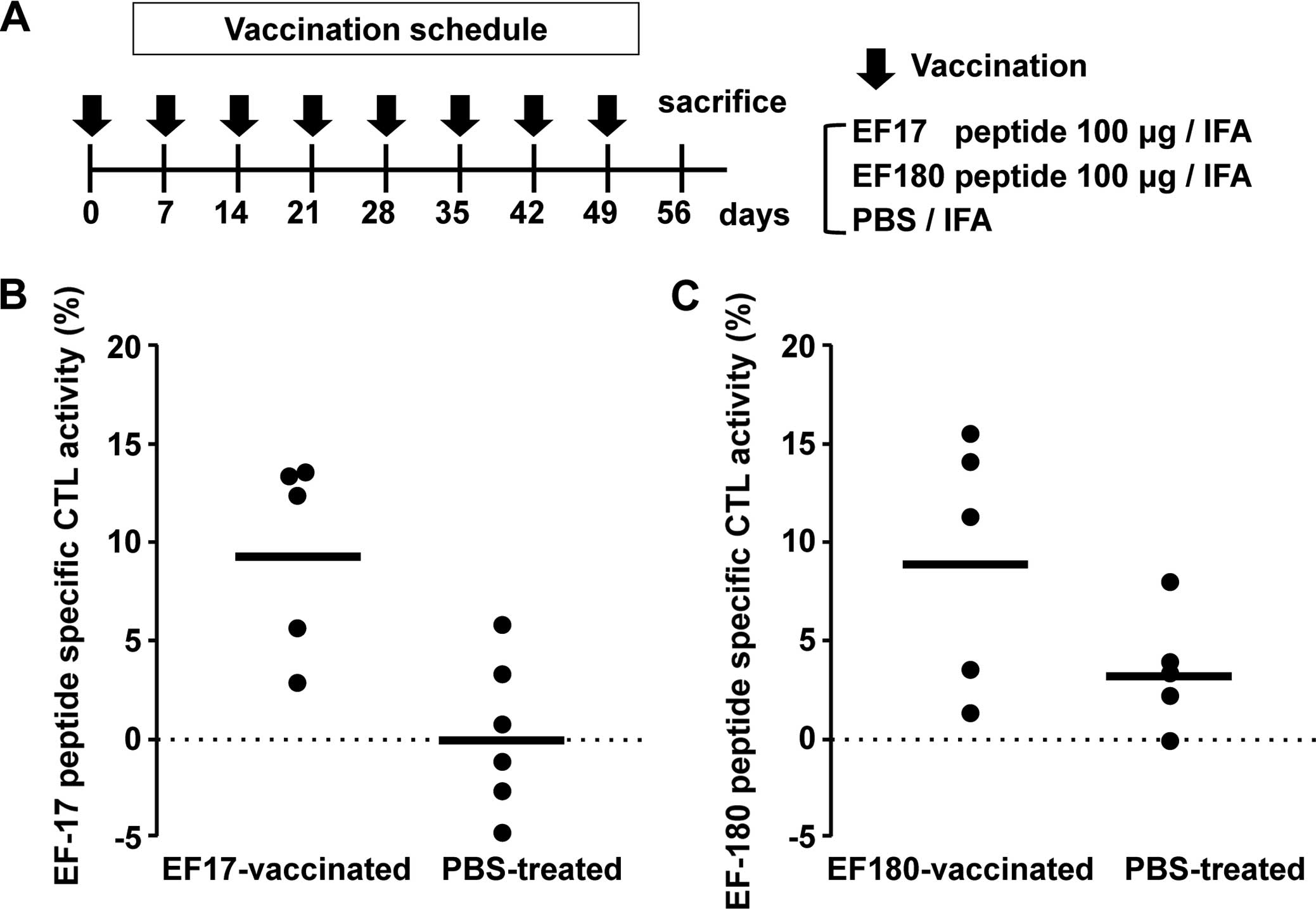
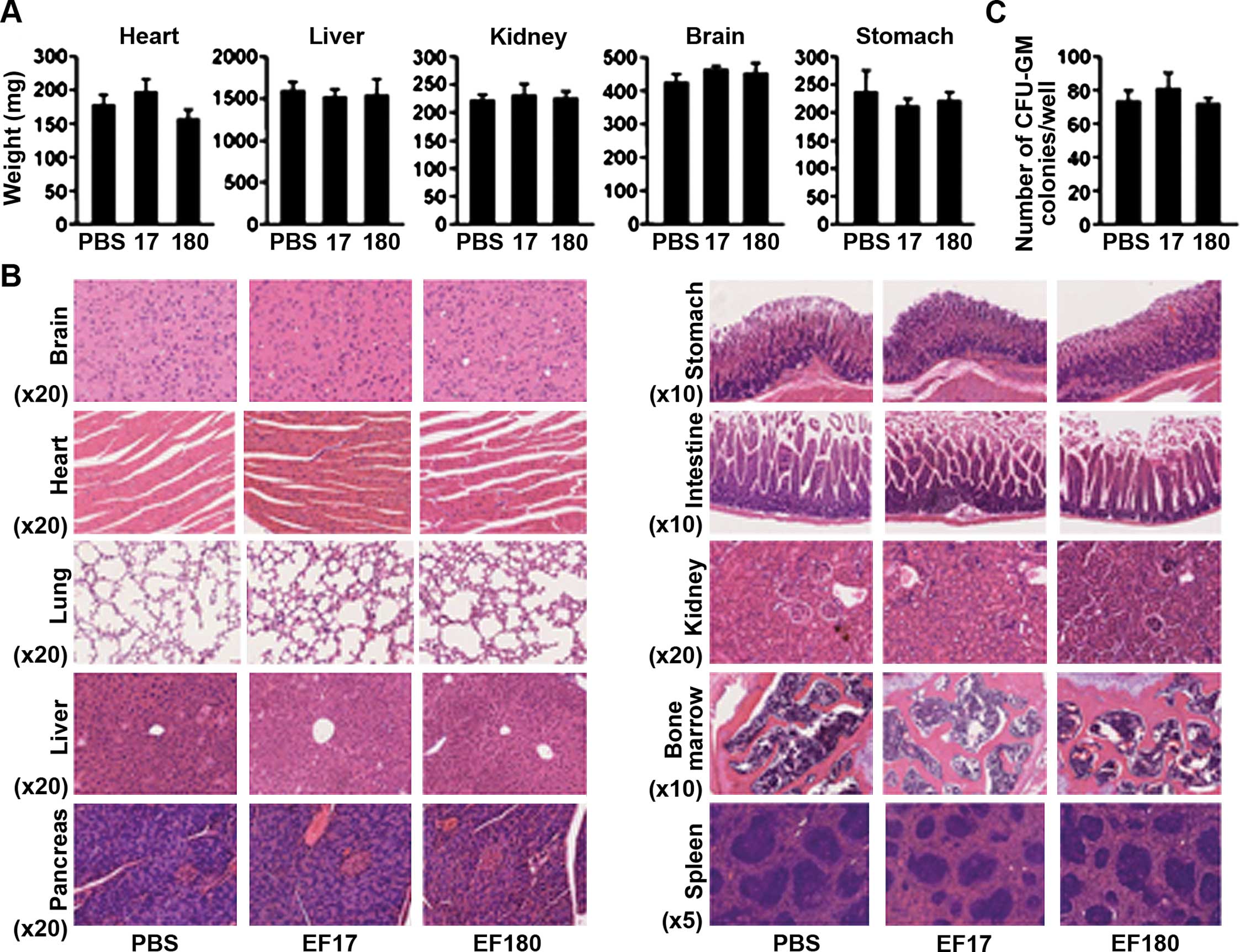
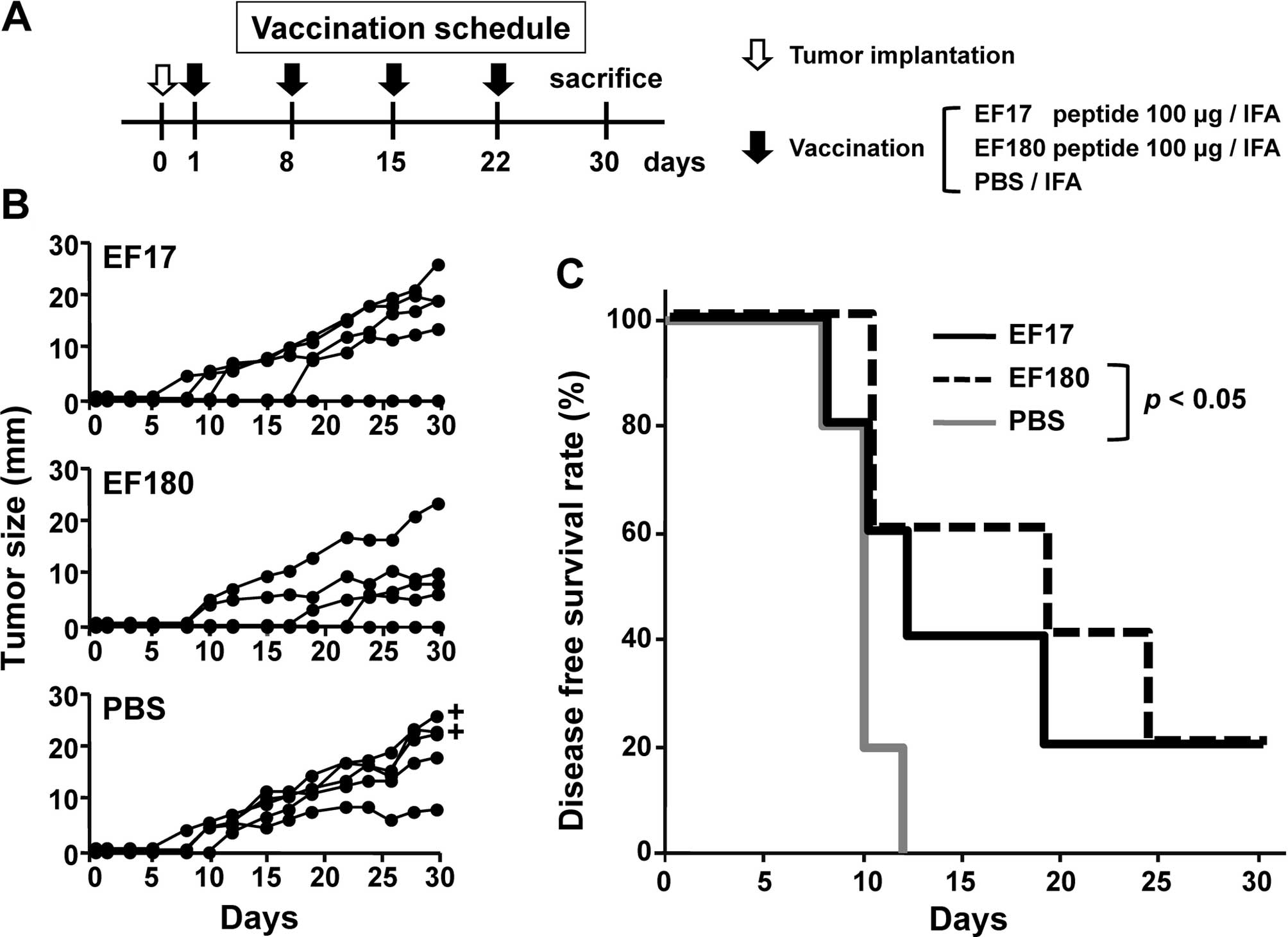
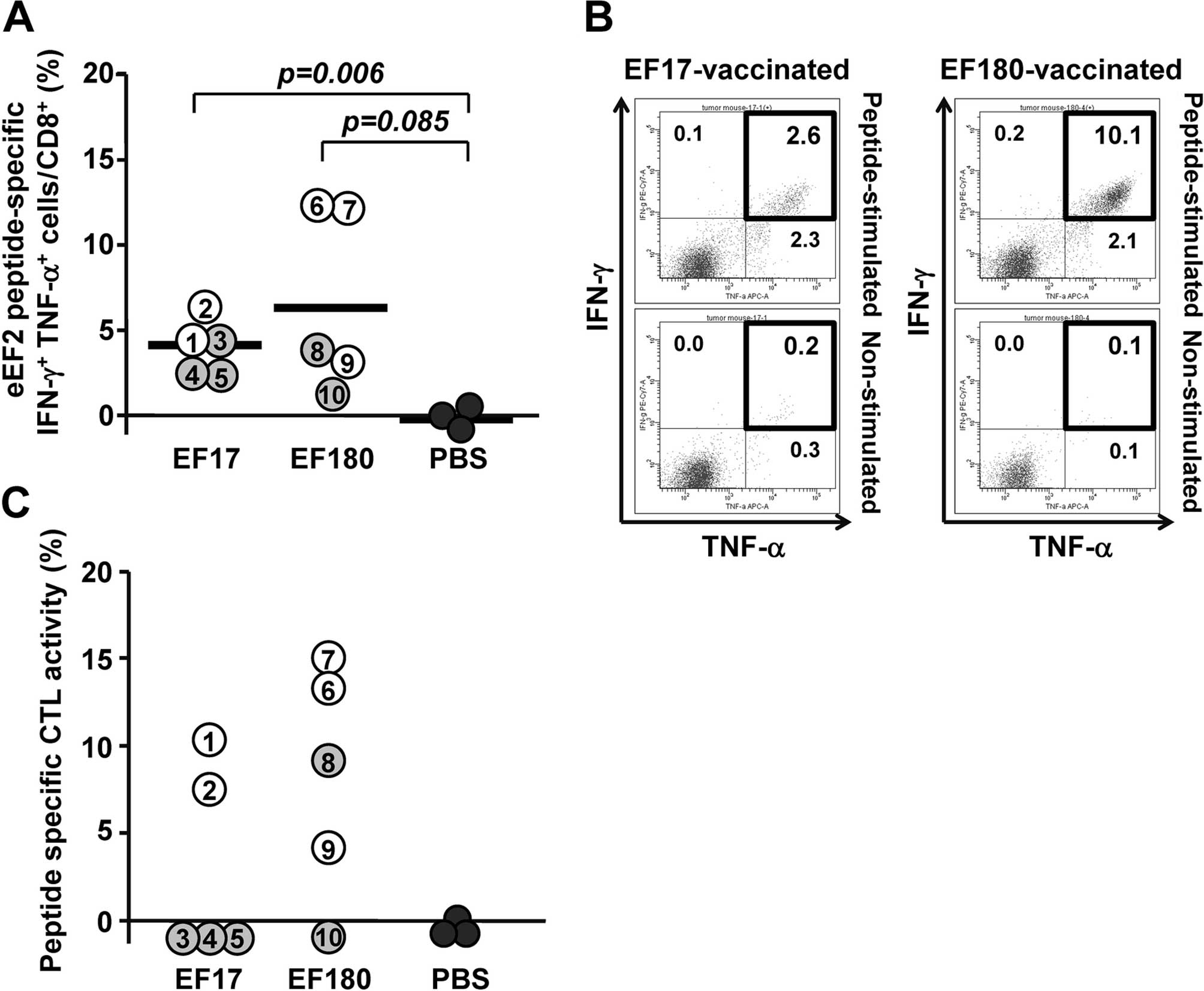
|
1
|
Madorsky Rowdo FP, Baron A, Urrutia M and
Mordoh J: Immunotherapy in cancer: A combat between tumors and the
immune system; you win some, you lose some. Front Immunol.
6:1272015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ott PA, Hodi FS and Robert C: CTLA-4 and
PD-1/PD-L1 blockade: New immunotherapeutic modalities with durable
clinical benefit in melanoma patients. Clin Cancer Res.
