|
1
|
Fernández-Fernández FJ and Sesma P:
Gastric cancer. Lancet. 374(1594): author reply. 1594–1595. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hartgrink HH, Jansen EP, van Grieken NC
and van de Velde CJ: Gastric cancer. Lancet. 374:477–490. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yamaoka Y, Kato M and Asaka M: Geographic
differences in gastric cancer incidence can be explained by
differences between Helicobacter pylori strains. Intern Med.
47:1077–1083. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tsugane S and Sasazuki S: Diet and the
risk of gastric cancer: Review of epidemiological evidence. Gastric
Cancer. 10:75–83. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bae JM, Lee EJ and Guyatt G: Citrus fruit
intake and stomach cancer risk: A quantitative systematic review.
Gastric Cancer. 11:23–32. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
He L and Hannon GJ: MicroRNAs: Small RNAs
with a big role in gene regulation. Nat Rev Genet. 5:522–531. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 131:11–29. 2007.
|
|
8
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Koturbash I, Zemp FJ, Pogribny I and
Kovalchuk O: Small molecules with big effects: The role of the
microRNAome in cancer and carcinogenesis. Mutat Res. 722:94–105.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Peláez N and Carthew RW: Biological
robustness and the role of microRNAs: A network perspective. Curr
Top Dev Biol. 99:237–255. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang H, Yang H, Zhang C, Jing Y, Wang C,
Liu C, Zhang R, Wang J, Zhang J, Zen K, et al: Investigation of
microRNA expression in human serum during the aging process. J
Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 70:102–109. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Calin GA, Sevignani C, Dumitru CD, Hyslop
T, Noch E, Yendamuri S, Shimizu M, Rattan S, Bullrich F, Negrini M,
et al: Human microRNA genes are frequently located at fragile sites
