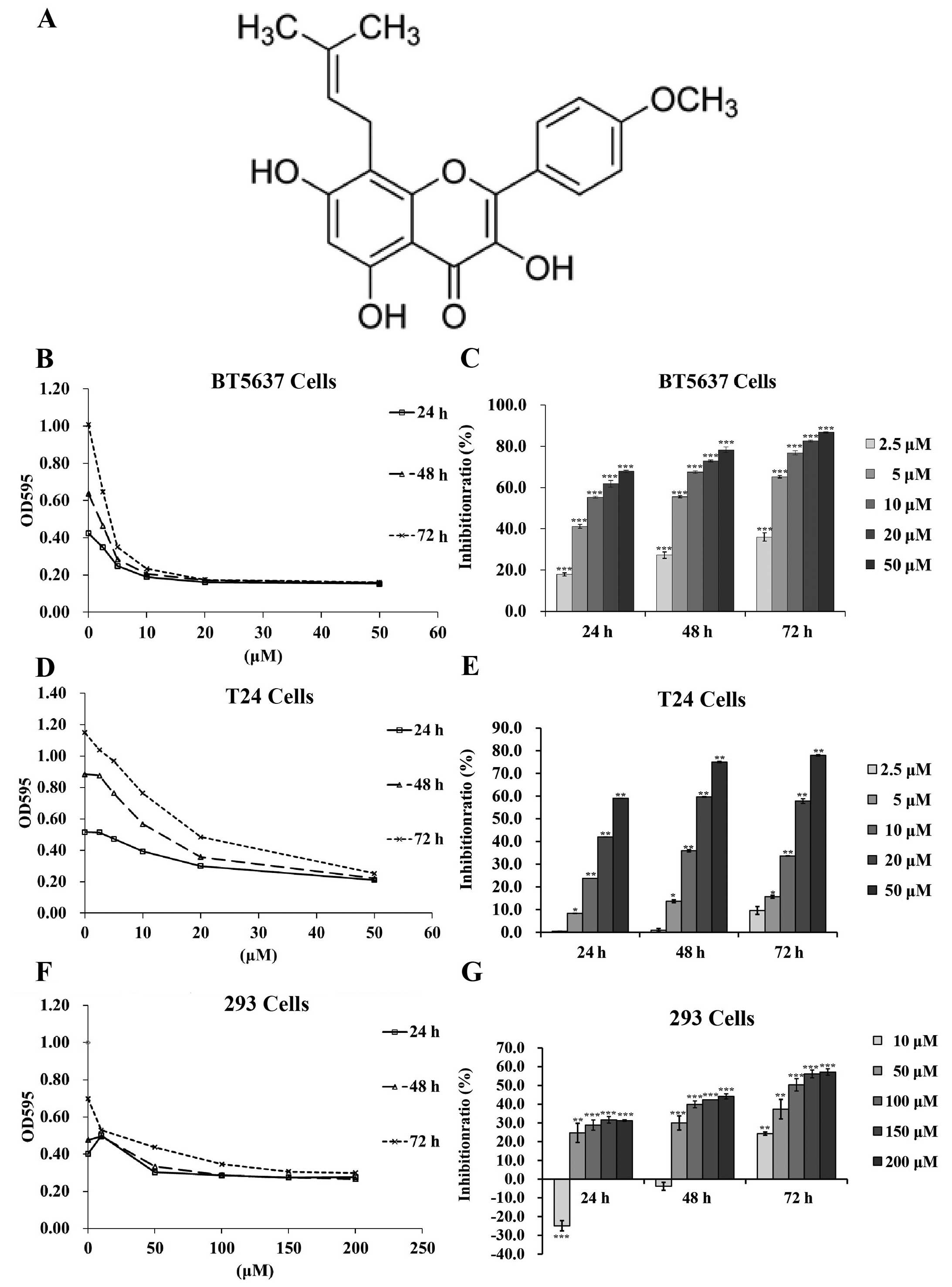
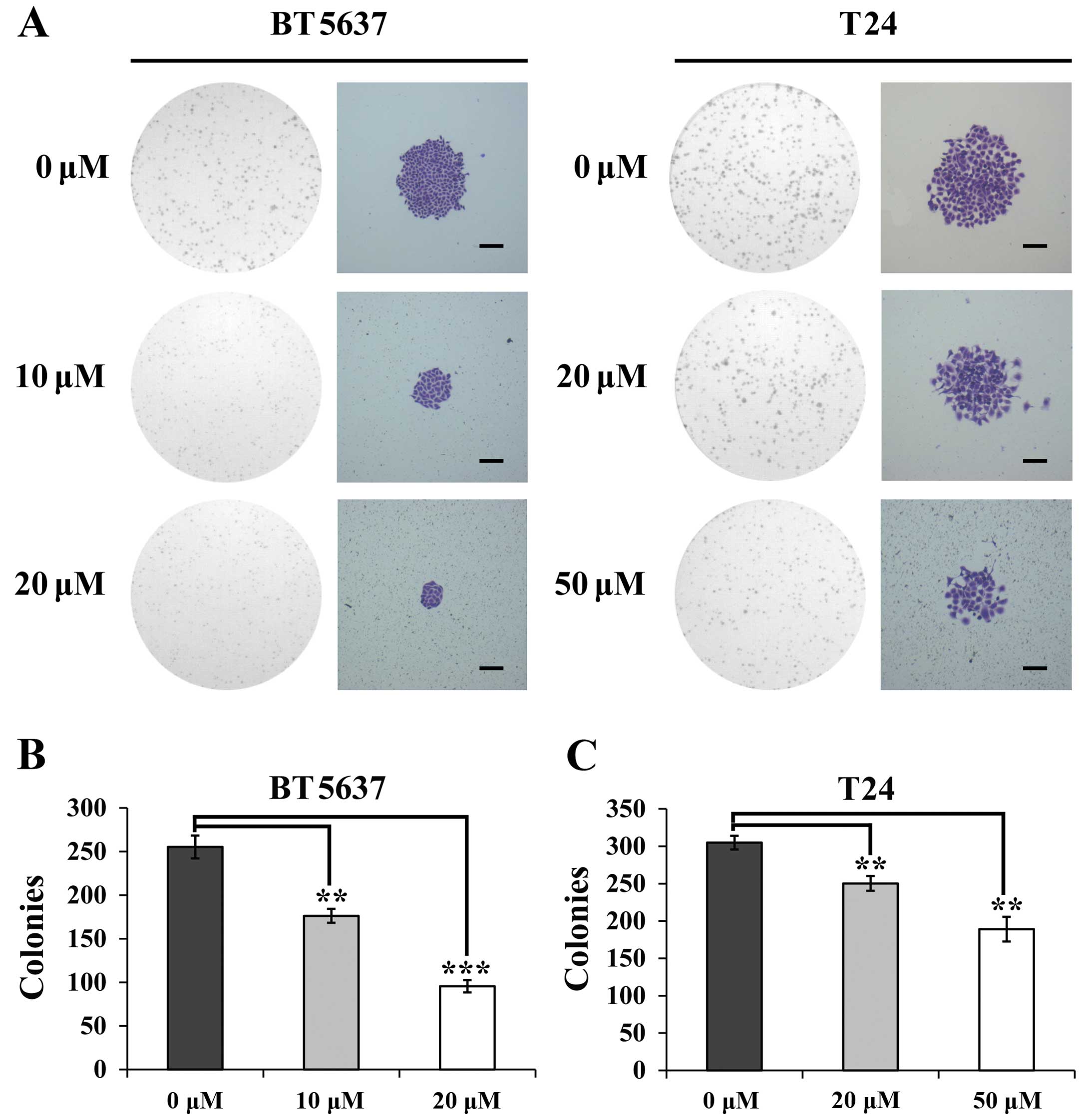
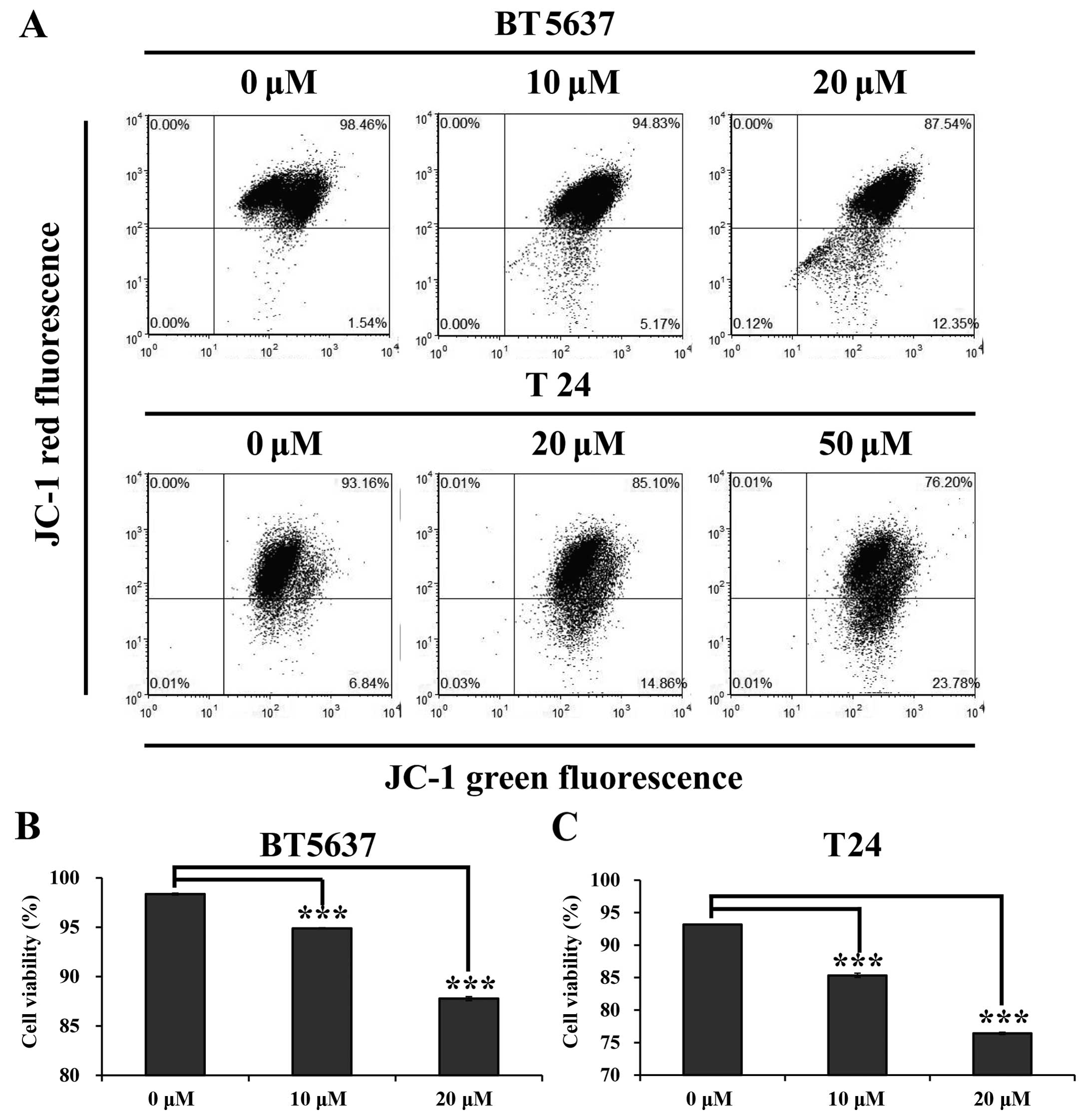
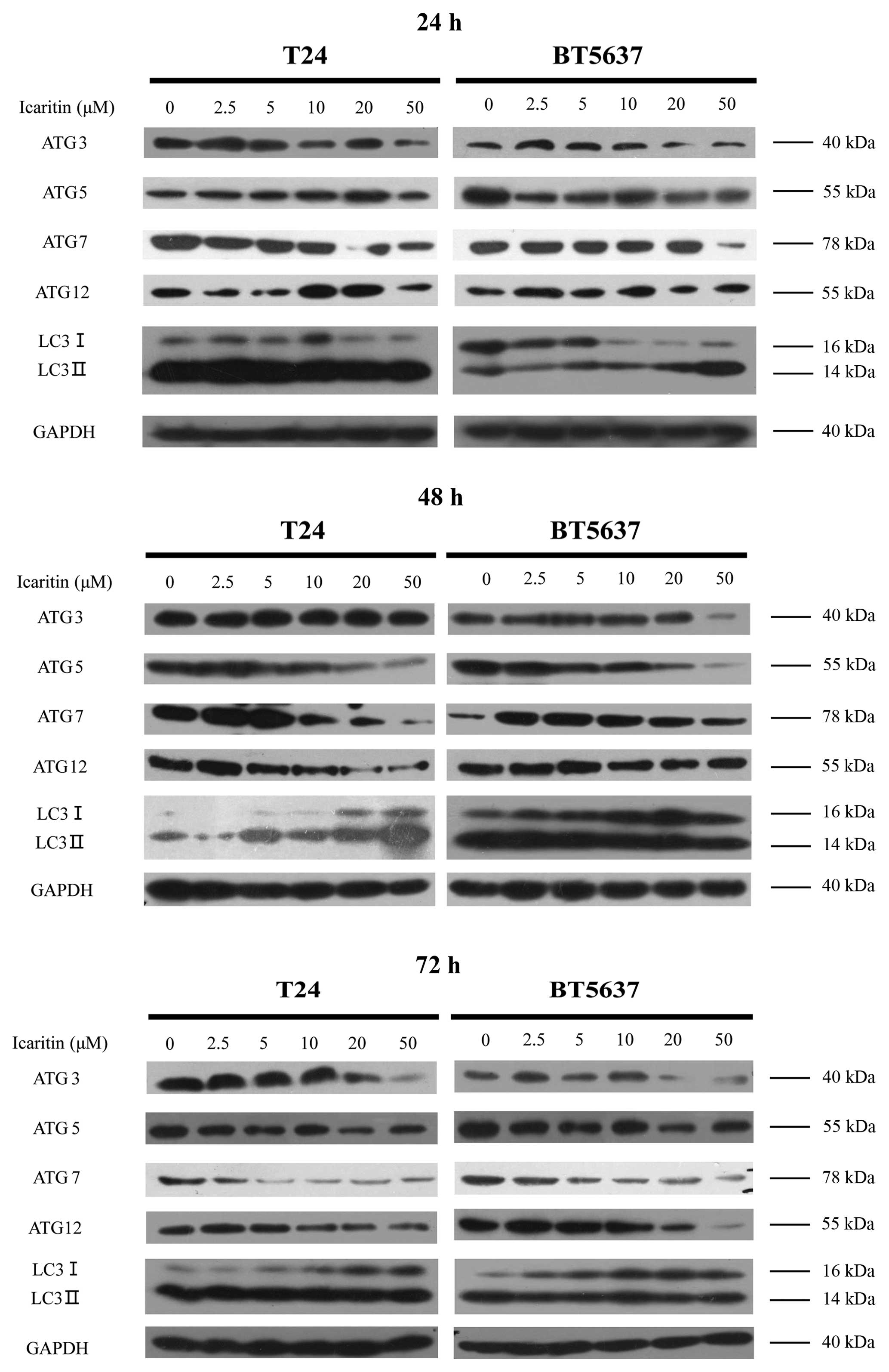
|
1
|
Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 64:9–29. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kaufman DS, Shipley WU and Feldman AS:
Bladder cancer. Lancet. 374:239–249. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Parekh DJ, Bochner BH and Dalbagni G:
Superficial and muscle-invasive bladder cancer: Principles of
management for outcomes assessments. J Clin Oncol. 24:5519–5527.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Herr HW: Natural history of superficial
bladder tumors: 10- to 20-year follow-up of treated patients. World
J Urol. 15:84–88. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Rübben H, Lutzeyer W, Fischer N, Deutz F,
Lagrange W and Giani G: Natural history and treatment of low and
high risk superficial bladder tumors. J Urol. 139:283–285.
