|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Cohen DJ and Ajani J: An expert opinion on
esophageal cancer therapy. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 12:225–239.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lagergren J and Lagergren P: Oesophageal
cancer. BMJ. 341:c62802010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
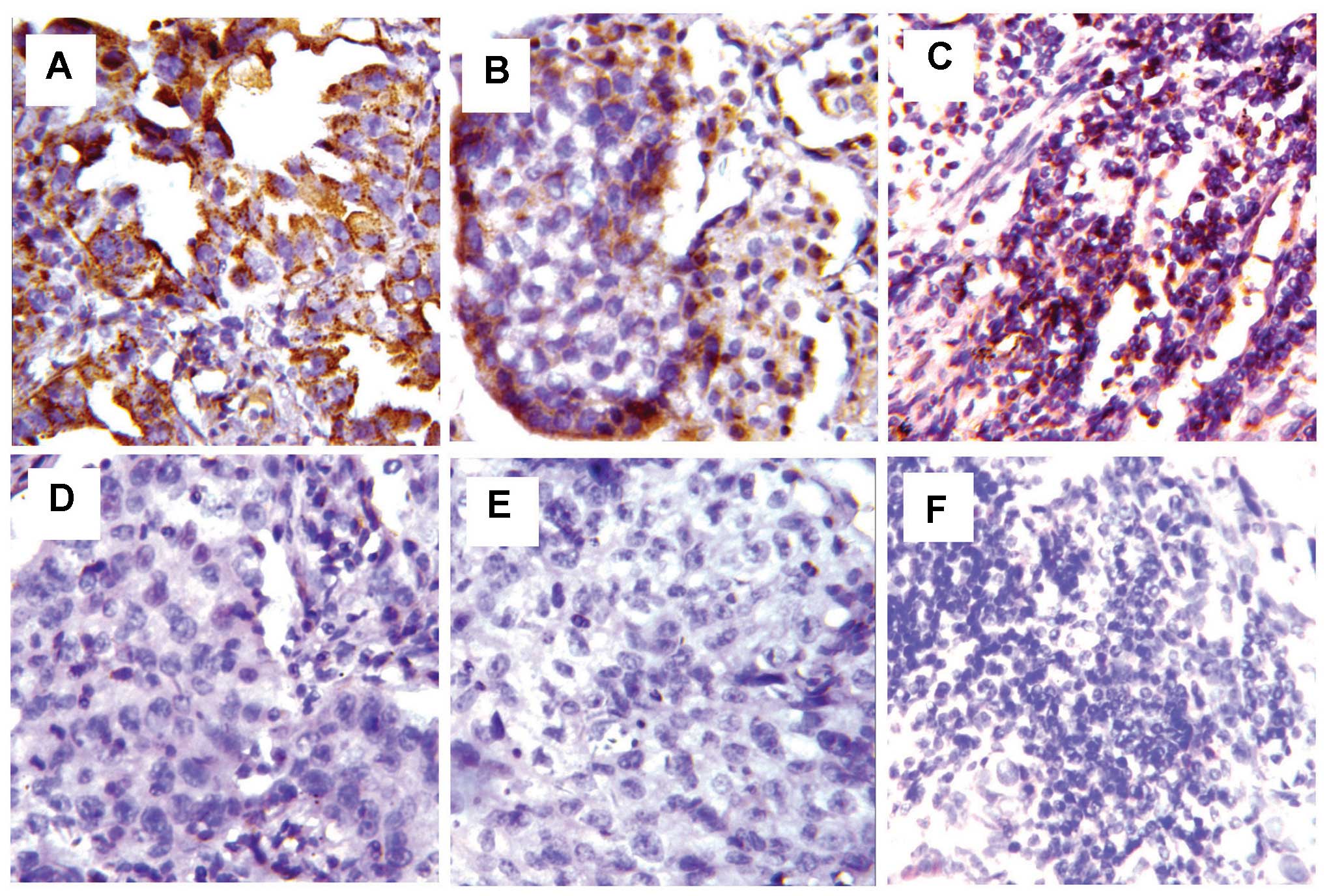
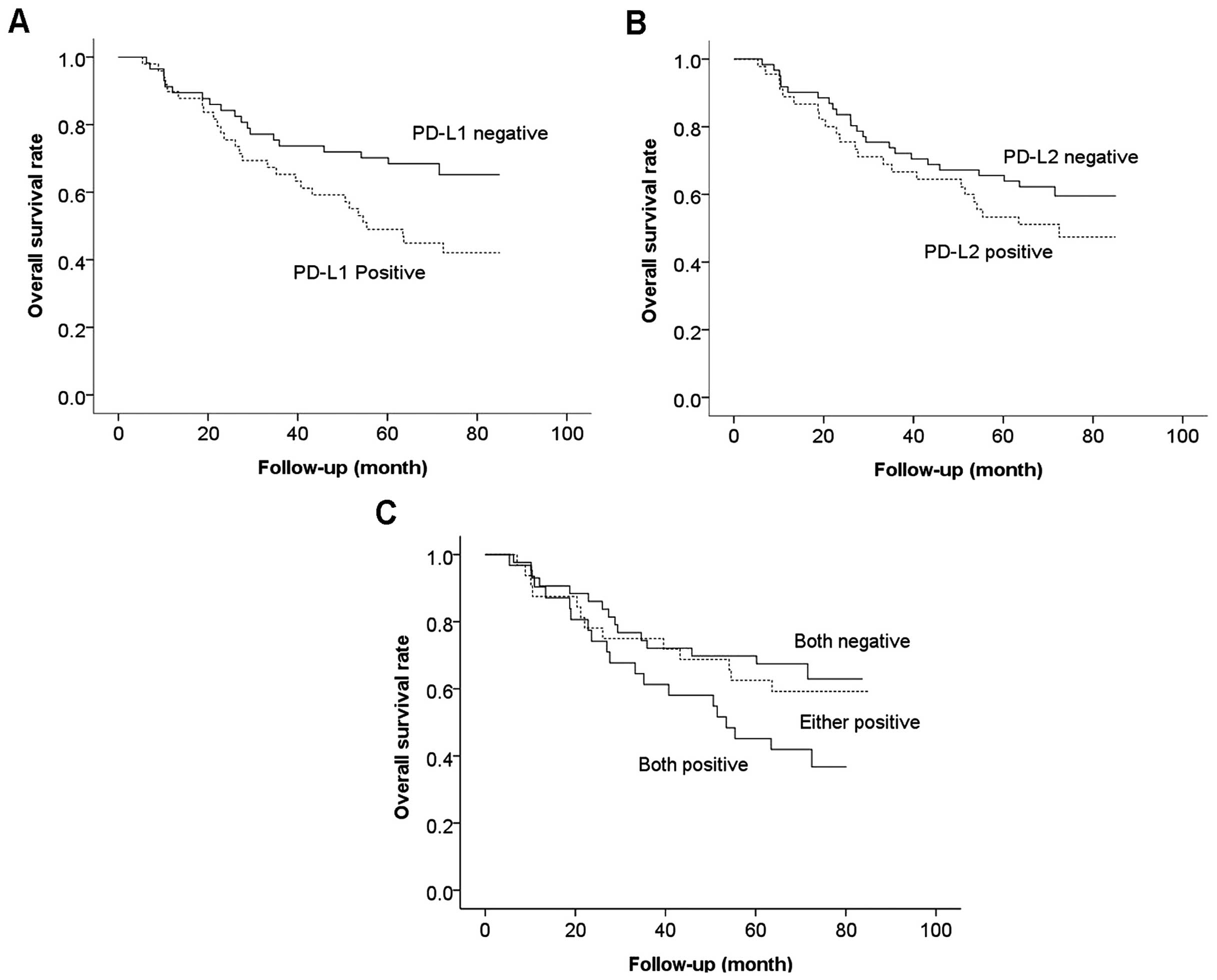
