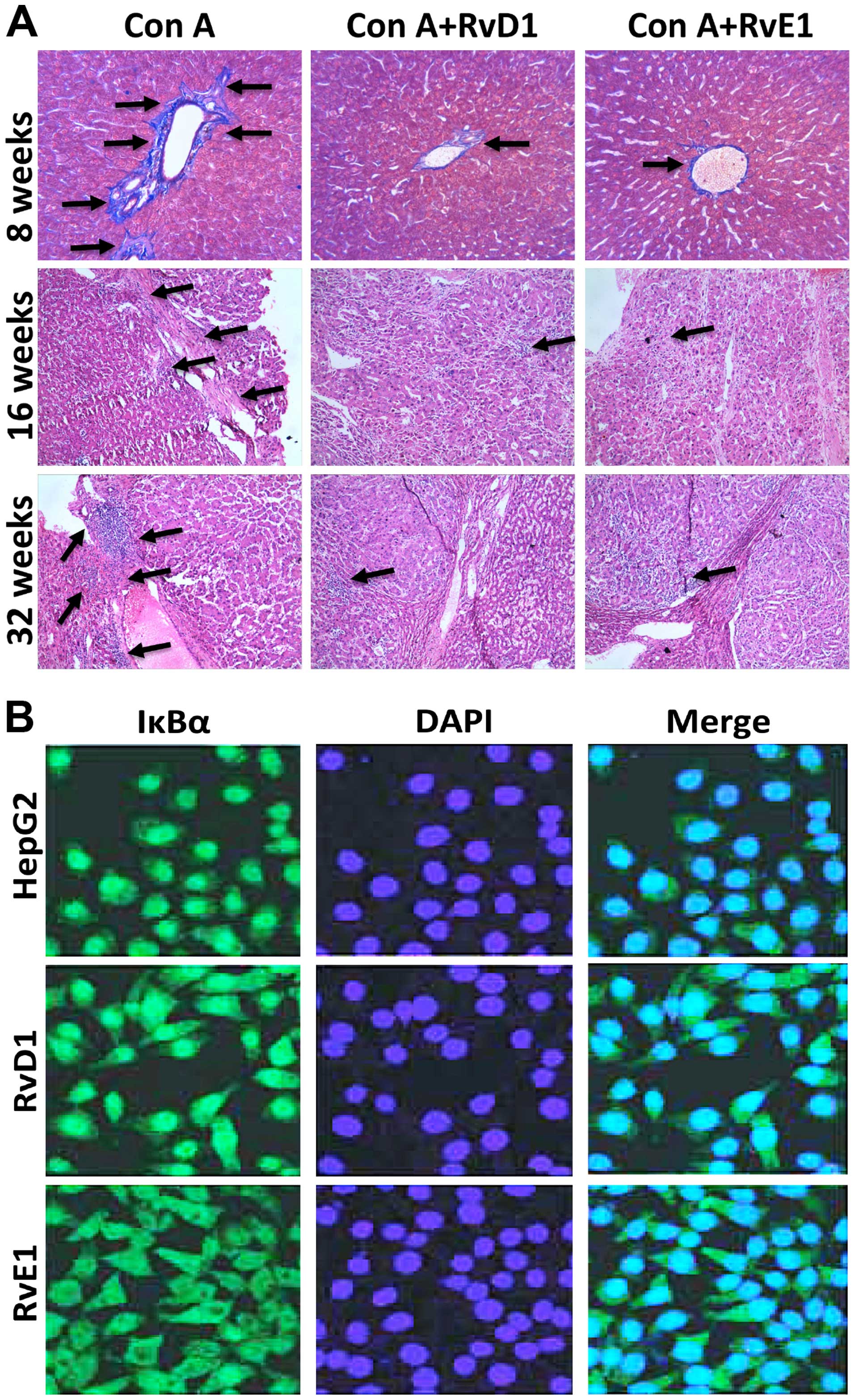
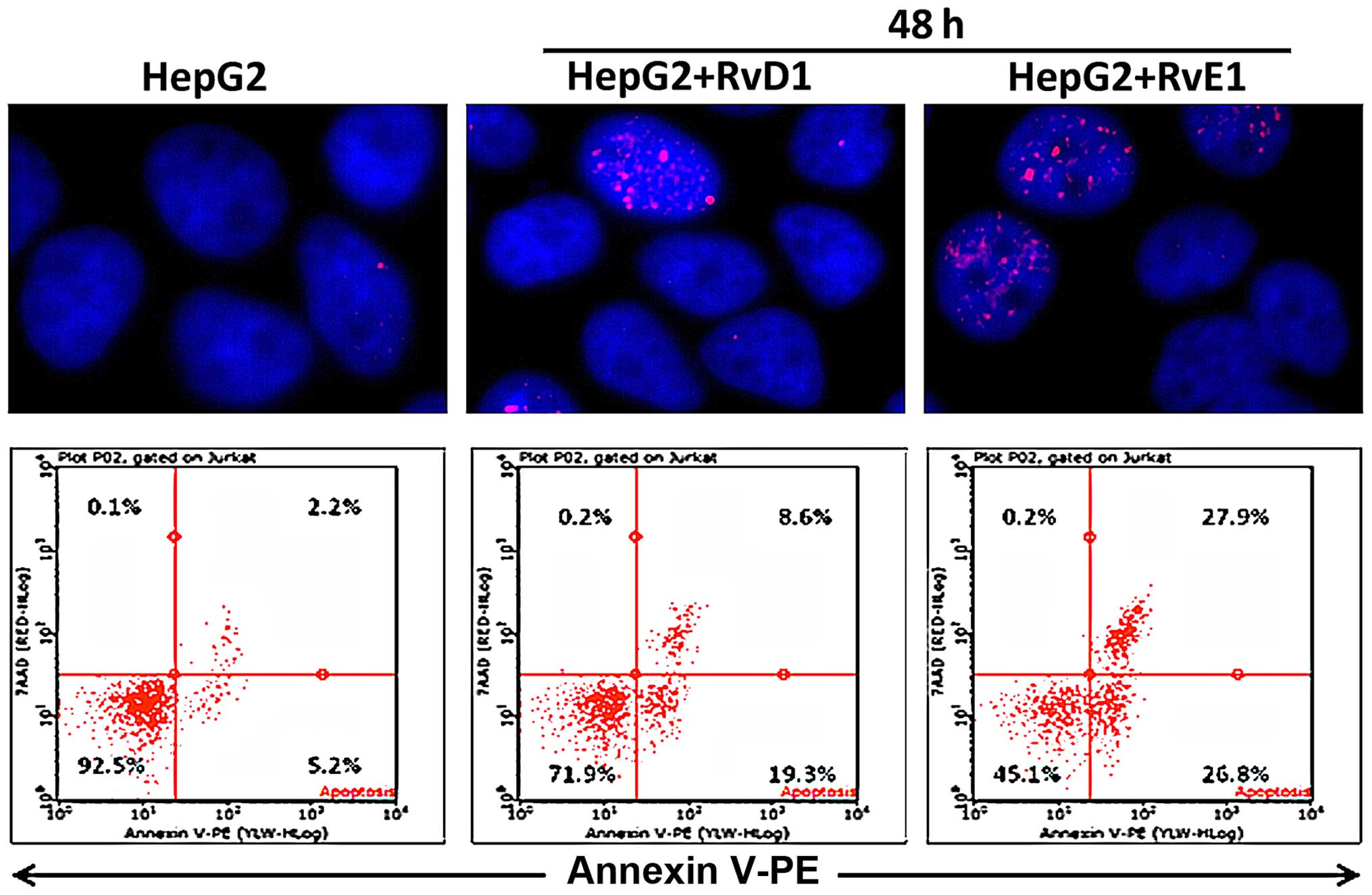
|
1
|
Minemura M, Tajiri K and Shimizu Y: Liver
involvement in systemic infection. World J Hepatol. 6:632–642.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Katoonizadeh A, Poustchi H and Malekzadeh
R: Hepatic progenitor cells in liver regeneration: Current advances
and clinical perspectives. Liver Int. 34:1464–1472. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Carbone M and Neuberger JM: Autoimmune
liver disease, autoimmunity and liver transplantation. J Hepatol.
