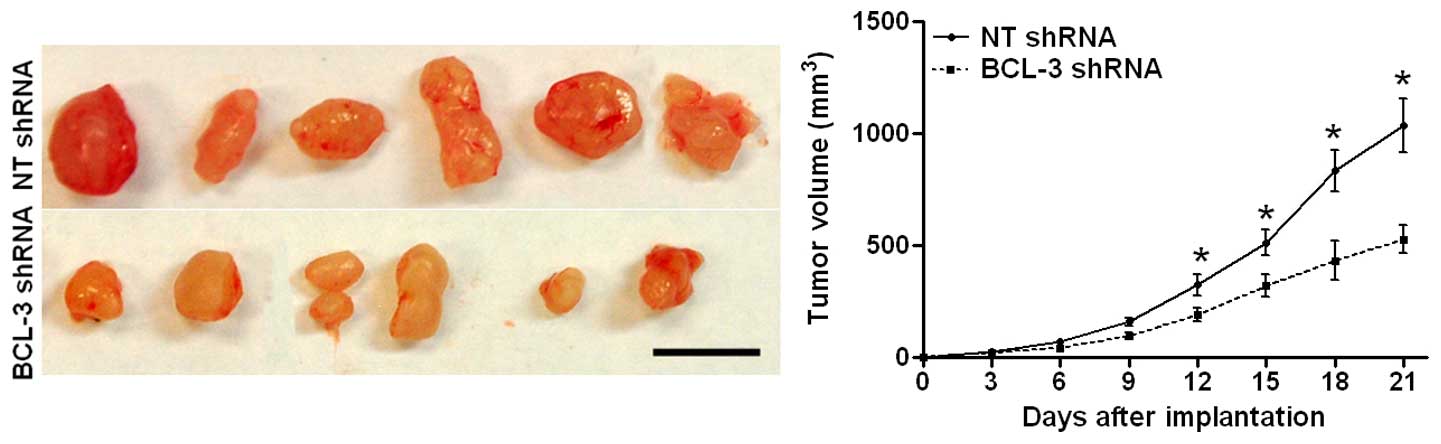
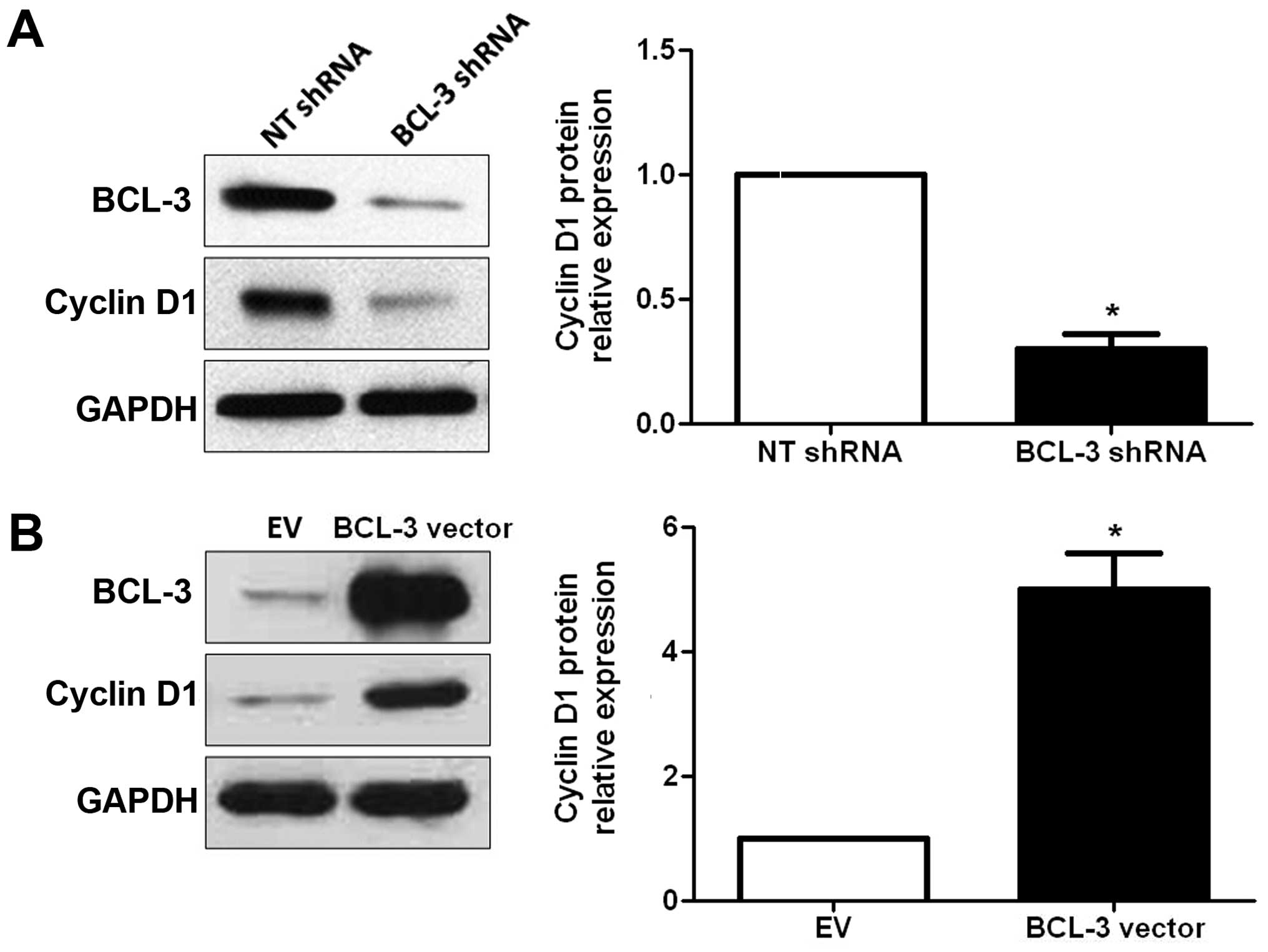
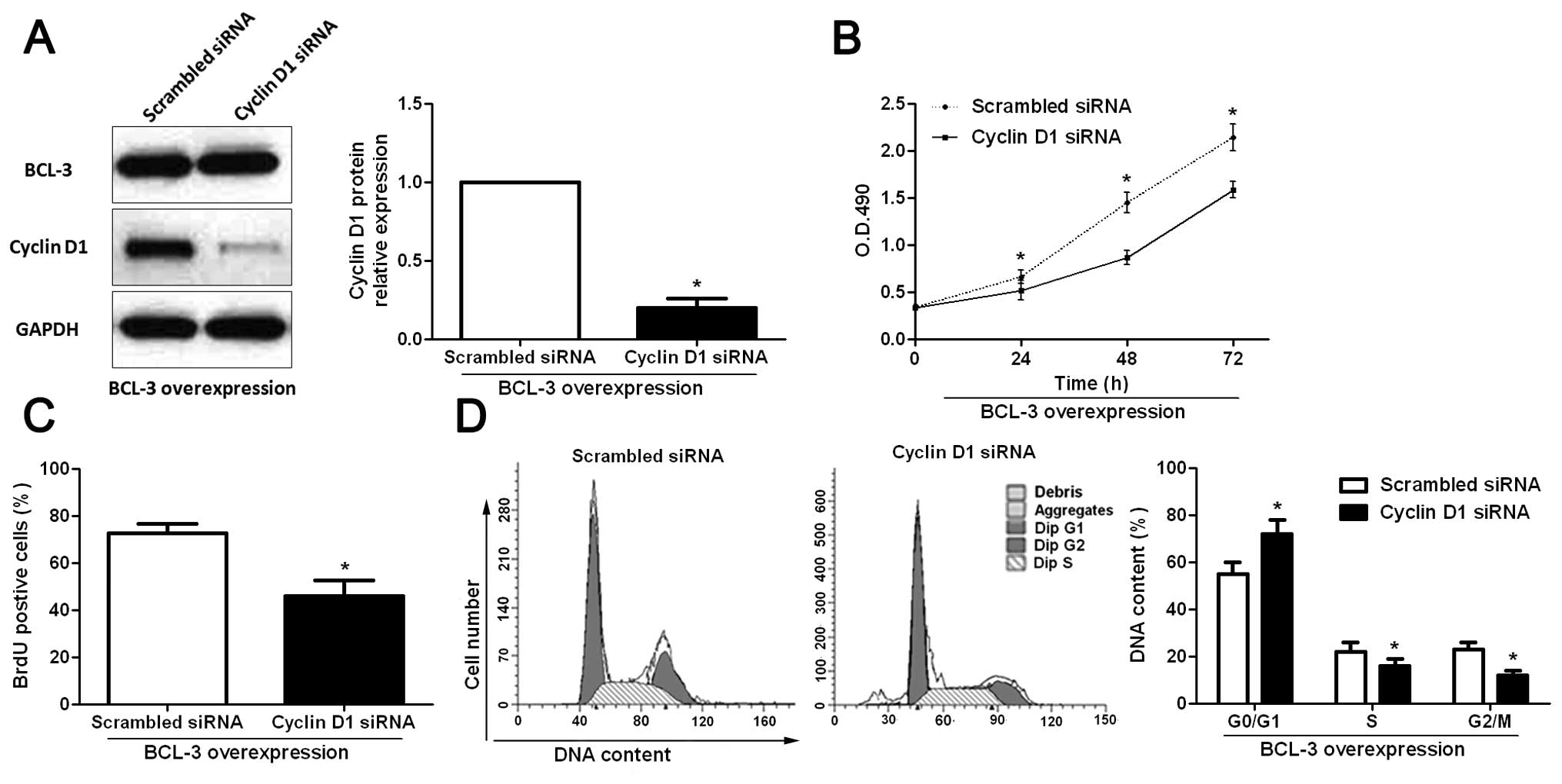
|
1
|
Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D,
Mathers C and Parkin DM: Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in
2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 127:2893–2917. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Forner A, Llovet JM and Bruix J:
Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 379:1245–1255. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kim SH, Choi SB, Lee JG, Kim SU, Park MS,
Kim do Y, Choi JS and Kim KS: Prognostic factors and 10-year
survival in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma after curative
hepatectomy. J Gastrointest Surg. 15:598–607. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hanazaki K, Kajikawa S, Shimozawa N,
Mihara M, Shimada K, Hiraguri M, Koide N, Adachi W and Amano J:
Survival and recurrence after hepatic resection of 386 consecutive
patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. J Am Coll Surg.
191:381–388. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bours V, Franzoso G, Azarenko V, Park S,
Kanno T, Brown K and Siebenlist U: The oncoprotein Bcl-3 directly
transactivates through kappa B motifs via association with
DNA-binding p50B homodimers. Cell. 72:729–739. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cogswell PC, Guttridge DC, Funkhouser WK
and Baldwin AS Jr: Selective activation of NF-kappa B subunits in
human breast cancer: Potential roles for NF-kappa B2/p52 and for
Bcl-3. Oncogene. 19:1123–1131. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Au WY, Horsman DE, Ohno H, Klasa RJ and
Gascoyne RD: Bcl-3/IgH translocation (14;19)(q32;q13) in
non-Hodgkin's lymphomas. Leuk Lymphoma. 43:813–816. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Canoz O, Rassidakis GZ, Admirand JH and
Medeiros LJ: Immunohistochemical detection of BCL-3 in lymphoid
neoplasms: A survey of 353 cases. Mod Pathol. 17:911–917. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Schlette E, Rassidakis GZ, Canoz O and
Medeiros LJ: Expression of bcl-3 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia
correlates with trisomy 12 and abnormalities of chromosome 19. Am J
Clin Pathol. 123:465–471. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Maldonado V and Melendez-Zajgla J: Role of
Bcl-3 in solid tumors. Mol Cancer. 10:1522011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Choi HJ, Lee JM, Kim H, Nam HJ, Shin HJ,
Kim D, Ko E, Noh DY, Kim KI, Kim JH, et al: Bcl3-dependent
stabilization of CtBP1 is crucial for the inhibition of apoptosis
and tumor progression in breast cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
400:396–402. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Thornburg NJ, Pathmanathan R and
Raab-Traub N: Activation of nuclear factor-kappaB p50
homodimer/Bcl-3 complexes in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Res.
