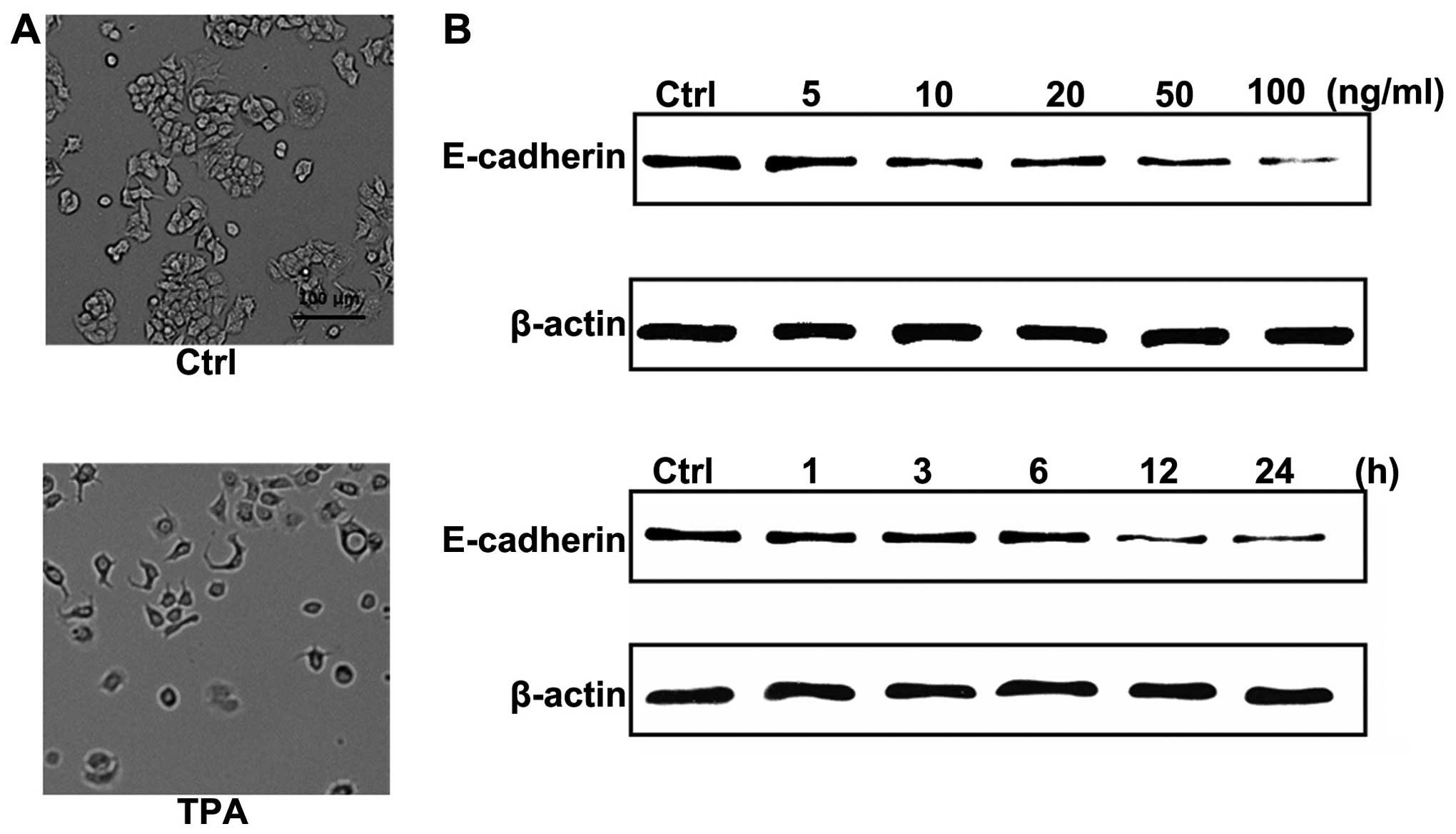
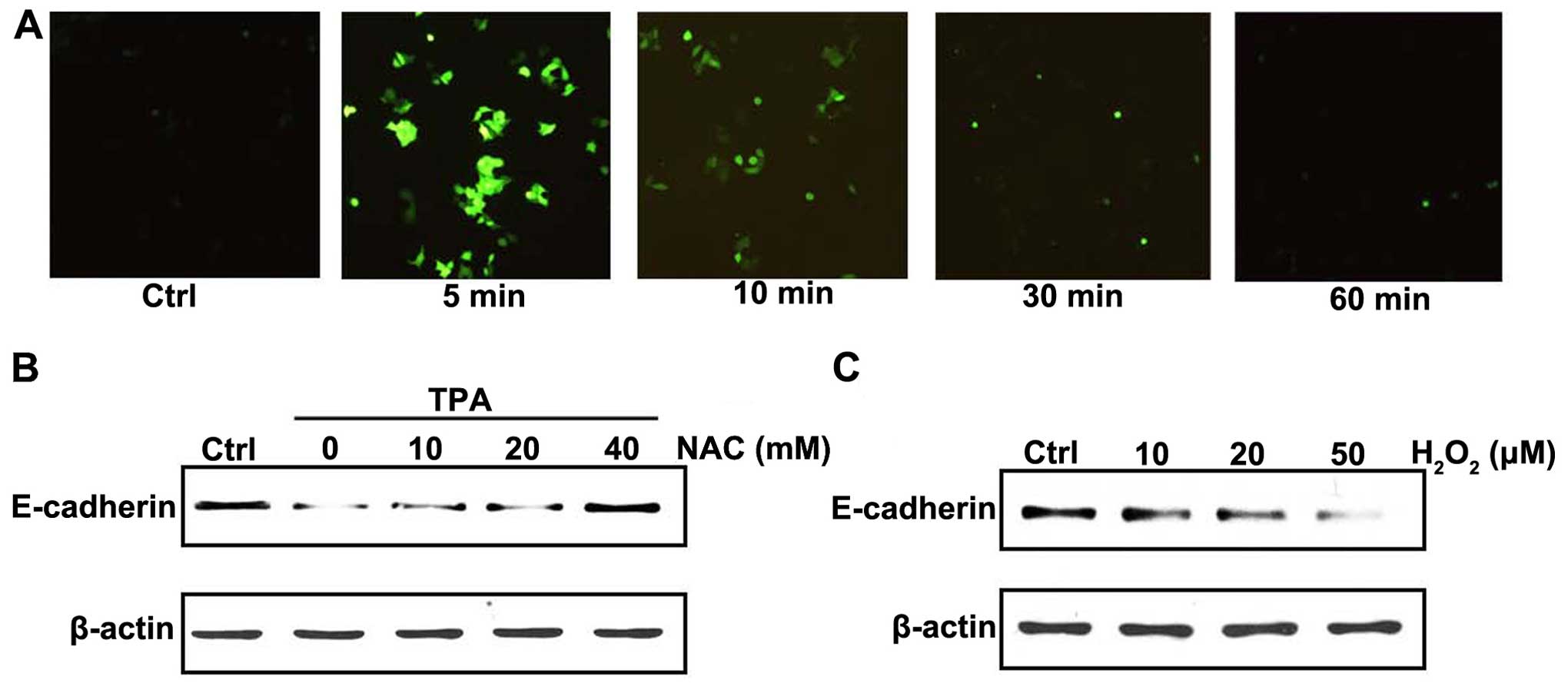
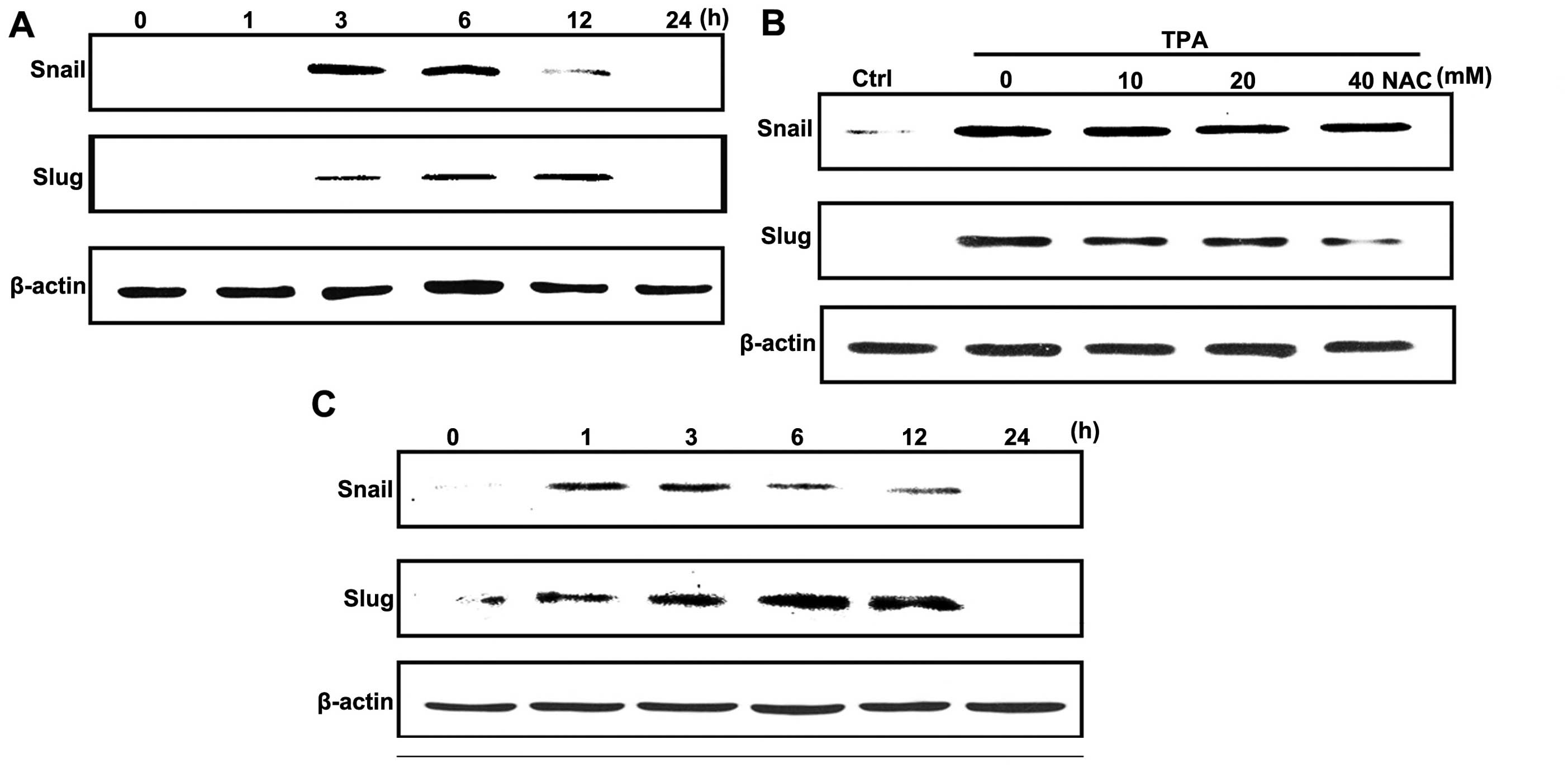
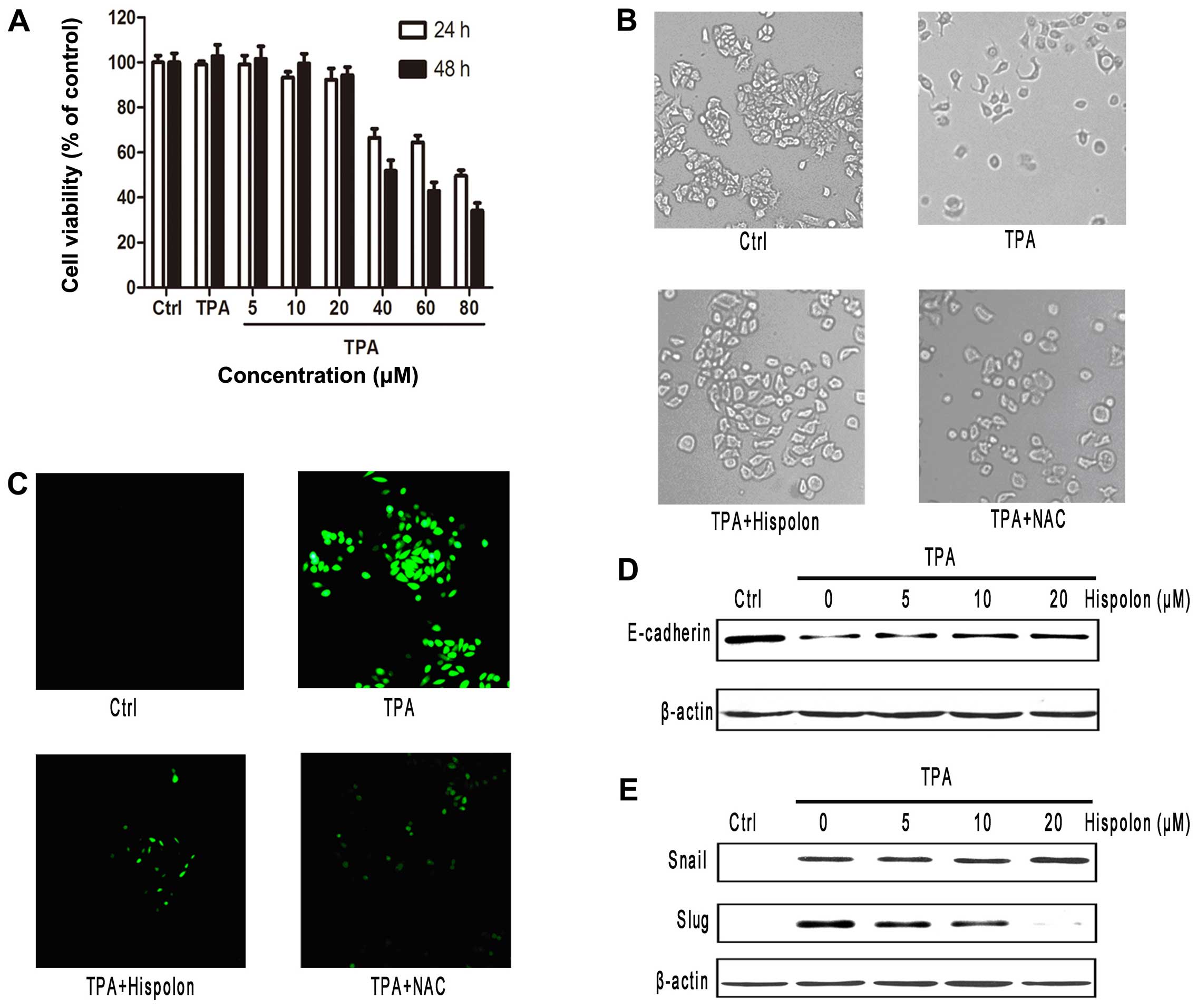
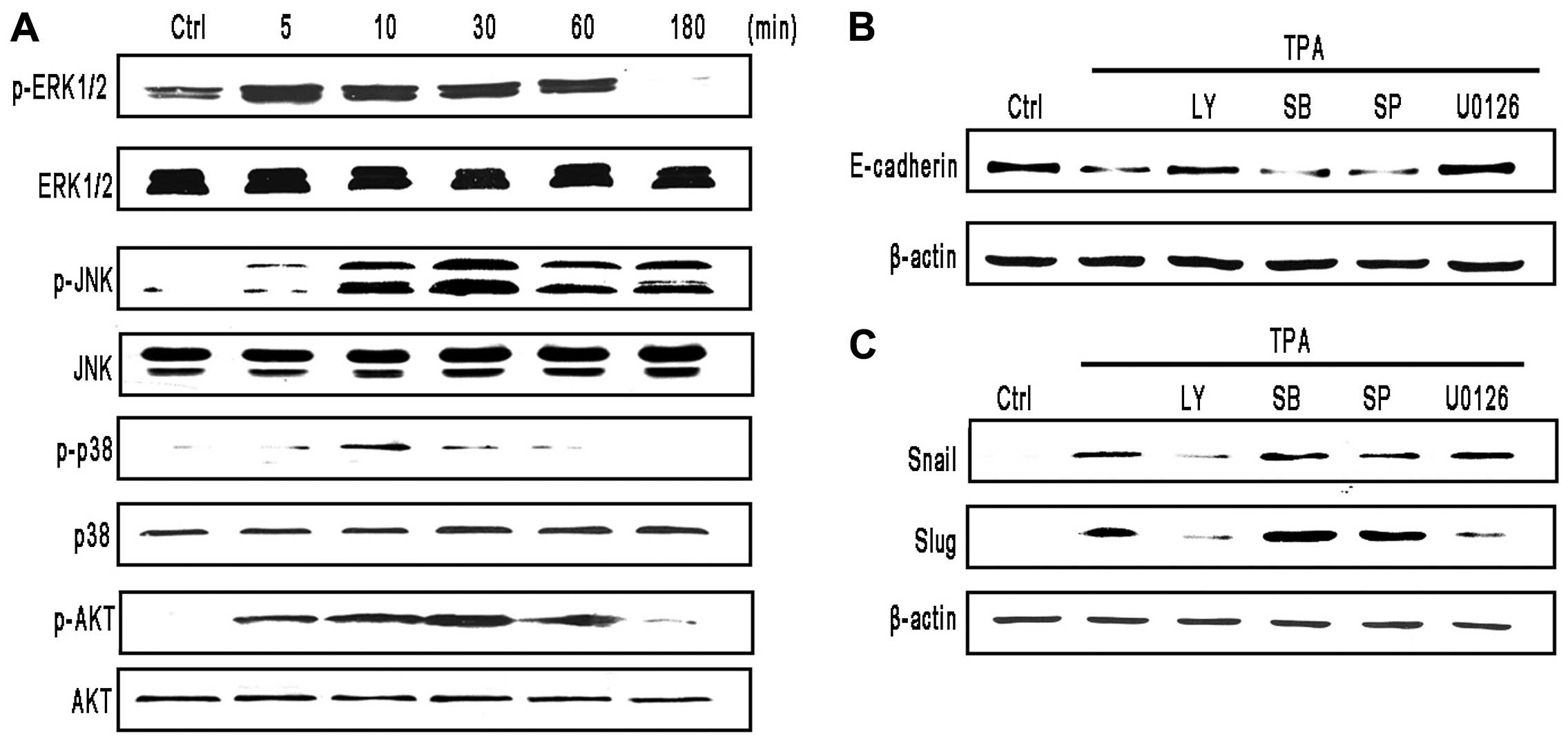
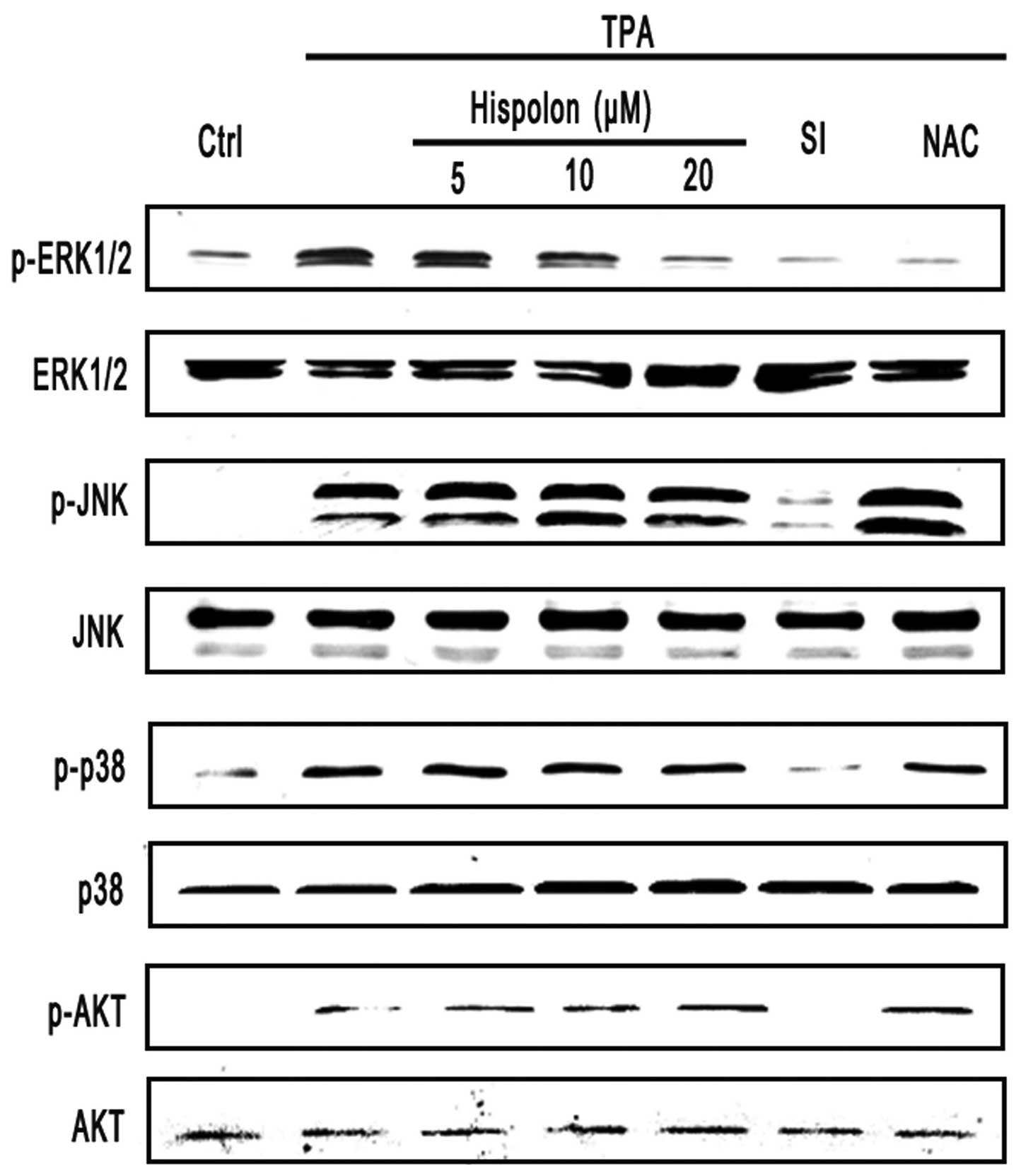
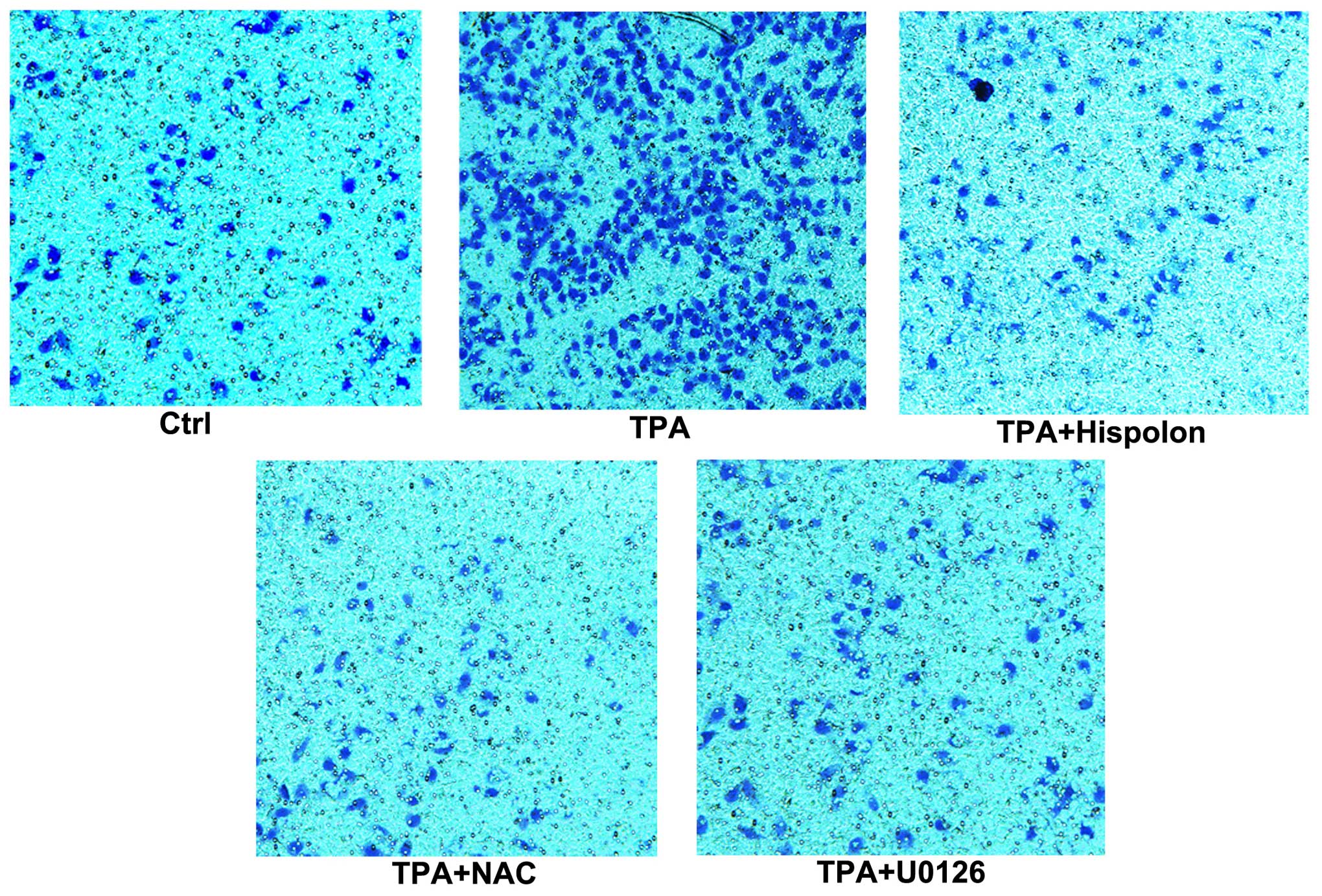
|
1
|
Jemal A, Center MM, DeSantis C and Ward
EM: Global patterns of cancer incidence and mortality rates and
trends. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 19:1893–1907. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Weigelt B, Hu Z, He X, Livasy C, Carey LA,
Ewend MG, Glas AM, Perou CM and Van't Veer LJ: Molecular portraits