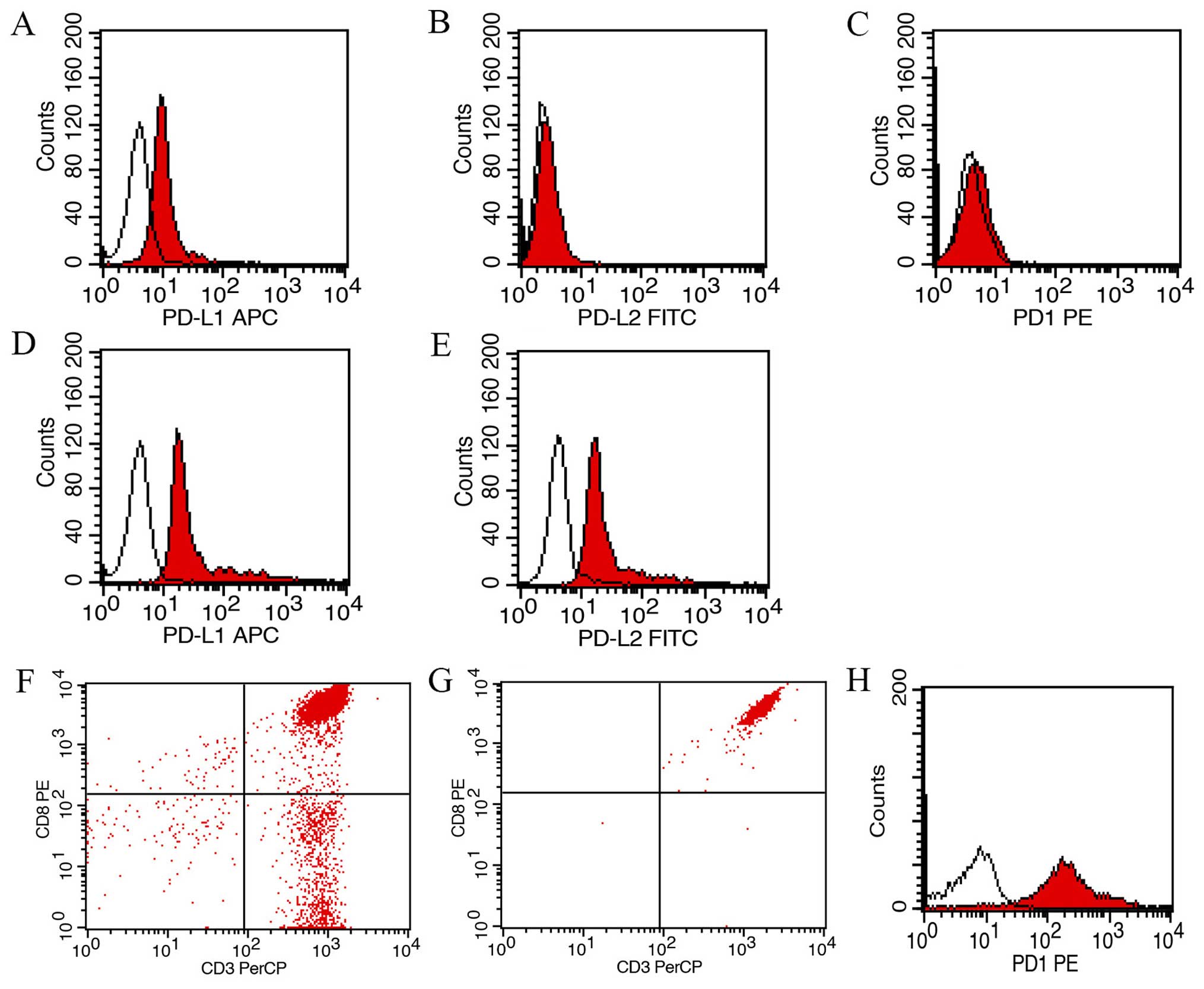
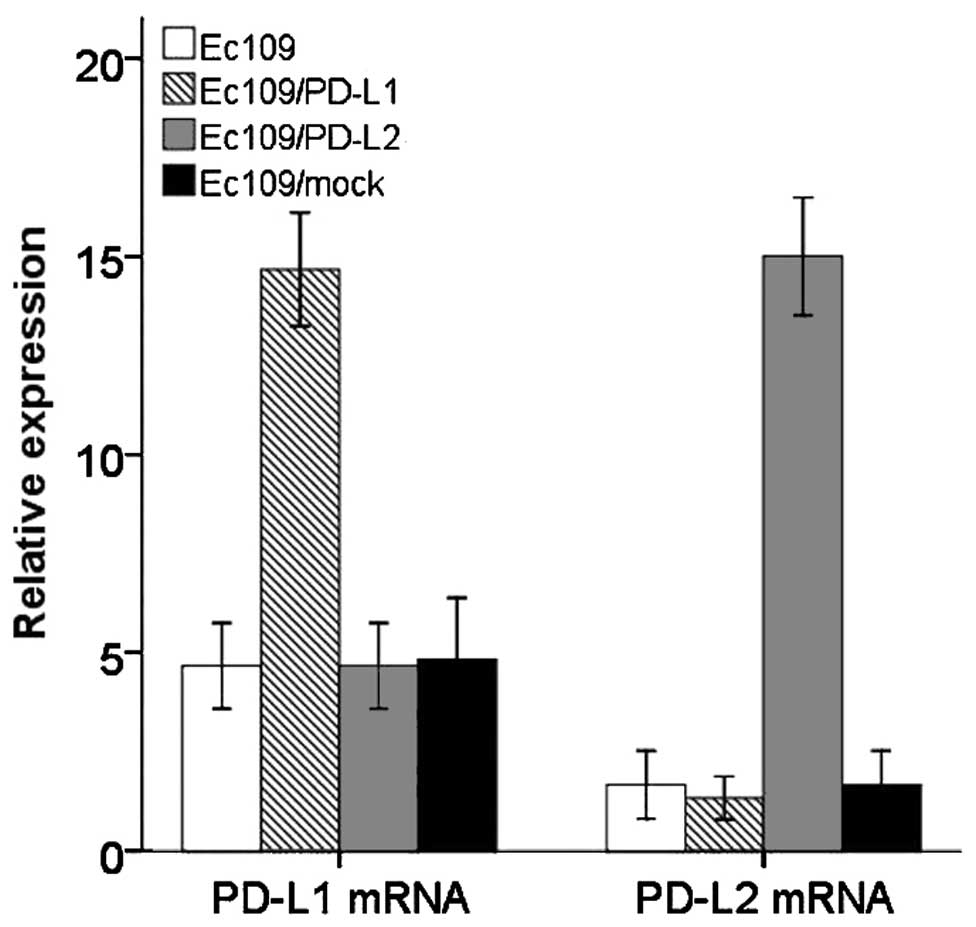
Cunningham D, Allum WH, Stenning SP,
Thompson JN, Van de Velde CJ, Nicolson M, Scarffe JH, Lofts FJ,
Falk SJ, Iveson TJ, et al: MAGIC Trial Participants: Perioperative
chemotherapy versus surgery alone for resectable gastroesophageal
cancer. N Engl J Med. 355:11–20. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Siewert JR, Lordick F, Ott K, Stein HJ,
Weber WA, Becker K, Peschel C, Fink U and Schwaiger M: Induction
chemotherapy in Barrett cancer: Influence on surgical risk and
outcome. Ann Surg. 246:624–628; discussion 628–631. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Gebski V, Burmeister B, Smithers BM, Foo
K, Zalcberg J, Simes J, Australasian Gastro-Intestinal and Trials
Group: Survival benefts from neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy or
chemotherapy in oesophageal carcinoma: A meta-analysis. Lancet
Oncol. 8:226–234. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Dong H, Strome SE, Salomao DR, Tamura H,
Hirano F, Flies DB, Roche PC, Lu J, Zhu G, Tamada K, et al:
Tumor-associated B7-H1 promotes T-cell apoptosis: A potential
mechanism of immune evasion. Nat Med. 8:793–800. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Dong H and Chen L: B7-H1 pathway and its
role in the evasion of tumor immunity. J Mol Med (Berl).
