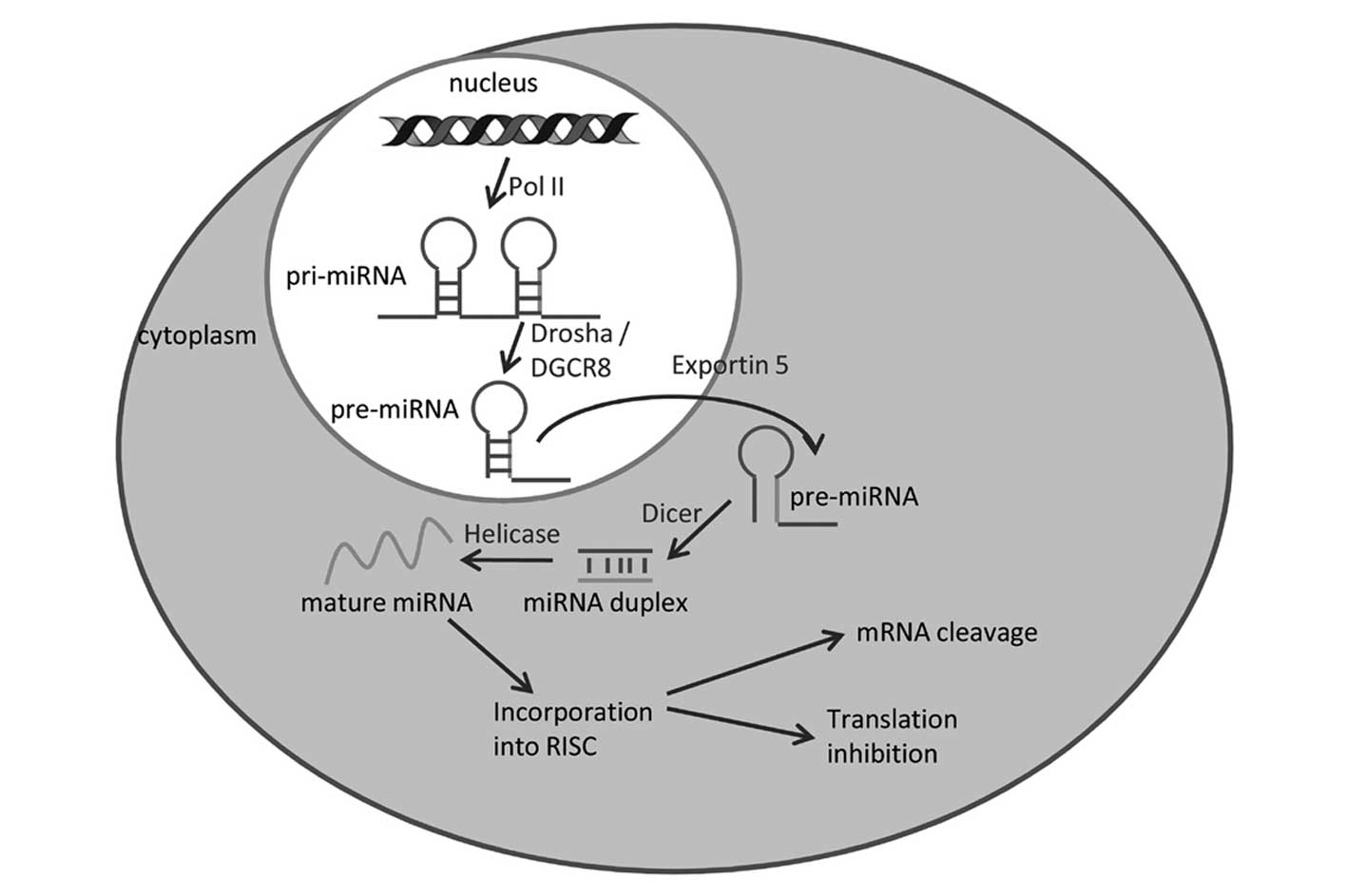
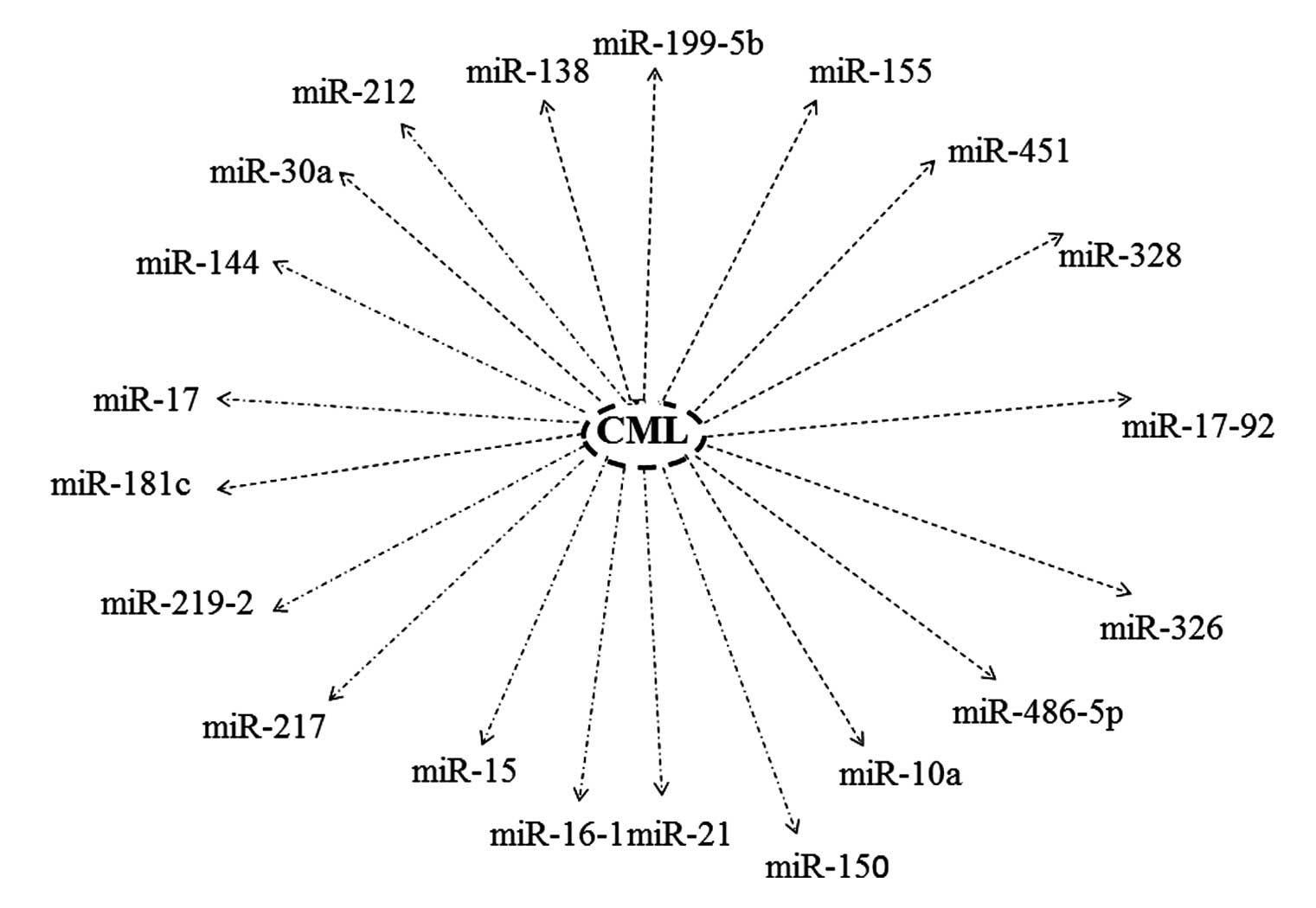
|
1
|
Faderl S, Talpaz M, Estrov Z, O'Brien S,
Kurzrock R and Kantarjian HM: The biology of chronic myeloid
leukemia. N Engl J Med. 341:164–172. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kantarjian HM, Dixon D, Keating MJ, Talpaz
M, Walters RS, McCredie KB and Freireich EJ: Characteristics of
accelerated disease in chronic myelogenous leukemia. Cancer.
61:1441–1446. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kantarjian HM, Deisseroth A, Kurzrock R,
Estrov Z and Talpaz M: Chronic myelogenous leukemia: A concise
update. Blood. 82:691–703. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Rudkin CT, Hungerford DA and Nowell PC:
DNA contents of chromosome Ph1 and chromosome 21 in
human chronic granulocytic leukemia. Science. 144:1229–1231. 1964.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Druker BJ: Translation of the Philadelphia
chromosome into therapy for CML. Blood. 112:4808–4817. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Holyoake DT: Recent advances in the
molecular and cellular biology of chronic myeloid leukaemia:
Lessons to be learned from the laboratory. Br J Haematol.