and 70-gene prognosis signature are preserved throughout the
metastatic process of breast cancer. Cancer Res. 65:9155–9158.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tsuji T, Ibaragi S and Hu GF:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cell cooperativity in
metastasis. Cancer Res. 69:7135–7139. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Polyak K and Weinberg RA: Transitions
between epithelial and mesenchymal states: Acquisition of malignant
and stem cell traits. Nat Rev Cancer. 9:265–273. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Miyoshi J and Takai Y: Structural and
functional associations of apical junctions with cytoskeleton.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1778:670–691. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Voulgari A and Pintzas A:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer metastasis: Mechanisms,
markers and strategies to overcome drug resistance in the clinic.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1796:75–90. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Doyle S, Evans AJ, Rakha EA, Green AR and
Ellis IO: Influence of E-cadherin expression on the mammographic
appearance of invasive nonlobular breast carcinoma detected at
screening. Radiology. 253:51–55. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Batlle E, Sancho E, Francí C, Domínguez D,
Monfar M, Baulida J and García De Herreros A: The transcription
factor snail is a repressor of E-cadherin gene expression in
epithelial tumour cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2:84–89. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Comijn J, Berx G, Vermassen P, Verschueren
K, van Grunsven L, Bruyneel E, Mareel M, Huylebroeck D and van Roy
F: The two-handed E box binding zinc finger protein SIP1
downregulates E-cadherin and induces invasion. Mol Cell.
7:1267–1278. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Peinado H, Olmeda D and Cano A: Snail, Zeb
and bHLH factors in tumour progression: An alliance against the
epithelial phenotype? Nat Rev Cancer. 7:415–428. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wu WS: The signaling mechanism of ROS in
tumor progression. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 25:695–705. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wu WS, Wu JR and Hu CT: Signal cross talks
for sustained MAPK activation and cell migration: The potential
role of reactive oxygen species. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 27:303–314.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Boonstra J and Post JA: Molecular events
associated with reactive oxygen species and cell cycle progression
in mammalian cells. Gene. 337:1–13. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hu CT, Wu JR, Cheng CC, Wang S, Wang HT,
Lee MC, Wang LJ, Pan SM, Chang TY and Wu WS: Reactive oxygen
species-mediated PKC and integrin signaling promotes tumor
progression of human hepatoma HepG2. Clin Exp Metastasis.
