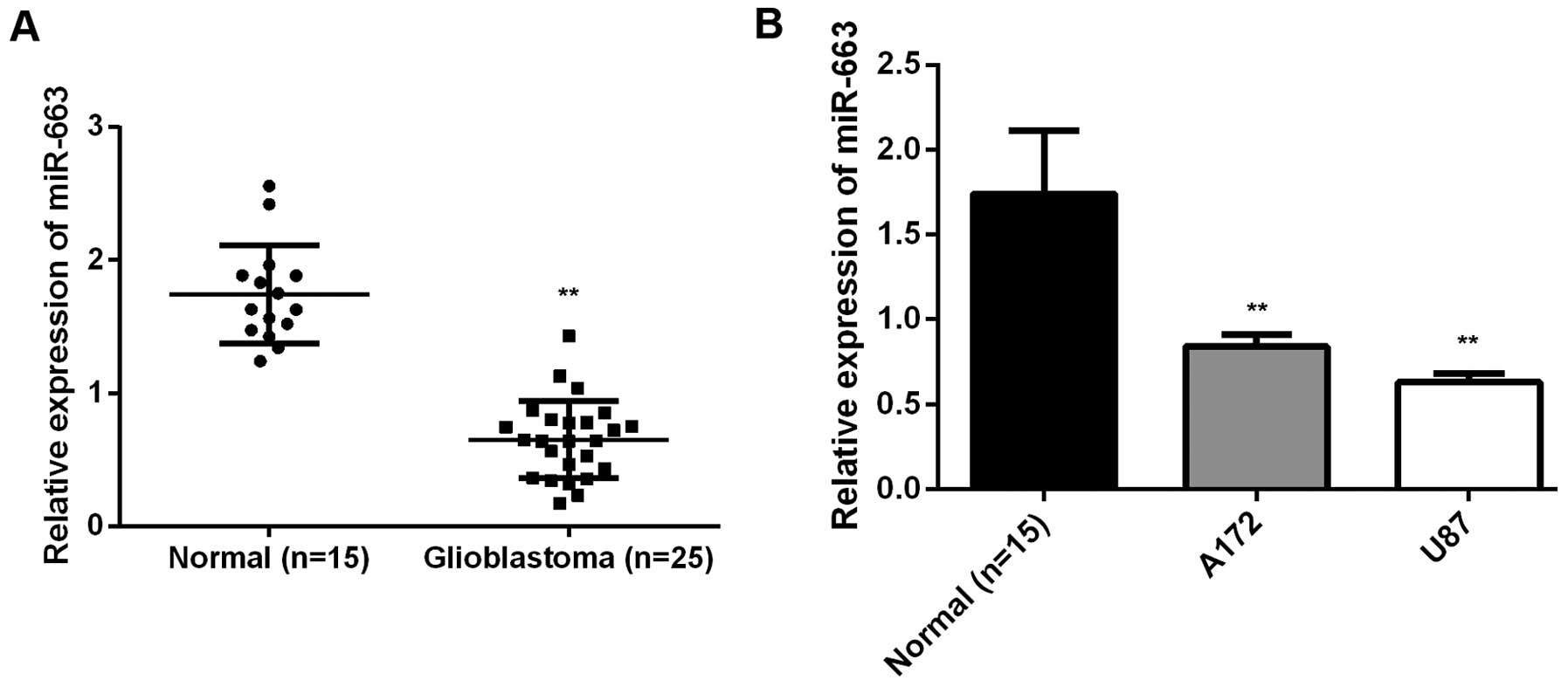
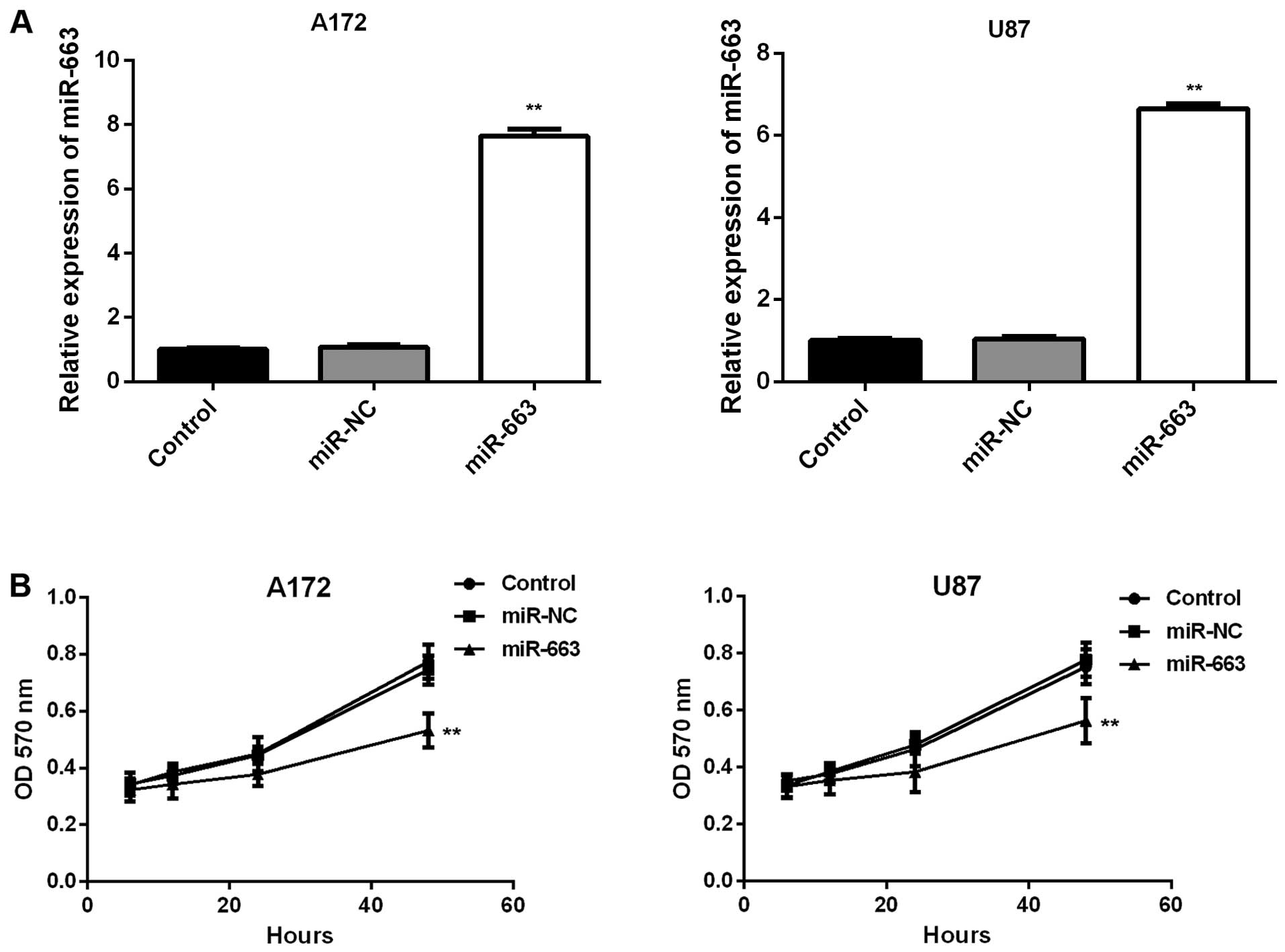
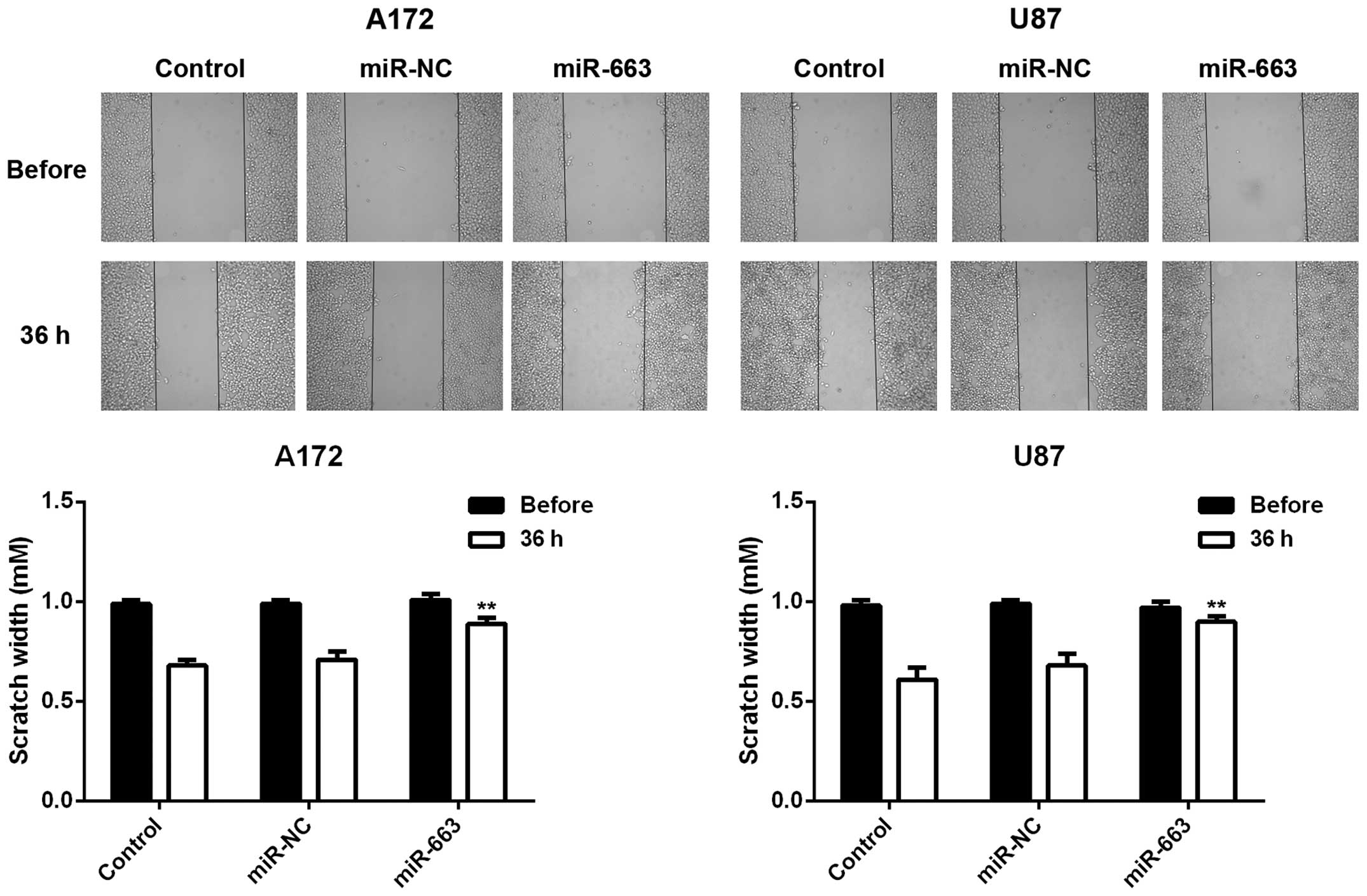
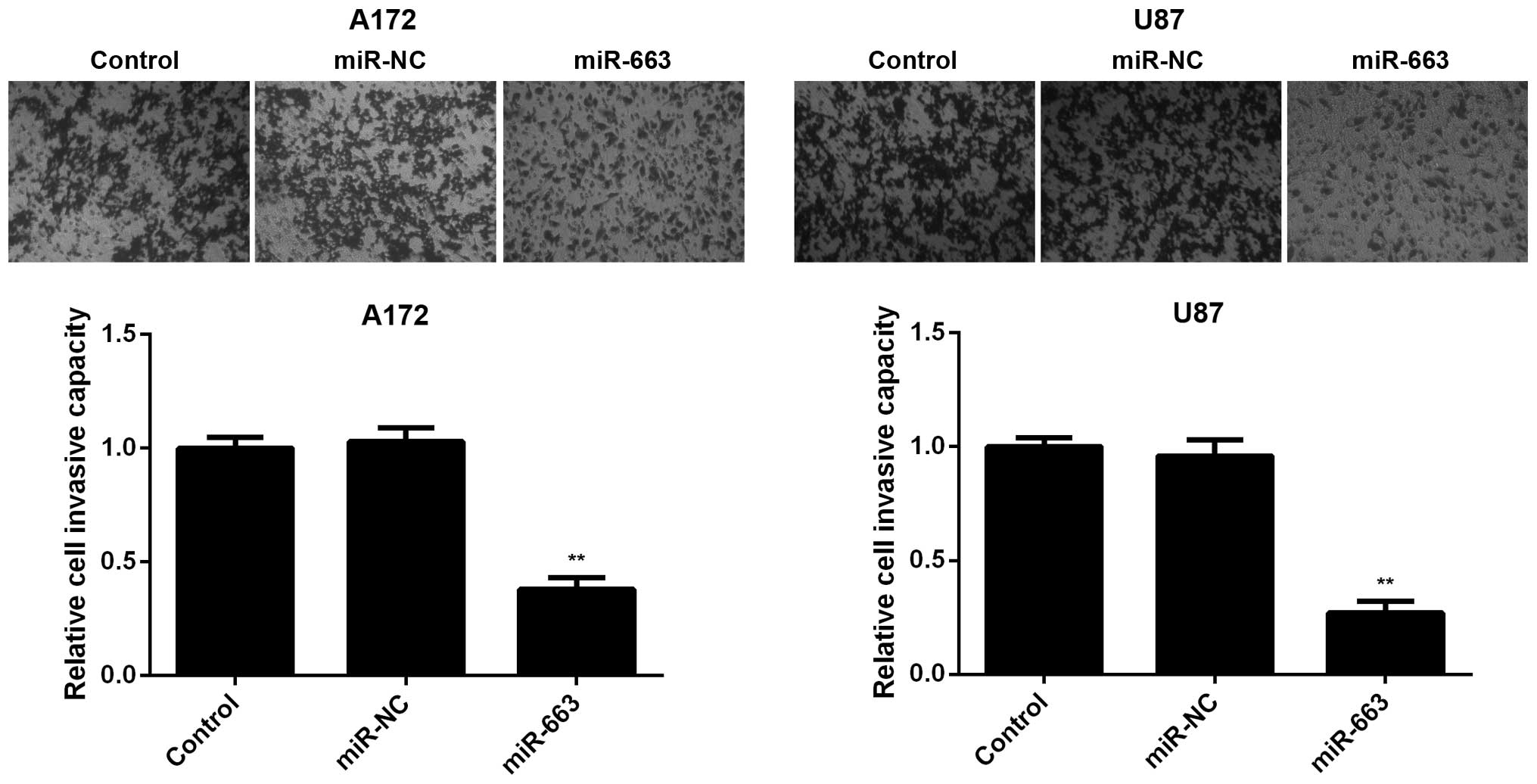
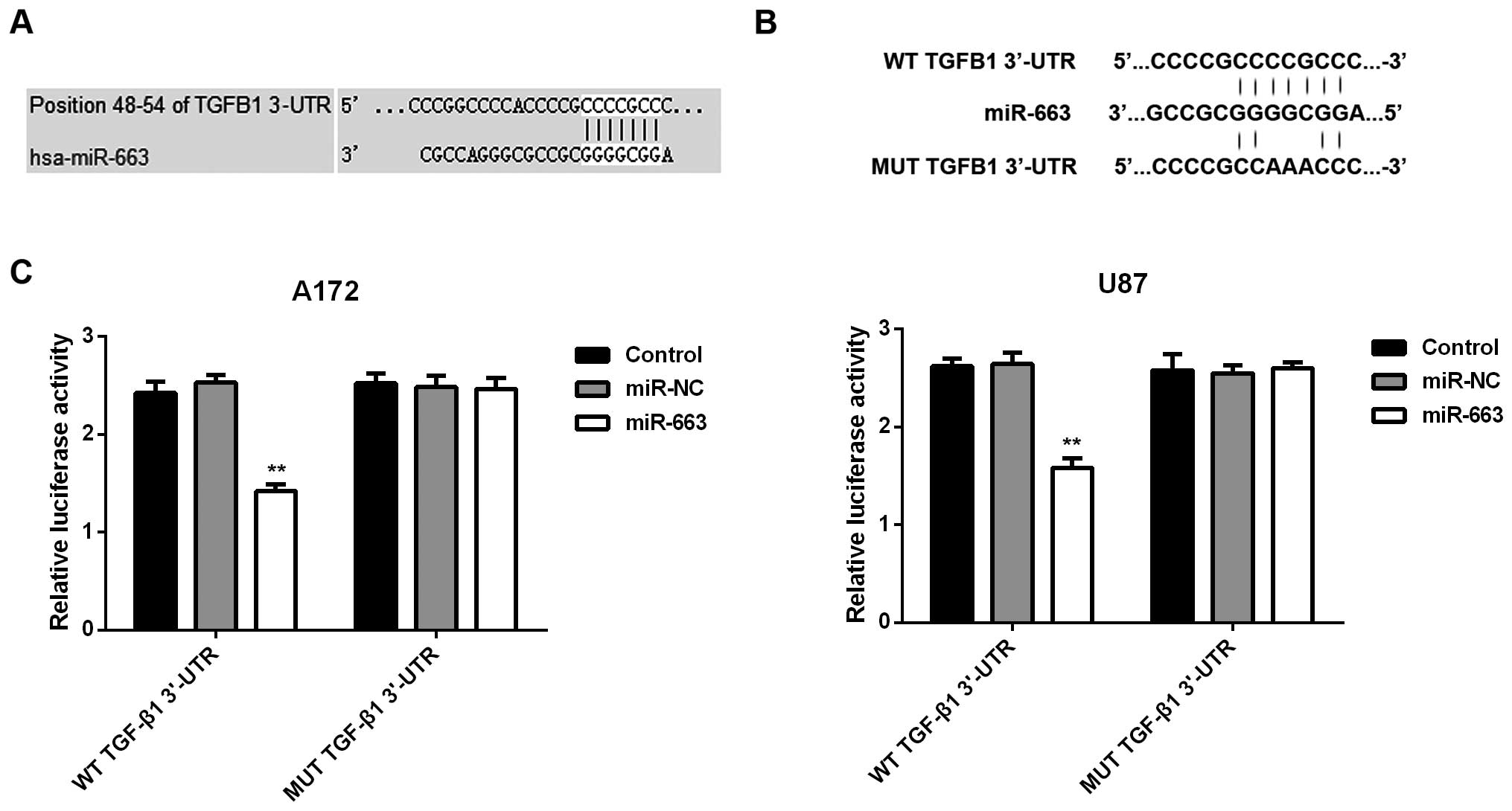
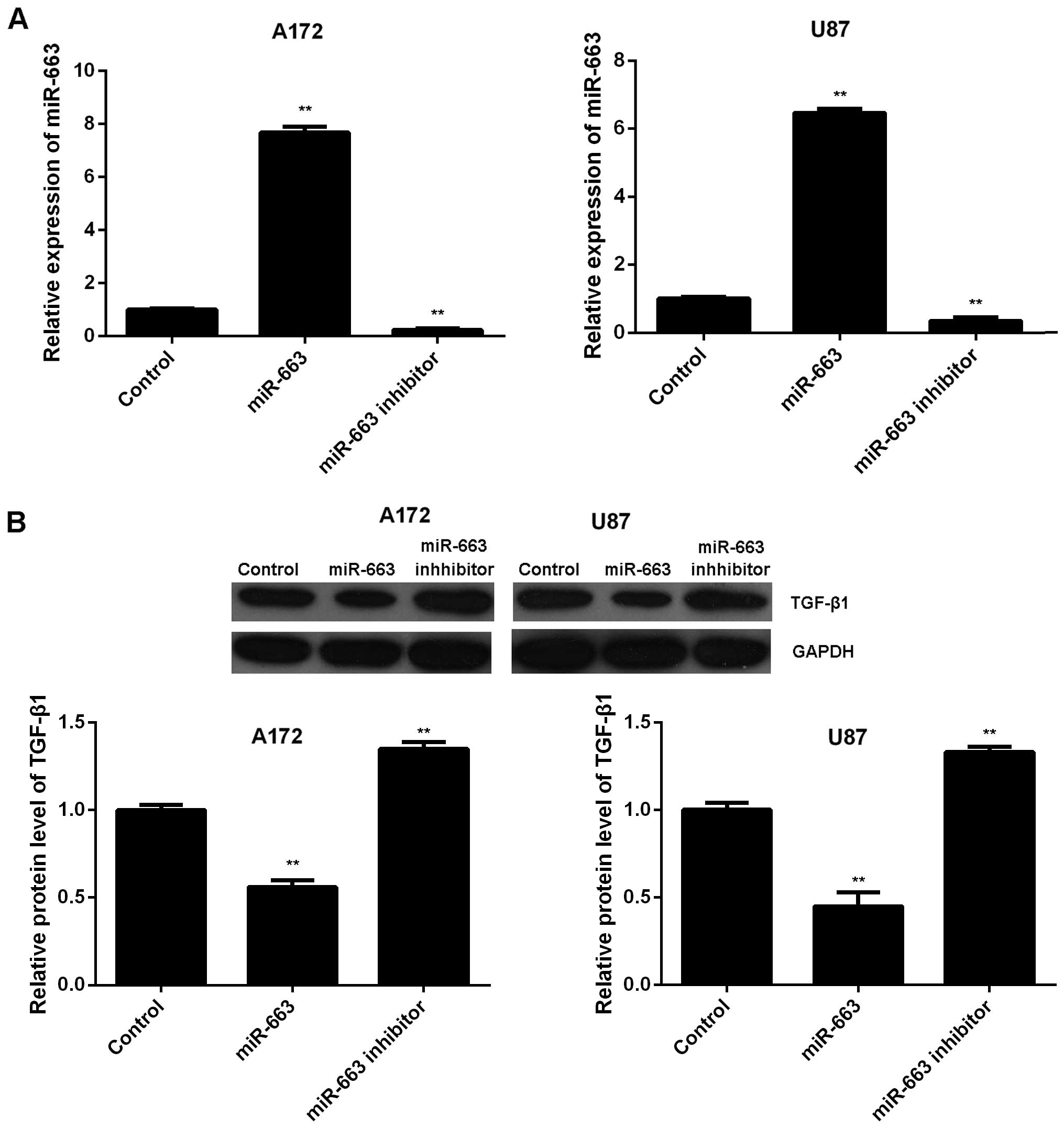
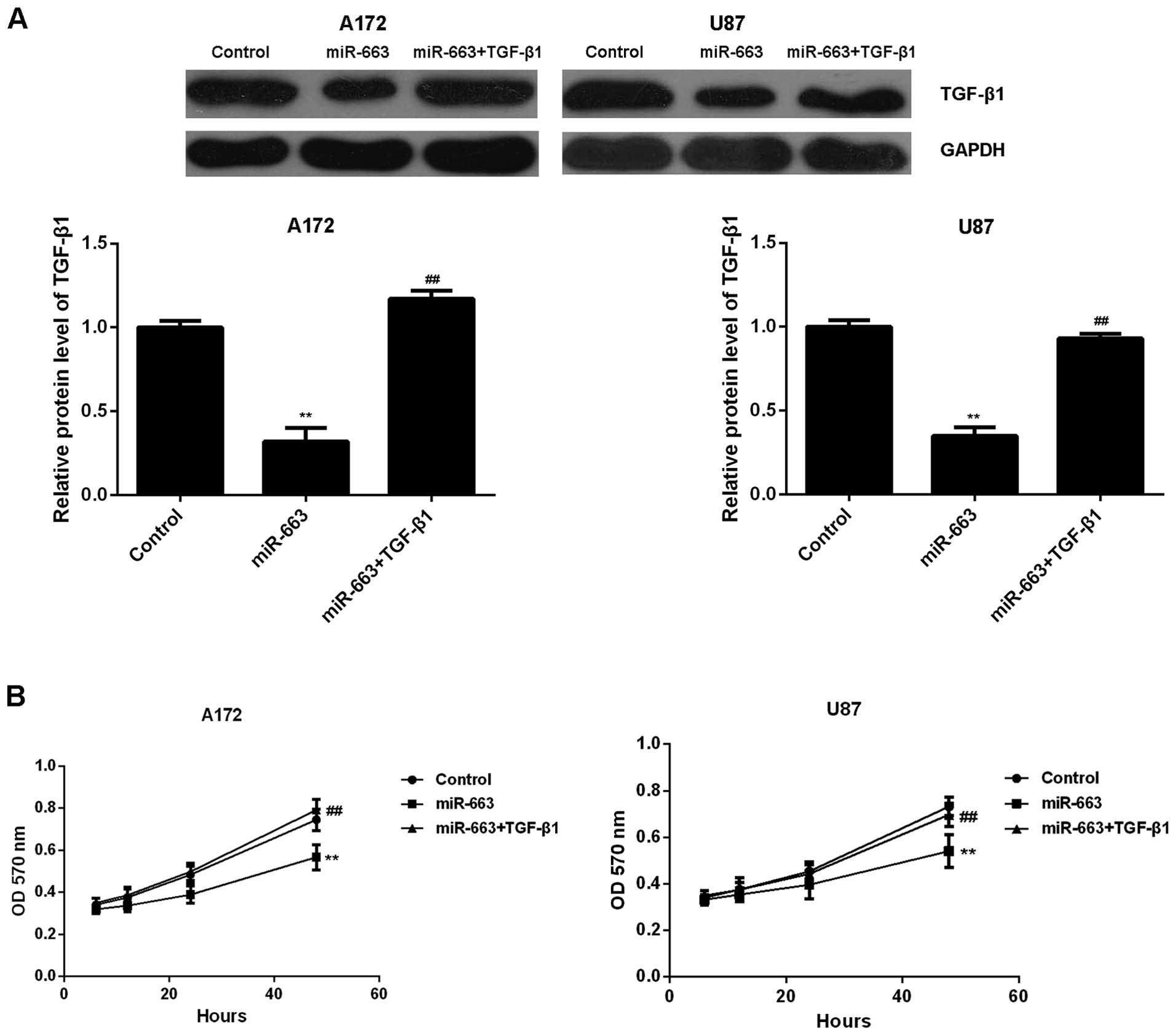
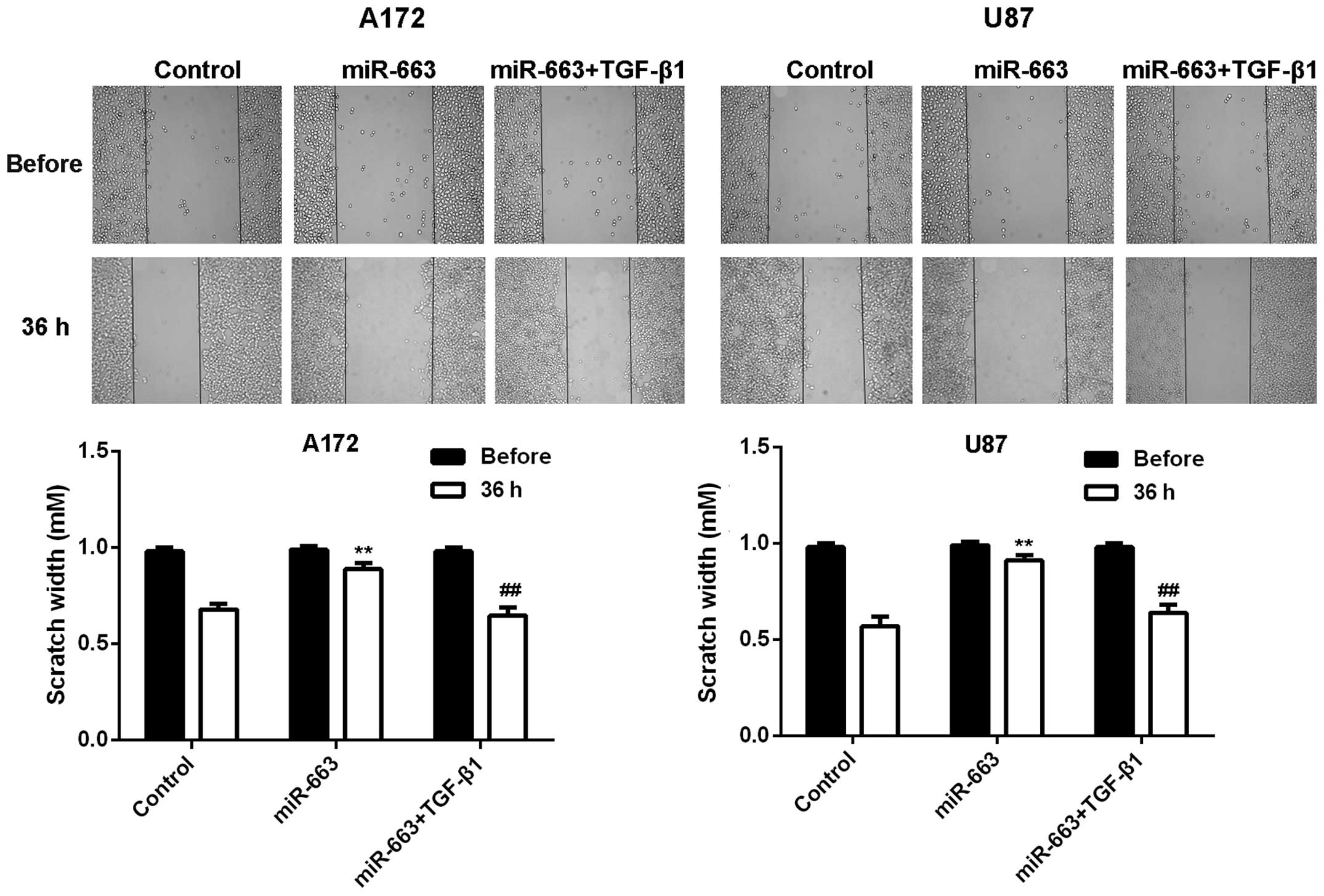
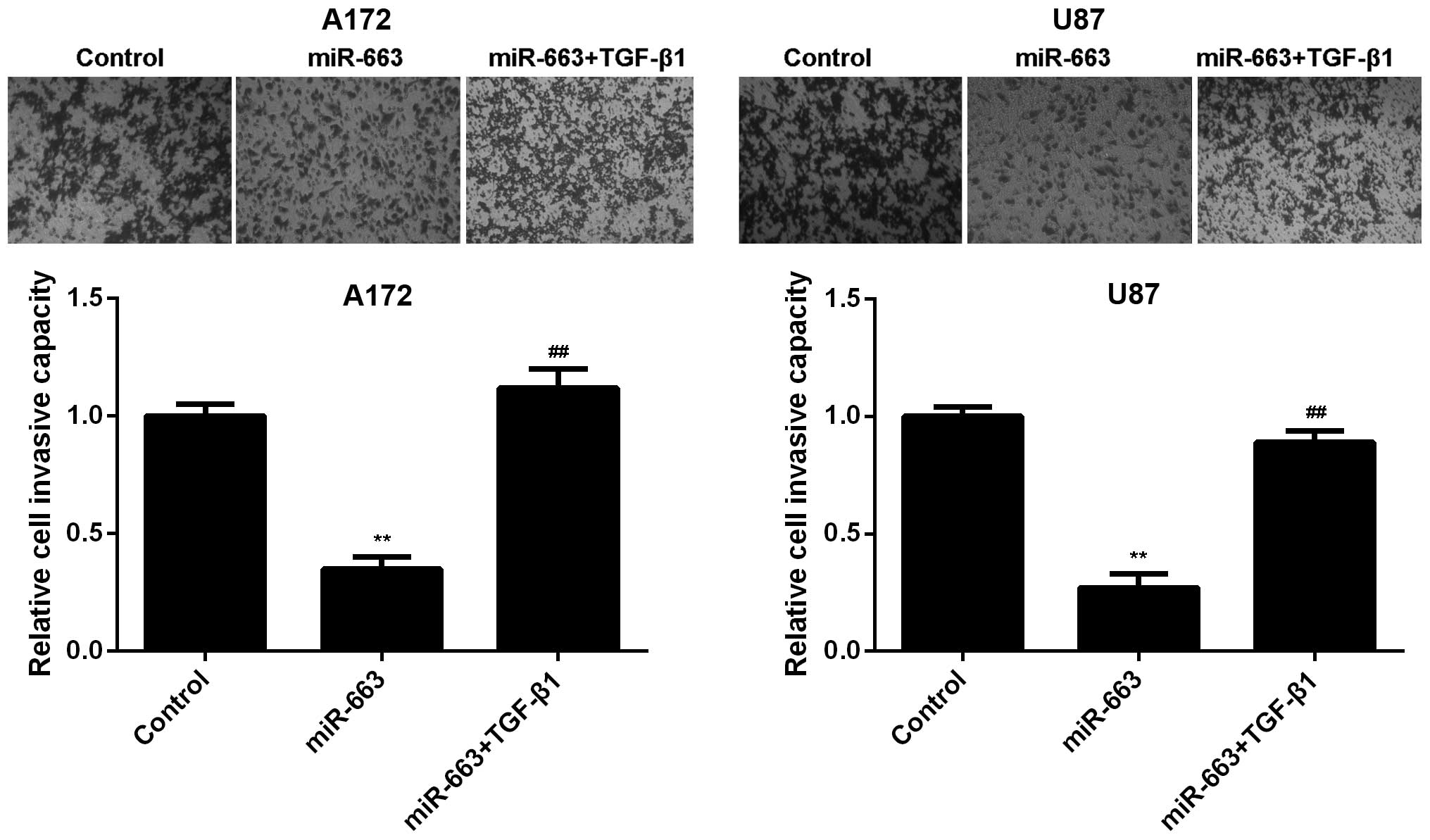
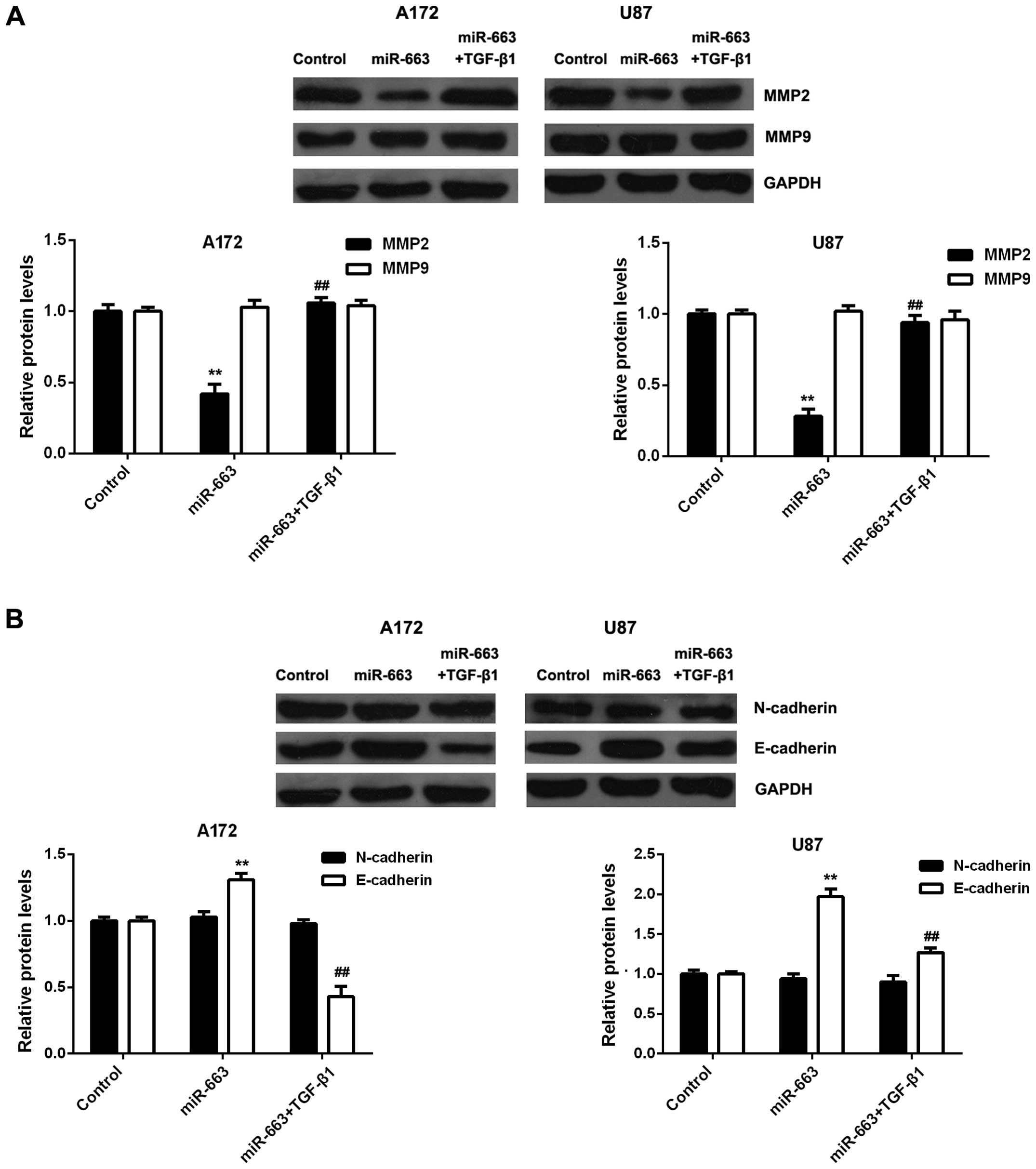
|
1
|
Goodenberger ML and Jenkins RB: Geneticss