1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Onrust SV, Wiseman LR and Goa KL:
Epirubicin: A review of its intravesical use in superficial bladder
cancer. Drugs Aging. 15:307–333. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wu H, Lien EJ and Lien LL: Chemical and
pharmacological investigations of Epimedium species: A survey. Prog
Drug Res. 60:1–57. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang Z, Zhang X, Wang H, Qi L and Lou Y:
Neuroprotective effects of icaritin against beta amyloid-induced
neurotoxicity in primary cultured rat neuronal cells via
estrogen-dependent pathway. Neuroscience. 145:911–922. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang Z, Wang H, Wu J, Zhu D, Zhang X, Ou
L, Yu Y and Lou Y: Enhanced co-expression of beta-tubulin III and
choline acetyltransferase in neurons from mouse embryonic stem
cells promoted by icaritin in an estrogen receptor-independent
manner. Chem Biol Interact. 179:375–385. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wo YB, Zhu DY, Hu Y, Wang ZQ, Liu J and
Lou YJ: Reactive oxygen species involved in prenylflavonoids,
icariin and icaritin, initiating cardiac differentiation of mouse
embryonic stem cells. J Cell Biochem. 103:1536–1550. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Zhu DY and Lou YJ: Inducible effects of
icariin, icaritin, and desmethylicaritin on directional
differentiation of embryonic stem cells into cardiomyocytes in
vitro. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 26:477–485. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Huang J, Yuan L, Wang X, Zhang TL and Wang
K: Icaritin and its glycosides enhance osteoblastic, but suppress
osteoclastic, differentiation and activity in vitro. Life Sci.
81:832–840. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chen MF, Qi L, Li Y, Zu XB, Dai YQ and
Zhang P: Icaritin induces growth inhibition and apoptosis of human
prostatic smooth muscle cells in an estrogen receptor-independent
manner. Amino Acids. 38:1505–1513. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Hong J, Zhang Z, Lv W, Zhang M, Chen C,
Yang S, Li S, Zhang L, Han D and Zhang W: Icaritin synergistically
enhances the radio-sensitivity of 4T1 breast cancer cells. PLoS
One. 8:e713472013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Tong JS, Zhang QH, Huang X, Fu XQ, Qi ST,
Wang YP, Hou Y, Sheng J and Sun QY: Icaritin causes sustained
ERK1/2 activation and induces apoptosis in human endometrial cancer
cells. PLoS One. 6:e167812011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Huang X, Zhu D and Lou Y: A novel
anticancer agent, icaritin, induced cell growth inhibition, G1
arrest and mitochondrial transmembrane potential drop in human
prostate carcinoma PC-3 cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 564:26–36. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Guo Y, Zhang X, Meng J and Wang ZY: An
anticancer agent icaritin induces sustained activation of the
extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) pathway and inhibits
growth of breast cancer cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 658:114–122. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li S, Priceman SJ, Xin H, Zhang W, Deng J,
Liu Y, Huang J, Zhu W, Chen M, Hu W, et al: Icaritin inhibits
JAK/STAT3 signaling and growth of renal cell carcinoma. PLoS One.
8:e816572013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yang ZJ, Chee CE, Huang S and Sinicrope
FA: The role of autophagy in cancer: Therapeutic implications. Mol
Cancer Ther. 10:1533–1541. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sun WL, Chen J, Wang YP and Zheng H:
Autophagy protects breast cancer cells from epirubicin-induced
apoptosis and facilitates epirubicin-resistance development.
