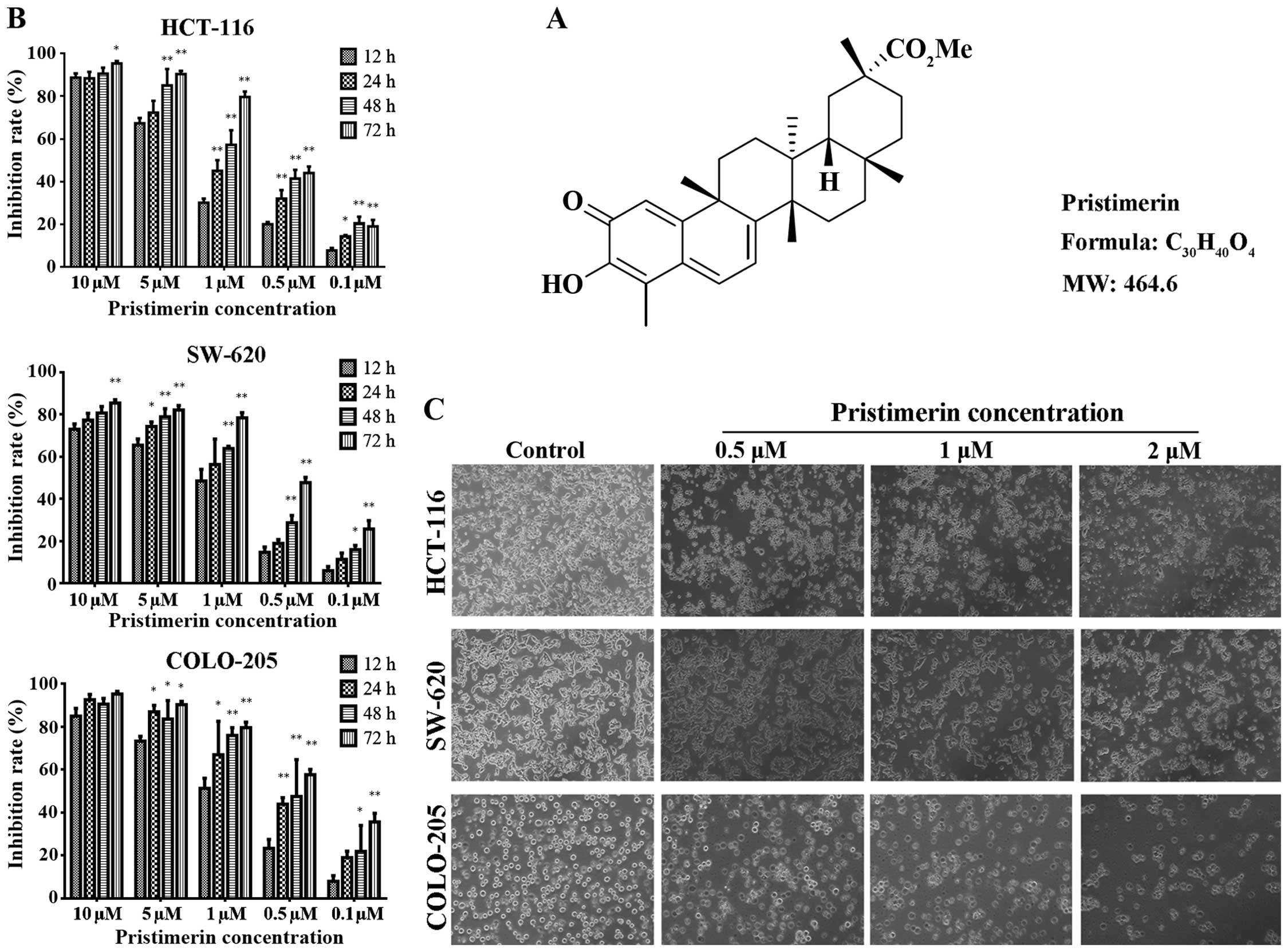
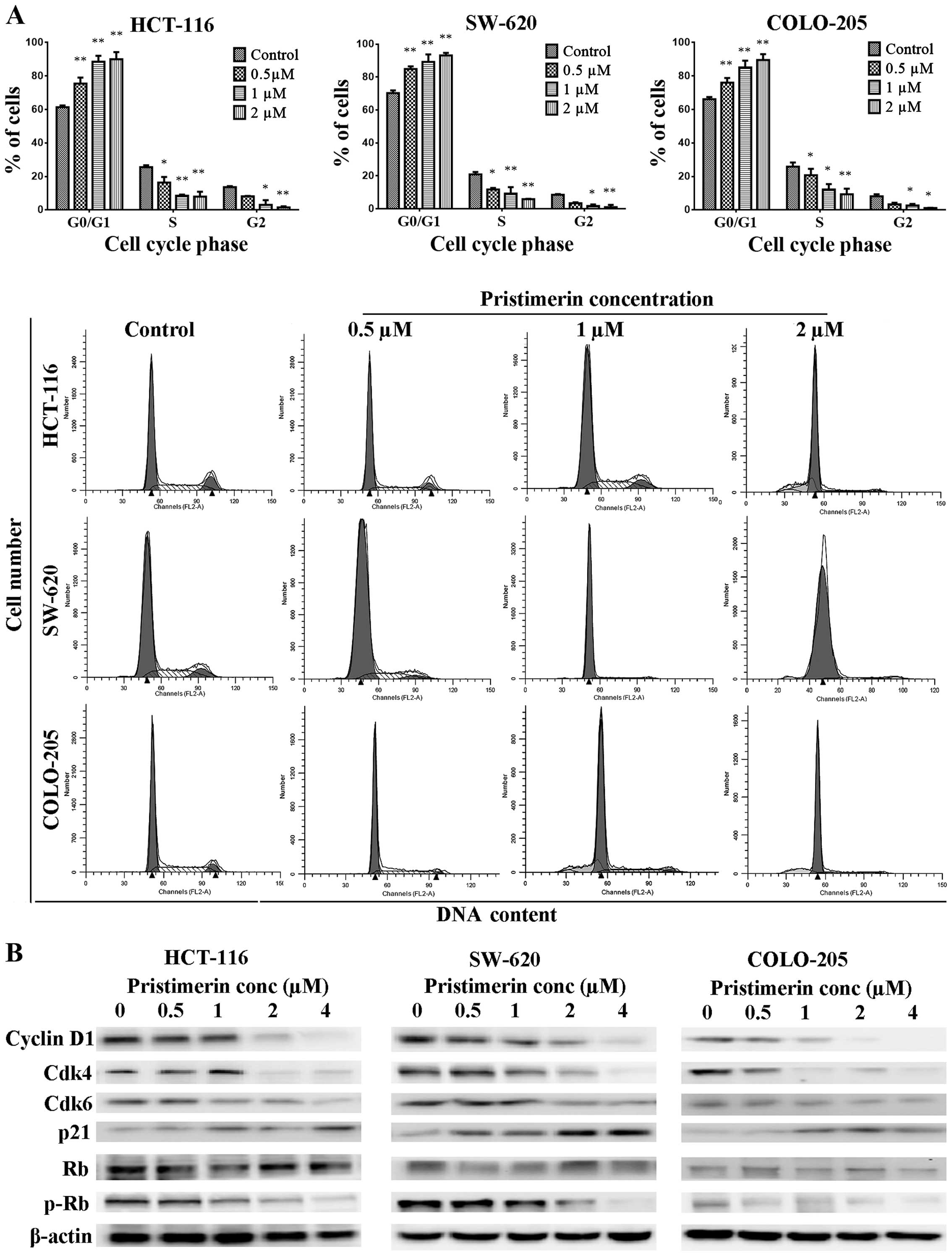
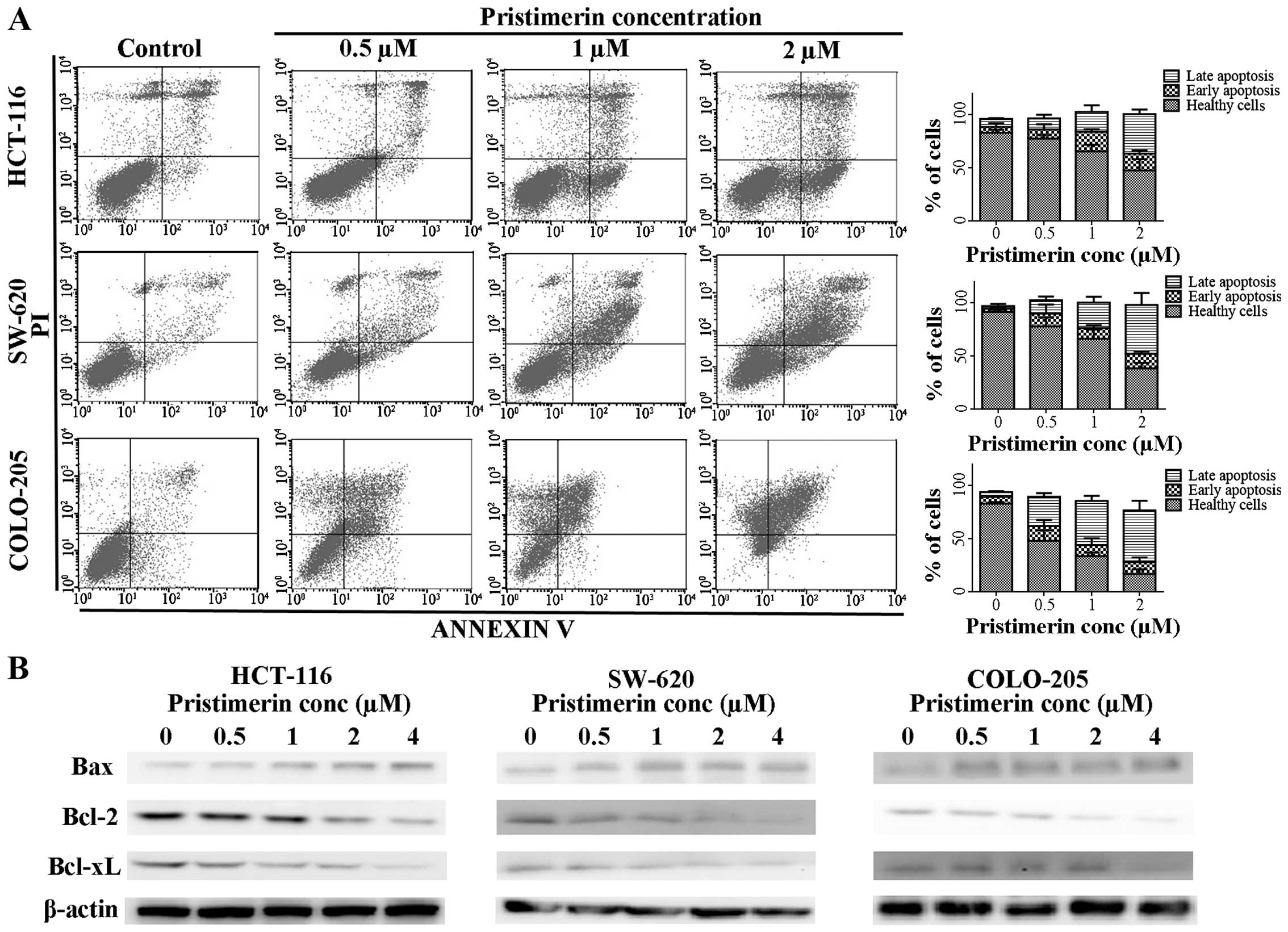
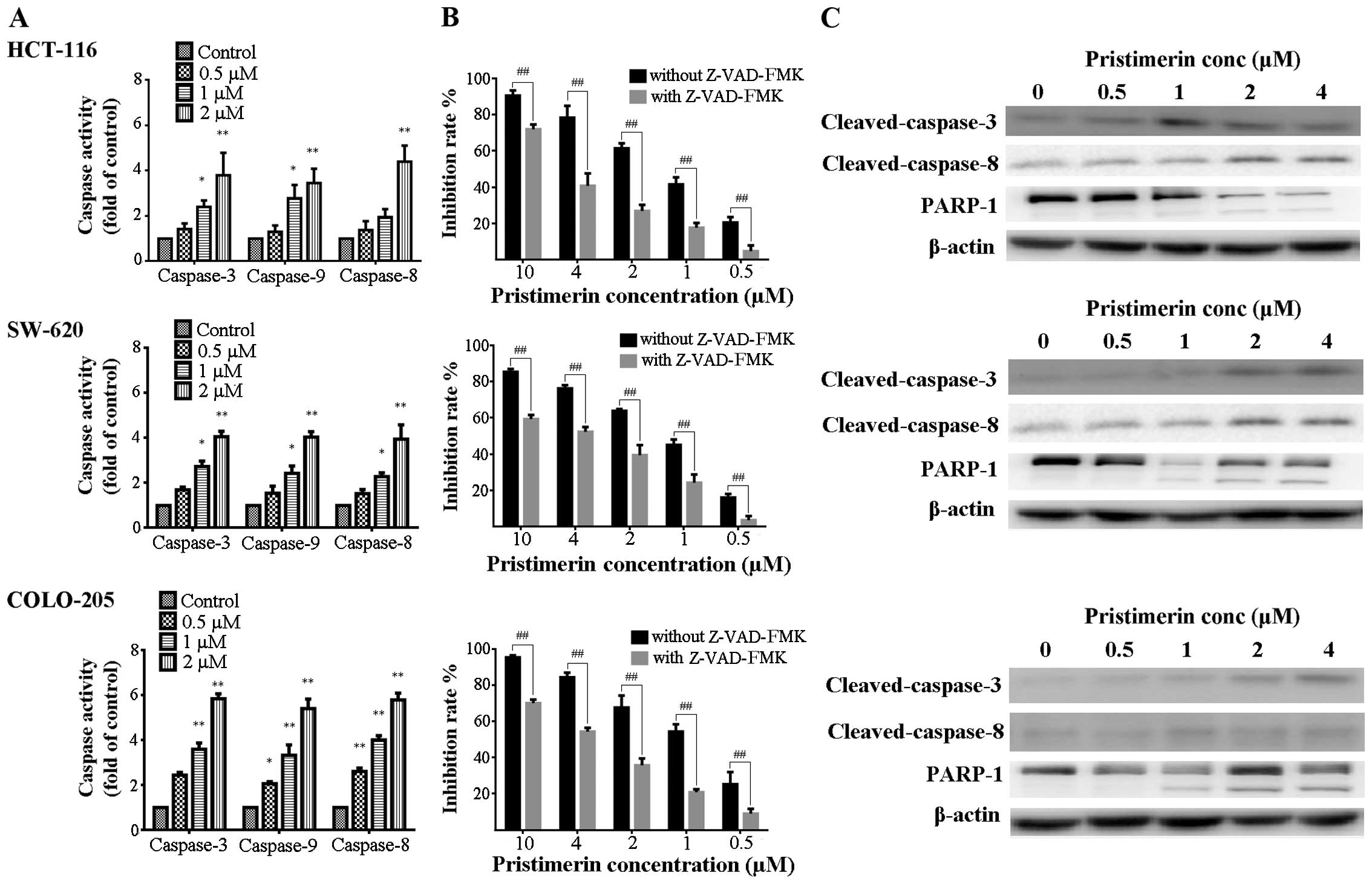
|
1
|
Tenesa A and Dunlop MG: New insights into
the aetiology of colorectal cancer from genome-wide association
studies. Nat Rev Genet. 10:353–358. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 64:9–29. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wood LD, Parsons DW, Jones S, Lin J,
Sjöblom T, Leary RJ, Shen D, Boca SM, Barber T, Ptak J, et al: The
genomic landscapes of human breast and colorectal cancers. Science.
318:1108–1113. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cancer Genome Atlas Network: Comprehensive
molecular characterization of human colon and rectal cancer.