63:8293–8301. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Pallares J, Martínez-Guitarte JL, Dolcet
X, Llobet D, Rue M, Palacios J, Prat J and Matias-Guiu X:
Abnormalities in the NF-kappaB family and related proteins in
endometrial carcinoma. J Pathol. 204:569–577. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Puvvada SD, Funkhouser WK, Greene K, Deal
A, Chu H, Baldwin AS, Tepper JE and O'Neil BH: NF-κB and Bcl-3
activation are prognostic in metastatic colorectal cancer.
Oncology. 78:181–188. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
15
|
Liu Z, Jiang Y, Hou Y, Hu Y, Cao X, Tao Y,
Xu C, Liu S, Wang S, Wang L, et al: The IκB family member Bcl-3
stabilizes c-Myc in colorectal cancer. J Mol Cell Biol. 5:280–282.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
de Souza Braga M, da Silva Paiva KB,
Foguer K, Barbosa Chaves KC, de Sá Lima L, Scavone C and Bellini
MH: Involvement of the NF-κB/p50/Bcl-3 complex in response to
antiangiogenic therapy in a mouse model of metastatic renal cell
carcinoma. Biomed Pharmacother. 68:873–879. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tu K, Yang W, Li C, Zheng X, Lu Z, Guo C,
Yao Y and Liu Q: Fbxw7 is an independent prognostic marker and
induces apoptosis and growth arrest by regulating YAP abundance in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Cancer. 13:1102014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Dou C, Wang Y, Li C, Liu Z, Jia Y, Li Q,
Yang W, Yao Y, Liu Q and Tu K: MicroRNA-212 suppresses tumor growth
of human hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting FOXA1. Oncotarget.
6:13216–13228. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Deane NG, Parker MA, Aramandla R, Diehl L,
Lee WJ, Washington MK, Nanney LB, Shyr Y and Beauchamp RD:
Hepatocellular carcinoma results from chronic cyclin D1
overexpression in transgenic mice. Cancer Res. 61:5389–5395.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Joo M, Kang YK, Kim MR, Lee HK and Jang
JJ: Cyclin D1 overexpression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver.
21:89–95. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Stacey DW: Cyclin D1 serves as a cell
cycle regulatory switch in actively proliferating cells. Curr Opin
Cell Biol. 15:158–163. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Severi T, van Malenstein H, Verslype C and
van Pelt JF: Tumor initiation and progression in hepatocellular
carcinoma: Risk factors, classification, and therapeutic targets.
Acta Pharmacol Sin. 31:1409–1420. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sun VC and Sarna L: Symptom management in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin J Oncol Nurs. 12:759–766. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Park SG, Chung C, Kang H, Kim JY and Jung
G: Up-regulation of cyclin D1 by HBx is mediated by NF-kappaB2/BCL3
complex through kappaB site of cyclin D1 promoter. J Biol Chem.
281:31770–31777. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Urban BC, Collard TJ, Eagle CJ, Southern
SL, Greenhough A, Hamdollah-Zadeh M, Ghosh A, Poulsom R, Paraskeva
C, Silver A, et al: BCL-3 expression promotes colorectal
tumorigenesis through activation of AKT signalling. Gut. Jun
1–2015.Epub ahead of print. piigutjnl-2014-308270. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Freiburghaus C, Janicke B,
Lindmark-Månsson H, Oredsson SM and Paulsson MA: Lactoferricin
treatment decreases the rate of cell proliferation of a human colon
cancer cell line. J Dairy Sci. 92:2477–2484. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zwijsen RM, Klompmaker R, Wientjens EB,
Kristel PM, van der Burg B and Michalides RJ: Cyclin D1 triggers
autonomous growth of breast cancer cells by governing cell cycle
exit. Mol Cell Biol. 16:2554–2560. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ahlqvist K, Saamarthy K, Syed Khaja AS,
Bjartell A and Massoumi R: Expression of Id proteins is regulated
by the Bcl-3 proto-oncogene in prostate cancer. Oncogene.
32:1601–1608. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|