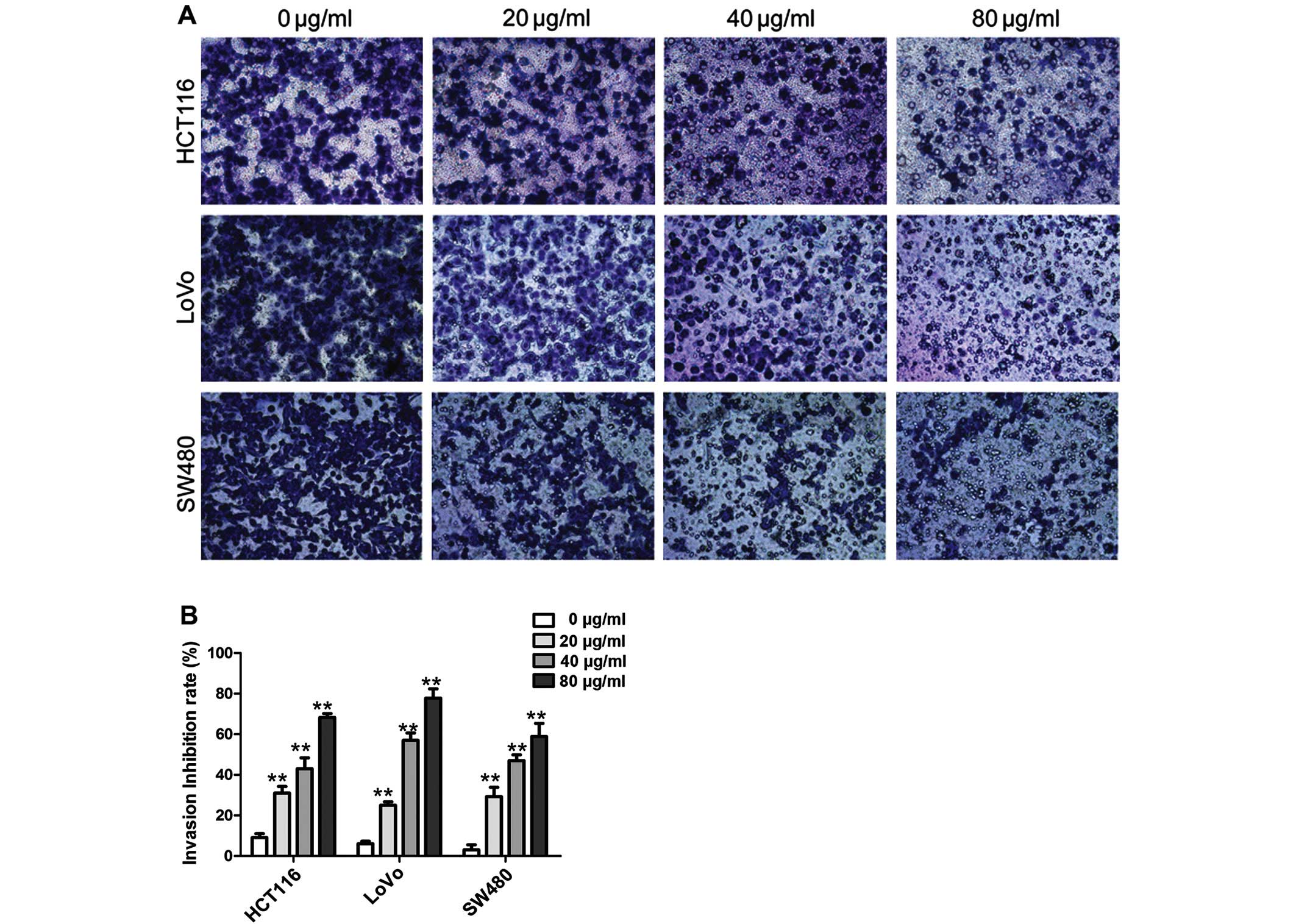
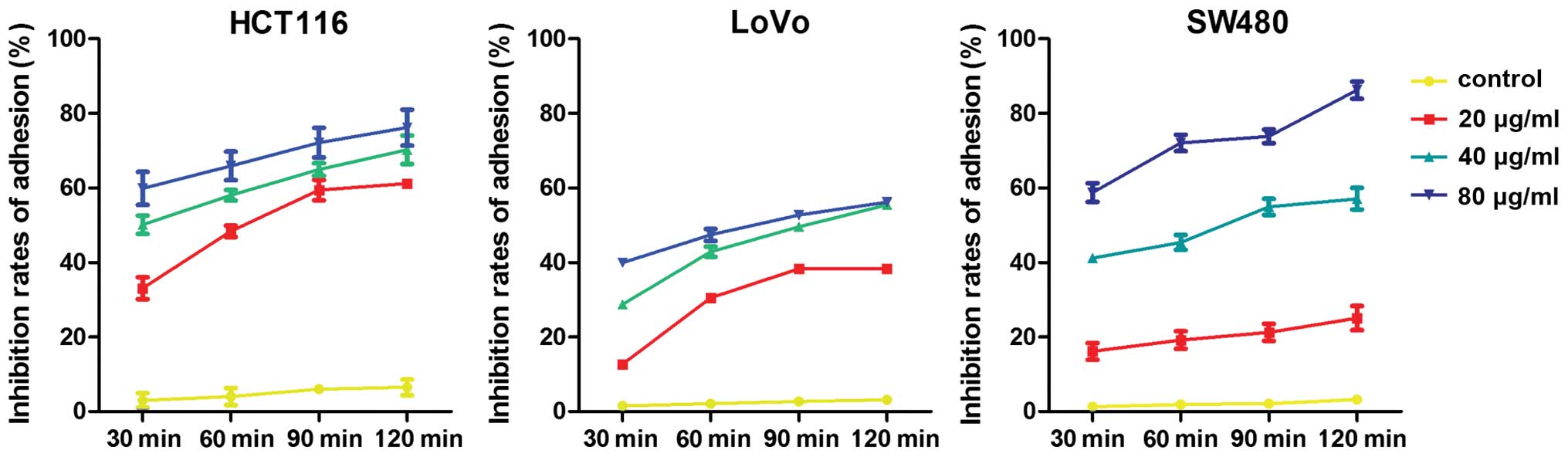
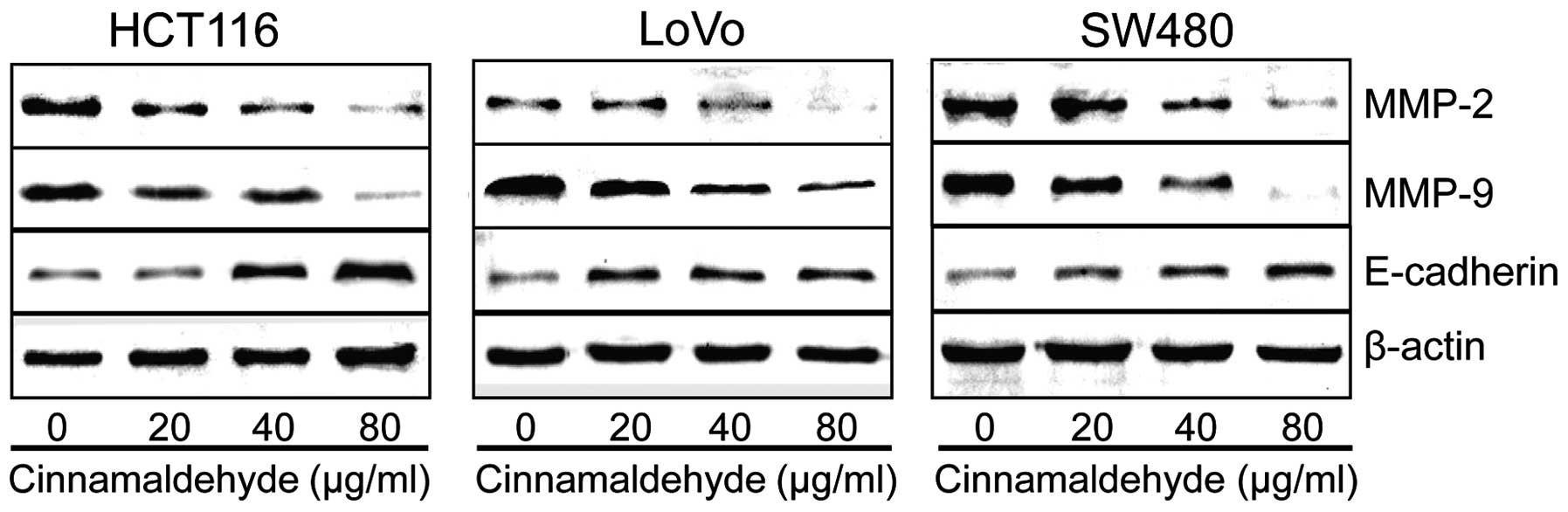
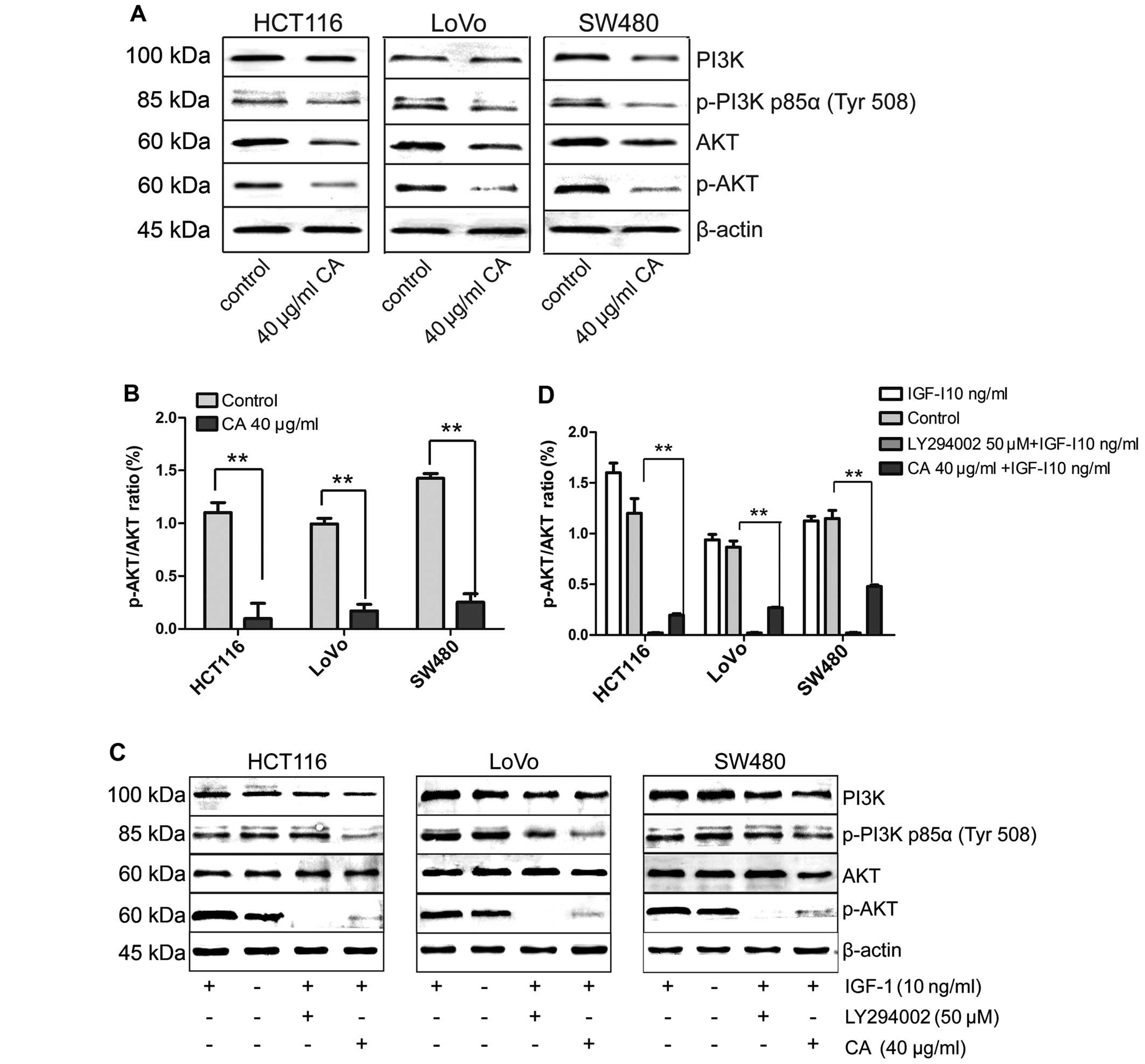
|
1
|
Siegel R, Desantis C and Jemal A:
Colorectal cancer statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 64:104–117.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Nosher JL, Ahmed I, Patel AN, Gendel V,
Murillo PG, Moss R and Jabbour SK: Non-operative therapies for
colorectal liver metastases. J Gastrointest Oncol. 6:224–240.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Jawed I, Wilkerson J, Prasad V, Duffy AG
and Fojo T: Colorectal cancer survival gains and novel treatment
regimens: A systematic review and analysis. JAMA Oncol. 1:787–795.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chang ST, Chen PF and Chang SC:
Antibacterial activity of leaf essential oils and their
constituents from Cinnamomum osmophloeum. J Ethnopharmacol.
