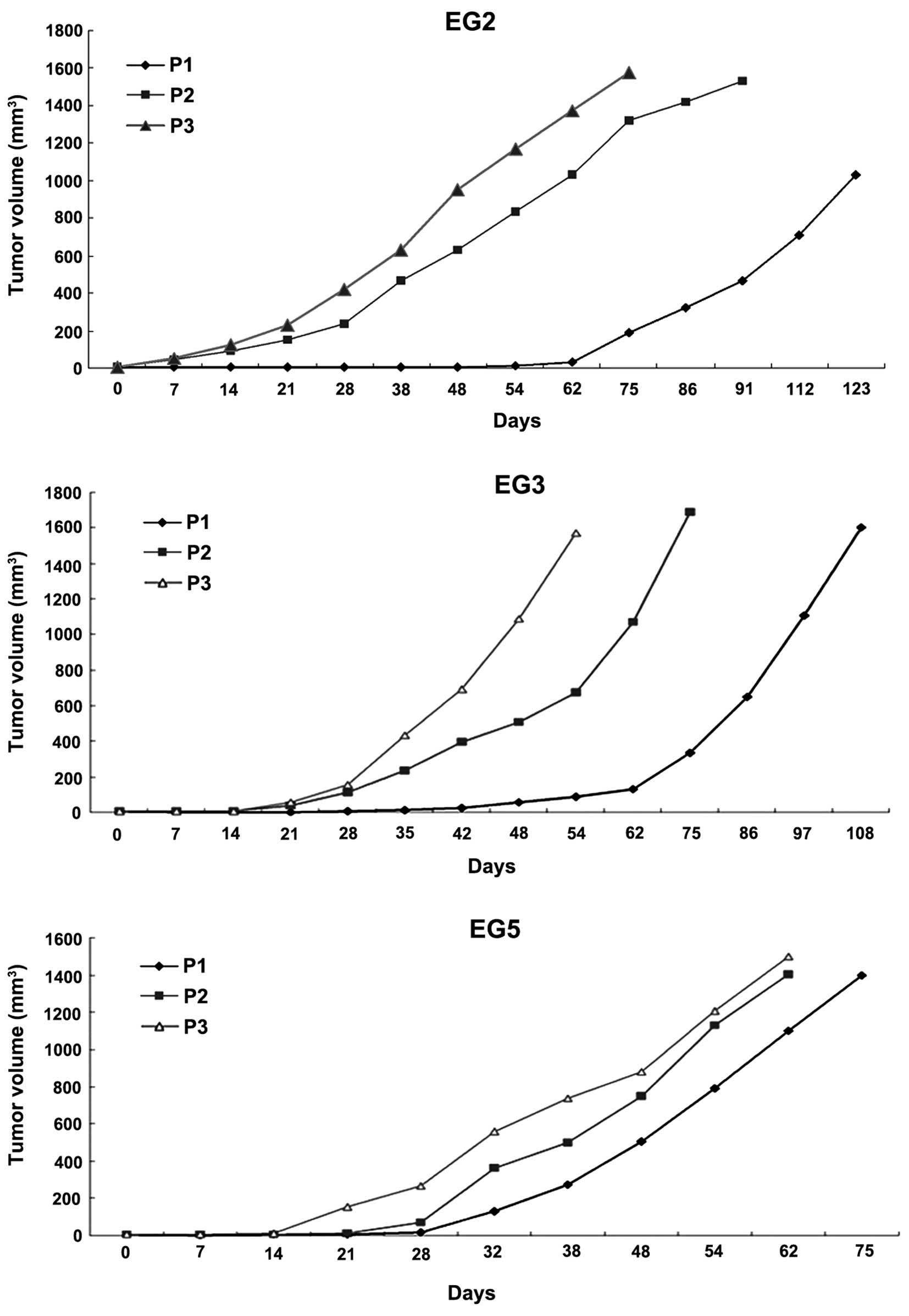
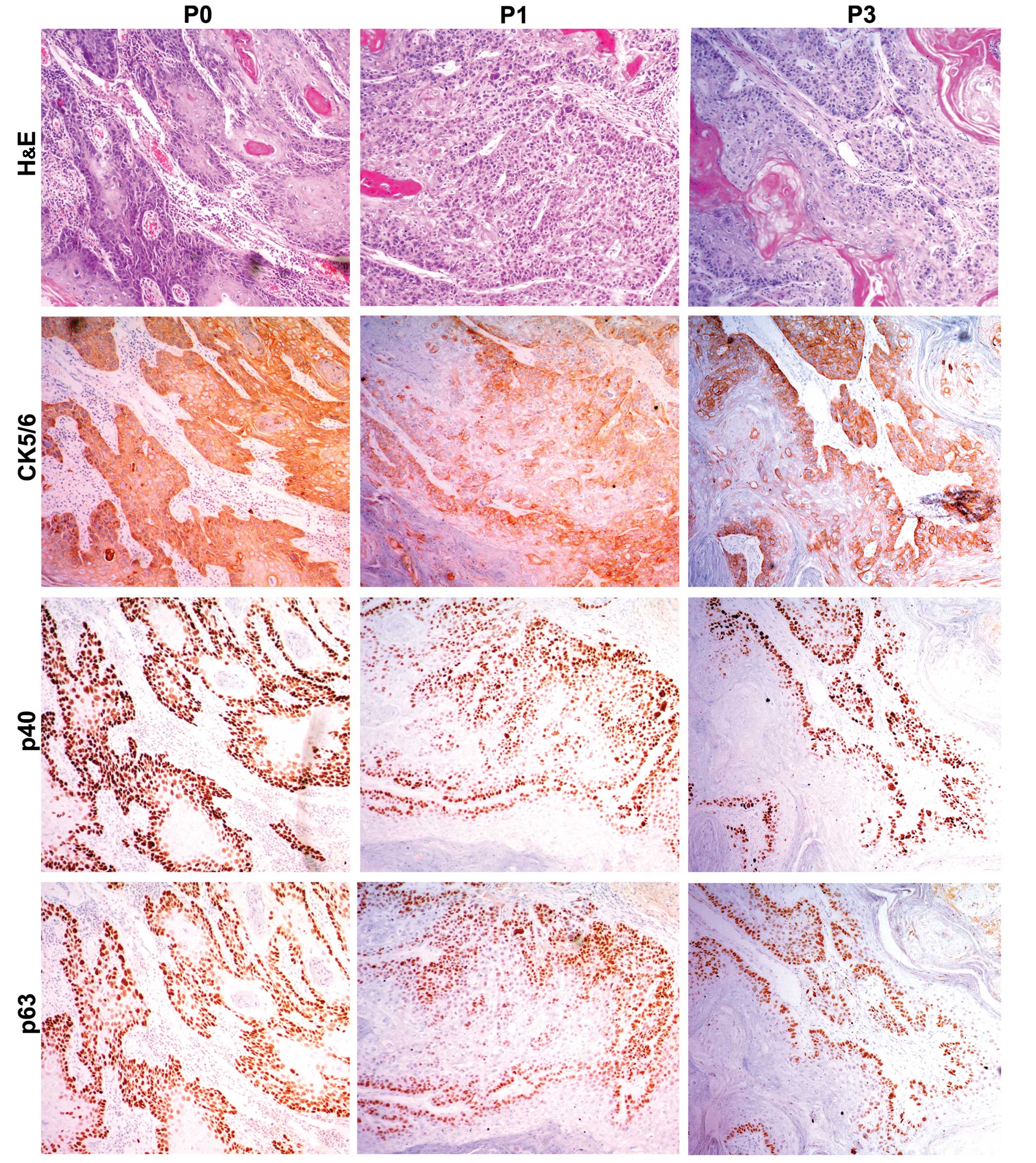
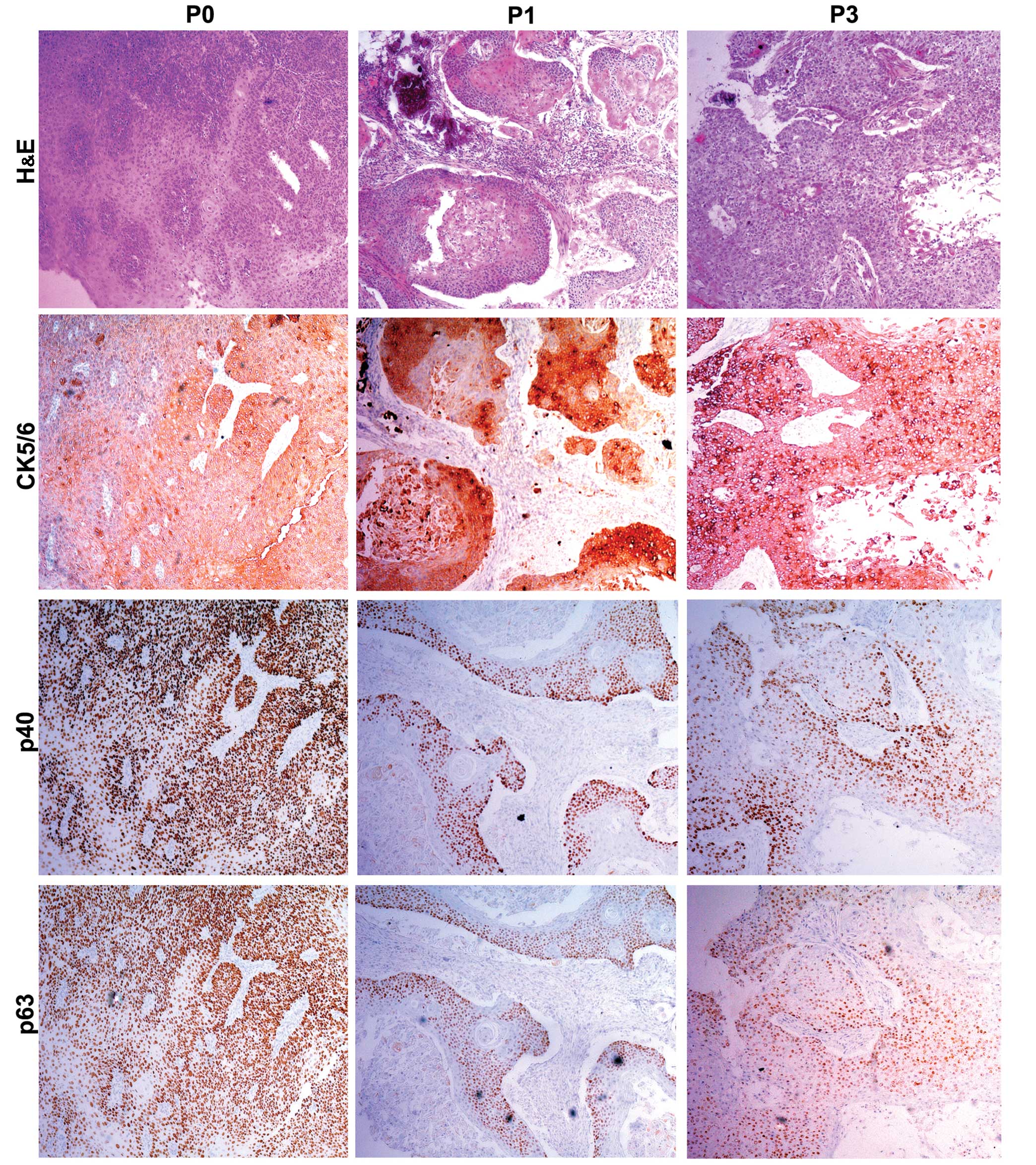
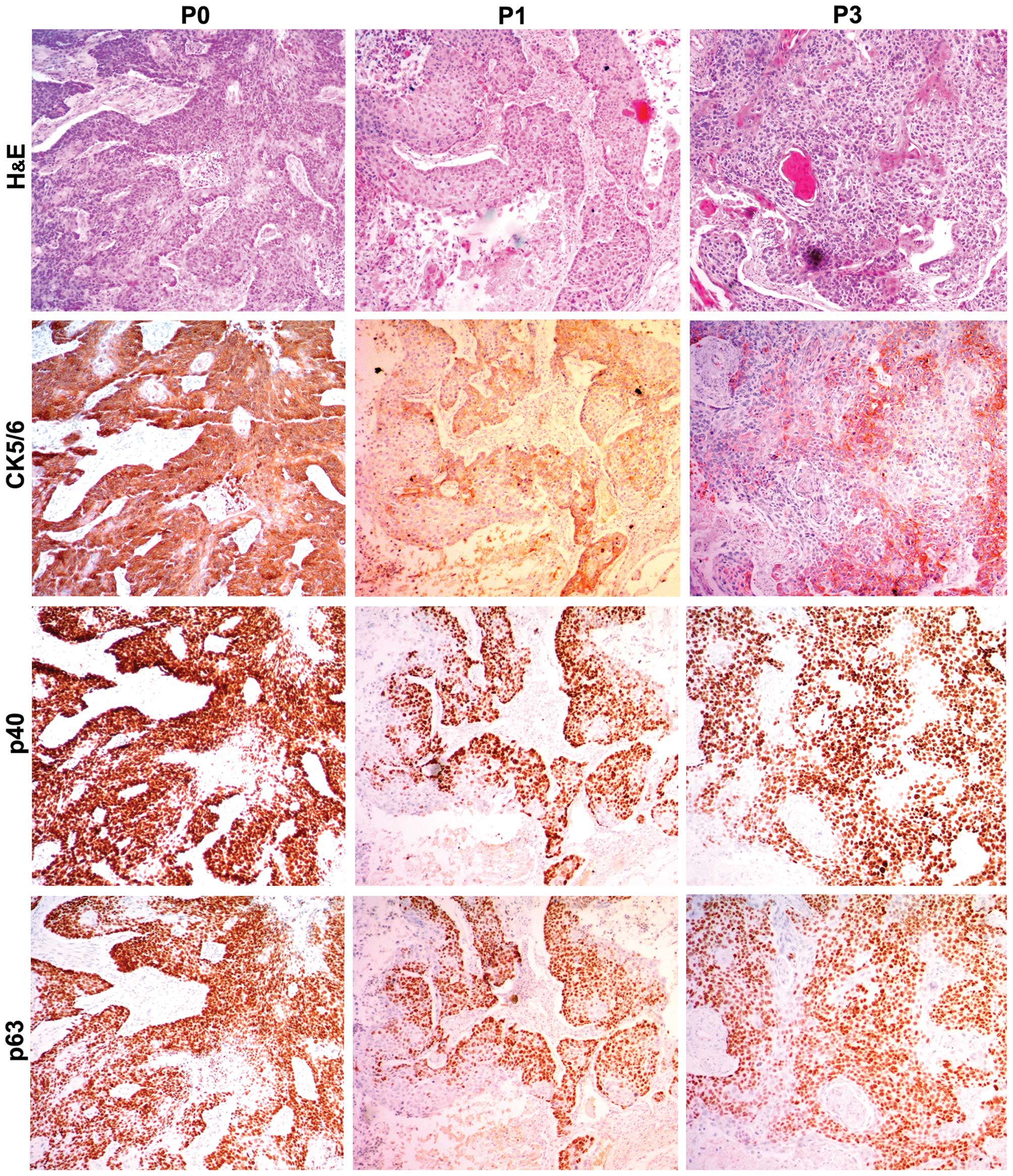
|
1
|
Zhao P, Dai M, Chen W and Li N: Cancer
trends in China. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 40:281–285. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Adachi Y, Ohashi H, Imsumran A, Yamamoto
H, Matsunaga Y, Taniguchi H, Nosho K, Suzuki H, Sasaki Y, Arimura
Y, et al: The effect of IGF-I receptor blockade for human
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma. Tumour Biol.
35:973–985. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Belkhiri A and El-Rifai W: Advances in
targeted therapies and new promising targets in esophageal cancer.