81:281–287. 2003.
|
|
9
|
Flies DB and Chen L: The new B7s: Playing
a pivotal role in tumor immunity. J Immunother. 30:251–260. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sharpe AH and Freeman GJ: The B7-CD28
superfamily. Nat Rev Immunol. 2:116–126. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ishida Y, Agata Y, Shibahara K and Honjo
T: Induced expression of PD-1, a novel member of the immunoglobulin
gene super-family, upon programmed cell death. EMBO J.
11:3887–3895. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Nishimura H and Honjo T: PD-1: An
inhibitory immunoreceptor involved in peripheral tolerance. Trends
Immunol. 22:265–268. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Dong H, Zhu G, Tamada K and Chen L: B7-H1,
a third member of the B7 family, co-stimulates T-cell proliferation
and interleukin-10 secretion. Nat Med. 5:1365–1369. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Freeman GJ, Long AJ, Iwai Y, Bourque K,
Chernova T, Nishimura H, Fitz LJ, Malenkovich N, Okazaki T, Byrne
MC, et al: Engagement of the PD-1 immunoinhibitory receptor by a
novel B7 family member leads to negative regulation of lymphocyte
activation. J Exp Med. 192:1027–1034. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tseng SY, Otsuji M, Gorski K, Huang X,
Slansky JE, Pai SI, Shalabi A, Shin T, Pardoll DM and Tsuchiya H:
B7-DC, a new dendritic cell molecule with potent costimulatory
properties for T cells. J Exp Med. 193:839–846. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Latchman Y, Wood CR, Chernova T, Chaudhary
D, Borde M, Chernova I, Iwai Y, Long AJ, Brown JA, Nunes R, et al:
PD-L2 is a second ligand for PD-1 and inhibits T cell activation.
Nat Immunol. 2:261–268. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mahoney KM, Freeman GJ and McDermott DF:
The next immune-checkpoint inhibitors: PD-1/PD-L1 blockade in
melanoma. Clin Ther. 37:764–782. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Massari F, Santoni M, Ciccarese C, Santini
D, Alfieri S, Martignoni G, Brunelli M, Piva F, Berardi R,
Montironi R, et al: PD-1 blockade therapy in renal cell carcinoma:
Current studies and future promises. Cancer Treat Rev. 41:114–121.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Suzuki H, Owada Y, Watanabe Y, Inoue T,
Fukuharav M, Yamaura T, Mutoh S, Okabe N, Yaginuma H, Hasegawa T,
et al: Recent advances in immunotherapy for non-small-cell lung
cancer. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 10:352–357. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Topalian SL, Hodi FS, Brahmer JR,
Gettinger SN, Smith DC, McDermott DF, Powderly JD, Carvajal RD,
Sosman JA, Atkins MB, et al: Safety, activity, and immune
correlates of anti-PD-1 antibody in cancer. N Engl J Med.