of adult glioma. Cancer Genet. 205:613–621. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Brower JV, Clark PA, Lyon W and Kuo JS:
MicroRNAs in cancer: Glioblastoma and glioblastoma cancer stem
cells. Neurochem Int. 77:68–77. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network:
Comprehensive genomic characterization defines human glioblastoma
genes and core pathways. Nature. 455:1061–1068. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Marumoto T and Saya H: Molecular biology
of glioma. Adv Exp Med Biol. 746:2–11. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Treiber T, Treiber N and Meister G:
Regulation of microRNA biogenesis and function. Thromb Haemost.
107:605–610. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fabbri M, Calore F, Paone A, Galli R and
Calin GA: Epigenetic regulation of miRNAs in cancer. Adv Exp Med
Biol. 754:137–148. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Ambros V: The functions of animal
microRNAs. Nature. 431:350–355. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hermansen SK and Kristensen BW: MicroRNA
biomarkers in glioblastoma. J Neurooncol. 114:13–23. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lehmann U, Hasemeier B, Römermann D,
Müller M, Länger F and Kreipe H: Epigenetic inactivation of
microRNA genes in mammary carcinoma. Verh Dtsch Ges Pathol.
91:214–220. 2007.In German.
|
|
10
|
Tili E, Michaille JJ, Adair B, Alder H,
Limagne E, Taccioli C, Ferracin M, Delmas D, Latruffe N and Croce
CM: Resveratrol decreases the levels of miR-155 by upregulating