and genomic regions involved in cancers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
101:2999–3004. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liu R, Chen X, Du Y, Yao W, Shen L, Wang
C, Hu Z, Zhuang R, Ning G, Zhang C, et al: Serum microRNA
expression profile as a biomarker in the diagnosis and prognosis of
pancreatic cancer. Clin Chem. 58:610–618. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Liu R, Zhang C, Hu Z, Li G, Wang C, Yang
C, Huang D, Chen X, Zhang H, Zhuang R, et al: A five-microRNA
signature identified from genome-wide serum microRNA expression
profiling serves as a fingerprint for gastric cancer diagnosis. Eur
J Cancer. 47:784–791. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
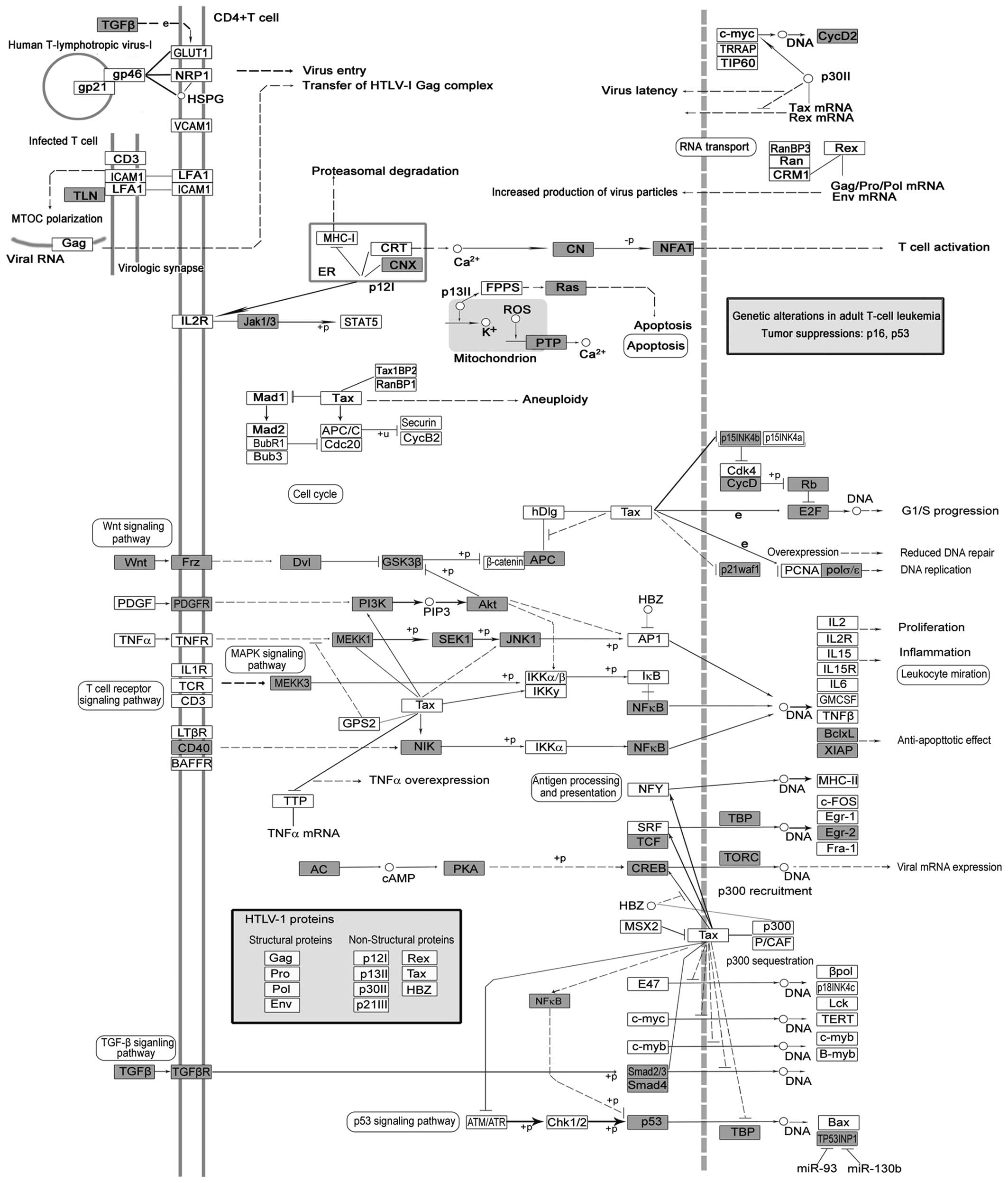
Wang C, Hu J, Lu M, Gu H, Zhou X, Chen X,
Zen K, Zhang CY, Zhang T, Ge J, et al: A panel of five serum miRNAs
as a potential diagnostic tool for early-stage renal cell
carcinoma. Sci Rep. 5:76102015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
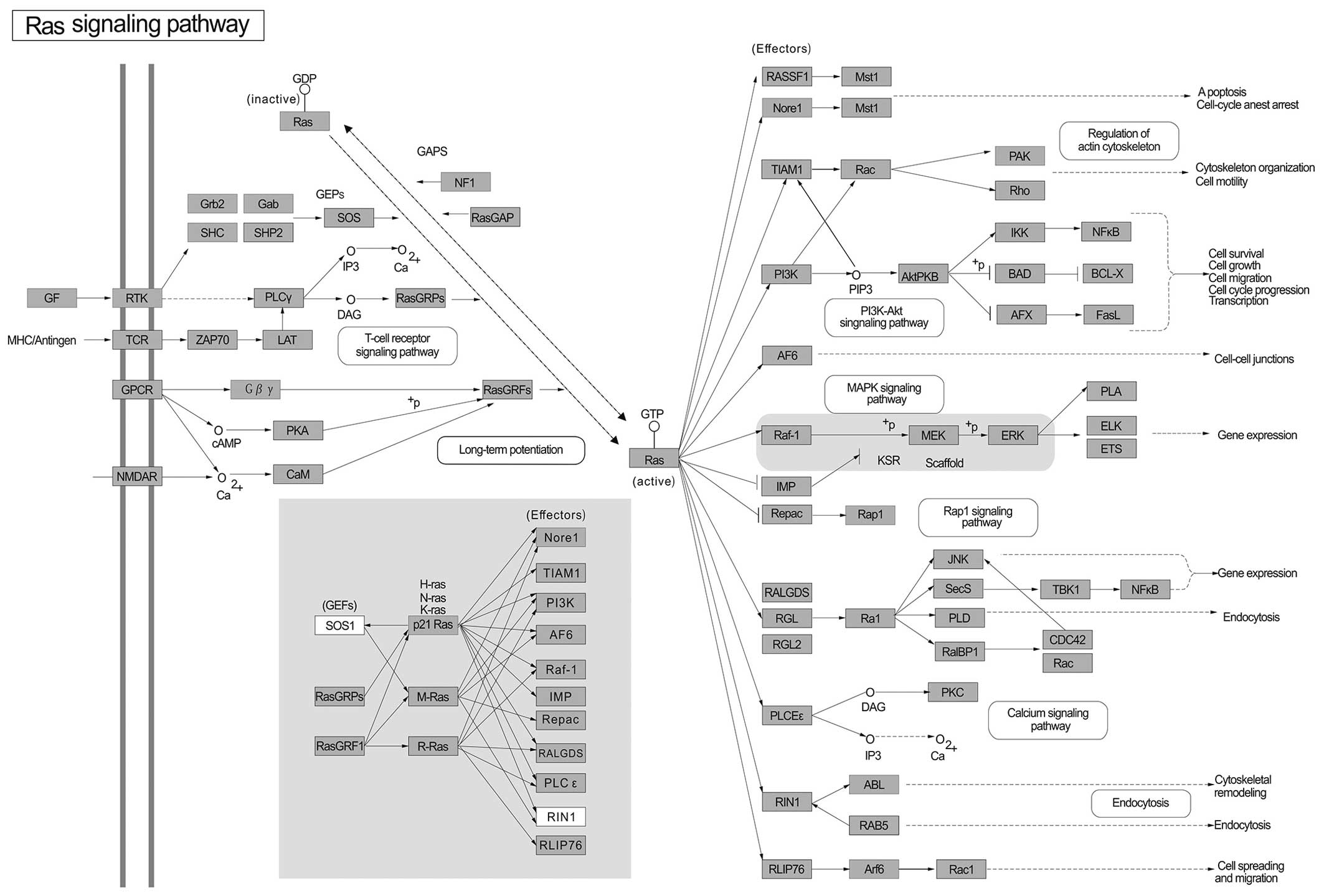
|
16
|
Luo Y, Wang C, Chen X, Zhong T, Cai X,
Chen S, Shi Y, Hu J, Guan X, Xia Z, et al: Increased serum and
urinary microRNAs in children with idiopathic nephrotic syndrome.
Clin Chem. 59:658–666. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Esquela-Kerscher A and Slack FJ: oncomirs
- microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:259–269. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Loscalzo J, Kohane I and Barabasi AL:
Human disease classification in the postgenomic era: A complex
systems approach to human pathobiology. Mol Syst Biol. 3:1242007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Taneja SS, Goddy G, Kibel AS, Penson DF
and Wei JT: Prostate cancer detection using a novel computerized
three-dimensional prostate biopsy template (Targetscan (Tm)):
Results of a multi-center prospective data registry. J Urol.
