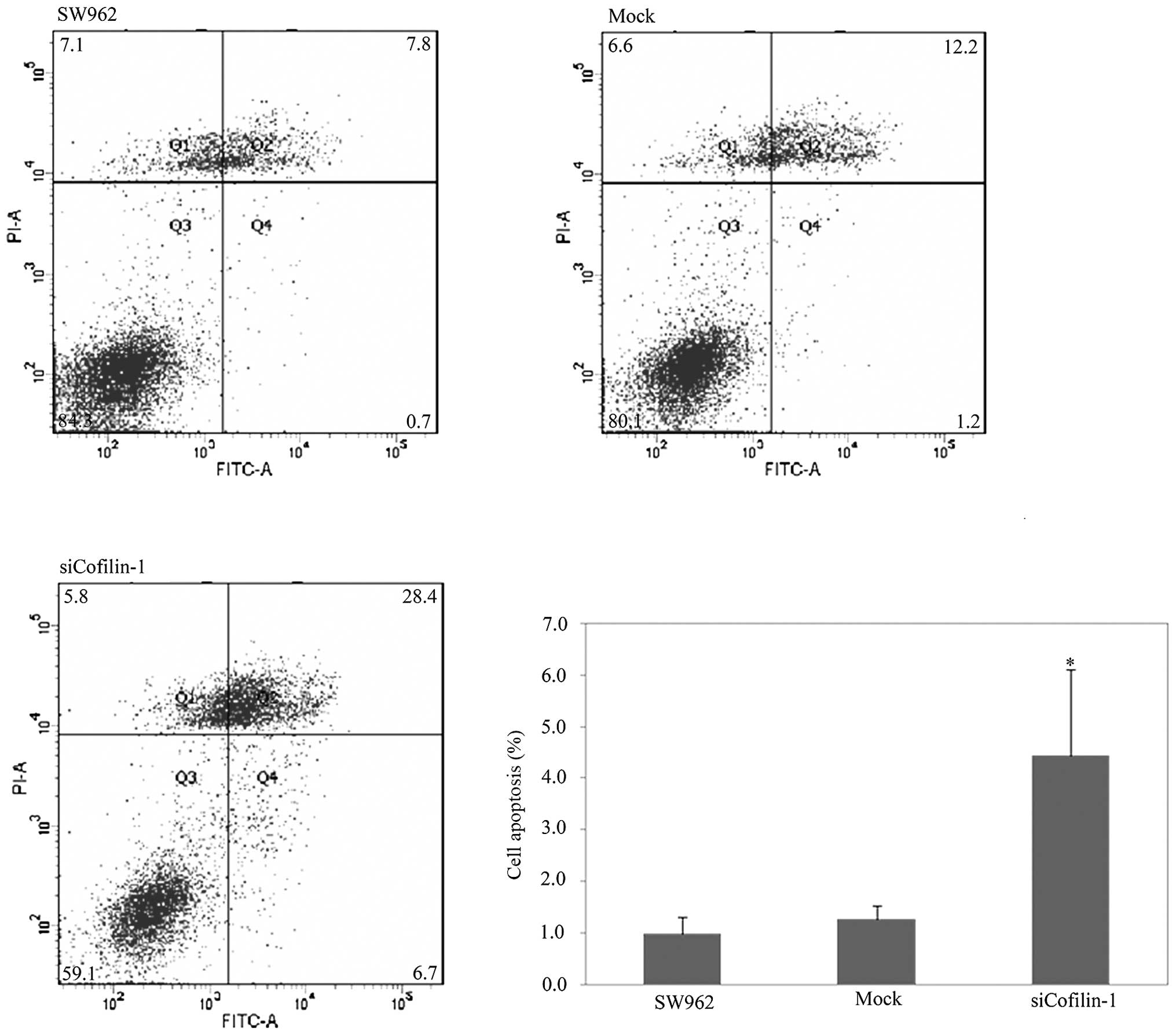
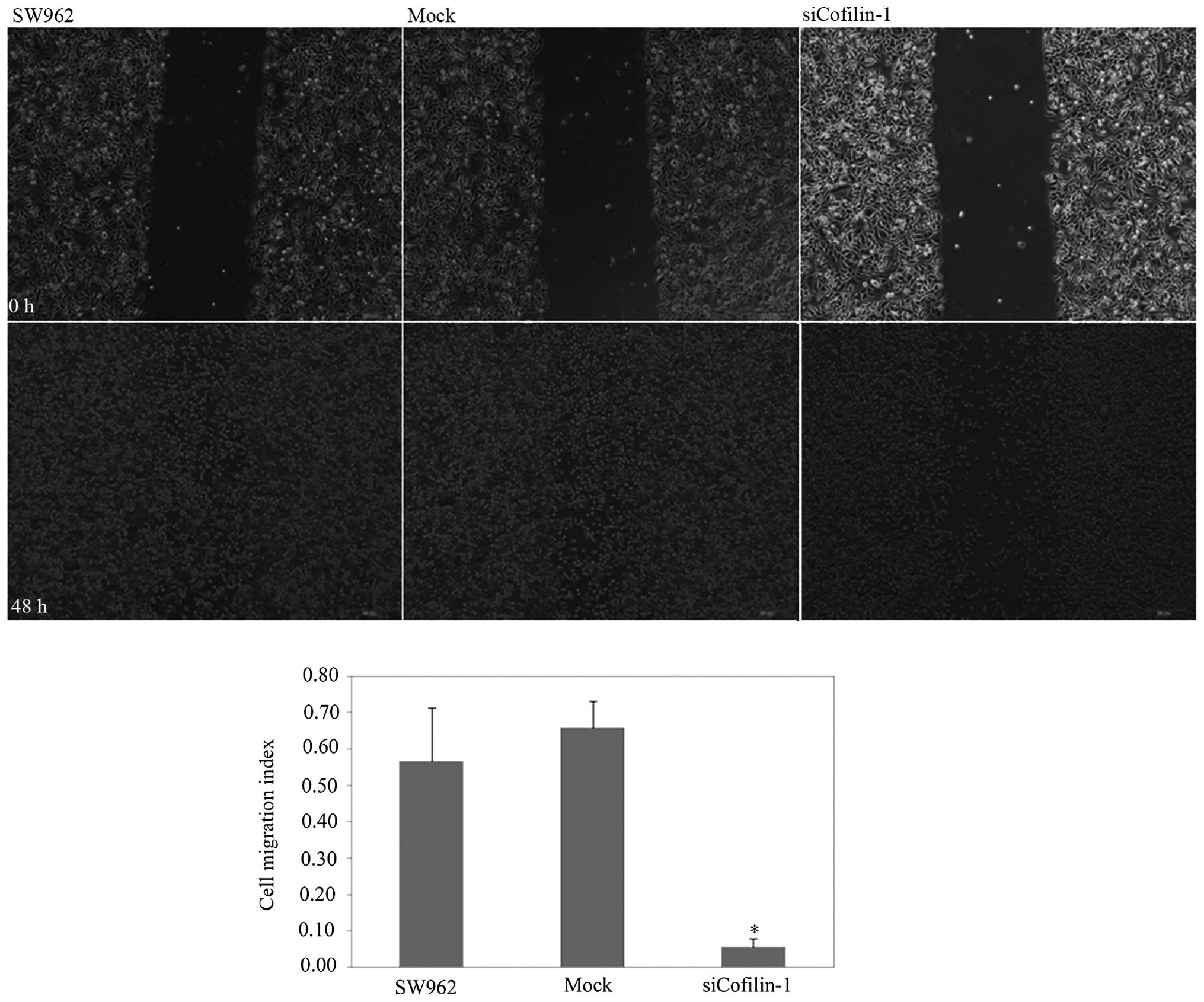
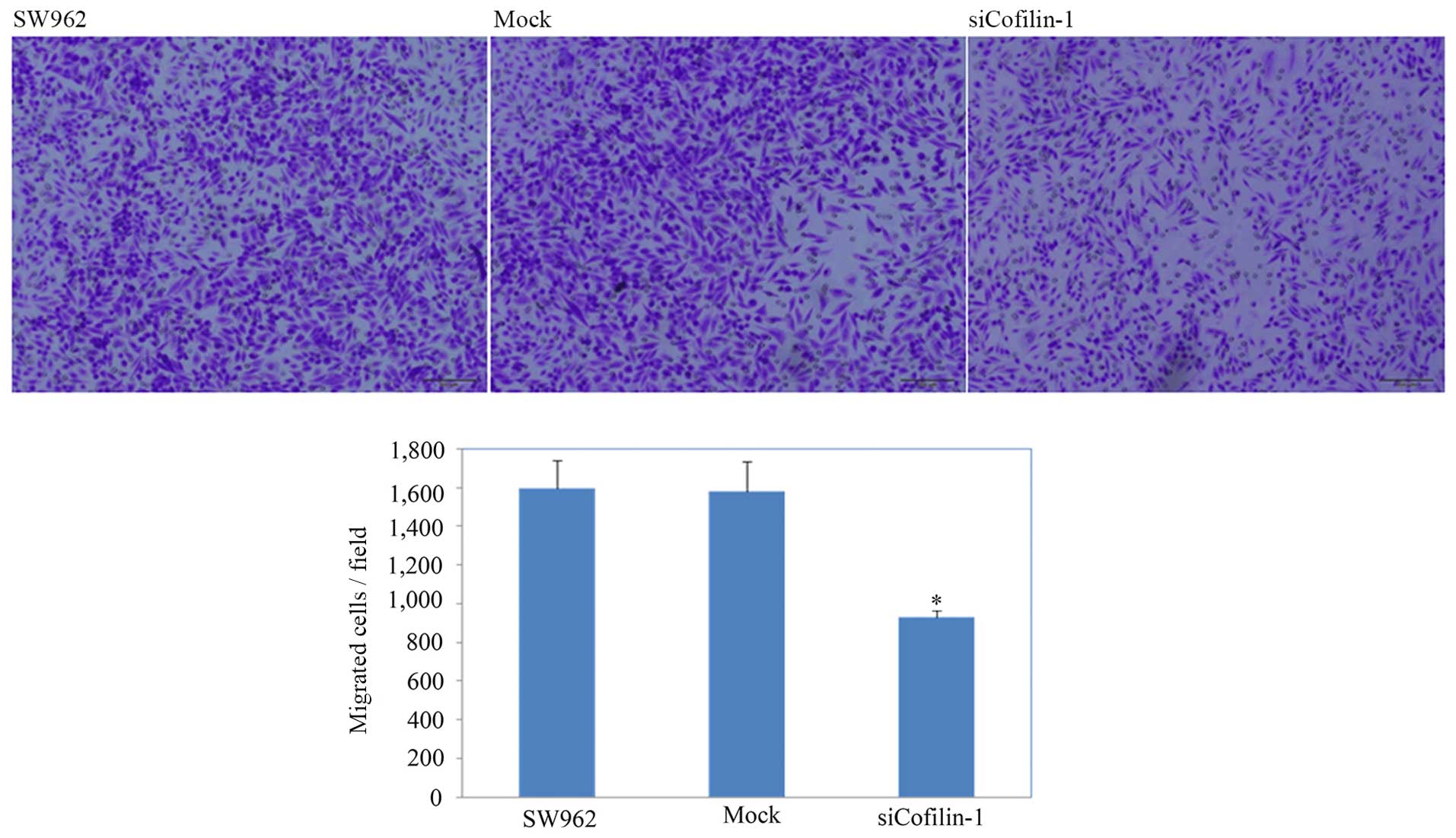
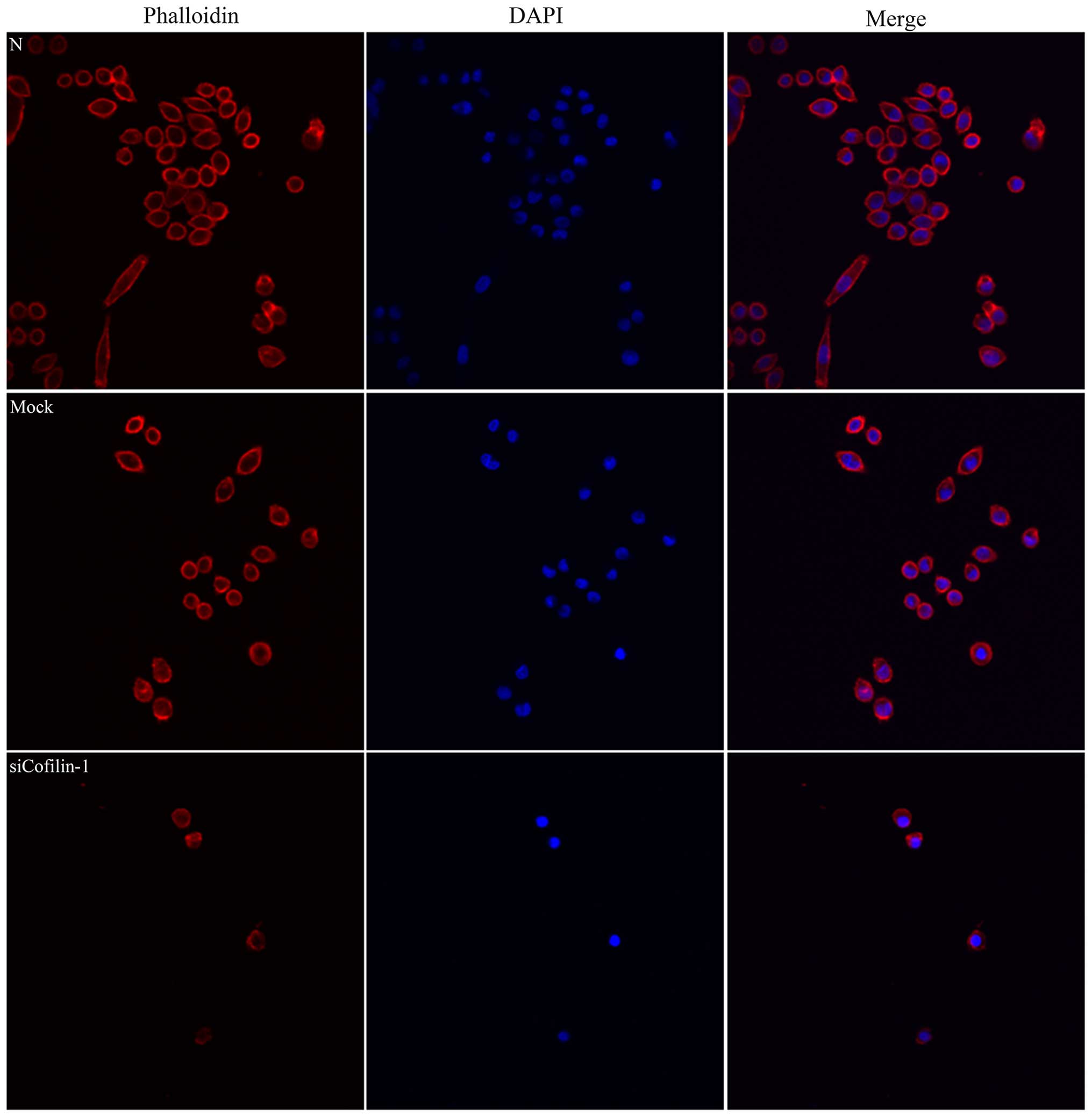
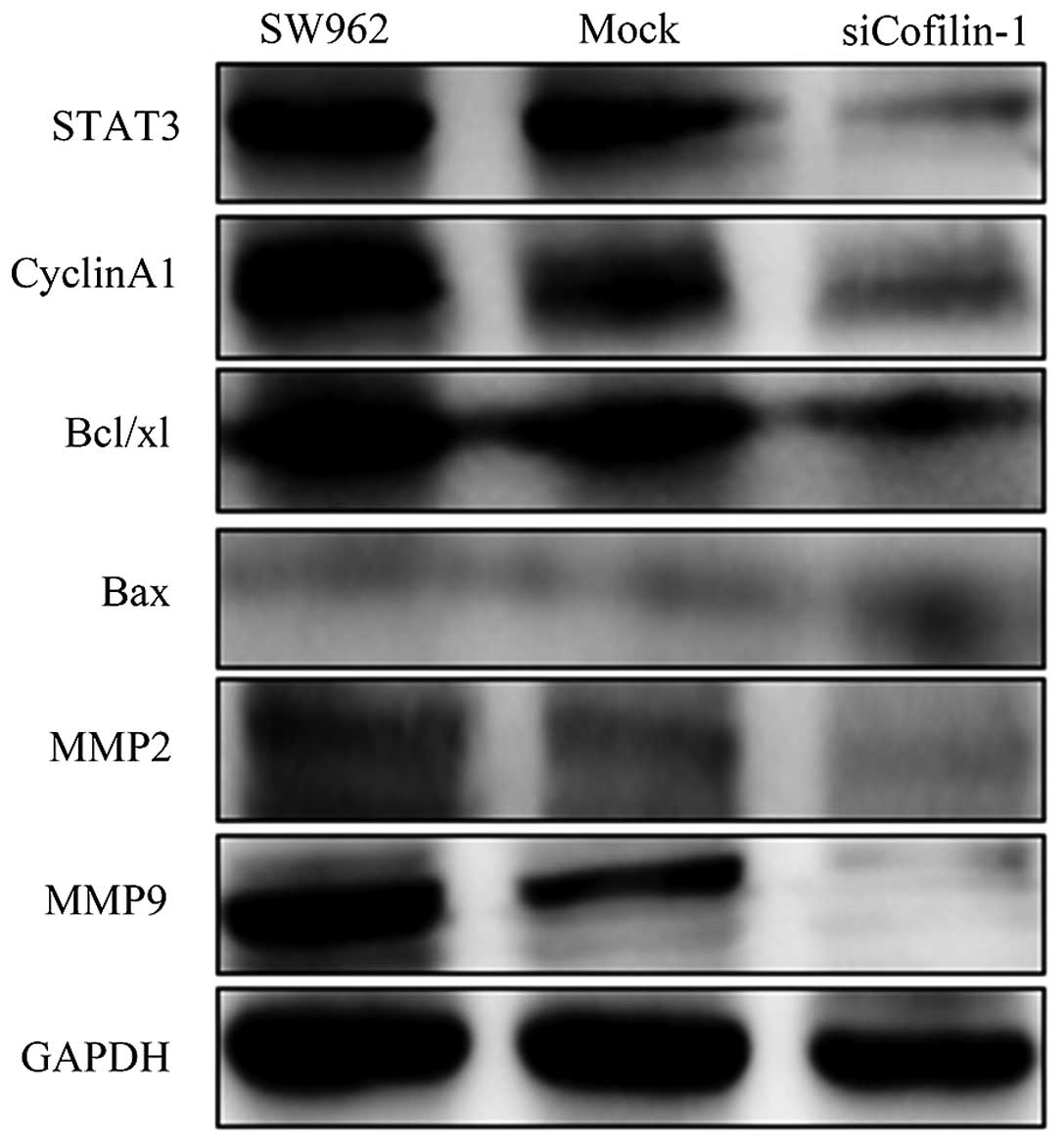