miR-663, a microRNA targeting JunB and JunD. Carcinogenesis.
31:1561–1566. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang Y, Zhou X, Xu X, Zhang M, Wang X,
Bai X, Li H, Kan L, Zhou Y, Niu H, et al: Waltonitone induces
apoptosis through mir-663-induced Bcl-2 downregulation in non-small
cell lung cancer. Tumour Biol. 36:871–876. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Pan J, Hu H, Zhou Z, Sun L, Peng L, Yu L,
Sun L, Liu J, Yang Z and Ran Y: Tumor-suppressive mir-663 gene
induces mitotic catastrophe growth arrest in human gastric cancer
cells. Oncol Rep. 24:105–112. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liu ZY, Zhang GL, Wang MM, Xiong YN and
Cui HQ: MicroRNA-663 targets TGFB1 and regulates lung cancer
proliferation. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 12:2819–2823.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Shi Y, Chen C, Zhang X, Liu Q, Xu JL,
Zhang HR, Yao XH, Jiang T, He ZC, Ren Y, et al: Primate-specific
miR-663 functions as a tumor suppressor by targeting PIK3CD and
predicts the prognosis of human glioblastoma. Clin Cancer Res.
20:1803–1813. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Shi Y, Chen C, Yu SZ, Liu Q, Rao J, Zhang
HR, Xiao HL, Fu TW, Long H, He ZC, et al: miR-663 suppresses
oncogenic function of CXCR4 in glioblastoma. Clin Cancer Res.
21:4004–4013. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhao L and Hantash BM: TGF-β1 regulates
differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Vitam Horm.