366:2443–2454. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Brahmer JR, Tykodi SS, Chow LQ, Hwu WJ,
Topalian SL, Hwu P, Drake CG, Camacho LH, Kauh J, Odunsi K, et al:
Safety and activity of anti-PD-L1 antibody in patients with
advanced cancer. N Engl J Med. 366:2455–2465. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Thompson RH, Kuntz SM, Leibovich BC, Dong
H, Lohse CM, Webster WS, Sengupta S, Frank I, Parker AS, Zincke H,
et al: Tumor B7-H1 is associated with poor prognosis in renal cell
carcinoma patients with long-term follow-up. Cancer Res.
66:3381–3385. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ohigashi Y, Sho M, Yamada Y, Tsurui Y,
Hamada K, Ikeda N, Mizuno T, Yoriki R, Kashizuka H, Yane K, et al:
Clinical significance of programmed death-1 ligand-1 and programmed
death-1 ligand-2 expression in human esophageal cancer. Clin Cancer
Res. 11:2947–2953. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Cordon-Cardo C, Fuks Z, Drobnjak M, Moreno
C, Eisenbach L and Feldman M: Expression of HLA-A,B,C antigens on
primary and metastatic tumor cell populations of human carcinomas.
Cancer Res. 51:6372–6380. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Restifo NP, Esquivel F, Kawakami Y,
Yewdell JW, Mulé JJ, Rosenberg SA and Bennink JR: Identification of
human cancers deficient in antigen processing. J Exp Med.
177:265–272. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ebrahimi B, Tucker SL, Li D, Abbruzzese JL
and Kurzrock R: Cytokines in pancreatic carcinoma: Correlation with
phenotypic characteristics and prognosis. Cancer. 101:2727–2736.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Pardoll D: Does the immune system see
tumors as foreign or self? Annu Rev Immunol. 21:807–839. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Liu X, Gao JX, Wen J, Yin L, Li O, Zuo T,
Gajewski TF, Fu YX, Zheng P and Liu Y: B7DC/PDL2 promotes tumor
immunity by a PD-1-independent mechanism. J Exp Med. 197:1721–1730.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Okazaki T, Maeda A, Nishimura H, Kurosaki
T and Honjo T: PD-1 immunoreceptor inhibits B cell
receptor-mediated signaling by recruiting src homology
2-domain-containing tyrosine phosphatase 2 to phosphotyrosine. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 98:13866–13871. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Thompson RH, Gillett MD, Cheville JC,
Lohse CM, Dong H, Webster WS, Krejci KG, Lobo JR, Sengupta S, Chen
L, et al: Costimulatory B7-H1 in renal cell carcinoma patients:
Indicator of tumor aggressiveness and potential therapeutic target.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:17174–17179. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Nakanishi J, Wada Y, Matsumoto K, Azuma M,
Kikuchi K and Ueda S: Overexpression of B7-H1 (PD-L1) significantly
associates with tumor grade and postoperative prognosis in human
urothelial cancers. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 56:1173–1182. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Nomi T, Sho M, Akahori T, Hamada K, Kubo
A, Kanehiro H, Nakamura S, Enomoto K, Yagita H, Azuma M, et al:
Clinical significance and therapeutic potential of the programmed
death-1 ligand/programmed death-1 pathway in human pancreatic
cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 13:2151–2157. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Loos M, Giese NA, Kleeff J, Giese T, Gaida
MM, Bergmann F, Laschinger M, W Büchler M and Friess H: Clinical
significance and regulation of the costimulatory molecule B7-H1 in
pancreatic cancer. Cancer Lett. 268:98–109. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wu C, Zhu Y, Jiang J, Zhao J, Zhang XG and
Xu N: Immunohistochemical localization of programmed death-1
ligand-1 (PD-L1) in gastric carcinoma and its clinical
significance. Acta Histochem. 108:19–24. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Hamanishi J, Mandai M, Iwasaki M, Okazaki
T, Tanaka Y, Yamaguchi K, Higuchi T, Yagi H, Takakura K, Minato N,
et al: Programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 and tumor-infiltrating
CD8+ T lymphocytes are prognostic factors of human
ovarian cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:3360–3365. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Gao Q, Wang XY, Qiu SJ, Yamato I, Sho M,
Nakajima Y, Zhou J, Li BZ, Shi YH, Xiao YS, et al: Overexpression
of PD-L1 significantly associates with tumor aggressiveness and
postoperative recurrence in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin
Cancer Res. 15:971–979. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Rosenberg SA: The immunotherapy of solid
cancers based on cloning the genes encoding tumor-rejection
antigens. Annu Rev Med. 47:481–491. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Cho Y, Miyamoto M, Kato K, Fukunaga A,
Shichinohe T, Kawarada Y, Hida Y, Oshikiri T, Kurokawa T, Suzuoki
M, et al: CD4+ and CD8+ T cells cooperate to
improve prognosis of patients with esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma. Cancer Res. 63:1555–1559. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Schumacher K, Haensch W, Röefzaad C and
Schlag PM: Prognostic significance of activated CD8(+) T cell
infiltrations within esophageal carcinomas. Cancer Res.