Oncotarget. 6:1348–1358. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Honjo S, Ajani JA, Scott AW, Chen Q,
Skinner HD, Stroehlein J, Johnson RL and Song S: Metformin
sensitizes chemotherapy by targeting cancer stem cells and the mTOR
pathway in esophageal cancer. Int J Oncol. 45:567–574.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Harb WA: Management of patients with
hormone receptor-positive breast cancer with visceral disease:
Challenges and treatment options. Cancer Manag Res. 7:37–46. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Geuna E, Milani A, Martinello R, Aversa C,
Valabrega G, Scaltriti M and Montemurro F: Buparlisib, an oral
pan-PI3K inhibitor for the treatment of breast cancer. Expert Opin
Investig Drugs. 24:421–431. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Inoue A, Saijo Y, Maemondo M, Gomi K,
Tokue Y, Kimura Y, Ebina M, Kikuchi T, Moriya T and Nukiwa T:
Severe acute interstitial pneumonia and gefitinib. Lancet.
361:137–139. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Baselga J, Rischin D, Ranson M, Calvert H,
Raymond E, Kieback DG, Kaye SB, Gianni L, Harris A, Bjork T, et al:
Phase I safety, pharmacokinetic, and pharmacodynamic trial of
ZD1839, a selective oral epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine
kinase inhibitor, in patients with five selected solid tumor types.
J Clin Oncol. 20:4292–4302. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Marangoni E, Vincent-Salomon A, Auger N,
Degeorges A, Assayag F, de Cremoux P, de Plater L, Guyader C, De
Pinieux G, Judde JG, et al: A new model of patient tumor-derived
breast cancer xenografts for preclinical assays. Clin Cancer Res.
13:3989–3998. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Moro M, Bertolini G, Tortoreto M,
Pastorino U, Sozzi G and Roz L: Patient-derived xenografts of non
small cell lung cancer: Resurgence of an old model for
investigation of modern concepts of tailored therapy and cancer
stem cells. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2012:5685672012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Siolas D and Hannon GJ: Patient-derived
tumor xenografts: Transforming clinical samples into mouse models.