28:851–863. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang Z, Li Y and Sarkar FH: Signaling
mechanism(s) of reactive oxygen species in epithelial-mesenchymal
transition reminiscent of cancer stem cells in tumor progression.
Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 5:74–80. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Hwang YS, Jeong M, Park JS, Kim MH, Lee
DB, Shin BA, Mukaida N, Ellis LM, Kim HR, Ahn BW, et al:
Interleukin-1beta stimulates IL-8 expression through MAP kinase and
ROS signaling in human gastric carcinoma cells. Oncogene.
23:6603–6611. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lin CW, Yang LY, Shen SC and Chen YC:
IGF-I plus E2 induces proliferation via activation of ROS-dependent
ERKs and JNKs in human breast carcinoma cells. J Cell Physiol.
212:666–674. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Binker MG, Binker-Cosen AA, Richards D,
Oliver B and Cosen-Binker LI: EGF promotes invasion by PANC-1 cells
through Rac1/ROS-dependent secretion and activation of MMP-2.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 379:445–450. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lee KH and Kim JR: Reactive oxygen species
regulate the generation of urokinase plasminogen activator in human
hepatoma cells via MAPK pathways after treatment with hepatocyte
growth factor. Exp Mol Med. 41:180–188. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wu WS, Tsai RK, Chang CH, Wang S, Wu JR
and Chang YX: Reactive oxygen species mediated sustained activation
of protein kinase C alpha and extracellular signal-regulated kinase
for migration of human hepatoma cell Hepg2. Mol Cancer Res.
4:747–758. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Mori K, Shibanuma M and Nose K: Invasive
potential induced under long-term oxidative stress in mammary
epithelial cells. Cancer Res. 64:7464–7472. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chen W, He FY and Li YQ: The apoptosis
effect of hispolon from Phellinus linteus (Berkeley & Curtis)
Teng on human epidermoid KB cells. J Ethnopharmacol. 105:280–285.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Mo S, Wang S, Zhou G, Yang Y, Li Y, Chen X
and Shi J: Phelligridins C-F: Cytotoxic
pyrano[4,3-c][2]benzopyran-1,6-dione and furo[3,2-c]pyran-4-one
derivatives from the fungus Phellinus igniarius. J Nat Prod.
67:823–828. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chen W, Zhao Z, Li L, Wu B, Chen SF, Zhou
H, Wang Y and Li YQ: Hispolon induces apoptosis in human gastric
cancer cells through a ROS-mediated mitochondrial pathway. Free
Radic Biol Med. 45:60–72. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Huang GJ, Deng JS, Huang SS and Hu ML:
Hispolon induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest of human
hepatocellular carcinoma Hep3B cells by modulating ERK
phosphorylation. J Agric Food Chem. 59:7104–7113. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Huang GJ, Yang CM, Chang YS, Amagaya S,
Wang HC, Hou WC, Huang SS and Hu ML: Hispolon suppresses SK-Hep1
human hepatoma cell metastasis by inhibiting matrix
metallo-proteinase-2/9 and urokinase-plasminogen activator through
the PI3K/Akt and ERK signaling pathways. J Agric Food Chem.
58:9468–9475. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Park SY, Kim YH, Kim Y and Lee SJ:
Frondoside A has an anti-invasive effect by inhibiting TPA-induced
MMP-9 activation via NF-κB and AP-1 signaling in human breast
cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 41:933–940. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Noh EM, Lee YR, Hur H and Kim JS: Radix
clematidis extract inhibits TPA-induced MMP-9 expression by
suppressing NF-κB activation in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells.
Mol Med Rep. 4:879–883. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wen-Sheng W: ERK signaling pathway is
involved in p15INK4b/p16INK4a expression and
HepG2 growth inhibition triggered by TPA and Saikosaponin a.
Oncogene. 22:955–963. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
He H, Davidson AJ, Wu D, Marshall FF,
Chung LW, Zhau HE, He D and Wang R: Phorbol ester
phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate induces epithelial to mesenchymal
transition in human prostate cancer ARCaP cells. Prostate.