61:3932–3936. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ropponen KM, Eskelinen MJ, Lipponen PK,
Alhava E and Kosma VM: Prognostic value of tumour-infiltrating
lymphocytes (TILs) in colorectal cancer. J Pathol. 182:318–324.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Schroder K, Hertzog PJ, Ravasi T and Hume
DA: Interferon-gamma: An overview of signals, mechanisms and
functions. J Leukoc Biol. 75:163–189. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Chemnitz JM, Parry RV, Nichols KE, June CH
and Riley JL: SHP-1 and SHP-2 associate with immunoreceptor
tyrosine-based switch motif of programmed death 1 upon primary
human T cell stimulation, but only receptor ligation prevents T
cell activation. J Immunol. 173:945–954. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Parry RV, Chemnitz JM, Frauwirth KA,
Lanfranco AR, Braunstein I, Kobayashi SV, Linsley PS, Thompson CB
and Riley JL: CTLA-4 and PD-1 receptors inhibit T-cell activation
by distinct mechanisms. Mol Cell Biol. 25:9543–9553. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Nurieva R, Thomas S, Nguyen T,
Martin-Orozco N, Wang Y, Kaja MK, Yu XZ and Dong C: T-cell
tolerance or function is determined by combinatorial costimulatory
signals. EMBO J. 25:2623–2633. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Riley JL: PD-1 signaling in primary T
cells. Immunol Rev. 229:114–125. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Rozali EN, Hato SV, Robinson BW, Lake RA
and Lesterhuis J: Programmed death ligand 2 in cancer-induced
immune suppression. Clin Dev Immunol. 2012(656340)2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Matsumoto K, Inoue H, Nakano T, Tsuda M,
Yoshiura Y, Fukuyama S, Tsushima F, Hoshino T, Aizawa H, Akiba H,
et al: B7-DC regulates asthmatic response by an IFN-gamma-dependent
mechanism. J Immunol. 172:2530–2541. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Ishiwata K, Watanabe N, Guo M, Tomihara K,
Brumlik MJ, Yagita H, Pardoll D, Chen L and Shin T: Costimulator
B7-DC attenuates strong Th2 responses induced by Nippostrongylus
brasiliensis. J Immunol. 184:2086–2094. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Wang S, Bajorath J, Flies DB, Dong H,
Honjo T and Chen L: Molecular modeling and functional mapping of
B7-H1 and B7-DC uncouple costimulatory function from PD-1
interaction. J Exp Med. 197:1083–1091. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Yang W, Chen PW, Li H, Alizadeh H and
Niederkorn JY: PD-L1: PD-1 interaction contributes to the
functional suppression of T-cell responses to human uveal melanoma
cells in vitro. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 49:2518–2525. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Topalian SL, Drake CG and Pardoll DM:
Targeting the PD-1/B7-H1(PD-L1) pathway to activate anti-tumor
immunity. Curr Opin Immunol. 24:207–212. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|