Nature. 487:330–337. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Newman DJ, Cragg GM and Snader KM: Natural
products as sources of new drugs over the period 1981–2002. J Nat
Prod. 66:1022–1037. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Brinker AM, Ma J, Lipsky PE and Raskin I:
Medicinal chemistry and pharmacology of genus Tripterygium
(Celastraceae). Phytochemistry. 68:732–766. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Dirsch VM, Kiemer AK, Wagner H and Vollmar
AM: The triterpenoid quinonemethide pristimerin inhibits induction
of inducible nitric oxide synthase in murine macrophages. Eur J
Pharmacol. 336:211–217. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Wu CC, Chan ML, Chen WY, Tsai CY, Chang FR
and Wu YC: Pristimerin induces caspase-dependent apoptosis in
MDA-MB-231 cells via direct effects on mitochondria. Mol Cancer
Ther. 4:1277–1285. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang Y, Zhou Y, Zhou H, Jia G, Liu J, Han
B, Cheng Z, Jiang H, Pan S and Sun B: Pristimerin causes G1 arrest,
induces apoptosis, and enhances the chemosensitivity to gemcitabine
in pancreatic cancer cells. PLoS One. 7:e438262012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Guo Y, Zhang W, Yan YY, Ma CG, Wang X,
Wang C and Zhao JL: Triterpenoid pristimerin induced HepG2 cells
apoptosis through ROS-mediated mitochondrial dysfunction. J BUON.
18:477–485. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Byun JY, Kim MJ, Eum DY, Yoon CH, Seo WD,
Park KH, Hyun JW, Lee YS, Lee JS, Yoon MY, et al: Reactive oxygen
species-dependent activation of Bax and poly(ADP-ribose)
polymerase-1 is required for mitochondrial cell death induced by
triterpenoid pristimerin in human cervical cancer cells. Mol
Pharmacol. 76:734–744. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liu YB, Gao X, Deeb D, Brigolin C, Zhang
Y, Shaw J, Pindolia K and Gautam SC: Ubiquitin-proteasomal
degradation of antiapoptotic survivin facilitates induction of
apoptosis in prostate cancer cells by pristimerin. Int J Oncol.
45:1735–1741. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yan YY, Bai JP, Xie Y, Yu JZ and Ma CG:
The triterpenoid pristimerin induces U87 glioma cell apoptosis
through reactive oxygen species-mediated mitochondrial dysfunction.
Oncol Lett. 5:242–248. 2013.
|
|
14
|
Yang H, Landis-Piwowar KR, Lu D, Yuan P,
Li L, Reddy GP, Yuan X and Dou QP: Pristimerin induces apoptosis by
targeting the proteasome in prostate cancer cells. J Cell Biochem.
103:234–244. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Tiedemann RE, Schmidt J, Keats JJ, Shi CX,
Zhu YX, Palmer SE, Mao X, Schimmer AD and Stewart AK:
Identification of a potent natural triterpenoid inhibitor of
proteosome chymotrypsin-like activity and NF-kappaB with
antimyeloma activity in vitro and in vivo. Blood. 113:4027–4037.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Liu C, Yu K, Shi X, Wang J, Lam PK, Wu RS
and Zhou B: Induction of oxidative stress and apoptosis by PFOS and
PFOA in primary cultured hepatocytes of freshwater tilapia
(Oreochromis niloticus). Aquat Toxicol. 82:135–143. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Milano G, Etienne-Grimaldi MC, Dahan L,
Francoual M, Spano JP, Benchimol D, Chazal M, Letoublon C, André T,
Gilly FN, et al: Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) status and
K-Ras mutations in colorectal cancer. Ann Oncol. 19:2033–2038.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Spano JP, Fagard R, Soria JC, Rixe O,
Khayat D and Milano G: Epidermal growth factor receptor signaling
in colorectal cancer: Preclinical data and therapeutic
perspectives. Ann Oncol. 16:189–194. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Costa PM, Ferreira PM, Bolzani VS, Furlan
M, de Freitas Formenton Macedo Dos Santos VA, Corsino J, de Moraes
MO, Costa-Lotufo LV, Montenegro RC and Pessoa C: Antiproliferative
activity of pristimerin isolated from Maytenus ilicifolia
(Celastraceae) in human HL-60 cells. Toxicol In Vitro. 22:854–863.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Call JA, Eckhardt SG and Camidge DR:
Targeted manipulation of apoptosis in cancer treatment. Lancet
Oncol. 9:1002–1011. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Morgan DO: Cyclin-dependent kinases:
Engines, clocks, and microprocessors. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol.
13:261–291. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bartek J, Bartkova J and Lukas J: The
retinoblastoma protein pathway and the restriction point. Curr Opin
Cell Biol. 8:805–814. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Coqueret O: New roles for p21 and p27
cell-cycle inhibitors: A function for each cell compartment?