113:11–23. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Asimakopoulos FA, Shteper PJ, Krichevsky
S, Fibach E, Polliack A, Rachmilewitz E, Ben-Neriah Y and
Ben-Yehuda D: ABL1 methylation is a distinct molecular event
associated with clonal evolution of chronic myeloid leukemia.
Blood. 94:2452–2460. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mancini M, Veljkovic N, Leo E, Aluigi M,
Borsi E, Galloni C, Iacobucci I, Barbieri E and Santucci MA:
Cytoplasmatic compartmentalization by Bcr-Abl promotes TET2
loss-of-function in chronic myeloid leukemia. J Cell Biochem.
113:2765–2774. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Huang Q, Yang Y, Li X and Huang S:
Transcription suppression of SARI (suppressor of AP-1, regulated by
IFN) by BCR-ABL in human leukemia cells. Tumour Biol. 32:1191–1197.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bixby D and Talpaz M: Mechanisms of
resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibitors in chronic myeloid
leukemia and recent therapeutic strategies to overcome resistance.
HHematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 1:461–476. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Mughal A, Aslam HM, Khan AM, Saleem S,
Umah R and Saleem M: Bcr-Abl tyrosine kinase inhibitors - current
status. Infect Agent Cancer. 8(23)2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Asaki T, Sugiyama Y, Hamamoto T,
Higashioka M, Umehara M, Naito H and Niwa T: Design and synthesis
of 3-substituted benzamide derivatives as Bcr-Abl kinase
inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 16:1421–1425. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Eck MJ and Manley PW: The interplay of
structural information and functional studies in kinase drug
design: Insights from BCR-Abl. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 21:288–295.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
An X, Tiwari AK, Sun Y, Ding P-R, Ashby CR
Jr and Chen ZS: BCR-ABL tyrosine kinase inhibitors in the treatment
of Philadelphia chromosome positive chronic myeloid leukemia: A
review. Leuk Res. 34:1255–1268. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Stein B and Smith BD: Treatment options
for patients with chronic myeloid leukemia who are resistant to or
unable to tolerate imatinib. Clin Ther. 32:804–820. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Thomas J, Wang L, Clark RE and Pirmohamed
M: Active transport of imatinib into and out of cells: Implications
for drug resistance. Blood. 104:3739–3745. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Jabbour E, Cortes J and Kantarjian H:
Nilotinib for the treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia: An
evidence-based review. Core Evid. 4:207–213. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Manley PW, Cowan-Jacob SW and Mestan J:
Advances in the structural biology, design and clinical development
of Bcr-Abl kinase inhibitors for the treatment of chronic myeloid
leukaemia. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1754:3–13. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Olivieri A and Manzione L: Dasatinib: A
new step in molecular target therapy. Ann Oncol. 18(Suppl 6):
vi42–vi46. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
O'Hare T, Shakespeare WC, Zhu X, Eide CA,
Rivera VM, Wang F, Adrian LT, Zhou T, Huang WS, Xu Q, et al:
AP24534, a pan-BCR-ABL inhibitor for chronic myeloid leukemia,
potently inhibits the T315I mutant and overcomes mutation-based
resistance. Cancer Cell. 16:401–412. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
FDA Drug Safety Communication: FDA asks
manufacturer of the leukemia drug Iclusig (ponatinib) to suspend
marketing and sales. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. 2013,
http://www.fda.gov/Drugs/DrugSafety/ucm373040.htm.
Accessed Nov 26, 2013.
|
|
22
|
Lipshultz SE, Diamond MB, Franco VI,
Aggarwal S, Leger K, Santos MV, Sallan SE and Chow EJ: Managing
chemotherapy-related cardiotoxicity in survivors of childhood
cancers. Paediatr Drugs. 16:373–389. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kimura S, Naito H, Segawa H, Kuroda J,
Yuasa T, Sato K, Yokota A, Kamitsuji Y, Kawata E, Ashihara E, et
al: NS-187, a potent and selective dual Bcr-Abl/Lyn tyrosine kinase
inhibitor, is a novel agent for imatinib-resistant leukemia. Blood.