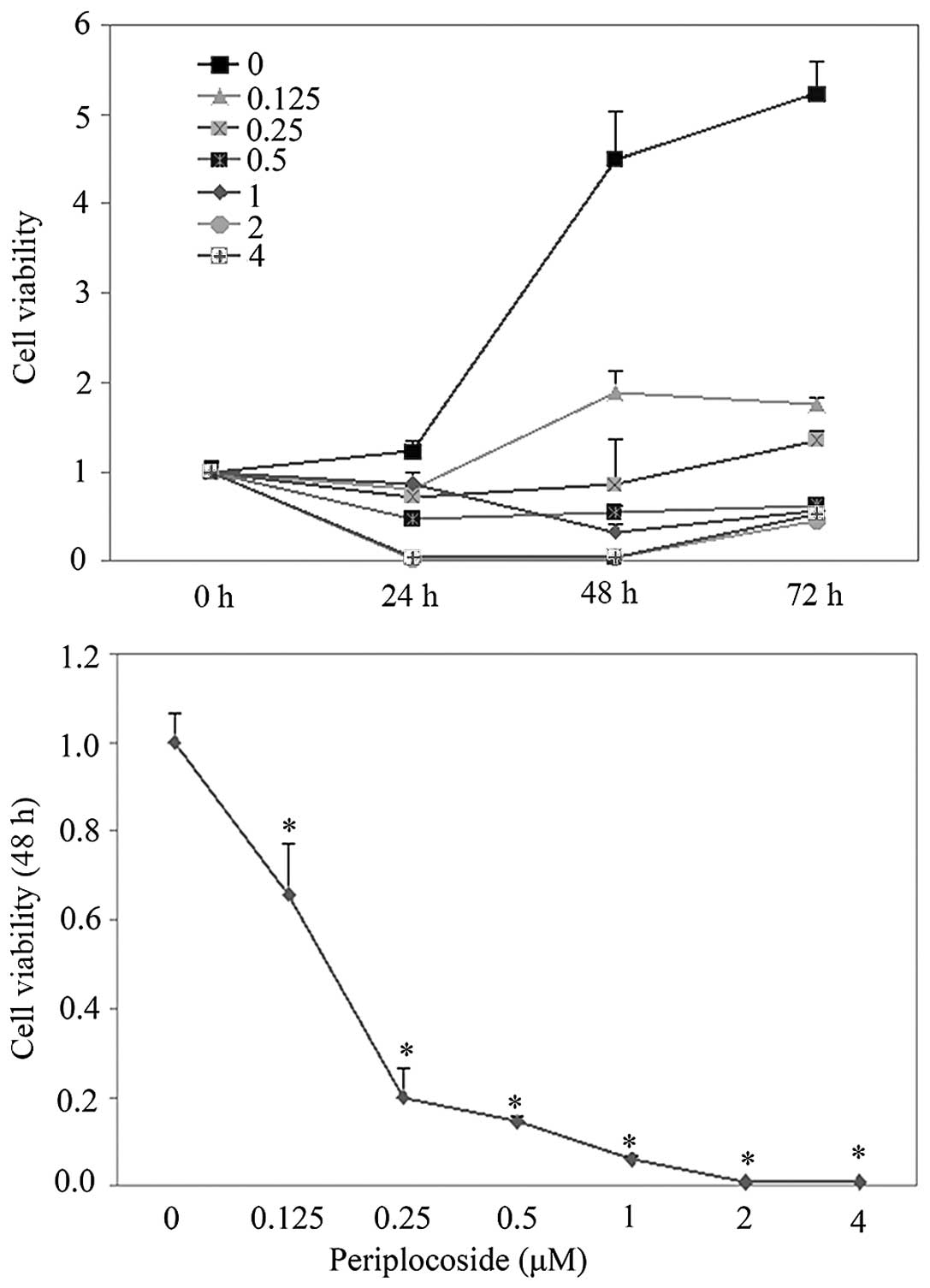
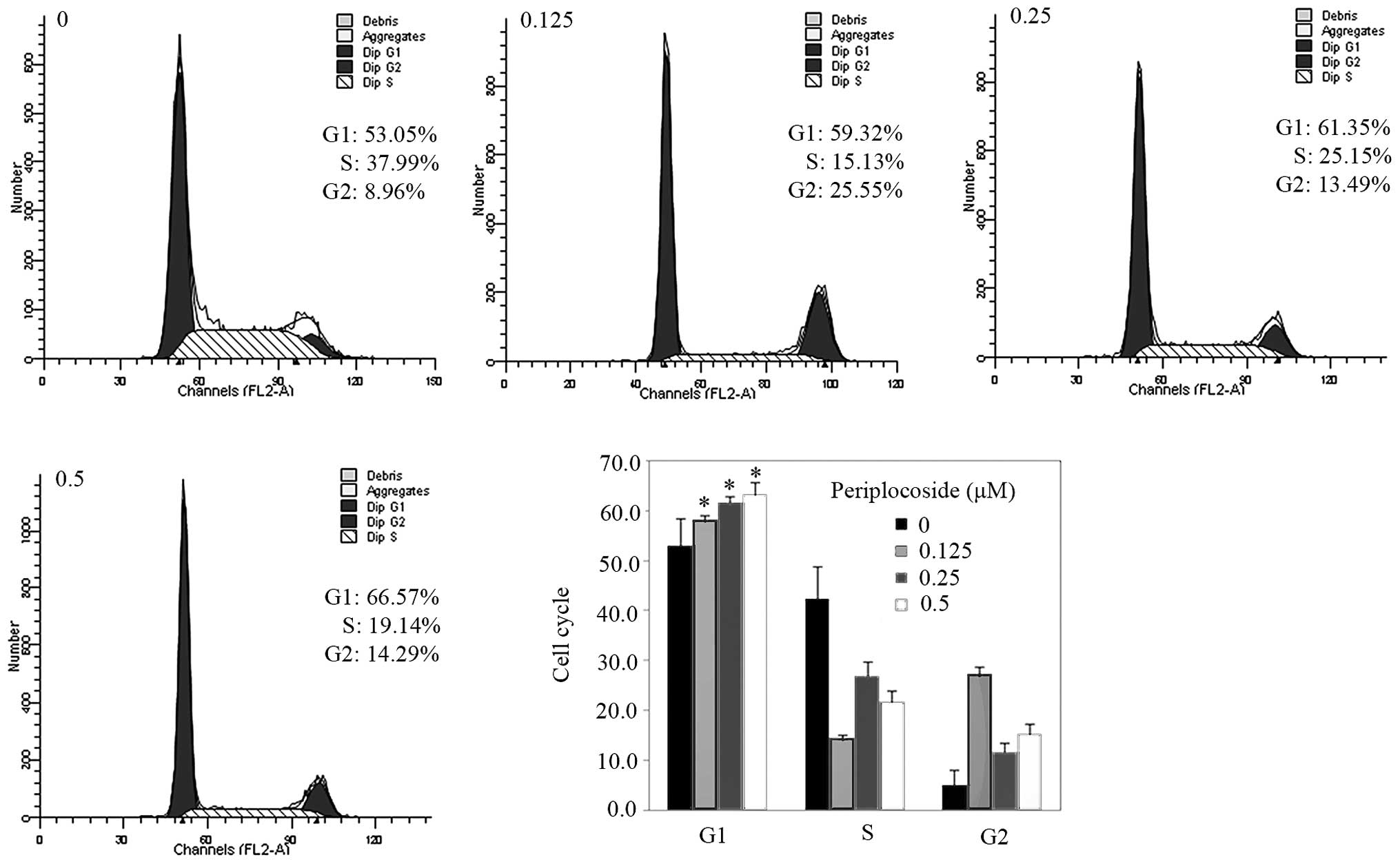
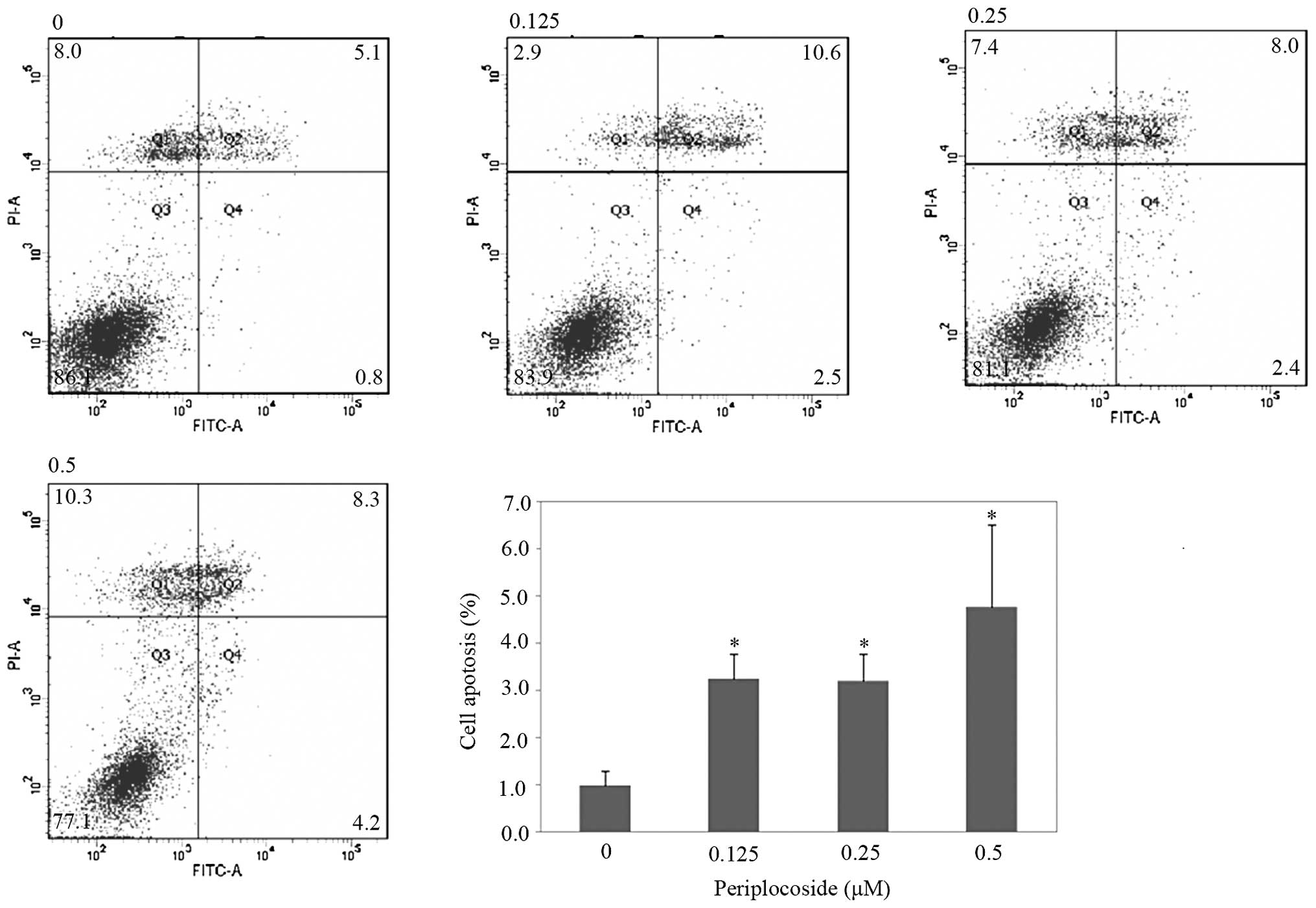
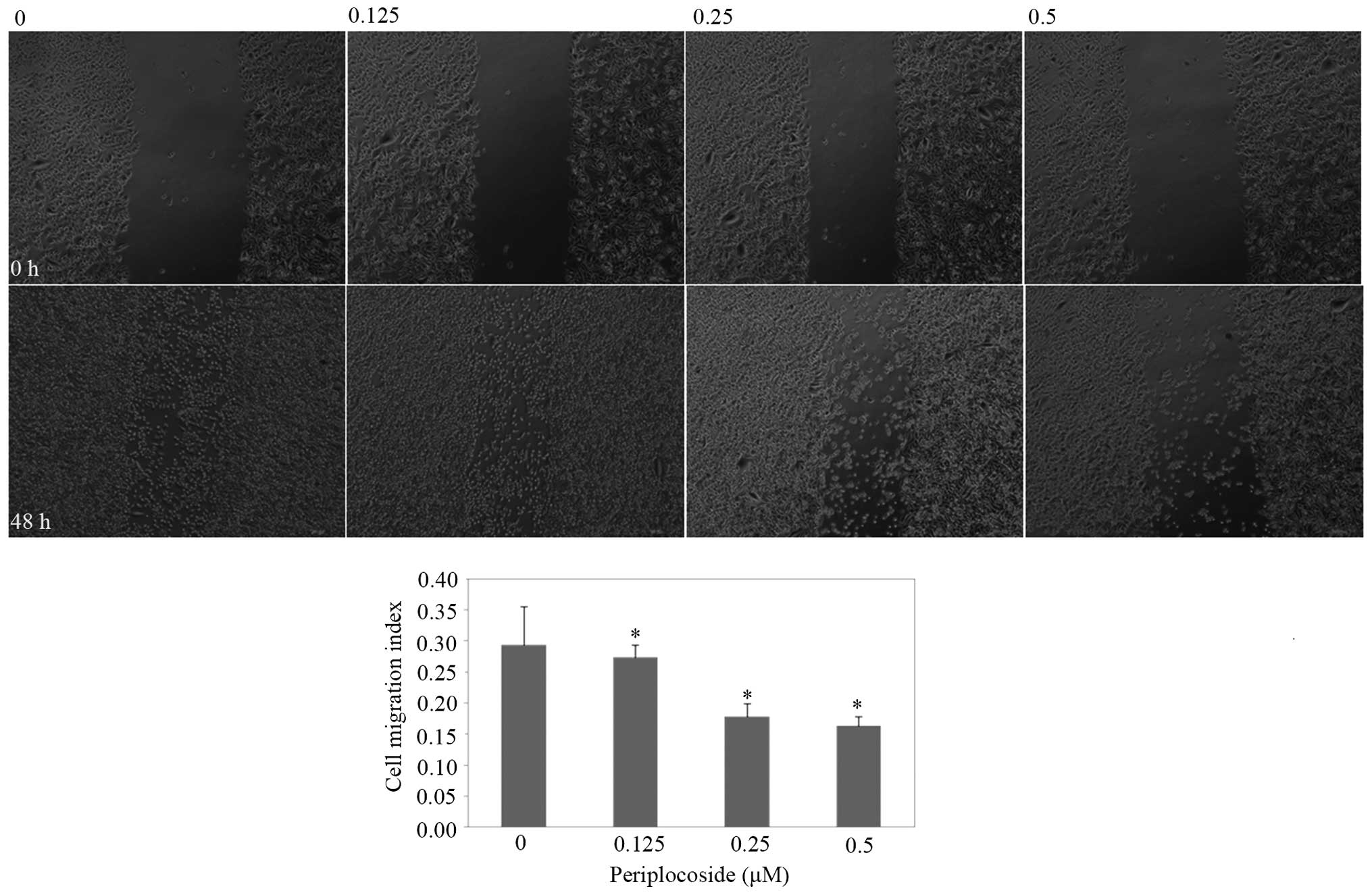