Trends. Cell Biol. 13:65–70. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Debatin KM: Activation of apoptosis
pathways by anticancer drugs. Adv Exp Med Biol. 457:237–244. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hengartner MO: The biochemistry of
apoptosis. Nature. 407:770–776. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lee JS, Yoon IS, Lee MS, Cha EY, Thuong
PT, Diep TT and Kim JR: Anticancer activity of pristimerin in
epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive SKBR3 human breast
cancer cells. Biol Pharm Bull. 36:316–325. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yasuda Y, Saito M, Yamamura T, Yaguchi T
and Nishizaki T: Extracellular adenosine induces apoptosis in
Caco-2 human colonic cancer cells by activating caspase-9/-3 via
A2a adenosine receptors. J Gastroenterol. 44:56–65.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Yang Y, Zhao S and Song J:
Caspase-dependent apoptosis and-independent poly(ADP-ribose)
polymerase cleavage induced by transforming growth factor β1. Int J
Biochem Cell Biol. 36:223–234. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Jacotot E, Costantini P, Laboureau E,
Zamzami N, Susin SA and Kroemer G: Mitochondrial membrane
permeabilization during the apoptotic process. Ann NY Acad Sci.
887:18–30. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Brunelle JK and Letai A: Control of
mitochondrial apoptosis by the Bcl-2 family. J Cell Sci.
122:437–441. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Scorrano L and Korsmeyer SJ: Mechanisms of
cytochrome c release by proapoptotic BCL-2 family members. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 304:437–444. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Llambi F and Green DR: Apoptosis and
oncogenesis: Give and take in the BCL-2 family. Curr Opin Genet
Dev. 21:12–20. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Porebska I, Harlozińska A and Bojarowski
T: Expression of the tyrosine kinase activity growth factor
receptors (EGFR, ERB B2, ERB B3) in colorectal adenocarcinomas and
adenomas. Tumour Biol. 21:105–115. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Raymond E, Faivre S and Armand JP:
Epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase as a target for
anticancer therapy. Drugs. 60(Suppl 1): S15–S42. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Balin-Gauthier D, Delord JP, Rochaix P,
Mallard V, Thomas F, Hennebelle I, Bugat R, Canal P and Allal C: In
vivo and in vitro antitumor activity of oxaliplatin in combination
with cetuximab in human colorectal tumor cell lines expressing
different level of EGFR. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 57:709–718.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Seshacharyulu P, Ponnusamy MP, Haridas D,
Jain M, Ganti AK and Batra SK: Targeting the EGFR signaling pathway
in cancer therapy. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 16:15–31. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
McCubrey JA, Steelman LS, Chappell WH,
Abrams SL, Wong EW, Chang F, Lehmann B, Terrian DM, Milella M,
Tafuri A, et al: Roles of the Raf/MEK/ERK pathway in cell growth,
malignant transformation and drug resistance. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1773:1263–1284. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Mu X, Shi W, Sun L, Li H, Jiang Z and
Zhang L: Pristimerin, a triterpenoid, inhibits tumor angiogenesis
by targeting VEGFR2 activation. Molecules. 17:6854–6868. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Vivanco I and Sawyers CL: The
phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase AKT pathway in human cancer. Nat Rev
Cancer. 2:489–501. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Sekulić A, Hudson CC, Homme JL, Yin P,
Otterness DM, Karnitz LM and Abraham RT: A direct linkage between
the phosphoinositide 3-kinase-AKT signaling pathway and the
mammalian target of rapamycin in mitogen-stimulated and transformed
cells. Cancer Res. 60:3504–3513. 2000.
|
|
42
|
Mayo MW and Baldwin AS: The transcription
factor NF-kappaB: Control of oncogenesis and cancer therapy
resistance. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1470:M55–M62. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Deeb D, Gao X, Liu YB, Pindolia K and
Gautam SC: Pristimerin, a quinonemethide triterpenoid, induces
apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cells through the inhibition of
pro-survival Akt/NF-κB/mTOR signaling proteins and anti-apoptotic
Bcl-2. Int J Oncol. 44:1707–1715. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|