106:3948–3954. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Horio T, Hamasaki T, Inoue T, Wakayama T,
Itou S, Naito H, Asaki T, Hayase H and Niwa T: Structural factors
contributing to the Abl/Lyn dual inhibitory activity of
3-substituted benzamide derivatives. Bioorg Med Chem Lett.
17:2712–2717. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Valent P: Standard treatment of
Ph+ CML in 2010: How, when and where not to use what
BCR/ABL1 kinase inhibitor? Eur J Clin Invest. 40:918–931. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Peláez N and Carthew RW: Biological
robustness and the role of microRNAs: A network perspective. Curr
Top Dev Biol. 99:237–255. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Nam JW, Rissland OS, Koppstein D,
Abreu-Goodger C, Jan CH, Agarwal V, Yildirim MA, Rodriguez A and
Bartel DP: Global analyses of the effect of different cellular
contexts on microRNA targeting. Mol Cell. 53:1031–1043. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Di Leva G, Garofalo M and Croce CM:
MicroRNAs in cancer. Annu Rev Pathol. 9:287–314. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
29
|
Lee R, Feinbaum R and Ambros V: The
heterochronic gene lin-4 of C. elegans encodes small RNAs with
antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell. 75:843–854. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kozomara A and Griffiths-Jones S: miRBase:
Integrating microRNA annotation and deep-sequencing data. Nucleic
Acids Res. 39:D152–D157. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
31
|
Tsai LM and Yu D: MicroRNAs in common
diseases and potential therapeutic applications. Clin Exp Pharmacol
Physiol. 37:102–107. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Esquela-Kerscher A and Slack FJ: Oncomirs
- microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:259–269. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Masaki S, Ohtsuka R, Abe Y, Muta K and
Umemura T: Expression patterns of microRNAs 155 and 451 during
normal human erythropoiesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
364:509–514. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wang Y and Blelloch R: Cell cycle
regulation by microRNAs in embryonic stem cells. Cancer Res.
69:4093–4096. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Subramanian S and Steer CJ: MicroRNAs as
gatekeepers of apoptosis. J Cell Physiol. 223:289–298.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Schwarz DS, Hutvágner G, Du T, Xu Z,
Aronin N and Zamore PD: Asymmetry in the assembly of the RNAi
enzyme complex. Cell. 115:199–208. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Berezikov E, Chung WJ, Willis J, Cuppen E
and Lai EC: Mammalian mirtron genes. Mol Cell. 28:328–336. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Hinske LC, Galante PA, Kuo WP and
Ohno-Machado L: A potential role for intragenic miRNAs on their
hosts' interactome. BMC Genomics. 11:533–541. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Bagga S, Bracht J, Hunter S, Massirer K,
Holtz J, Eachus R and Pasquinelli AE: Regulation by let-7 and lin-4
miRNAs results in target mRNA degradation. Cell. 122:553–563. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ørom UA, Nielsen FC and Lund AH:
MicroRNA-10a binds the 5′UTR of ribosomal protein mRNAs and
enhances their translation. Mol Cell. 30:460–471. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Vasudevan S, Tong Y and Steitz JA:
Switching from repression to activation: microRNAs can up-regulate
translation. Science. 318:1931–1934. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Pillai RS, Bhattacharyya SN, Artus CG,
Zoller T, Cougot N, Basyuk E, Bertrand E and Filipowicz W:
Inhibition of translational initiation by let-7 MicroRNA in human
cells. Science. 309:1573–1576. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Hendrickson DG, Hogan DJ, McCullough HL,
Myers JW, Herschlag D, Ferrell JE and Brown PO: Concordant
regulation of translation and mRNA abundance for hundreds of
targets of a human microRNA. PLoS Biol. 7:e10002382009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Choe J, Cho H, Lee HC and Kim YK:
microRNA/Argonaute 2 regulates nonsense-mediated messenger RNA
decay. EMBO Rep. 11:380–386. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Cuccato G, Polynikis A, Siciliano V,
Graziano M, di Bernardo M and di Bernardo D: Modeling RNA
interference in mammalian cells. BMC Syst Biol. 5:19–24. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Hemida MG, Ye X, Thair S and Yang D:
Exploiting the therapeutic potential of microRNAs in viral
diseases: Expectations and limitations. Mol Diagn Ther. 14:271–282.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Bader AG, Brown D and Winkler M: The
promise of microRNA replacement therapy. Cancer Res. 70:7027–7030.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Chen CZ: MicroRNAs as oncogenes and tumor
suppressors. N Engl J Med. 353:1768–1771. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, Alvarez-Saavedra
E, Lamb J, Peck D, Sweet-Cordero A, Ebert BL, Mak RH, Ferrando AA,
et al: MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature.
