, Elliott R, Colombero A, Elliott G, Scully S,
et al: Osteoprotegerin ligand is a cytokine that regulates
osteoclast differentiation and activation. Cell. 93:165–176. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Anderson DM, Maraskovsky E, Billingsley
WL, Dougall WC, Tometsko ME, Roux ER, Teepe MC, DuBose RF, Cosman D
and Galibert L: A homologue of the TNF receptor and its ligand
enhance T-cell growth and dendritic-cell function. Nature.
390:175–179. 1997. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Fata JE, Kong YY, Li J, Sasaki T,
Irie-Sasaki J, Moorehead RA, Elliott R, Scully S, Voura EB, Lacey
DL, et al: The osteoclast differentiation factor
osteoprotegerin-ligand is essential for mammary gland development.
Cell. 103:41–50. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Schramek D, Leibbrandt A, Sigl V, Kenner
L, Pospisilik JA, Lee HJ, Hanada R, Joshi PA, Aliprantis A,
Glimcher L, et al: Osteoclast differentiation factor RANKL controls
development of progestin-driven mammary cancer. Nature. 468:98–102.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Rossi SW, Kim MY, Leibbrandt A, Parnell
SM, Jenkinson WE, Glanville SH, McConnell FM, Scott HS, Penninger
JM, Jenkinson EJ, et al: RANK signals from
CD4+3− inducer cells regulate development of
Aire-expressing epithelial cells in the thymic medulla. J Exp Med.
204:1267–1272. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Jones DH, Nakashima T, Sanchez OH,
Kozieradzki I, Komarova SV, Sarosi I, Morony S, Rubin E, Sarao R,
Hojilla CV, et al: Regulation of cancer cell migration and bone
metastasis by RANKL. Nature. 440:692–696. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hanada R, Hanada T, Sigl V, Schramek D and
Penninger JM: RANKL/RANK-beyond bones. J Mol Med (Berl).
89:647–656. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Cheng ML and Fong L: Effects of
RANKL-targeted therapy in immunity and cancer. Front Oncol.
3:3292014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Palafox M, Ferrer I, Pellegrini P, Vila S,
Hernandez-Ortega S, Urruticoechea A, Climent F, Soler MT, Muñoz P,
Viñals F, et al: RANK induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition and
stemness in human mammary epithelial cells and promotes
tumorigenesis and metastasis. Cancer Res. 72:2879–2888. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hsu CJ, Lin TY, Kuo CC, Tsai CH, Lin MZ,
Hsu HC, Fong YC and Tang CH: Involvement of integrin up-regulation
in RANKL/RANK pathway of chondrosarcomas migration. J Cell Biochem.
111:138–147. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Armstrong AP, Miller RE, Jones JC, Zhang
J, Keller ET and Dougall WC: RANKL acts directly on RANK-expressing
prostate tumor cells and mediates migration and expression of tumor
metastasis genes. Prostate. 68:92–104. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Chen LM, Kuo CH, Lai TY, Lin YM, Su CC,
Hsu HH, Tsai FJ, Tsai CH, Huang CY and Tang CH: RANKL increases
migration of human lung cancer cells through intercellular adhesion
molecule-1 up-regulation. J Cell Biochem. 112:933–941. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Murdoch C and Finn A: Chemokine receptors
and their role in inflammation and infectious diseases. Blood.
95:3032–3043. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Mantovani A, Savino B, Locati M, Zammataro
L, Allavena P and Bonecchi R: The chemokine system in cancer
biology and therapy. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 21:27–39. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Vicari AP and Caux C: Chemokines in
cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 13:143–154. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Nickel R, Beck LA, Stellato C and
Schleimer RP: Chemokines and allergic disease. J Allergy Clin
Immunol. 104:723–742. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liu LB, Xie F, Chang KK, Li MQ, Meng YH,
Wang XH, Li H, Li DJ and Yu JJ: Hypoxia promotes the proliferation
of cervical carcinoma cells through stimulating the secretion of
IL-8. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 7:575–583. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Secchiero P, Corallini F, Barbarotto E,
Melloni E, di Iasio MG, Tiribelli M and Zauli G: Role of the
RANKL/RANK system in the induction of interleukin-8 (IL-8) in B
chronic lymphocytic leukemia (B-CLL) cells. J Cell Physiol.
207:158–164. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Xie F, Meng YH, Liu LB, Chang KK, Li H, Li
MQ and Li DJ: Cervical carcinoma cells stimulate the angiogenesis
through TSLP promoting growth and activation of vascular
endothelial cells. Am J Reprod Immunol. 70:69–79. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chu GC and Chung LW: RANK-mediated
signaling network and cancer metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev.
33:497–509. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Meng YH, Li H, Chen X, Liu LB, Shao J,
Chang KK, Du MR, Jin LP, Li MQ and Li DJ: RANKL promotes the growth
of decidual stromal cells in an autocrine manner via CCL2/CCR2
interaction in human early pregnancy. Placenta. 34:663–671. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Deivendran S, Marzook KH and Radhakrishna
Pillai M: The role of inflammation in cervical cancer. Adv Exp Med
Biol. 816:377–399. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Husseinzadeh N and Davenport SM: Role of
toll-like receptors in cervical, endometrial and ovarian cancers: A
review. Gynecol Oncol. 135:359–363. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Castrilli G, Tatone D, Diodoro MG, Rosini
S, Piantelli M and Musiani P: Interleukin 1alpha and interleukin 6
promote the in vitro growth of both normal and neoplastic human
cervical epithelial cells. Br J Cancer. 75:855–859. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Tang ZN, Zhang F, Tang P, Qi XW and Jiang
J: Hypoxia induces RANK and RANKL expression by activating HIF-1α
in breast cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 408:411–416.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wada T, Nakashima T, Hiroshi N and
Penninger JM: RANKL-RANK signaling in osteoclastogenesis and bone
disease. Trends Mol Med. 12:17–25. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Wang L, Guo H, Yang L, Dong L, Lin C,
Zhang J, Lin P and Wang X: Morusin inhibits human cervical cancer
stem cell growth and migration through attenuation of NF-κB
activity and apoptosis induction. Mol Cell Biochem. 379:7–18. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kim SH, Kim SH, Kim YB, Jeon YT, Lee SC
and Song YS: Genistein inhibits cell growth by modulating various
mitogen-activated protein kinases and AKT in cervical cancer cells.
Ann NY Acad Sci. 1171:495–500. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Rashmi R, DeSelm C, Helms C, Bowcock A,
Rogers BE, Rader JL, Grigsby PW and Schwarz JK: AKT inhibitors
promote cell death in cervical cancer through disruption of mTOR
signaling and glucose uptake. PLoS One. 9:e929482014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Bendre MS, Margulies AG, Walser B, Akel
NS, Bhattacharrya S, Skinner RA, Swain F, Ramani V, Mohammad KS,
Wessner LL, et al: Tumor-derived interleukin-8 stimulates
osteolysis independent of the receptor activator of nuclear
factor-kappaB ligand pathway. Cancer Res. 65:11001–11009. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Bouganim N and Clemons MJ: Bone-targeted
agents in the treatment of bone metastases: RANK outsider or new
kid on the block? Future Oncol. 7:381–383. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Sordillo EM and Pearse RN: RANK-Fc: A
therapeutic antagonist for RANK-L in myeloma. Cancer. 97(Suppl):
S802–S812. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|