19:5300–5309. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Cranmer LD and Hersh E: The role of the
CTLA4 blockade in the treatment of malignant melanoma. Cancer
Invest. 25:613–631. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sarnaik AA and Weber JS: Recent advances
using anti-CTLA-4 for the treatment of melanoma. Cancer J.
15:169–173. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Tsai KK, Zarzoso I and Daud AI: PD-1 and
PD-L1 antibodies for melanoma. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 10:3111–3116.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Anagnostou VK and Brahmer JR: Cancer
immunotherapy: A future paradigm shift in the treatment of
non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 21:976–984. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Guibert N, Delaunay M and Mazières J:
Targeting the immune system to treat lung cancer: Rationale and
clinical experience. Ther Adv Respir Dis. 9:105–120. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Monjazeb AM, Zamora AE, Grossenbacher SK,
Mirsoian A, Sckisel GD and Murphy WJ: Immunoediting and antigen
loss: Overcoming the achilles heel of immunotherapy with antigen
non-specific therapies. Front Oncol. 3:1972013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kim JE and Lim M: The role of checkpoints
in the treatment of GBM. J Neurooncol. 123:413–423. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Howell M, Lee R, Bowyer S, Fusi A and
Lorigan P: Optimal management of immune-related toxicities
associated with check-point inhibitors in lung cancer. Lung Cancer.