181:712. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Mi H and Thomas P: PANTHER pathway: An
ontology-based pathway database coupled with data analysis tools.
Methods Mol Biol. 563:123–140. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Mi H, Guo N, Kejariwal A and Thomas PD:
PANTHER version 6: Protein sequence and function evolution data
with expanded representation of biological pathways. Nucleic Acids
Res. 35:D247–D252. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Huang DW, Sherman BT, Tan Q, Collins JR,
Alvord WG, Roayaei J, Stephens R, Baseler MW, Lane HC and Lempicki
RA: The DAVID Gene Functional Classification Tool: A novel
biological module-centric algorithm to functionally analyze large
gene lists. Genome Biol. 8:R1832007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kanehisa M, Araki M, Goto S, Hattori M,
Hirakawa M, Itoh M, Katayama T, Kawashima S, okuda S, Tokimatsu T,
et al: KEGG for linking genomes to life and the environment.
Nucleic Acids Res. 36:D480–D484. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
24
|
Han C, Yu Z, Duan Z and Kan Q: Role of
microRNA-1 in human cancer and its therapeutic potentials. Biomed
Res Int. 2014:4283712014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Nohata N, Hanazawa T, enokida H and Seki
N: microRNA-1/133a and microRNA-206/133b clusters: Dysregulation
and functional roles in human cancers. Oncotarget. 3:9–21. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Liu YN, Yin JJ, Abou-Kheir W, Hynes PG,
Casey OM, Fang L, Yi M, Stephens RM, Seng V, Sheppard-Tillman H, et
al: miR-1 and miR-200 inhibit EMT via Slug-dependent and
tumorigenesis via Slug-independent mechanisms. Oncogene.
32:296–306. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Reid JF, Sokolova V, Zoni E, Lampis A,
Pizzamiglio S, Bertan C, Zanutto S, Perrone F, Camerini T, Gallino
G, et al: miRNA profiling in colorectal cancer highlights miR-1
involvement in MET-dependent proliferation. Mol Cancer Res.