60:210–223. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Rognant N: Acute kidney injury in patients
with chronic liver disease. World J Hepatol. 7:993–1000. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Li Y, Yang Y, Feng Y, Yan J, Fan C, Jiang
S and Qu Y: A review of melatonin in hepatic ischemia/reperfusion
injury and clinical liver disease. Ann Med. 46:503–511. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zheng F, Devoogdt N, Sparkes A, Morias Y,
Abels C, Stijlemans B, Lahoutte T, Muyldermans S, De Baetselier P,
Schoonooghe S, et al: Monitoring liver macrophages using nanobodies
targeting Vsig4: Concanavalin A induced acute hepatitis as
paradigm. Immunobiology. 220:200–209. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Lee JH, Won JH, Choi JM, Cha HH, Jang YJ,
Park S, Kim HG, Kim HC and Kim DK: Protective effect of ellagic
acid on concanavalin A-induced hepatitis via toll-like receptor and
mitogen-activated protein kinase/nuclear factor κB signaling
pathways. J Agric Food Chem. 62:10110–10117. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tu CT, Han B, Yao QY, Zhang YA, Liu HC and
Zhang SC: Curcumin attenuates Concanavalin A-induced liver injury
in mice by inhibition of Toll-like receptor (TLR) 2, TLR4 and TLR9
expression. Int Immunopharmacol. 12:151–157. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Serhan CN: Resolution phase of
inflammation: Novel endogenous anti-inflammatory and proresolving
lipid mediators and pathways. Annu Rev Immunol. 25:101–137. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Chiocchetti A: Resolvin(g) innate
immunodeficiencies? Blood. 124:2761–2763. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Qiu W, Guo K, Yi L, Gong Y, Huang L and
Zhong W: Resolvin E1 reduces hepatic fibrosis in mice with
Schistosoma japonicum infection. Exp Ther Med. 7:1481–1485.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gyurko R and van Dyke TE: The role of
polyunsaturated ω-3 fatty acid eicosapentaenoic acid-derived
resolvin E1 (RvE1) in bone preservation. Crit Rev Immunol.
34:347–357. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Williams R: Global challenges in liver
disease. Hepatology. 44:521–526. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
UK National Statistics. http://www.statistics.gov.uk/.
|
|
15
|
Morgan B: Fatty liver disease: The liver
labyrinth. Nature. 516:S8–S9. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ray K: NAFLD: Obeticholic acid for the
treatment of fatty liver disease - NASH no more? Nat Rev
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 12:12015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Kelley CE, Brown AJ, Diehl AM and Setji
TL: Review of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in women with
polycystic ovary syndrome. World J Gastroenterol. 20:14172–14184.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Pawlak M, Lefebvre P and Staels B:
Molecular mechanism of PPARα action and its impact on lipid
metabolism, inflammation and fibrosis in non-alcoholic fatty liver
disease. J Hepatol. 62:720–733. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Rius B, López-vicario C, González-Périz A,
Morán-Salvador E, García-Alonso V, Clária J and Titos E: Resolution
of inflammation in obesity-induced liver disease. Front Immunol.
3:2572012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sass G, Heinlein S, Agli A, Bang R,
Schümann J and Tiegs G: Cytokine expression in three mouse models
of experimental hepatitis. Cytokine. 19:115–120. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Mohamed DI, Elmelegy AA, El-Aziz LF, Abdel
Kawy HS, El-Samad AA and El-Kharashi OA: Fenofibrate A peroxisome
proliferator activated receptor-α agonist treatment ameliorates
Concanavalin A-induced hepatitis in rats. Eur J Pharmacol.
721:35–42. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ponmari G, Annamalai A, Gopalakrishnan VK,
Lakshmi PT and Guruvayoorappan C: NF-κB activation and
proinflammatory cytokines mediated protective effect of Indigofera
caerulea Roxb on CCl4 induced liver damage in rats. Int
Immunopharmacol. 23:672–680. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sahin H, Borkham-Kamphorst E, Do O NT,
Berres ML, Kaldenbach M, Schmitz P, Weiskirchen R, Liedtke C,
Streetz KL, Maedler K, et al: Proapoptotic effects of the
chemokine, CXCL 10 are mediated by the noncognate receptor TLR4 in
hepatocytes. Hepatology. 57:797–805. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Hsieh MJ, Lin CW, Yang SF, Chen MK and
Chiou HL: Glabridin inhibits migration and invasion by
transcriptional inhibition of matrix metalloproteinase 9 through
modulation of NF-κB and AP-1 activity in human liver cancer cells.
Br J Pharmacol. 171:3037–3050. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hasenfuss SC, Bakiri L, Thomsen MK,
Williams EG, Auwerx J and Wagner EF: Regulation of steatohepatitis
and PPARγ signaling by distinct AP-1 dimers. Cell Metab. 19:84–95.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Liu C, Gao S, Qu Z, Wang Q, Zhu F, Guo C,
Hou L, Wu P, Shi Y and Zhang L: NCPP treatment alleviates
ConA-induced hepatitis via reducing CD4+T activation and
NO production. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 34:962–967. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|