Autophagy. 7:1035–1044. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Xie JM, Li B, Yu HP, Gao QG, Li W, Wu HR
and Qin ZH: TIGAR has a dual role in cancer cell survival through
regulating apoptosis and autophagy. Cancer Res. 74:5127–5138. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chen WC, Hsu KY, Hung CM, Lin YC, Yang NS,
Ho CT, Kuo SC and Way TD: The anti-tumor efficiency of
pterostilbene is promoted with a combined treatment of Fas
signaling or autophagy inhibitors in triple negative breast cancer
cells. Food Funct. 5:1856–1865. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Tang Q, Li G, Wei X, Zhang J, Chiu JF,
Hasenmayer D, Zhang D and Zhang H: Resveratrol-induced apoptosis is
enhanced by inhibition of autophagy in esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 336:325–337. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Cui Q, Tashiro S, Onodera S, Minami M and
Ikejima T: Autophagy preceded apoptosis in oridonin-treated human
breast cancer MCF-7 cells. Biol Pharm Bull. 30:859–864. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhang XQ, Dunner K Jr and Benedict WF:
Autophagy is induced by adenoviral-mediated interferon alpha
treatment in interferon resistant bladder cancer and normal
urothelial cells as a cell death protective mechanism but not by
the bystander factors produced. Cancer Gene Ther. 17:579–584. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sang H, Zhang L and Li J:
Anti-benzopyrene-7,8-diol-9,10-epoxide induces apoptosis via
mitochondrial pathway in human bronchiolar epithelium cells
independent of the mitochondria permeability transition pore. Food
Chem Toxicol. 50:2417–2423. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chou TC, Motzer RJ, Tong Y and Bosl GJ:
Computerized quantitation of synergism and antagonism of taxol,
topotecan, and cisplatin against human teratocarcinoma cell growth:
A rational approach to clinical protocol design. J Natl Cancer
Inst. 86:1517–1524. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
McBride HM, Neuspiel M and Wasiak S:
Mitochondria: More than just a powerhouse. Curr Biol. 16:R551–R560.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yang CC, Chen GW, Lu HF, Wang DY, Chen YS
and Chung JG: Paclitaxel (taxol) inhibits the arylamine
N-acetyltransferase activity and gene expression (mRNA NAT1) and
2-aminofluo-rene-DNA adduct formation in human bladder carcinoma
cells (T24 and TSGH 8301). Pharmacol Toxicol. 92:287–294. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li S, Dong P, Wang J, Zhang J, Gu J, Wu X,
Wu W, Fei X, Zhang Z, Wang Y, et al: Icariin, a natural flavonol
glycoside, induces apoptosis in human hepatoma SMMC-7721 cells via
a ROS/JNK-dependent mitochondrial pathway. Cancer Lett.
298:222–230. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Weinberg F and Chandel NS: Mitochondrial
metabolism and cancer. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1177:66–73. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Mizushima N and Yoshimori T: How to
interpret LC3 immunoblotting. Autophagy. 3:542–545. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Tanida I, Ueno T and Kominami E: LC3 and
Autophagy. Methods Mol Biol. 445:77–88. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yamaguchi M, Noda NN, Yamamoto H, Shima T,
Kumeta H, Kobashigawa Y, Akada R, Ohsumi Y and Inagaki F:
Structural insights into Atg10-mediated formation of the
autophagy-essential Atg12-Atg5 conjugate. Structure. 20:1244–1254.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhu J, Li Z, Zhang G, Meng K, Kuang W, Li
J, Zhou X, Li R, Peng H, Dai C, et al: Icaritin shows potent
anti-leukemia activity on chronic myeloid leukemia in vitro and in
vivo by regulating MAPK/ERK/JNK and JAK2/STAT3/AKT signalings. PLoS
One. 6:e237202011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Chittaranjan S, Bortnik S, Dragowska WH,
Xu J, Abeysundara N, Leung A, Go NE, DeVorkin L, Weppler SA, Gelmon
K, et al: Autophagy inhibition augments the anticancer effects of
epirubicin treatment in anthracycline-sensitive and -resistant
triple-negative breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 20:3159–3173. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|