88:117–123. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Spahn CM, Gomez-Lorenzo MG, Grassucci RA,
Jørgensen R, Andersen GR, Beckmann R, Penczek PA, Ballesta JP and
Frank J: Domain movements of elongation factor eEF2 and the
eukaryotic 80S ribosome facilitate tRNA translocation. EMBO J.
23:1008–1019. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Taylor DJ, Nilsson J, Merrill AR, Andersen
GR, Nissen P and Frank J: Structures of modified eEF2 80S ribosome
complexes reveal the role of GTP hydrolysis in translocation. EMBO
J. 26:2421–2431. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Redpath NT, Price NT, Severinov KV and
Proud CG: Regulation of elongation factor-2 by multisite
phosphorylation. Eur J Biochem. 213:689–699. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Carlberg U, Nilsson A and Nygård O:
Functional properties of phosphorylated elongation factor 2. Eur J
Biochem. 191:639–645. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Gismondi A, Caldarola S, Lisi G, Juli G,
Chellini L, Iadevaia V, Proud CG and Loreni F: Ribosomal stress
activates eEF2K-eEF2 pathway causing translation elongation
inhibition and recruitment of terminal oligopyrimidine (TOP) mRNAs
on polysomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 42:12668–12680. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kenney JW, Moore CE, Wang X and Proud CG:
Eukaryotic elongation factor 2 kinase, an unusual enzyme with
multiple roles. Adv Biol Regul. 55:15–27. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Verpelli C, Piccoli G, Zibetti C, Zanchi
A, Gardoni F, Huang K, Brambilla D, Di Luca M, Battaglioli E and
Sala C: Synaptic activity controls dendritic spine morphology by
modulating eEF2-dependent BDNF synthesis. J Neurosci. 30:5830–5842.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Belelovsky K, Elkobi A, Kaphzan H, Nairn
AC and Rosenblum K: A molecular switch for translational control in
taste memory consolidation. Eur J Neurosci. 22:2560–2568. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Im HI, Nakajima A, Gong B, Xiong X, Mamiya
T, Gershon ES, Zhuo M and Tang YP: Post-training dephosphorylation
of eEF-2 promotes protein synthesis for memory consolidation. PLoS
One. 4:e74242009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Leprivier G, Remke M, Rotblat B, Dubuc A,
Mateo AR, Kool M, Agnihotri S, El-Naggar A, Yu B, Somasekharan SP,
et al: The eEF2 kinase confers resistance to nutrient deprivation
by blocking translation elongation. Cell. 153:1064–1079. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang X, Regufe da Mota S, Liu R, Moore CE,
Xie J, Lanucara F, Agarwala U, Pyr Dit Ruys S, Vertommen D, Rider
MH, et al: Eukaryotic elongation factor 2 kinase activity is
controlled by multiple inputs from oncogenic signaling. Mol Cell
Biol. 34:4088–4103. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Nakamura J, Aoyagi S, Nanchi I, Nakatsuka
S, Hirata E, Shibata S, Fukuda M, Yamamoto Y, Fukuda I, Tatsumi N,
et al: Overexpression of eukaryotic elongation factor eEF2 in
gastrointestinal cancers and its involvement in G2/M progression in
the cell cycle. Int J Oncol. 34:1181–1189. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Oji Y, Tatsumi N, Fukuda M, Nakatsuka S,
Aoyagi S, Hirata E, Nanchi I, Fujiki F, Nakajima H, Yamamoto Y, et
al: The translation elongation factor eEF2 is a novel
tumor-associated antigen overexpressed in various types of cancers.