435:834–838. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Zhang H, Luo XQ, Zhang P, Huang LB, Zheng
YS, Wu J, Zhou H, Qu LH, Xu L and Chen YQ: MicroRNA patterns
associated with clinical prognostic parameters and CNS relapse
prediction in pediatric acute leukemia. PLoS One. 4:e78262009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Labbaye C and Testa U: The emerging role
of MIR-146A in the control of hematopoiesis, immune function and
cancer. J Hematol Oncol. 5(13)2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Calin GA, Ferracin M, Cimmino A, Di Leva
G, Shimizu M, Wojcik SE, Iorio MV, Visone R, Sever NI, Fabbri M, et
al: A MicroRNA signature associated with prognosis and progression
in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 353:1793–1801. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Garzon R, Volinia S, Liu CG,
Fernandez-Cymering C, Palumbo T, Pichiorri F, Fabbri M, Coombes K,
Alder H, Nakamura T, et al: MicroRNA signatures associated with
cytogenetics and prognosis in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood.
111:3183–3189. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Gimenes-Teixeira HL, Lucena-Araujo AR, Dos
Santos GA, Zanette DL, Scheucher PS, Oliveira LC, Dalmazzo LF,
Silva-Júnior WA, Falcão RP and Rego EM: Increased expression of
miR-221 is associated with shorter overall survival in T-cell acute
lymphoid leukemia. Exp Hematol Oncol. 2(10)2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Jongen-Lavrencic M, Sun SM, Dijkstra MK,
Valk PJ and Löwenberg B: MicroRNA expression profiling in relation
to the genetic heterogeneity of acute myeloid leukemia. Blood.
111:5078–5085. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Fernando TR, Rodriguez-Malave NI and Rao
DS: MicroRNAs in B cell development and malignancy. J Hematol
Oncol. 5(7)2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Calin GA, Dumitru CD, Shimizu M, Bichi R,
Zupo S, Noch E, Aldler H, Rattan S, Keating M, Rai K, et al:
Frequent deletions and down-regulation of micro-RNA genes miR15 and
miR16 at 13q14 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 99:15524–15529. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Cimmino A, Calin GA, Fabbri M, Iorio MV,
Ferracin M, Shimizu M, Wojcik SE, Aqeilan RI, Zupo S, Dono M, et
al: miR-15 and miR-16 induce apoptosis by targeting BCL2. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 102:13944–13949. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Xu L, Xu Y, Jing Z, Wang X, Zha X, Zeng C,
Chen S, Yang L, Luo G, Li B, et al: Altered expression pattern of
miR-29a, miR-29b and the target genes in myeloid leukemia. Exp
Hematol Oncol. 3(17)2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Seca H, Lima RT, Lopes-Rodrigues V,
Guimaraes JE, Almeida GM and Vasconcelos MH: Targeting miR-21
induces autophagy and chemosensitivity of leukemia cells. Curr Drug
Targets. 14:1135–1143. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Calin GA, Sevignani C, Dumitru CD, Hyslop
T, Noch E, Yendamur S, Shimizu M, Rattan S, Bullrich F, Negrini M,
et al: Human microRNA genes are frequently located at fragile sites
and genomic regions involved in cancers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
101:2999–3004. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Agirre X, Jiménez-Velasco A, San
José-Enériz E, Garate L, Bandrés E, Cordeu L, Aparicio O, Saez B,
Navarro G, Vilas-Zornoza A, et al: Down-regulation of hsa-miR-10a
in chronic myeloid leukemia CD34+ cells increases
USF2-mediated cell growth. Mol Cancer Res. 6:1830–1840. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Wang LS, Li L, Li L, Chu S, Shiang KD, Li
M, Sun HY, Xu J, Xiao FJ, Sun G, et al: MicroRNA-486 regulates
normal eryth-ropoiesis and enhances growth and modulates drug
response in CML progenitors. Blood. 125:1302–1313. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
64
|
Babashah S, Sadeghizadeh M, Hajifathali A,
Tavirani MR, Zomorod MS, Ghadiani M and Soleimani M: Targeting of
the signal transducer Smo links microRNA-326 to the oncogenic
Hedgehog pathway in CD34+ CML stem/progenitor cells. Int
J Cancer. 133:579–589. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Venturini L, Battmer K, Castoldi M,
Schultheis B, Hochhaus A, Muckenthaler MU, Ganser A, Eder M and
Scherr M: Expression of the miR-17-92 polycistron in chronic
myeloid leukemia (CML) CD34+ cells. Blood.