77:123–127. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Koh WS, Yoon SY, Kwon BM, Jeong TC, Nam KS
and Han MY: Cinnamaldehyde inhibits lymphocyte proliferation and
modulates T-cell differentiation. Int J Immunopharmacol.
20:643–660. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ka H, Park HJ, Jung HJ, Choi JW, Cho KS,
Ha J and Lee KT: Cinnamaldehyde induces apoptosis by ROS-mediated
mitochondrial permeability transition in human promyelocytic
leukemia HL-60 cells. Cancer Lett. 196:143–152. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
López P, Sánchez C, Batlle R and Nerín C:
Solid- and vapor-phase antimicrobial activities of six essential
oils: Susceptibility of selected foodborne bacterial and fungal
strains. J Agric Food Chem. 53:6939–6946. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Imai T, Yasuhara K, Tamura T, Takizawa T,
Ueda M, Hirose M and Mitsumori K: Inhibitory effects of
cinnamaldehyde on
4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone-induced lung
carcinogenesis in rasH2 mice. Cancer Lett. 175:9–16. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Huang TC, Chung YL, Wu ML and Chuang SM:
Cinnamaldehyde enhances Nrf2 nuclear translocation to upregulate
phase II detoxifying enzyme expression in HepG2 cells. J Agric Food
Chem. 59:5164–5171. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wu SJ, Ng LT and Lin CC: Effects of
vitamin E on the cinnamaldehyde-induced apoptotic mechanism in
human PLC/PRF/5 cells. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 31:770–776.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chew EH, Nagle AA, Zhang Y, Scarmagnani S,
Palaniappan P, Bradshaw TD, Holmgren A and Westwell AD:
Cinnamaldehydes inhibit thioredoxin reductase and induce Nrf2:
Potential candidates for cancer therapy and chemoprevention. Free
Radic Biol Med. 48:98–111. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Suman S, Kurisetty V, Das TP, Vadodkar A,
Ramos G, Lakshmanaswamy R and Damodaran C: Activation of AKT
signaling promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and tumor
growth in colorectal cancer cells. Mol Carcinog. 53(Suppl 1):
E151–E160. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Johnson SM, Gulhati P, Rampy BA, Han Y,
Rychahou PG, Doan HQ, Weiss HL and Evers BM: Novel expression
patterns of PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway components in
colorectal cancer. J Am Coll Surg. 210:767–778. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Osaki M, Oshimura M and Ito H: PI3K-Akt
pathway: Its functions and alterations in human cancer. Apoptosis.
9:667–676. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Vivanco I and Sawyers CL: The
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase AKT pathway in human cancer. Nat Rev
Cancer. 2:489–501. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li Y, Wang SJ, Xia W, Rahman K, Zhang Y,
Peng H, Zhang H and Qin LP: Effects of tatariside G isolated from
Fagopyrum tataricum roots on apoptosis in human cervical cancer
HeLa cells. Molecules. 19:11145–11159. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Xu C, Sun G, Yuan G, Wang R and Sun X:
Effects of platycodin D on proliferation, apoptosis and PI3K/Akt
signal pathway of human glioma U251 cells. Molecules.
