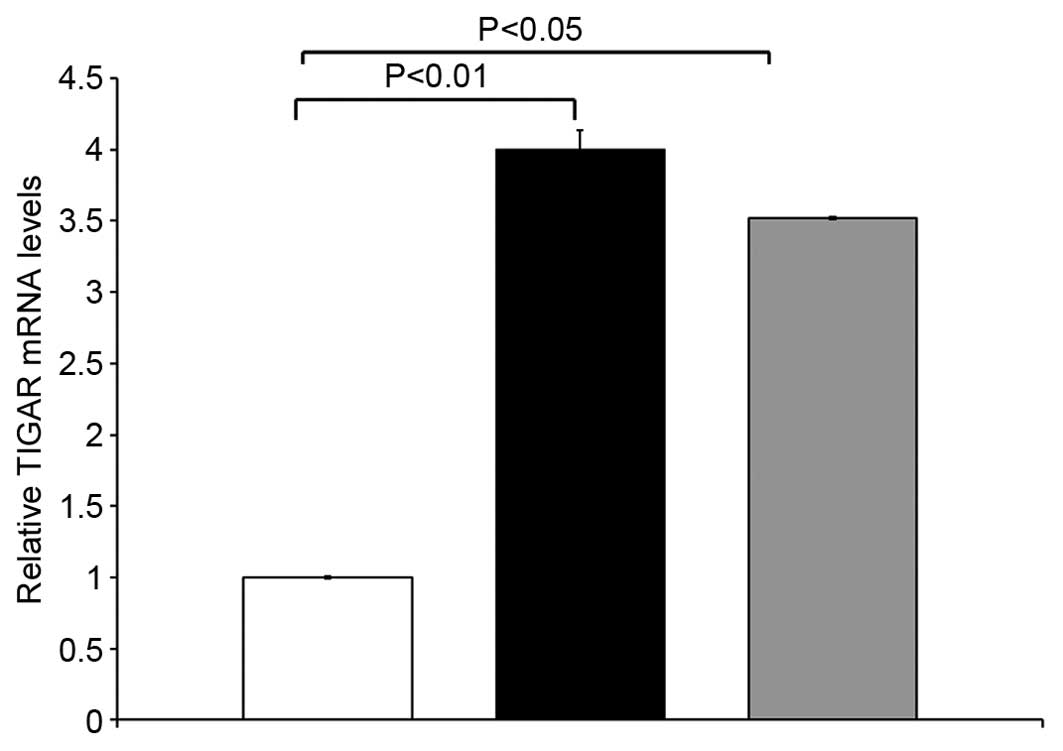
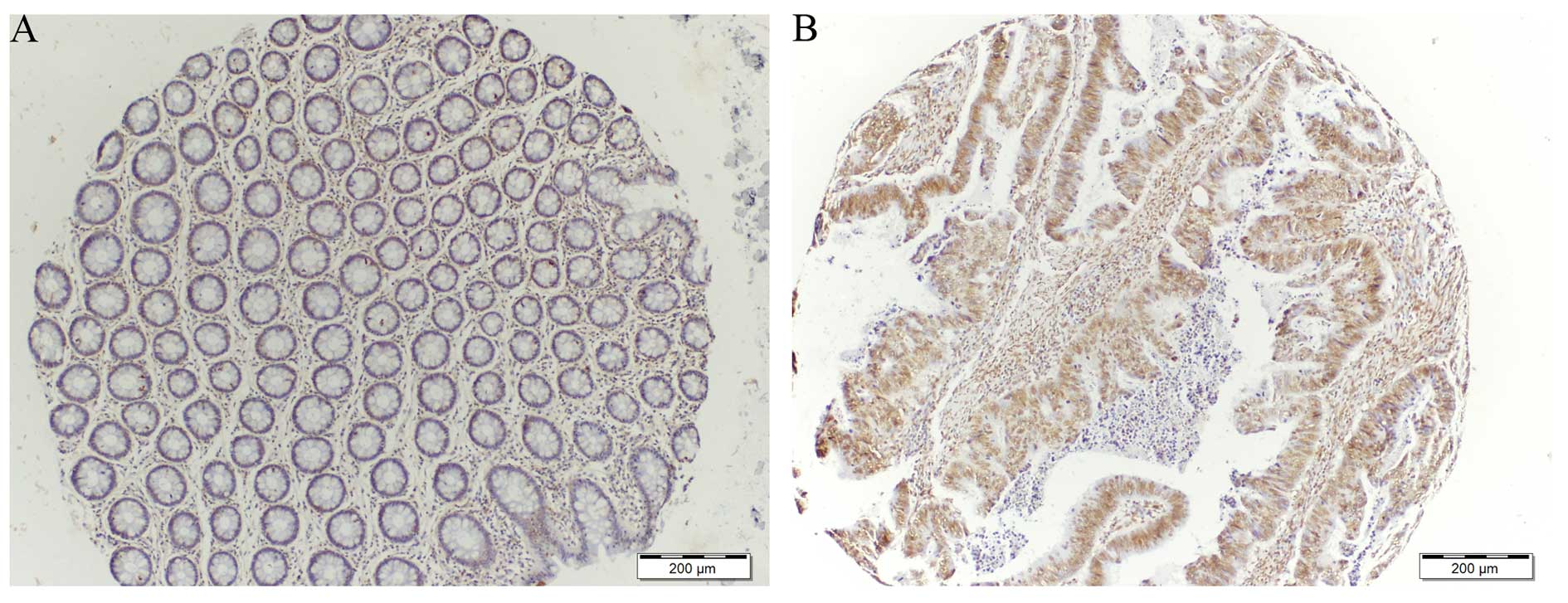
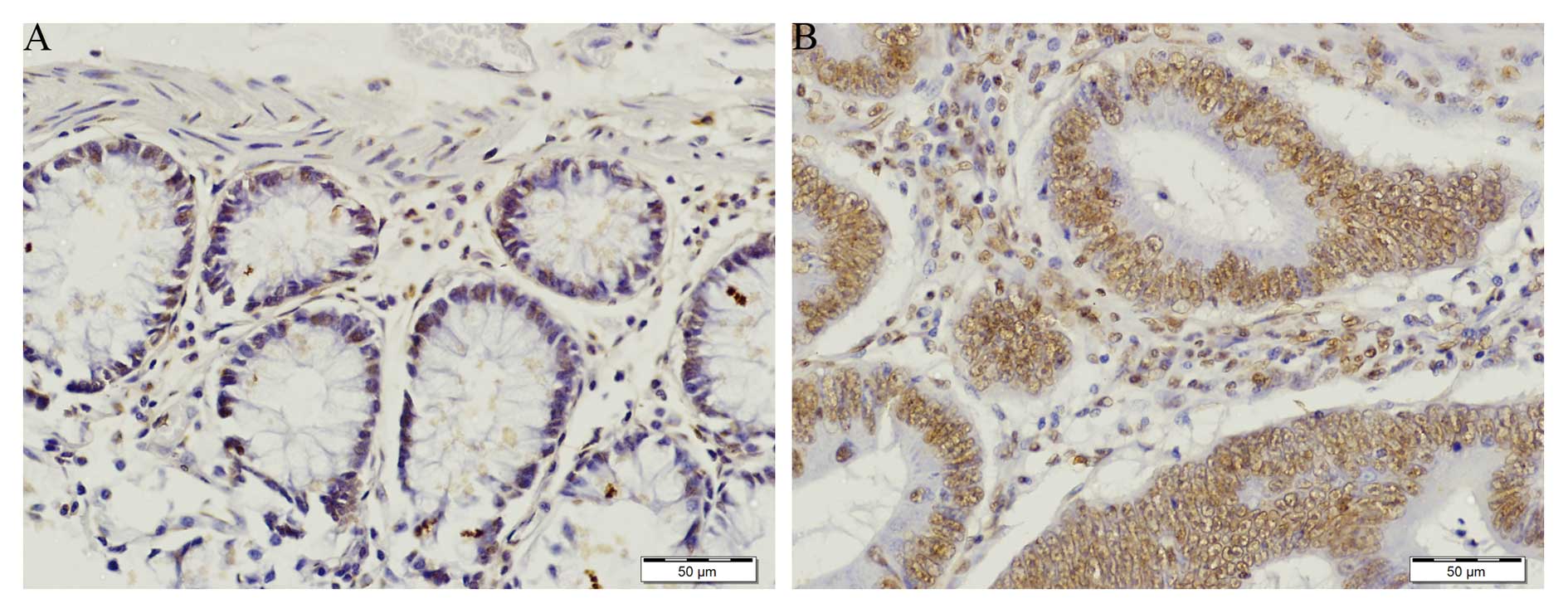
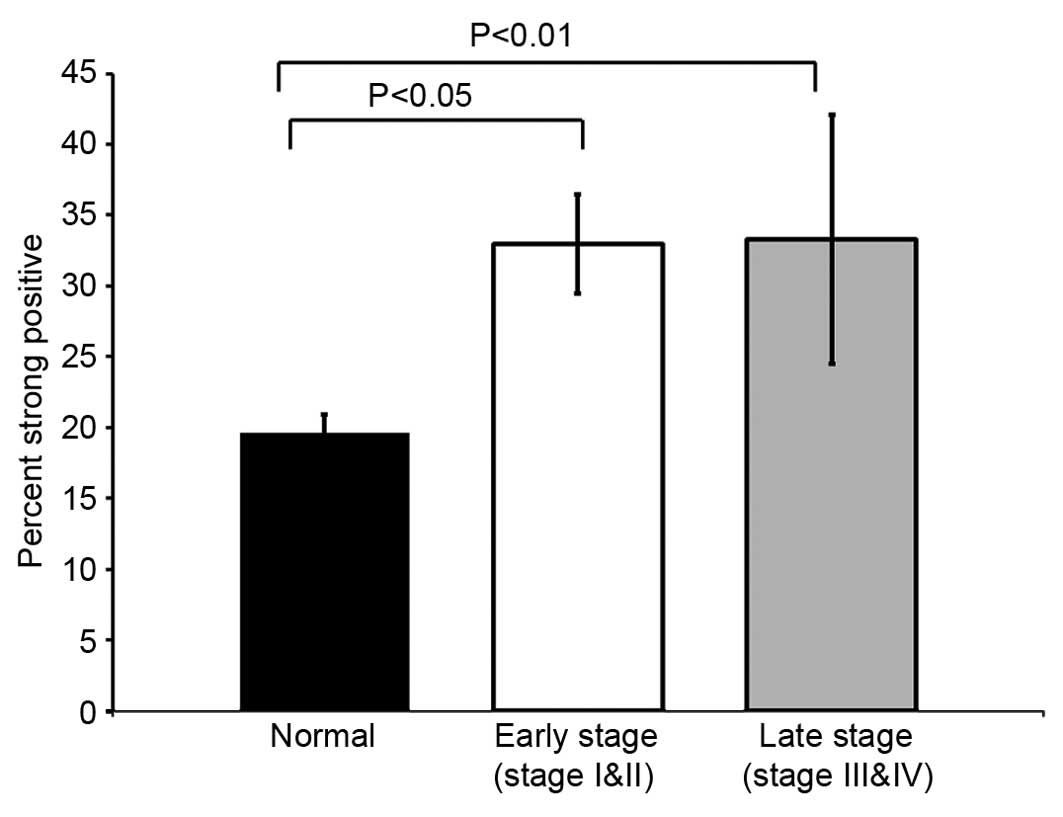
|
1
|
Lao VV and Grady WM: Epigenetics and
colorectal cancer. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 8:686–700. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lin L, Piao J, Gao W, Piao Y, Jin G, Ma Y,
Li J and Lin Z: DEK over expression as an independent biomarker for
poor prognosis in colorectal cancer. BMC Cancer. 13:3662013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Pitule P, Vycital O, Bruha J, Novak P,
Hosek P, Treska V, Hlavata I, Soucek P, Kralickova M and Liska V:
Differential expression and prognostic role of selected genes in
