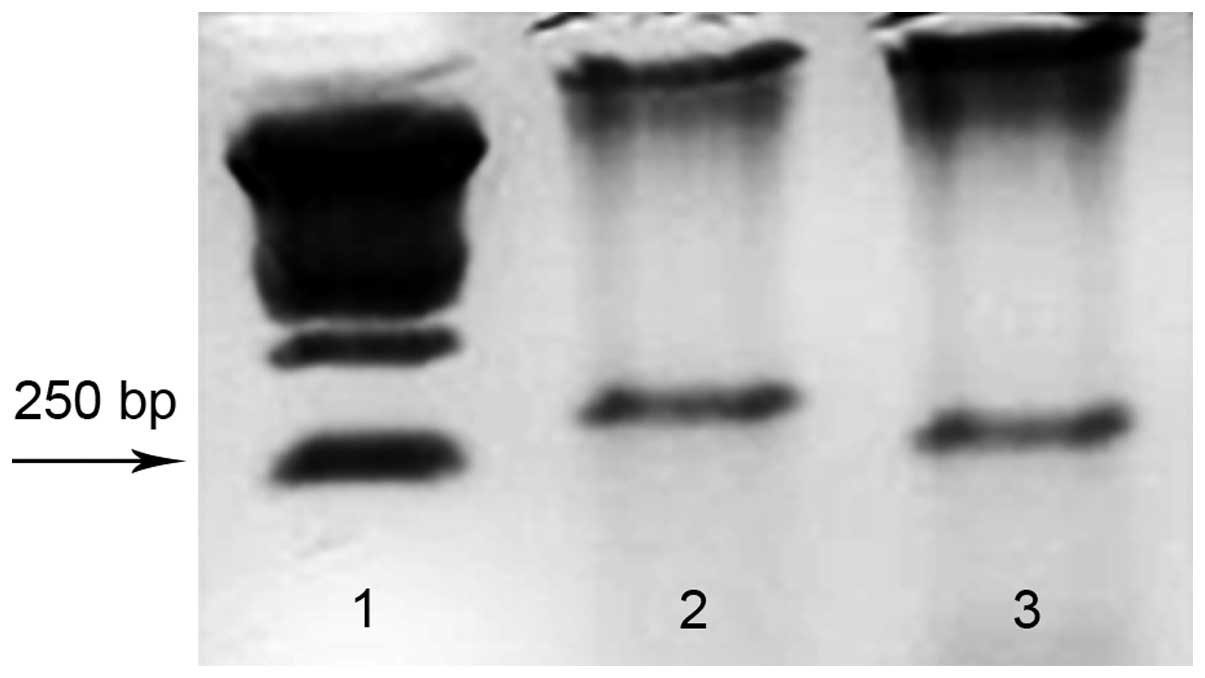
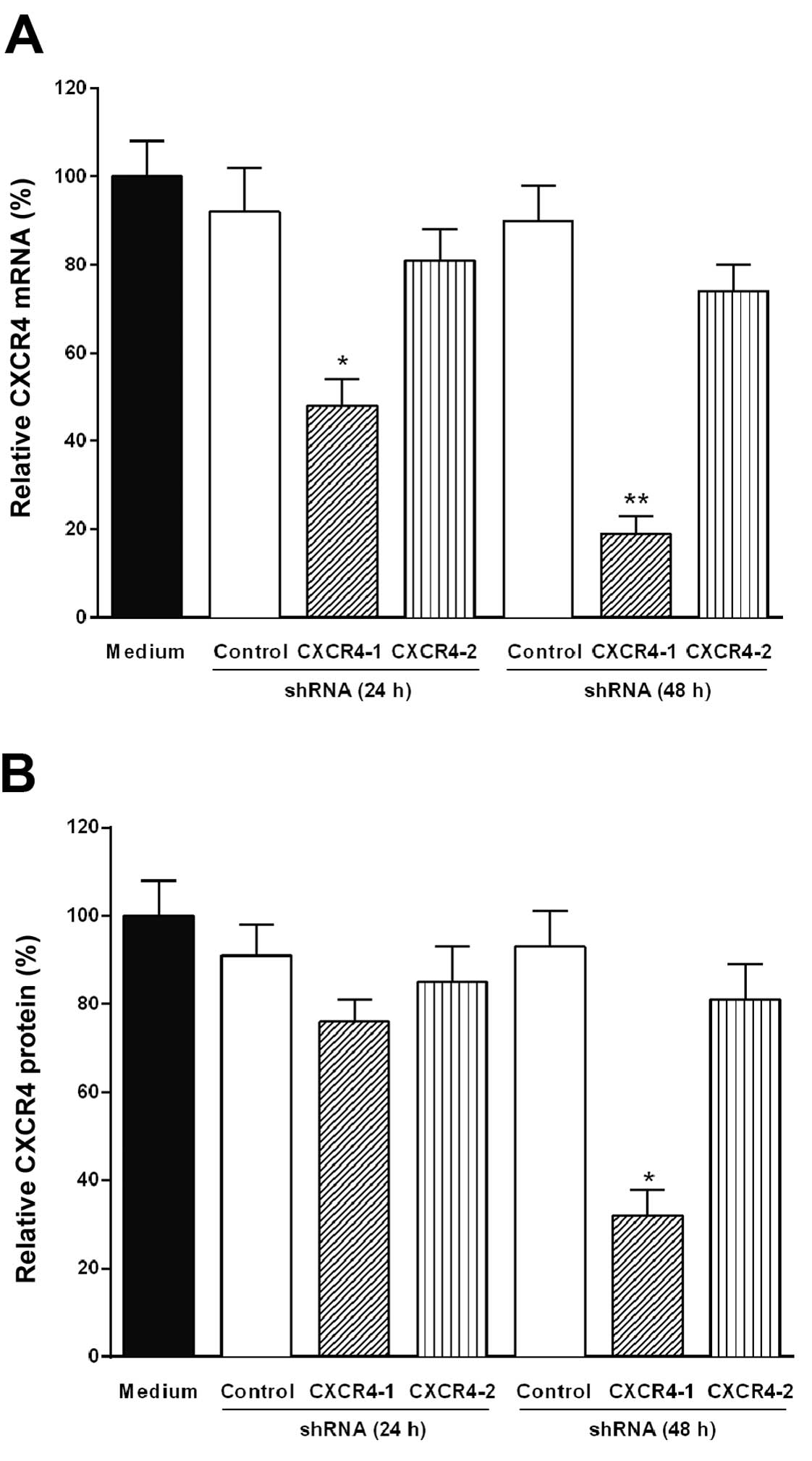
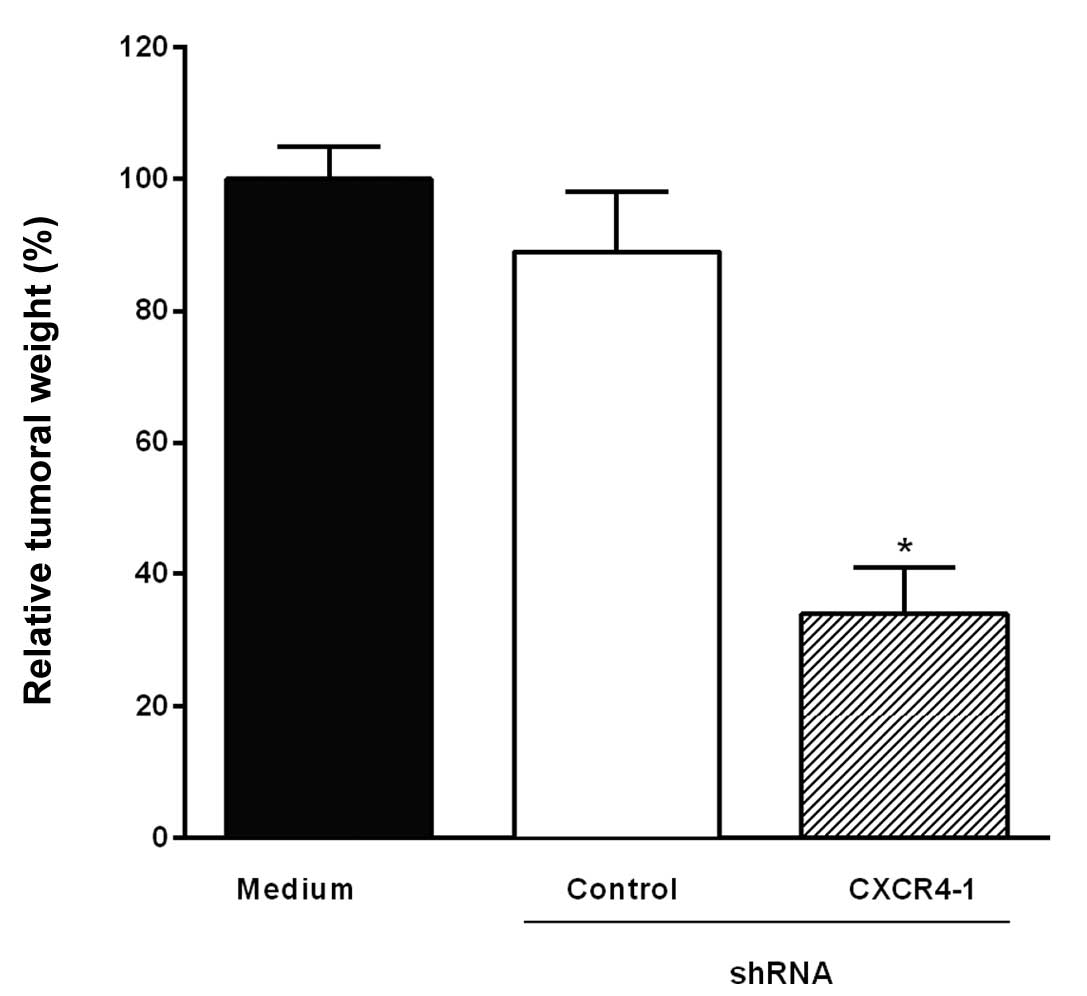
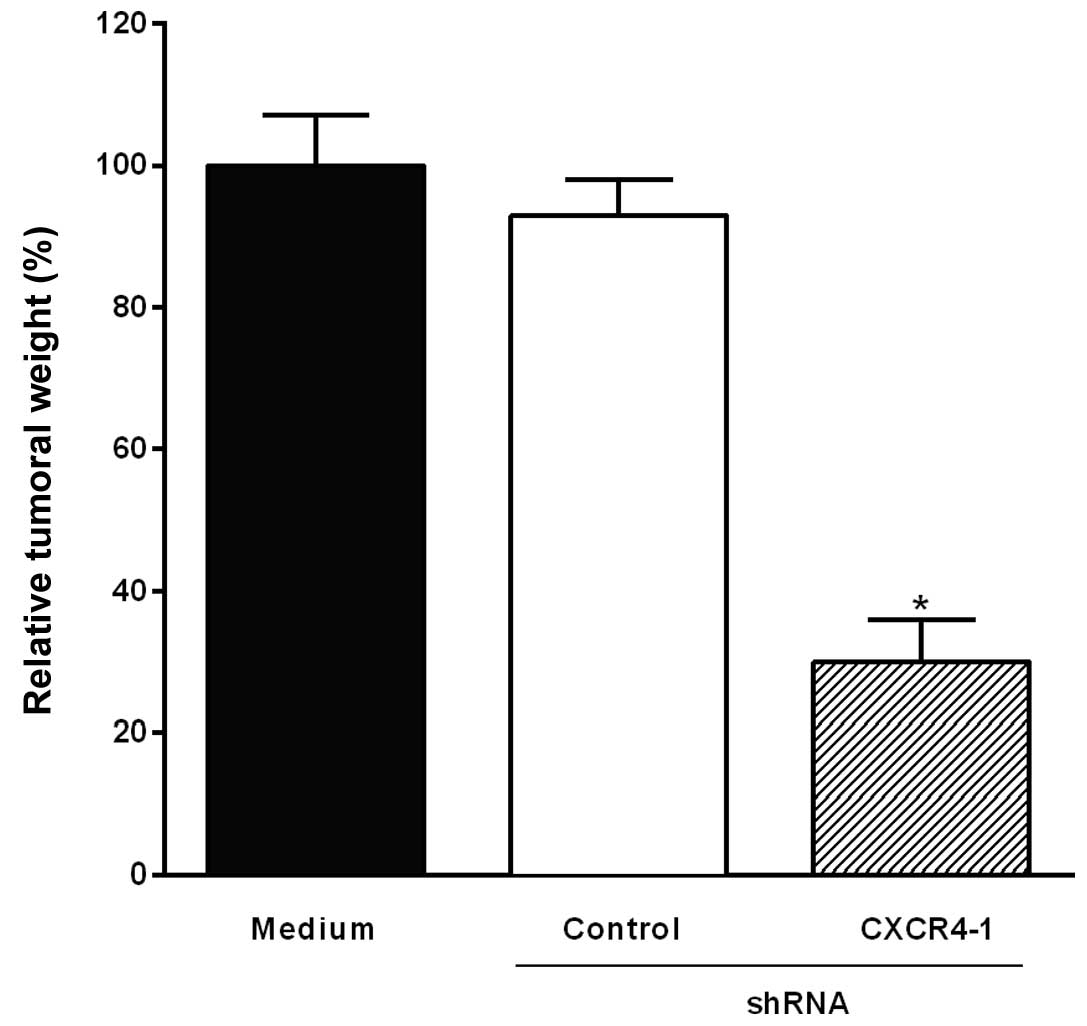
|
1
|
Murdoch C: CXCR4: Chemokine receptor
extraordinaire. Immunol Rev. 177:175–184. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Zlotnik A: Chemokines in neoplastic
progression. Semin Cancer Biol. 14:181–185. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Toyozawa S, Kaminaka C, Furukawa F,
Nakamura Y, Matsunaka H and Yamamoto Y: Chemokine receptor CXCR4 is
a novel marker for the progression of cutaneous malignant
melanomas. Acta Histochem Cytochem. 45:293–299. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Mitchell B, Leone D, Feller JK, Bondzie P,
Yang S, Park HY and Mahalingam M: Correlation of chemokine receptor
CXCR4 mRNA in primary cutaneous melanoma with established
histopathologic prognosticators and the BRAF status. Melanoma Res.