109:4399–4405. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Eiring AM, Harb JG, Neviani P, Garton C,
Oaks JJ, Spizzo R, Liu S, Schwind S, Santhanam R, Hickey CJ, et al:
miR-328 functions as an RNA decoy to modulate hnRNP E2 regulation
of mRNA translation in leukemic blasts. Cell. 140:652–665. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Chang JS, Santhanam R, Trotta R, Neviani
P, Eiring AM, Briercheck E, Ronchetti M, Roy DC, Calabretta B,
Caligiuri MA, et al: High levels of the BCR/ABL oncoprotein are
required for the MAPK-hnRNP E2 dependent suppression of
C/EBPalpha-driven myeloid differentiation. Blood. 110:994–1003.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Perrotti D, Cesi V, Trotta R, Guerzoni C,
Santilli G, Campbell K, Iervolino A, Condorelli F,
Gambacorti-Passerini C, Caligiuri MA, et al: BCR-ABL suppresses
C/EBPalpha expression through inhibitory action of hnRNP E2. Nat
Genet. 30:48–58. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Machová Poláková K, Lopotová T, Klamová H,
Burda P, Trněný M, Stopka T and Moravcová J: Expression patterns of
microRNAs associated with CML phases and their disease related
targets. Mol Cancer. 10(41)2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Flamant S, Ritchie W, Guilhot J, Holst J,
Bonnet ML, Chomel JC, Guilhot F, Turhan AG and Rasko JE: Micro-RNA
response to imatinib mesylate in patients with chronic myeloid
leukemia. Haematologica. 95:1325–1333. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Rokah OH, Granot G, Ovcharenko A, Modai S,
Pasmanik-Chor M, Toren A, Shomron N and Shpilberg O: Downregulation
of miR-31, miR-155, and miR-564 in chronic myeloid leukemia cells.
PLoS One. 7:e355012012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Suresh S, McCallum L, Lu W, Lazar N,
Perbal B and Irvine AE: MicroRNAs 130a/b are regulated by BCR-ABL
and down-regulate expression of CCN3 in CML. J Cell Commun Signal.
5:183–191. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Hershkovitz-Rokah O, Modai S,
Pasmanik-Chor M, Toren A, Shomron N, Raanani P, Shpilberg O and
Granot G: Restoration of miR-424 suppresses BCR-ABL activity and
sensitizes CML cells to imatinib treatment. Cancer Lett.
360:245–256. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Fallah P, Amirizadeh N, Poopak B, Toogeh
G, Arefian E, Kohram F, Hosseini Rad SM, Kohram M, Teimori Naghadeh
H and Soleimani M: Expression pattern of key microRNAs in patients
with newly diagnosed chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic phase. Int
J Lab Hematol. 37:560–568. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Bhamidipati PK, Kantarjian H, Cortes J,
Cornelison AM and Jabbour E: Management of imatinib-resistant
patients with chronic myeloid leukemia. Ther Adv Hematol.
4:103–117. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Taganov KD, Boldin MP, Chang KJ and
Baltimore D: NF-kappaB-dependent induction of microRNA miR-146, an
inhibitor targeted to signaling proteins of innate immune
responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:12481–12486. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Duncan EA, Goetz CA, Stein SJ, Mayo KJ,
Skaggs BJ, Ziegelbauer K, Sawyers CL and Baldwin AS: IkappaB kinase
beta inhibition induces cell death in imatinib-resistant and T315I
Dasatinib-resistant BCR-ABL+ cells. Mol Cancer Ther.