10:504–515. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yan D, Dong XE, Chen X, Wang L, Lu C, Wang
J, Qu J and Tu L: MicroRNA-1/206 targets c-Met and inhibits
rhabdomyosarcoma development. J Biol Chem. 284:29596–29604. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Nasser MW, Datta J, Nuovo G, Kutay H,
Motiwala T, Majumder S, Wang B, Suster S, Jacob ST and Ghoshal K:
Down-regulation of micro-RNA-1 (miR-1) in lung cancer. Suppression
of tumorigenic property of lung cancer cells and their
sensitization to doxorubicin-induced apoptosis by miR-1. J Biol
Chem. 283:33394–33405. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wang F, Song G, Liu M, Li X and Tang H:
miRNA-1 targets fibronectin1 and suppresses the migration and
invasion of the Hep2 laryngeal squamous carcinoma cell line. FEBS
Lett. 585:3263–3269. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Leone V, D'Angelo D, Rubio I, de Freitas
PM, Federico A, Colamaio M, Pallante P, Medeiros-Neto G and Fusco
A: miR-1 is a tumor suppressor in thyroid carcinogenesis targeting
CCND2, CXCR4, and SDF-1alpha. J Clin endocrinol Metab.
96:E1388–E1398. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Li D, Liu Y, Li H, Peng JJ, Tan Y, Zou Q,
Song XF, Du M, Yang ZH, Tan Y, et al: MicroRNA-1 promotes apoptosis
of hepatocarcinoma cells by targeting apoptosis inhibitor-5
(API-5). FEBS Lett. 589:68–76. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Li D, Yang P, Li H, Cheng P, Zhang L, Wei
D, Su X, Peng J, Gao H, Tan Y, et al: MicroRNA-1 inhibits
proliferation of hepatocarcinoma cells by targeting endothelin-1.
Life Sci. 91:440–447. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Tominaga E, Yuasa K, Shimazaki S and
Hijikata T: MicroRNA-1 targets Slug and endows lung cancer A549
cells with epithelial and anti-tumorigenic properties. Exp Cell
Res. 319:77–88. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Jung YJ, Kim JW, Park SJ, Min By, Jang ES,
Kim NY, Jeong SH, Shin CM, Lee SH, Park YS, et al: c-Myc-mediated
overexpression of miR-17-92 suppresses replication of hepatitis B
virus in human hepatoma cells. J Med Virol. 85:969–978. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Chang CC, Yang YJ, Li YJ, Chen ST, Lin BR,
Wu TS, Lin SK, Kuo My and Tan CT: MicroRNA-17/20a functions to
inhibit cell migration and can be used a prognostic marker in oral
squamous cell carcinoma. Oral oncol. 49:923–931. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Fan MQ, Huang CB, Gu Y, Xiao Y, Sheng JX
and Zhong L: Decrease expression of microRNA-20a promotes cancer
cell proliferation and predicts poor survival of hepatocellular
carcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 32:212013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
No authors listed. miR-20a facilitates
metastasis of osteosarcoma cells to lung tissue. Bonekey Rep.
1:762012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Yoshino H, Seki N, Itesako T, Chiyomaru T,
Nakagawa M and Enokida H: Aberrant expression of microRNAs in
bladder cancer. Nat Rev Urol. 10:396–404. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Li X, Zhang Z, Yu M, Li L, Du G, Xiao W
and Yang H: Involvement of miR-20a in promoting gastric cancer
progression by targeting early growth response 2 (eGR2). Int J Mol
Sci. 14:16226–16239. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Li X, Pan JH, Song B, Xiong EQ, Chen ZW,
Zhou ZS and Su YP: Suppression of CX43 expression by miR-20a in the
progression of human prostate cancer. Cancer Biol Ther. 13:890–898.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zhao S, Yao DS, Chen JY and Ding N:
Aberrant expression of miR-20a and miR-203 in cervical cancer.
Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 14:2289–2293. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zhao S, Yao D, Chen J, Ding N and Ren F:
miR-20a promotes cervical cancer proliferation and metastasis in
vitro and in vivo. PLoS One. 10:e01209052015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zhou J, Liu R, Luo C, Zhou X, Xia K, Chen
X, Zhou M, Zou Q, Cao P and Cao K: miR-20a inhibits cutaneous
squamous cell carcinoma metastasis and proliferation by directly
targeting LIMK1. Cancer Biol Ther. 15:1340–1349. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Xie J, Liu M, Li Y, Nie Y, Mi Q and Zhao
S: ovarian tumor-associated microRNA-20a decreases natural killer
cell cytotoxicity by downregulating MICA/B expression. Cell Mol
Immunol. 11:495–502. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Yan H, Wu J, Liu W, Zuo Y, Chen S, Zhang
S, Zeng M and Huang W: MicroRNA-20a overexpression inhibited
proliferation and metastasis of pancreatic carcinoma cells. Hum
Gene Ther. 21:1723–1734. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Guttilla IK and White BA: Coordinate
regulation of FOXO1 by miR-27a, miR-96, and miR-182 in breast
cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 284:23204–23216. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Li S, Li J, Fei BY, Shao D, Pan Y, Mo ZH,
Sun BZ, Zhang D, Zheng X, Zhang M, et al: miR-27a promotes
hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation through suppression of
its target gene peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ. Chin
Med J (Engl). 128:941–947. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Acunzo M, Romano G, Palmieri D, Laganá A,
Garofalo M, Balatti V, Drusco A, Chiariello M, Nana-Sinkam P and
Croce CM: Cross-talk between MET and EGFR in non-small cell lung
cancer involves miR-27a and Sprouty2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
110:8573–8578. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Salah Z, Arafeh R, Maximov V, Galasso M,
Khawaled S, Abou-Sharieha S, Volinia S, Jones KB, Croce CM and
Aqeilan RI: miR-27a and miR-27a* contribute to metastatic
properties of osteosarcoma cells. Oncotarget. 6:4920–4935. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Peng H, Wang X, Zhang P, Sun T, Ren X and
Xia Z: miR-27a promotes cell proliferation and metastasis in renal
cell carcinoma. Int J Clin exp Pathol. 8:2259–2266. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Chen Z, Ma T, Huang C, Zhang L, Lv X, Xu
T, Hu T and Li J: miR-27a modulates the MDR1/P-glycoprotein
expression by inhibiting FZD7/β-catenin pathway in hepatocellular
carcinoma cells. Cell Signal. 25:2693–2701. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Deng Y, Bai H and Hu H: rs11671784 G/A
variation in miR-27a decreases chemo-sensitivity of bladder cancer
by decreasing miR-27a and increasing the target RUNX-1 expression.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 458:321–327. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Li Z, Hu S, Wang J, Cai J, Xiao L, Yu L
and Wang Z: miR-27a modulates MDR1/P-glycoprotein expression by
targeting HIPK2 in human ovarian cancer cells. Gynecol oncol.
119:125–130. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Tanaka K, Miyata H, Sugimura K, Fukuda S,
Kanemura T, Yamashita K, Miyazaki Y, Takahashi T, Kurokawa Y,
Yamasaki M, et al: miR-27 is associated with chemoresistance in
esophageal cancer through transformation of normal fibroblasts to
cancer-associated fibroblasts. Carcinogenesis. 36:894–903. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Zhang H, Li M, Han Y, Hong L, Gong T, Sun
L and Zheng X: Down-regulation of miR-27a might reverse multidrug
resistance of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Dig Dis Sci.
55:2545–2551. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Zhao X, Yang L and Hu J: Down-regulation
of miR-27a might inhibit proliferation and drug resistance of
gastric cancer cells. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 30:552011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Zhu H, Wu H, Liu X, evans BR, Medina DJ,
Liu CG and Yang JM: Role of microRNA miR-27a and miR-451 in the
regulation of MDR1/P-glycoprotein expression in human cancer cells.