Cancer Res. 73:5315–5319. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tian H, Hou L, Xiong YM, Huang JX, She YJ,
Bi XB and Song XR: miR-218 suppresses tumor growth and enhances the
chemosensitivity of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma to
cisplatin. Oncol Rep. 33:981–989. 2015.
|
|
13
|
Napier KJ, Scheerer M and Misra S:
Esophageal cancer: A Review of epidemiology, pathogenesis, staging
workup and treatment modalities. World J Gastrointest Oncol.
6:112–120. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Uemura N and Kondo T: Current status of
predictive biomarkers for neoadjuvant therapy in esophageal cancer.
World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol. 5:322–334. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Morton CL and Houghton PJ: Establishment
of human tumor xenografts in immunodeficient mice. Nat Protoc.
2:247–250. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Dong SW, Zhang H, Wang BL, Sun P, Wang YG
and Zhang P: Effect of the downregulation of SMYD3 expression by
RNAi on RIZ1 expression and proliferation of esophageal squamous
cell carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 32:1064–1070. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Blobel GA, Moll R, Franke WW, Kayser KW
and Gould VE: The intermediate filament cytoskeleton of malignant
mesotheliomas and its diagnostic significance. Am J Pathol.
121:235–247. 1985.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ye S, Lee KB, Park MH, Lee JS and Kim SM:
p63 regulates growth of esophageal squamous carcinoma cells via the
Akt signaling pathway. Int J Oncol. 44:2153–2159. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Thépot A, Hautefeuille A, Cros MP,
Abedi-Ardekani B, Pétré A, Damour O, Krutovskikh V and Hainaut P:
Intraepithelial p63-dependent expression of distinct components of
cell adhesion complexes in normal esophageal mucosa and squamous
cell carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 127:2051–2062. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lin DC, Hao JJ, Nagata Y, Xu L, Shang L,
Meng X, Sato Y, Okuno Y, Varela AM, Ding LW, et al: Genomic and
molecular characterization of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
Nat Genet. 46:467–473. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Song Y, Li L, Ou Y, Gao Z, Li E, Li X,
Zhang W, Wang J, Xu L, Zhou Y, et al: Identification of genomic
alterations in oesophageal squamous cell cancer. Nature. 509:91–95.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li B, Li J, Xu WW, Guan XY, Qin YR, Zhang
LY, Law S, Tsao SW and Cheung AL: Suppression of esophageal tumor
growth and chemoresistance by directly targeting the PI3K/AKT
pathway. Oncotarget. 5:11576–11587. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hou G, Yang S, Zhou Y, Wang C, Zhao W and
Lu Z: Targeted inhibition of mTOR signaling improves sensitivity of
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells to cisplatin. J Immunol
Res. 2014:8457632014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Huang Y, Xi Q, Chen Y, Wang J, Peng P, Xia
S and Yu S: A dual mTORC1 and mTORC2 inhibitor shows antitumor
activity in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells and sensitizes
them to cisplatin. Anticancer Drugs. 24:889–898. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ciccarelli A and Giustetto M: Role of ERK
signaling in activity-dependent modifications of histone proteins.
Neuropharmacology. 80:34–44. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Bhalla S, Evens AM, Dai B, Prachand S,
Gordon LI and Gartenhaus RB: The novel anti-MEK small molecule
AZD6244 induces BIM-dependent and AKT-independent apoptosis in
diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood. 118:1052–1061. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang J, Zhi H, Zhou C, Ding F, Luo A,
Zhang X, Sun Y, Wang X, Wu M and Liu Z: Up-regulation of
fibronectin in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma is associated
with activation of the Erk pathway. J Pathol. 207:402–409. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sakamoto C: STAT1 and STAT3 might be
regulated differently in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J
Gastroenterol. 37:575–577. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wang Z, Zhu S, Shen M, Liu J, Wang M, Li
C, Wang Y, Deng A and Mei Q: STAT3 is involved in esophageal
carcinogenesis through regulation of Oct-1. Carcinogenesis.
34:678–688. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Qing Y and Stark GR: Alternative
activation of STAT1 and STAT3 in response to interferon-gamma. J
Biol Chem. 279:41679–41685. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Regis G, Pensa S, Boselli D, Novelli F and
Poli V: Ups and downs: the STAT1:STAT3 seesaw of Interferon and
gp130 receptor signalling. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 19:351–359. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|