Int J Oncol. 44:1461–1469. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Oka Y, Udaka K, Tsuboi A, Elisseeva OA,
Ogawa H, Aozasa K, Kishimoto T and Sugiyama H: Cancer immunotherapy
targeting Wilms' tumor gene WT1 product. J Immunol. 164:1873–1880.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Nakajima H, Oka Y, Tsuboi A, Tatsumi N,
Yamamoto Y, Fujiki F, Li Z, Murao A, Morimoto S, Hosen N, et al:
Enhanced tumor immunity of WT1 peptide vaccination by interferon-β
administration. Vaccine. 30:722–729. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Liu G, Ying H, Zeng G, Wheeler CJ, Black
KL and Yu JS: HER-2, gp100, and MAGE-1 are expressed in human
glioblastoma and recognized by cytotoxic T cells. Cancer Res.
64:4980–4986. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Riker AI, Kammula US, Panelli MC, Wang E,
Ohnmacht GA, Steinberg SM, Rosenberg SA and Marincola FM: Threshold
levels of gene expression of the melanoma antigen gp100 correlate
with tumor cell recognition by cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Int J
Cancer. 86:818–826. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Budhu S, Wolchok J and Merghoub T: The
importance of animal models in tumor immunity and immunotherapy.
Curr Opin Genet Dev. 24:46–51. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hunder NN, Wallen H, Cao J, Hendricks DW,
Reilly JZ, Rodmyre R, Jungbluth A, Gnjatic S, Thompson JA and Yee
C: Treatment of metastatic melanoma with autologous CD4+
T cells against NY-ESO-1. N Engl J Med. 358:2698–2703. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Fujiki F, Oka Y, Kawakatsu M, Tsuboi A,
Tanaka-Harada Y, Hosen N, Nishida S, Shirakata T, Nakajima H,
Tatsumi N, et al: A clear correlation between WT1-specific Th
response and clinical response in WT1 CTL epitope vaccination.
Anticancer Res. 30:2247–2254. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Topalian SL: MHC class II restricted tumor
antigens and the role of CD4+ T cells in cancer
immunotherapy. Curr Opin Immunol. 6:741–745. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Bourgeois C and Tanchot C: Mini-review CD4
T cells are required for CD8 T cell memory generation. Eur J
Immunol. 33:3225–3231. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ridge JP, Di Rosa F and Matzinger P: A
conditioned dendritic cell can be a temporal bridge between a
CD4+ T-helper and a T-killer cell. Nature. 393:474–478.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Fujiki F, Oka Y, Tsuboi A, Kawakami M,
Kawakatsu M, Nakajima H, Elisseeva OA, Harada Y, Ito K, Li Z, et
al: Identification and characterization of a WT1 (Wilms Tumor Gene)
protein-derived HLA-DRB1*0405-restricted 16-mer helper
peptide that promotes the induction and activation of WT1-specific
cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Immunother. 30:282–293. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Fujiki F, Oka Y, Kawakatsu M, Tsuboi A,
Nakajima H, Elisseeva OA, Harada Y, Li Z, Tatsumi N, Kamino E, et
al: A WT1 protein-derived, naturally processed 16-mer peptide, WT1,
is a promiscuous helper peptide for induction of WT1-specific 332
Th1-type CD4+ T cells. Microbiol Immunol. 52:591–600.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Shedlock DJ and Shen H: Requirement for
CD4 T cell help in generating functional CD8 T cell memory.
Science. 300:337–339. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Janssen EM, Lemmens EE, Wolfe T, Christen
U, von Herrath MG and Schoenberger SP: CD4+ T cells are
required for secondary expansion and memory in CD8+ T
lymphocytes. Nature. 421:852–856. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Quezada SA, Simpson TR, Peggs KS, Merghoub
T, Vider J, Fan X, Blasberg R, Yagita H, Muranski P, Antony PA, et
al: Tumor-reactive CD4+ T cells develop cytotoxic
activity and eradicate large established melanoma after transfer
into lymphopenic hosts. J Exp Med. 207:637–650. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lin Y, Fujiki F, Katsuhara A, Oka Y,
Tsuboi A, Aoyama N, Tanii S, Nakajima H, Tatsumi N, Morimoto S, et
al: HLA-DPB1*05: 01-restricted WT1332-specific
TCR-transduced CD4+ T lymphocytes display a helper
activity for WT1-specific CTL induction and a cytotoxicity against
leukemia cells. J Immunother. 36:159–170. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|