19:21411–21423. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hulkower KI and Herber RL: Cell migration
and invasion assays as tools for drug discovery. Pharmaceutics.
3:107–124. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wu N, Luo J, Jiang B, Wang L, Wang S, Wang
C, Fu C, Li J and Shi D: Marine bromophenol
bis(2,3-dibromo-4,5-dihydroxy-phenyl)-methane inhibits the
proliferation, migration, and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma
cells via modulating β1-integrin/FAK signaling. Mar Drugs.
13:1010–1025. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li Y, Gu JF, Zou X, Wu J, Zhang MH, Jiang
J, Qin D, Zhou JY, Liu BX, Zhu YT, et al: The anti-lung cancer
activities of steroidal saponins of P. polyphylla Smith var.
chinensis (Franch.) Hara through enhanced immunostimulation in
experimental Lewis tumor-bearing C57BL/6 mice and induction of
apoptosis in the A549 cell line. Molecules. 18:12916–12936. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zinkel S, Gross A and Yang E: BCL2 family
in DNA damage and cell cycle control. Cell Death Differ.
13:1351–1359. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gupta S, Afaq F and Mukhtar H: Involvement
of nuclear factor-kappa B, Bax and Bcl-2 in induction of cell cycle
arrest and apoptosis by apigenin in human prostate carcinoma cells.
Oncogene. 21:3727–3738. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bae GY, Choi SJ, Lee JS, Jo J, Lee J, Kim
J and Cha HJ: Loss of E-cadherin activates EGFR-MEK/ERK signaling,
which promotes invasion via the ZEB1/MMP2 axis in non-small cell
lung cancer. Oncotarget. 4:2512–2522. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Park KS, Kim SJ, Kim KH and Kim JC:
Clinical characteristics of TIMP2, MMP2, and MMP9 gene
polymorphisms in colorectal cancer. J Gastroenterol Hepatol.
26:391–397. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Cavdar Z, Canda AE, Terzi C, Sarioglu S,
Fuzun M and Oktay G: Role of gelatinases (matrix metalloproteinases
2 and 9), vascular endothelial growth factor and endostatin on
clinicopathological behaviour of rectal cancer. Colorectal Dis.
13:154–160. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Bauvois B: New facets of matrix
metalloproteinases MMP-2 and MMP-9 as cell surface transducers:
Outside-in signaling and relationship to tumor progression. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1825:29–36. 2012.
|
|
27
|
Wang H, Duan L, Zou Z, Li H, Yuan S, Chen
X, Zhang Y, Li X, Sun H, Zha H, et al: Activation of the
PI3K/Akt/mTOR/p70S6K pathway is involved in S100A4-induced
viability and migration in colorectal cancer cells. Int J Med Sci.
11:841–849. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ryu YL, Jung KH, Son MK, Yan HH, Kim SJ,
Shin S, Hong S and Hong SS: Anticancer activity of HS-527, a novel
inhibitor targeting PI3-kinase in human pancreatic cancer cells.
Cancer Lett. 353:68–77. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhang X, Li XR and Zhang J: Current status
and future perspectives of PI3K and mTOR inhibitor as anticancer
drugs in breast cancer. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 13:175–187. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Elumalai P, Arunkumar R, Benson CS,
Sharmila G and Arunakaran J: Nimbolide inhibits IGF-I-mediated
PI3K/Akt and MAPK signalling in human breast cancer cell lines
(MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231). Cell Biochem Funct. 32:476–484.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yamaguchi K, Lee SH, Kim JS, Wimalasena J,
Kitajima S and Baek SJ: Activating transcription factor 3 and early
growth response 1 are the novel targets of LY294002 in a
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-independent pathway. Cancer Res.