Biochem Pharmacol. 76:582–588. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Ren YQ, Fu F and Han J: miR-27a modulates
radiosensitivity of triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) cells by
targeting CDC27. Med Sci Monit. 21:1297–1303. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Kariya A, Furusawa Y, Yunoki T, Kondo T
and Tabuchi Y: A microRNA-27a mimic sensitizes human oral squamous
cell carcinoma HSC-4 cells to hyperthermia through downregulation
of Hsp110 and Hsp90. Int J Mol Med. 34:334–340. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Coutinho-Camillo CM, Lourenço SV, de
Araújo Lima L, Kowalski LP and Soares FA: expression of
apoptosis-regulating miRNAs and target mRNAs in oral squamous cell
carcinoma. Cancer Genet. 208:382–389. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Hong JH, Roh KS, Suh SS, Lee S, Sung SW,
Park JK, Byun JH and Kang JH: The expression of microRNA-34a is
inversely correlated with c- MET and CDK6 and has a prognostic
significance in lung adenocarcinoma patients. Tumour Biol. Jun
25–2015, (Epub ahead of print) http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-3428-9.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Isosaka M, Niinuma T, Nojima M, Kai M,
Yamamoto E, Maruyama R, Nobuoka T, Nishida T, Kanda T, Taguchi T,
et al: A screen for epigenetically silenced microRNA genes in
gastrointestinal stromal tumors. PLoS One. 10:e01337542015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Lin L, Jiang H, Huang M, Hou X, Sun X,
Jiang X, Dong X, Sun X, Zhou B and Qiao H: Depletion of histone
deacetylase 1 inhibits metastatic abilities of gastric cancer cells
by regulating the miR-34a/CD44 pathway. Oncol Rep. 34:663–672.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Liu C, Kelnar K, Liu B, Chen X,
Calhoun-Davis T, Li H, Patrawala L, Yan H, Jeter C, Honorio S, et
al: The microRNA miR-34a inhibits prostate cancer stem cells and
metastasis by directly repressing CD44. Nat Med. 17:211–215. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Lu G, Sun Y, An S, Xin S, Ren X, Zhang D,
Wu P, Liao W, Ding Y and Liang L: MicroRNA-34a targets FMNL2 and
E2F5 and suppresses the progression of colorectal cancer. Exp Mol
Pathol. 99:173–179. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Wei B, Huang QE, Huang SR, Mai W and Zhong
XG: MicroRNA 34a attenuates the proliferation, invasion and
metastasis of gastric cancer cells via downregulation of MET. Mol
Med Rep. 12:5255–5261. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Yu L, Xiong J, Guo L, Miao L, Liu S and
Guo F: The effects of lanthanum chloride on proliferation and
apoptosis of cervical cancer cells: Involvement of let-7a and
miR-34a microRNAs. Biometals. 28:879–890. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Hermeking H: The miR-34 family in cancer
and apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 17:193–199. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Kasinski AL and Slack FJ: miRNA-34
prevents cancer initiation and progression in a therapeutically
resistant K-ras and p53-induced mouse model of lung adenocarcinoma.
Cancer Res. 72:5576–5587. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
He L, He X, Lowe SW and Hannon GJ:
microRNAs join the p53 network - another piece in the
tumour-suppression puzzle. Nat Rev Cancer. 7:819–822. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Qiao P, Li G, Bi W, Yang L, Yao L and Wu
D: microRNA-34a inhibits epithelial mesenchymal transition in human
cholangiocarcinoma by targeting Smad4 through transforming growth
factor-beta/Smad pathway. BMC Cancer. 15:4692015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Alemar B, Izetti P, Gregório C, Macedo GS,
Castro MA, Osvaldt AB, Matte U and Ashton-Prolla P: miRNA-21 and
miRNA-34a are potential minimally invasive biomarkers for the
diagnosis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Pancreas. Aug
10–2015.Epub ahead of print. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Shi Y and Huang A: effects of sorafenib on
lung metastasis in rats with hepatocellular carcinoma: The role of
microRNAs. Tumour Biol. May 31–2015.(Epub ahead of print)
http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-3565-1.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Lin J, Huang S, Wu S, Ding J, Zhao Y,
Liang L, Tian Q, Zha R, Zhan R and He X: MicroRNA-423 promotes cell
growth and regulates G(1)/S transition by targeting p21Cip1/Waf1 in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Carcinogenesis. 32:1641–1647. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Stiuso P, Potenza N, Lombardi A,
Ferrandino I, Monaco A, Zappavigna S, Vanacore D, Mosca N,
Castiello F, Porto S, et al: MicroRNA-423-5p promotes autophagy in
cancer cells and is increased in serum from hepatocarcinoma
patients treated with sorafenib. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids.
4:e2332015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Liu J, Wang X, Yang X, Liu Y, Shi Y, Ren J
and Guleng B: miRNA423-5p regulates cell proliferation and invasion
by targeting trefoil factor 1 in gastric cancer cells. Cancer Lett.