colorectal cancer patients. Anticancer Res. 33:4855–4865.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Vousden KH and Lu X: Live or let die: The
cell's response to p53. Nat Rev Cancer. 2:594–604. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Jen KY and Cheung VG: Identification of
novel p53 target genes in ionizing radiation response. Cancer Res.
65:7666–7673. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bensaad K, Tsuruta A, Selak MA, Vidal MN,
Nakano K, Bartrons R, Gottlieb E and Vousden KH: TIGAR, a
p53-inducible regulator of glycolysis and apoptosis. Cell.
126:107–120. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kimata M, Matoba S, Iwai-Kanai E, Nakamura
H, Hoshino A, Nakaoka M, Katamura M, Okawa Y, Mita Y, Okigaki M, et
al: p53 and TIGAR regulate cardiac myocyte energy homeostasis under
hypoxic stress. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 299:H1908–H1916.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Peña-Rico MA, Calvo-Vidal MN,
Villalonga-Planells R, Martínez-Soler F, Giménez-Bonafé P,
Navarro-Sabaté À, Tortosa A, Bartrons R and Manzano A: TP53 induced
glycolysis and apoptosis regulator (TIGAR) knockdown results in
radio-sensitization of glioma cells. Radiother Oncol. 101:132–139.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Yin L, Kosugi M and Kufe D: Inhibition of
the MUC1-C oncoprotein induces multiple myeloma cell death by
down-regulating TIGAR expression and depleting NADPH. Blood.