70:1119–1126. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Radisky DC, Levy DD, Littlepage LE, Liu H,
Nelson CM, Fata JE, Leake D, Godden EL, Albertson DG, Nieto MA, et
al: Rac1b and reactive oxygen species mediate MMP-3-induced EMT and
genomic instability. Nature. 436:123–127. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Traore K, Sharma RB, Burek CL and Trush
MA: Role of ROS and MAPK in TPA-induced ICAM-1 expression in the
myeloid ML-1 cell line. J Cell Biochem. 100:1010–1021. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Dong R, Wang Q, He XL, Chu YK, Lu JG and
Ma QJ: Role of nuclear factor kappa B and reactive oxygen species
in the tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced epithelial-mesenchymal
transition of MCF-7 cells. Braz J Med Biol Res. 40:1071–1078. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kurrey NK, K A and Bapat SA: Snail and
Slug are major determinants of ovarian cancer invasiveness at the
transcription level. Gynecol Oncol. 97:155–165. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Leong KG, Niessen K, Kulic I, Raouf A,
Eaves C, Pollet I and Karsan A: Jagged1-mediated Notch activation
induces epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition through Slug-induced
repression of E-cadherin. J Exp Med. 204:2935–2948. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Martin TA, Goyal A, Watkins G and Jiang
WG: Expression of the transcription factors snail, slug, and twist
and their clinical significance in human breast cancer. Ann Surg
Oncol. 12:488–496. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ben-Porath I, Thomson MW, Carey VJ, Ge R,
Bell GW, Regev A and Weinberg RA: An embryonic stem cell-like gene
expression signature in poorly differentiated aggressive human
tumors. Nat Genet. 40:499–507. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Côme C, Magnino F, Bibeau F, De Santa
Barbara P, Becker KF, Theillet C and Savagner P: Snail and slug
play distinct roles during breast carcinoma progression. Clin
Cancer Res. 12:5395–5402. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Hour MJ, Tsai SC, Wu HC, Lin MW, Chung JG,
Wu JB, Chiang JH, Tsuzuki M and Yang JS: Antitumor effects of the
novel quinazolinone MJ-33: Inhibition of metastasis through the
MAPK, AKT, NF-κB and AP-1 signaling pathways in DU145 human
prostate cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 41:1513–1519. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Phung TL, Ziv K, Dabydeen D, Eyiah-Mensah
G, Riveros M, Perruzzi C, Sun J, Monahan-Earley RA, Shiojima I,
Nagy JA, et al: Pathological angiogenesis is induced by sustained
Akt signaling and inhibited by rapamycin. Cancer Cell. 10:159–170.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Grille SJ, Bellacosa A, Upson J,
Klein-Szanto AJ, van Roy F, Lee-Kwon W, Donowitz M, Tsichlis PN and
Larue L: The protein kinase Akt induces epithelial mesenchymal
transition and promotes enhanced motility and invasiveness of
squamous cell carcinoma lines. Cancer Res. 63:2172–2178.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Larue L and Bellacosa A:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in development and cancer: Role
of phosphatidylinositol 3′ kinase/AKT pathways. Oncogene.
24:7443–7454. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Woo JH, Lim JH, Kim YH, Suh SI, Min DS,
Chang JS, Lee YH, Park JW and Kwon TK: Resveratrol inhibits phorbol
myristate acetate-induced matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression by
inhibiting JNK and PKC delta signal transduction. Oncogene.
23:1845–1853. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Lin CW, Hou WC, Shen SC, Juan SH, Ko CH,
Wang LM and Chen YC: Quercetin inhibition of tumor invasion via
suppressing PKC delta/ERK/AP-1-dependent matrix metalloproteinase-9
activation in breast carcinoma cells. Carcinogenesis. 29:1807–1815.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Woo MS, Jung SH, Kim SY, Hyun JW, Ko KH,
Kim WK and Kim HS: Curcumin suppresses phorbol ester-induced matrix
metalloproteinase-9 expression by inhibiting the PKC to MAPK
signaling pathways in human astroglioma cells. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 335:1017–1025. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Lee HS, Seo EY, Kang NE and Kim WK:
[6]-Gingerol inhibits metastasis of MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer
cells. J Nutr Biochem. 19:313–319. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Yagihashi S, Miura Y and Yagasaki K:
Inhibitory effect of gingerol on the proliferation and invasion of
hepatoma cells in culture. Cytotechnology. 57:129–136. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Lu TL, Huang GJ, Lu TJ, Wu JB, Wu CH, Yang
TC, Iizuka A and Chen YF: Hispolon from Phellinus linteus has
antiproliferative effects via MDM2-recruited ERK1/2 activity in
breast and bladder cancer cells. Food Chem Toxicol. 47:2013–2021.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Sun YS, Zhao Z and Zhu HP: Hispolon
inhibits TPA-induced invasion by reducing MMP-9 expression through
the NF-κB signaling pathway in MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer
cells. Oncol Lett. 10:536–542. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Al Saleh S, Al Mulla F and Luqmani YA:
Estrogen receptor silencing induces epithelial to mesenchymal
transition in human breast cancer cells. PLoS One. 6:e206102011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Bouris P, Skandalis SS, Piperigkou Z,
Afratis N, Karamanou K, Aletras AJ, Moustakas A, Theocharis AD and
Karamanos NK: Estrogen receptor alpha mediates epithelial to
mesenchymal transition, expression of specific matrix effectors and
functional properties of breast cancer cells. Matrix Biol.
43:42–60. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Jang EH, Jang SY, Cho IH, Hong D, Jung B,
Park MJ and Kim JH: Hispolon inhibits the growth of estrogen
receptor positive human breast cancer cells through modulation of
estrogen receptor alpha. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 463:917–922.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|