347:98–104. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Lu X and Lu J: The significance of
detection of serum miR-423-5p and miR-484 for diagnosis of
colorectal cancer. Clin Lab. 61:187–190. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Ali S, Saleh H, Sethi S, Sarkar FH and
Philip PA: MicroRNA profiling of diagnostic needle aspirates from
patients with pancreatic cancer. Br J Cancer. 107:1354–1360. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Zhao H, Gao A, Zhang Z, Tian R, Luo A, Li
M, Zhao D, Fu L, Fu L, Dong JT, et al: Genetic analysis and
preliminary function study of miR-423 in breast cancer. Tumour
Biol. 36:4763–4771. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Yan W, Liu Y, Yang P, Wang Z, You Y and
Jiang T: MicroRNA profiling of Chinese primary glioblastoma reveals
a temozolomide-chemoresistant subtype. Oncotarget. 6:11676–11682.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Wang D, Qiu C, Zhang H, Wang J, Cui Q and
Yin Y: Human microRNA oncogenes and tumor suppressors show
significantly different biological patterns: From functions to
targets. PLoS One. 5:e130672010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Lv H, Pei J, Liu H, Wang H and Liu J: A
polymorphism site in the pre-miR-34a coding region reduces miR-34a
expression and promotes osteosarcoma cell proliferation and
migration. Mol Med Rep. 10:2912–2916. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Kisseljov FL: MicroRNAs and cancer. Mol
Biol. 48:197–206. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Tutar L, Tutar E and Tutar Y: MicroRNAs
and cancer; an overview. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 15:430–437. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Li Y, Che Q, Bian Y, Zhou Q, Jiang F, Tong
H, Ke J, Wang K and Wan XP: Autocrine motility factor promotes
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in endometrial cancer via MAPK
signaling pathway. Int J oncol. 47:1017–1024. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Zhao L, Wang Y, Yan Q, Lv W, Zhang Y and
He S: Exogenous hydrogen sulfide exhibits anti-cancer effects
though p38 MAPK signaling pathway in C6 glioma cells. Biol Chem.
396:1247–1253. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Yan H, Xin S, Wang H, Ma J, Zhang H and
Wei H: Baicalein inhibits MMP-2 expression in human ovarian cancer
cells by suppressing the p38 MAPK-dependent NF-κB signaling
pathway. Anticancer Drugs. 26:649–656. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Nakareangrit W, Thiantanawat A,
Visitnonthachai D, Watcharasit P and Satayavivad J: Sodium arsenite
inhibited genomic estrogen signaling but induced pERα (Ser118) via
MAPK pathway in breast cancer cells. Environ Toxicol. Mar
2–2015.Epub ahead of print. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
Chang L, Graham PH, Ni J, Hao J, Bucci J,
Cozzi PJ and Li Y: Targeting PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway in the
treatment of prostate cancer radioresistance. Crit Rev Oncol
Hematol. Jul 18–2015.Epub ahead of print. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Xia P and Xu Xy: PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling
pathway in cancer stem cells: From basic research to clinical
application. Am J Cancer Res. 5:1602–1609. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Wang L, Wu J, Lu J, Ma R, Sun D and Tang
J: Regulation of the cell cycle and PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway
by tanshinone I in human breast cancer cell lines. Mol Med Rep.
11:931–939. 2015.
|
|
93
|
Zuidervaart W, van Nieuwpoort F, Stark M,
Dijkman R, Packer L, Borgstein AM, Pavey S, van der Velden P, Out
C, Jager MJ, et al: Activation of the MAPK pathway is a common
event in uveal melanomas although it rarely occurs through mutation
of BRAF or RAS. Br J Cancer. 92:2032–2038. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Wagner EF and Nebreda AR: Signal
integration by JNK and p38 MAPK pathways in cancer development. Nat
Rev Cancer. 9:537–549. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
O'Connell RM, Taganov KD, Boldin MP, Cheng
G and Baltimore D: MicroRNA-155 is induced during the macrophage
inflammatory response. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:1604–1609. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Mateescu B, Batista L, Cardon M, Gruosso
T, de Feraudy Y, Mariani O, Nicolas A, Meyniel JP, Cottu P,
Sastre-Garau X, et al: miR-141 and miR-200a act on ovarian
tumorigenesis by controlling oxidative stress response. Nat Med.