24:621–625. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Payne AS and Cornelius LA: The role of
chemokines in melanoma tumor growth and metastasis. J Invest
Dermatol. 118:915–922. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Longo-Imedio MI, Longo N, Treviño I,
Lázaro P and Sánchez-Mateos P: Clinical significance of CXCR3 and
CXCR4 expression in primary melanoma. Int J Cancer. 117:861–865.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Scala S, Ottaiano A, Ascierto PA, Cavalli
M, Simeone E, Giuliano P, Napolitano M, Franco R, Botti G and
Castello G: Expression of CXCR4 predicts poor prognosis in patients
with malignant melanoma. Clin Cancer Res. 11:1835–1841. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Scala S, Giuliano P, Ascierto PA, Ieranò
C, Franco R, Napolitano M, Ottaiano A, Lombardi ML, Luongo M,
Simeone E, et al: Human melanoma metastases express functional
CXCR4. Clin Cancer Res. 12:2427–2433. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Duda DG, Kozin SV, Kirkpatrick ND, Xu L,
Fukumura D and Jain RK: CXCL12 (SDF1α)-CXCR4/CXCR7 pathway
inhibition: An emerging sensitizer for anticancer therapies? Clin
Cancer Res. 17:2074–2080. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Fidler IJ: Biological behavior of
malignant melanoma cells correlated to their survival in vivo.
Cancer Res. 35:218–224. 1975.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
André ND, Silva VAO, Ariza CB, Watanabe
MAE and De Lucca FL: In vivo silencing of CXCR4 with jetPEI/CXCR4
shRNA nanoparticles inhibits pulmonary metastasis of B16-F10
melanoma cells. Mol Med Rep. 12:8320–8326. 2015.
|
|
12
|
Li Z, Li N, Wu M, Li X, Luo Z and Wang X:
Expression of miR-126 suppresses migration and invasion of colon
cancer cells by targeting CXCR4. Mol Cell Biochem. 381:233–242.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Díaz MR and Vivas-Mejia PE: Nanoparticles
as drug delivery systems in cancer medicine: Emphasis on
RNAi-containing nanoliposomes. Pharmaceuticals (Basel).
6:1361–1380. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Li CX, Parker A, Menocal E, Xiang S,
Borodyansky L and Fruehauf JH: Delivery of RNA interference. Cell
Cycle. 5:2103–2109. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sakurai Y, Hatakeyama H, Sato Y, Hyodo M,
Akita H and Harashima H: Gene silencing via RNAi and siRNA
quantification in tumor tissue using MEND, a liposomal siRNA
delivery system. Mol Ther. 21:1195–1203. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Deharvengt SJ, Gunn JR, Pickett SB and
Korc M: Intratumoral delivery of shRNA targeting cyclin D1
attenuates pancreatic cancer growth. Cancer Gene Ther. 17:325–333.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
17
|
André ND, Silva VAO, Watanabe MAE and De
Lucca FL: Intratumoral injection of PKR shRNA expressing plasmid
inhibits B16-F10 melanoma growth. Oncol Rep. 32:2267–2273.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kumar R, Yoneda J, Fidler IJ and Dong Z:
GM-CSF-transduced B16 melanoma cells are highly susceptible to
lysis by normal murine macrophages and poorly tumorigenic in
immune-compromised mice. J Leukoc Biol. 65:102–108. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Deng Y, Wang CC, Choy KW, Du Q, Chen J,
Wang Q, Li L, Chung TK and Tang T: Therapeutic potentials of gene
silencing by RNA interference: Principles, challenges, and new
strategies. Gene. 538:217–227. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li T, Wu M, Zhu YY, Chen J and Chen L:
Development of RNA interference-based therapeutics and application
of multi-target small interfering RNAs. Nucleic Acid Ther.
24:302–312. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chatterjee S, Behnam Azad B and Nimmagadda
S: The intricate role of CXCR4 in cancer. Adv Cancer Res.
124:31–82. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Heesen M, Berman MA, Benson JD, Gerard C
and Dorf ME: Cloning of the mouse fusin gene, homologue to a human
HIV-1 co-factor. J Immunol. 157:5455–5460. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|