66:2376–2384. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Samani AA, Yakar S, LeRoith D and Brodt P:
The role of the IGF system in cancer growth and metastasis:
Overview and recent insights. Endocr Rev. 28:20–47. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Mitsiades CS, Mitsiades N, Poulaki V,
Schlossman R, Akiyama M, Chauhan D, Hideshima T, Treon SP, Munshi
NC, Richardson PG, et al: Activation of NF-kappaB and upregulation
of intracellular anti-apoptotic proteins via the IGF-1/Akt
signaling in human multiple myeloma cells: Therapeutic
implications. Oncogene. 21:5673–5683. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhou L, Lu Y, Yang G and Wu J: Research on
tumorigenicity of cinnamaldehyde in melanoma cell lines and its
mechanism. Tumour Biol. 35:5717–5722. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yun M, Lee D, Park MN, Kim EO, Sohn EJ,
Kwon BM and Kim SH: Cinnamaldehyde derivative (CB-PIC) sensitizes
chemo-resistant cancer cells to drug-induced apoptosis via
suppression of MDR1 and its upstream STAT3 and AKT signalling. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 35:1821–1830. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Liao BC, Hsieh CW, Liu YC, Tzeng TT, Sun
YW and Wung BS: Cinnamaldehyde inhibits the tumor necrosis
factor-alpha-induced expression of cell adhesion molecules in
endothelial cells by suppressing NF-kappaB activation: Effects upon
IkappaB and Nrf2. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 229:161–171. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Matthews GM, Newbold A and Johnstone RW:
Intrinsic and extrinsic apoptotic pathway signaling as determinants
of histone deacetylase inhibitor antitumor activity. Adv Cancer
Res. 116:165–197. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Jagtap P and Szabó C: Poly(ADP-ribose)
polymerase and the therapeutic effects of its inhibitors. Nat Rev
Drug Discov. 4:421–440. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Soldani C and Scovassi AI:
Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 cleavage during apoptosis: An update.
Apoptosis. 7:321–328. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Su CC, Chen JY, Din ZH, Su JH, Yang ZY,
Chen YJ, Wang RY and Wu YJ: 13-Acetoxysarcocrassolide induces
apoptosis on human gastric carcinoma cells through
mitochondria-related apoptotic pathways: p38/JNK activation and
PI3K/AKT suppression. Mar Drugs. 12:5295–5315. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Reed JC: Regulation of apoptosis by bcl-2
family proteins and its role in cancer and chemoresistance. Curr
Opin Oncol. 7:541–546. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Yin C, Knudson CM, Korsmeyer SJ and Van
Dyke T: Bax suppresses tumorigenesis and stimulates apoptosis in
vivo. Nature. 385:637–640. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Yates CM, McGettrick HM, Nash GB and
Rainger GE: Adhesion of tumor cells to matrices and endothelium.
Methods Mol Biol. 1070:57–75. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Liu SQ, Su YJ, Qin MB, Mao YB, Huang JA
and Tang GD: Sphingosine kinase 1 promotes tumor progression and
confers malignancy phenotypes of colon cancer by regulating the
focal adhesion kinase pathway and adhesion molecules. Int J Oncol.
42:617–626. 2013.
|
|
46
|
Gao XH, Yang XQ, Wang BC, Liu SP and Wang
FB: Overexpression of twist and matrix metalloproteinase-9 with
metastasis and prognosis in gastric cancer. Asian Pac J Cancer
Prev. 14:5055–5060. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Samuels Y and Ericson K: Oncogenic PI3K
and its role in cancer. Curr Opin Oncol. 18:77–82. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Richardson CJ, Schalm SS and Blenis J:
PI3-kinase and TOR: PIKTORing cell growth. Semin Cell Dev Biol.
15:147–159. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Dunlap J, Le C, Shukla A, Patterson J,
Presnell A, Heinrich MC, Corless CL and Troxell ML:
Phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase and AKT1 mutations occur early in
breast carcinoma. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 120:409–418. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Paradiso A, Mangia A, Azzariti A and
Tommasi S: Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in breast cancer: Where
from here? Clin Cancer Res. 13:5988–5990. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Wu Y, Yakar S, Zhao L, Hennighausen L and
LeRoith D: Circulating insulin-like growth factor-I levels regulate
colon cancer growth and metastasis. Cancer Res. 62:1030–1035.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Akagi Y, Liu W, Zebrowski B, Xie K and
Ellis LM: Regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor
expression in human colon cancer by insulin-like growth factor-I.
Cancer Res. 58:4008–4014. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|