17:1627–1635. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Shao N, Lu Z, Zhang Y, Wang M, Li W, Hu Z,
Wang S and Lin Y: Interleukin-8 upregulates integrin β3 expression
and promotes estrogen receptor-negative breast cancer cell invasion
by activating the PI3K/Akt/NF-κB pathway. Cancer Lett. 364:165–172.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Yue S, Li J, Lee SY, Lee HJ, Shao T, Song
B, Cheng L, Masterson TA, Liu X, Ratliff TL, et al: Cholesteryl
ester accumulation induced by PTEN loss and PI3K/AKT activation
underlies human prostate cancer aggressiveness. Cell Metab.
19:393–406. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Graham RM, Middleton A, Benito DA, Uddin
R, Zhang B, Walters W, Bregy A, Vanni S and Komotar RJ: Targeting
cancer stem cells via inhibition of PI3K/AKT pathway alone and in
combination with autophagy blockade. Mol Cancer Ther. 14:B392015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
100
|
Prasad SB, Yadav SS, Das M, Modi A, Kumari
S, Pandey LK, Singh S, Pradhan S and Narayan G: PI3K/AKT
pathway-mediated regulation of p27(Kip1) is associated with cell
cycle arrest and apoptosis in cervical cancer. Cell oncol (Dordr).
38:215–225. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
101
|
Mabuchi S, Kuroda H, Takahashi R and
Sasano T: The PI3K/AKT/MTOR pathway as a therapeutic target in
ovarian cancer. Gynecol oncol. 137:173–179. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Jin D, Yang JP, Hu JH, Wang LN and Zuo JL:
MCP-1 stimulates spinal microglia via PI3K/Akt pathway in bone
cancer pain. Brain Res. 1599:158–167. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Fang F and Wang L, Zhang S, Fang Q, Hao F,
Sun Y, Zhao L, Chen S, Liao H and Wang L: CD147 modulates autophagy
through the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in human prostate cancer PC-3
cells. Oncol Lett. 9:1439–1443. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Cárdenas A, Kong M, Alvarez A, Valdivia A,
Quest AF and Leyton L: PAR-3 and Syndecan-4 are involved in
astrocyte adhesion induced by neuronal Thy-1 ocyte adhesion. Glia.
63:E102. 2015.
|
|
105
|
Xie M, He J, He C and Wei S: γ secretase
inhibitor BMS-708163 reverses resistance to eGFR inhibitor via the
PI3K/Akt pathway in lung cancer. J Cell Biochem. 116:1019–1027.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Xue B, Huang W, Yuan X, Xu B, Lou Y, Zhou
Q, Ran F, Ge Z, Li R and Cui J: YSY01A, a novel proteasome
inhibitor, induces cell cycle arrest on G2 phase in MCF-7 cells via
eRα and PI3K/Akt pathways. J Cancer. 6:319–326. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
107
|
Niu NK, Wang ZL, Pan ST, Ding HQ, Au GH,
He ZX, Zhou ZW, Xiao G, Yang YX, Zhang X, et al: Pro-apoptotic and
pro-autophagic effects of the Aurora kinase A inhibitor alisertib
(MLN8237) on human osteosarcoma U-2 OS and MG-63 cells through the
activation of mitochondria-mediated pathway and inhibition of p38
MAPK/PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. Drug Des Devel Ther.
9:1555–1584. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Gatza ML, Watt JC and Marriott SJ:
Cellular transformation by the HTLV-I Tax protein, a
jack-of-all-trades. Oncogene. 22:5141–5149. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Bai XT and Nicot C: miR-28-3p is a
cellular restriction factor that inhibits human T cell leukemia
virus, type 1 (HTLV-1) replication and virus infection. J Biol
Chem. 290:5381–5390. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Drosten M, Sum EY, Lechuga CG,
Simón-Carrasco L, Jacob HK, García-Medina R, Huang S, Beijersbergen
RL, Bernards R and Barbacid M: Loss of p53 induces cell
proliferation via Ras-independent activation of the Raf/Mek/erk
signaling pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 111:15155–15160. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Manousaridis I, Mavridou S, Goerdt S,
Leverkus M and Utikal J: Cutaneous side effects of inhibitors of
the RAS/RAF/MeK/eRK signalling pathway and their management. J Eur
Acad Dermatol Venereol. 27:11–18. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
112
|
Noser JA, Sakuma R, Lee PWK and Ikeda Y:
The Ras/Raf-1/MeK/eRK signaling pathway dictates host cell
permissiveness to VSV infection. Mol Ther. 13:S371. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
113
|
Dancey JE: Agents targeting ras signaling
pathway. Curr Pharm Des. 8:2259–2267. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|