87:127–141. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Perera M, Tsang CS, Distel RJ, Lacy JN,
Ohno-Machado L, Ricchiuti V, Samaranayake LP, Smejkal GB, Smith MG,
Trachtenberg AJ, et al: TGF-beta1 interactome: Metastasis and
beyond. Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 7:217–229. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Caraci F, Battaglia G, Bruno V, Bosco P,
Carbonaro V, Giuffrida ML, Drago F, Sortino MA, Nicoletti F and
Copani A: TGF-β1 pathway as a new target for neuroprotection in
Alzheimer's disease. CNS Neurosci Ther. 17:237–249. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Liu YN, Zha WJ, Ma Y, Chen FF, Zhu W, Ge
A, Zeng XN and Huang M: Galangin attenuates airway remodelling by
inhibiting TGF-β1-mediated ROS generation and MAPK/Akt
phosphorylation in asthma. Sci Rep. 5:117582015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Chen W, Zhong X, Wei Y, Liu Y, Yi Q, Zhang
G, He L, Chen F, Liu Y and Luo J: TGF-β regulates survivin to
affect cell cycle and the expression of EGFR and MMP9 in
glioblastoma. Mol Neurobiol. Feb 17–2015.(Epub ahead of print)
http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s12035-015-9121-6.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Joseph JV, Conroy S, Tomar T,
Eggens-Meijer E, Bhat K, Copray S, Walenkamp AM, Boddeke E,
Balasubramanyian V, Wagemakers M, et al: TGF-β is an inducer of
ZEB1-dependent mesenchymal transdifferentiation in glioblastoma
that is associated with tumor invasion. Cell Death Dis.
5:e14432014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Liu Z, Long X, Chao C, Yan C, Wu Q, Hua S,
Zhang Y, Wu A and Fang W: Knocking down CDK4 mediates the elevation
of let-7c suppressing cell growth in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. BMC
Cancer. 14:2742014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Calin GA and Croce CM: MicroRNA signatures
in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:857–866. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lv S, Sun B, Dai C, Shi R, Zhou X, Lv W,
Zhong X, Wang R and Ma W: The downregulation of microRNA-146a
modulates TGF-β signaling pathways activity in glioblastoma. Mol
Neurobiol. 52:1257–1262. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Yao Y, Ma J, Xue Y, Wang P, Li Z, Li Z, Hu
Y, Shang X and Liu Y: miR-449a exerts tumor-suppressive functions
in human glioblastoma by targeting Myc-associated zinc-finger
protein. Mol Oncol. 9:640–656. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Yu JM, Sun W, Hua F, Xie J, Lin H, Zhou DD
and Hu ZW: BCL6 induces EMT by promoting the ZEB1-mediated
transcription repression of E-cadherin in breast cancer cells.
Cancer Lett. 365:190–200. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wang Z, Wang B, Shi Y, Xu C, Xiao HL, Ma
LN, Xu SL, Yang L, Wang QL, Dang WQ, et al: Oncogenic miR-20a and
miR-106a enhance the invasiveness of human glioma stem cells by
directly targeting TIMP-2. Oncogene. 34:1407–1419. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Tivnan A and McDonald KL: Current progress
for the use of miRNAs in glioblastoma treatment. Mol Neurobiol.
48:757–768. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhao S, Liu H, Liu Y, Wu J, Wang C, Hou X,
Chen X, Yang G, Zhao L, Che H, et al: miR-143 inhibits glycolysis
and depletes stemness of glioblastoma stem-like cells. Cancer Lett.
333:253–260. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Xiao S, Yang Z, Lv R, Zhao J, Wu M, Liao Y
and Liu Q: miR-135b contributes to the radioresistance by targeting
GSK3β in human glioblastoma multiforme cells. PLoS One.
9:e1088102014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Xu F, Li F, Zhang W and Jia P: Growth of
glioblastoma is inhibited by miR-133-mediated EGFR suppression.
Tumour Biol. Jul 3–2015.Epub ahead of print. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Jiang Y, Yin L, Jing H and Zhang H:
MicroRNA-219-5p exerts tumor suppressor function by targeting ROBO1
in glioblastoma. Tumour Biol. Jun 17–2015.Epub ahead of print.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Huang BS, Luo QZ, Han Y, Li XB, Cao LJ and
Wu LX: micro-RNA-223 promotes the growth and invasion of
glioblastoma cells by targeting tumor suppressor PAX6. Oncol Rep.
30:2263–2269. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Xu J, Xu W and Zhu J: Propofol suppresses
proliferation and invasion of glioma cells by upregulating
microRNA-218 expression. Mol Med Rep. 12:4815–4820. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Shi L, Fei X, Wang Z and You Y: PI3K
inhibitor combined with miR-125b inhibitor sensitize TMZ-induced
anti-glioma stem cancer effects through inactivation of
Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. Jul
14–2015.Epub ahead of print. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Scarpa S, Coppa A, Ragano-Caracciolo M,
Mincione G, Giuffrida A, Modesti A and Colletta G: Transforming
growth factor beta regulates differentiation and proliferation of
human neuroblastoma. Exp Cell Res. 229:147–154. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wang J, Li Y, Wang X and Jiang C: Ursolic
acid inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis in human
glioblastoma cell lines U251 by suppressing TGF-β1/miR-21/PDCD4
pathway. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 111:106–112. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Hu W, Xu S, Yao B, Hong M, Wu X, Pei H,
Chang L, Ding N, Gao X, Ye C, et al: miR-663 inhibits
radiation-induced bystander effects by targeting TGFB1 in a
feedback mode. RNA Biol. 11:1189–1198. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Hong Q, Yu S, Geng X, Duan L, Zheng W, Fan
M, Chen X and Wu D: High concentrations of uric acid inhibit
endothelial cell migration via miR-663 which regulates phosphatase
and tensin homolog by targeting transforming growth factor-β1.
Microcirculation. 22:306–314. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Liu L, Dai Q, Min Z and Zhang M:
Transforming growth factor β1 enhances the invasiveness of human
glioma cell line via ERK/MAPK pathway. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue
Bao. 33:1744–1747. 2013.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Li W, Kidiyoor A, Hu Y, Guo C, Liu M, Yao
X, Zhang Y, Peng B and Zheng J: Evaluation of transforming growth
factor-β1 suppress Pokemon/epithelial-mesenchymal transition
expression in human bladder cancer cells. Tumour Biol.
36:1155–1162. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|