7:391–397. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Xu C, Fu H, Gao L, Wang L, Wang W, Li J,
Li Y, Dou L, Gao X, Luo X, et al: BCR-ABL/GATA1/miR-138 mini
circuitry contributes to the leukemogenesis of chronic myeloid
leukemia. Oncogene. 33:44–54. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Turrini E, Haenisch S, Laechelt S, Diewock
T, Bruhn O and Cascorbi I: MicroRNA profiling in K-562 cells under
imatinib treatment: Influence of miR-212 and miR-328 on ABCG2
expression. Pharmacogenet Genomics. 22:198–205. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Yu Y, Yang L, Zhao M, Zhu S, Kang R,
Vernon P, Tang D and Cao L: Targeting microRNA-30a-mediated
autophagy enhances imatinib activity against human chronic myeloid
leukemia cells. Leukemia. 26:1752–1760. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Shibuta T, Honda E, Shiotsu H, Tanaka Y,
Vellasamy S, Shiratsuchi M and Umemura T: imatinib induces
demethylation of miR-203 gene: An epigenetic mechanism of
anti-tumor effect of imatinib. Leuk Res. 37:1278–1286. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
San José-Enériz E, Román-Gómez J,
Jiménez-Velasco A, Garate L, Martin V, Cordeu L, Vilas-Zornoza A,
Rodríguez-Otero P, Calasanz MJ, Prósper F, et al: MicroRNA
expression profiling in imatinib-resistant chronic myeloid leukemia
patients without clinically significant ABL1-mutations. Mol Cancer.
8(69)2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Lopotová T, Záčková M, Klamová H and
Moravcová J: MicroRNA-451 in chronic myeloid leukemia:
miR-451-BCR-ABL regulatory loop? Leuk Res. 35:974–977. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Scholl V, Hassan R and Zalcberg IR:
miRNA-451: A putative predictor marker of imatinib therapy response
in chronic myeloid leukemia. Leuk Res. 36:119–121. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Zimmerman EI, Dollins CM, Crawford M,
Grant S, Nana-Sinkam SP, Richards KL, Hammond SM and Graves LM: Lyn
kinase-dependent regulation of miR181 and myeloid cell leukemia-1
expression: Implications for drug resistance in myelogenous
leukemia. Mol Pharmacol. 78:811–817. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Liu L, Wang S, Chen R, Wu Y, Zhang B,
Huang S, Zhang J, Xiao F, Wang M and Liang Y: Myc induced
miR-144/451 contributes to the acquired imatinib resistance in
chronic myelogenous leukemia cell K562. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
425:368–373. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
You RI, Ho CL, Hung HM and Chao TS:
Identification of nilotinib-altered microRNA expression patterns in
imatinib-resistant chronic myeloid leukemia cells. Biomark Genomic
Med. 5:71–73. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
88
|
Firatligil B, Biray Avci C and Baran Y:
miR-17 in imatinib resistance and response to tyrosine kinase
inhibitors in chronic myeloid leukemia cells. J BUON. 18:437–441.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Mosakhani N, Mustjoki S and Knuutila S:
Down-regulation of miR-181c in imatinib-resistant chronic myeloid
leukemia. Mol Cytogenet. 6(27)2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Ohyashiki JH, Ohtsuki K, Mizoguchi I,
Yoshimoto T, Katagiri S, Umezu T and Ohyashiki K: Downregulated
microRNA-148b in circulating PBMCs in chronic myeloid leukemia
patients with undetectable minimal residual disease: A possible
biomarker to discontinue imatinib safely. Drug Des Devel Ther.
8:1151–1159. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Lin H, Rothe K, Ruschmann J, Petriv O,
O'Neill K, Knapp D, Brinkman RR, Birol I, Forrest DL, Hansen C, et
al: Identification of new microRNA biomarkers and candidate target
genes in primitive CML cells using global comparative RNA analyses.
3133 Poster AHA; 2014
|
|
92
|
Joshi D, Chandrakala S, Korgaonkar S,
Ghosh K and Vundinti BR: Down-regulation of miR-199b associated
with imatinib drug resistance in 9q34.1 deleted BCR/ABL positive
CML patients. Gene. 542:109–112. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Nishioka C, Ikezoe T, Yang J, Nobumoto A,
Tsuda M and Yokoyama A: Downregulation of miR-217 correlates with
resistance of Ph+ leukemia cells to ABL tyrosine kinase
inhibitors. Cancer Sci. 105:297–307. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|