119:810–816. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
10
|
Lui VW, Lau CP, Cheung CS, Ho K, Ng MH,
Cheng SH, Hong B, Tsao SW, Tsang CM, Lei KI, et al: An RNA-directed
nucleoside anti-metabolite,
1-(3-C-ethynyl-beta-d-ribo-pentofuranosyl) cytosine (ECyd), elicits
antitumor effect via TP53-induced glycolysis and apoptosis
regulator (TIGAR) downregulation. Biochem Pharmacol. 79:1772–1780.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wanka C, Steinbach JP and Rieger J:
Tp53-induced glycolysis and apoptosis regulator (TIGAR) protects
glioma cells from starvation-induced cell death by up-regulating
respiration and improving cellular redox homeostasis. J Biol Chem.
287:33436–33446. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ye L, Zhao X, Lu J, Qian G, Zheng JC and
Ge S: Knockdown of TIGAR by RNA interference induces apoptosis and
autophagy in HepG2 hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 437:300–306. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Cheung EC, Athineos D, Lee P, Ridgway RA,
Lambie W, Nixon C, Strathdee D, Blyth K, Sansom OJ and Vousden KH:
TIGAR is required for efficient intestinal regeneration and
tumorigenesis. Dev Cell. 25:463–477. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Cooper HS, Murthy SN, Shah RS and
Sedergran DJ: Clinicopathologic study of dextran sulfate sodium
experimental murine colitis. Lab Invest. 69:238–249.
1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Won KY, Lim SJ, Kim GY, Kim YW, Han SA,
Song JY and Lee DK: Regulatory role of p53 in cancer metabolism via
SCO2 and TIGAR in human breast cancer. Hum Pathol. 43:221–228.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Sinha S, Ghildiyal R, Mehta VS and Sen E:
ATM-NFκB axis-driven TIGAR regulates sensitivity of glioma cells to
radiomimetics in the presence of TNFα. Cell Death Dis. 4:e6152013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Lui VW, Wong EY, Ho K, Ng PK, Lau CP, Tsui
SK, Tsang CM, Tsao SW, Cheng SH, Ng MH, et al: Inhibition of c-Met
down-regulates TIGAR expression and reduces NADPH production
leading to cell death. Oncogene. 30:1127–1134. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Barker N, Ridgway RA, van Es JH, van de
Wetering M, Begthel H, van den Born M, Danenberg E, Clarke AR,
Sansom OJ and Clevers H: Crypt stem cells as the cells-of-origin of
intestinal cancer. Nature. 457:608–611. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Rimm DL, Camp RL, Charette LA, Costa J,
Olsen DA and Reiss M: Tissue microarray: A new technology for
amplification of tissue resources. Cancer J. 7:24–31.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Bu XD, Li N, Tian XQ, Li L, Wang JS, Yu XJ
and Huang PL: Altered expression of MUC2 and MUC5AC in progression
of colorectal carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 16:4089–4094. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Alam M, Rajabi H, Ahmad R, Jin C and Kufe
D: Targeting the MUC1-C oncoprotein inhibits self-renewal capacity
of breast cancer cells. Oncotarget. 5:2622–2634. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ahmad R, Raina D, Trivedi V, Ren J, Rajabi
H, Kharbanda S and Kufe D: MUC1 oncoprotein activates the IkappaB
kinase beta complex and constitutive NF-kappaB signalling. Nat Cell
Biol. 9:1419–1427. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Vogelstein B, Lane D and Levine AJ:
Surfing the p53 network. Nature. 408:307–310. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Matoba S, Kang JG, Patino WD, Wragg A,
Boehm M, Gavrilova O, Hurley PJ, Bunz F and Hwang PM: p53 regulates
mitochondrial respiration. Science. 312:1650–1653. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Budanov AV, Sablina AA, Feinstein E,
Koonin EV and Chumakov PM: Regeneration of peroxiredoxins by
p53-regulated sestrins, homologs of bacterial AhpD. Science.
304:596–600. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Cosentino C, Grieco D and Costanzo V: ATM
activates the pentose phosphate pathway promoting anti-oxidant
defence and DNA repair. EMBO J. 30:546–555. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|