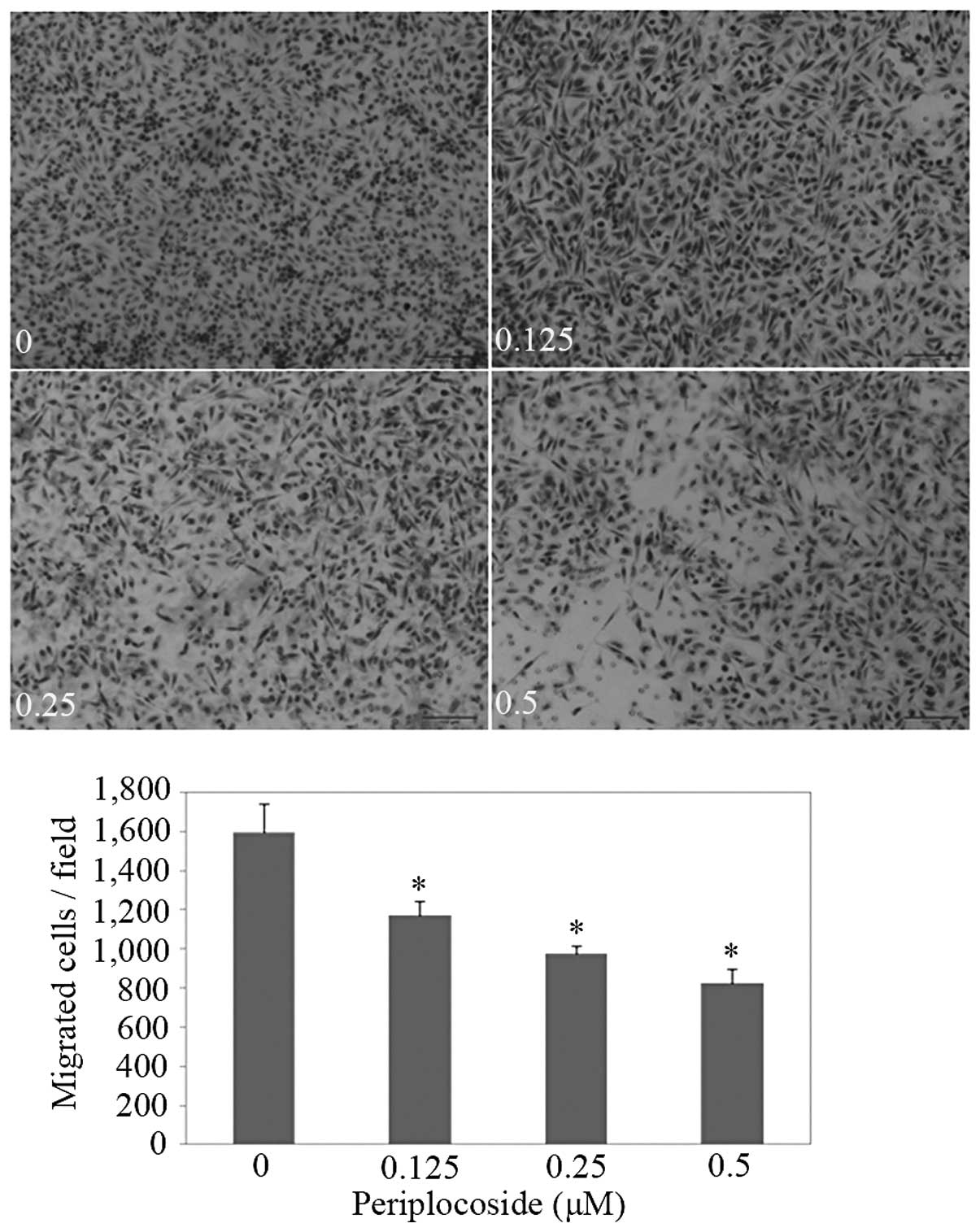
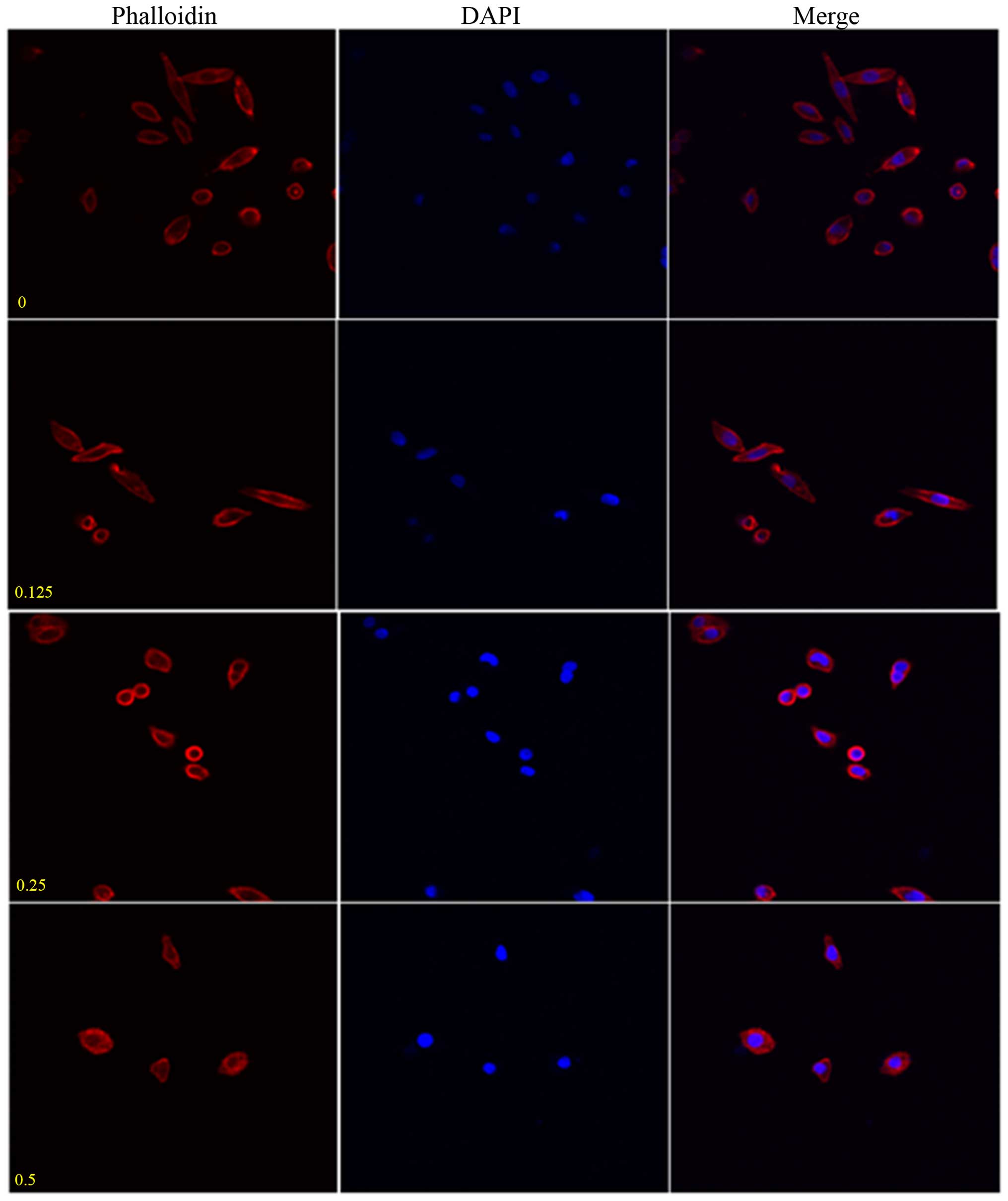
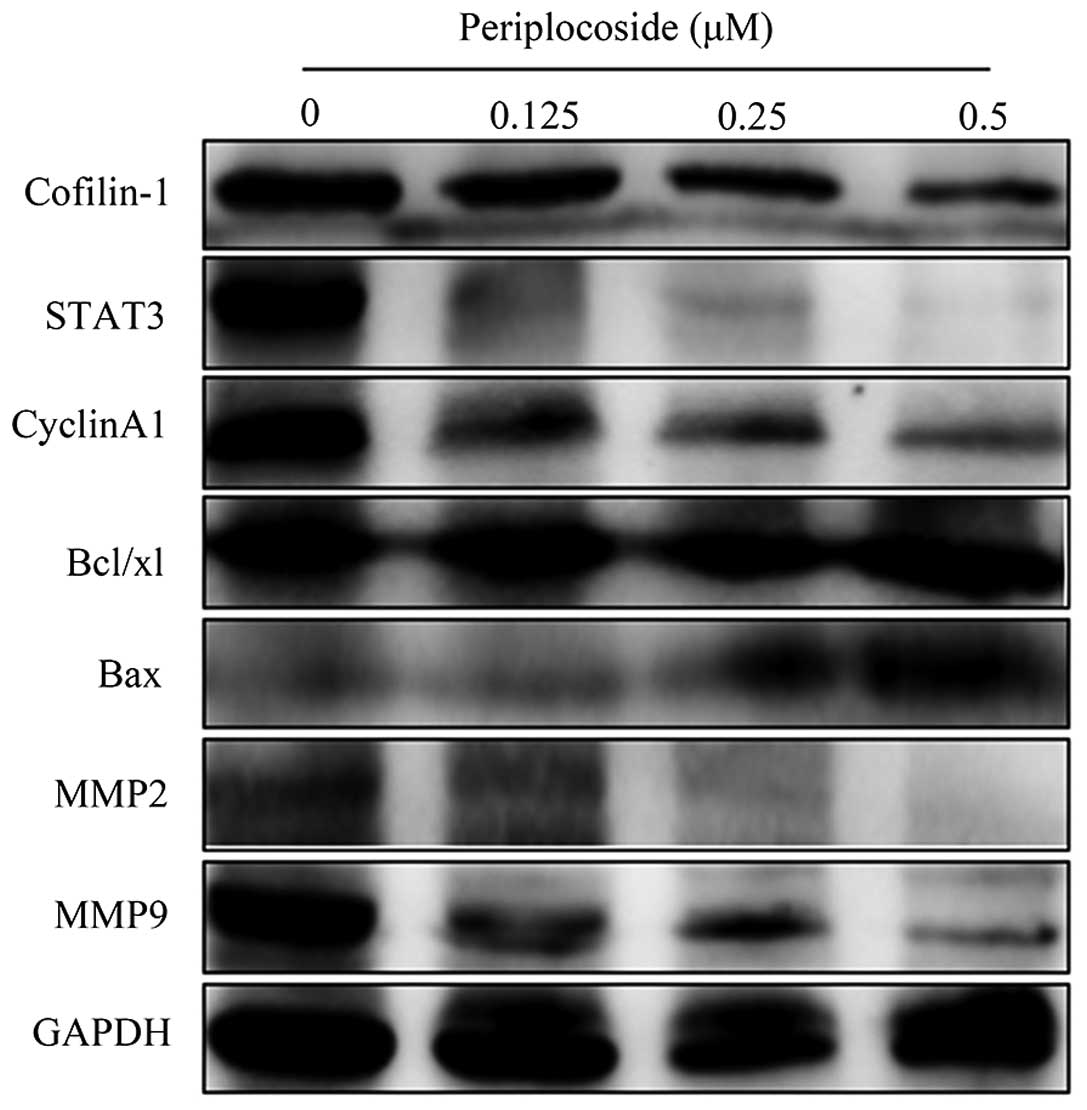
|
1
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 63:11–30. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sideri M, Jones RW, Wilkinson EJ, Preti M,
Heller DS, Scurry J, Haefner H and Neill S: Squamous vulvar
intraepithelial neoplasia: 2004 modified terminology, ISSVD Vulvar
Oncology Subcommittee. J Reprod Med. 50:807–810. 2005.
|
|
3
|
Buttmann-Schweiger N, Klug SJ, Luyten A,
Holleczek B, Heitz F, du Bois A and Kraywinkel K: Incidence
patterns and temporal trends of invasive nonmelanotic vulvar tumors
in Germany 1999–2011. A population-based cancer registry analysis.
PLoS One. 10:e01280732015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Akhtar-Danesh N, Elit L and Lytwyn A:
Trends in incidence and survival of women with invasive vulvar
cancer in the United States and Canada: A population-based study.
Gynecol Oncol. 134:314–318. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Marsden DE and Hacker NF: Contemporary
management of primary carcinoma of the vulva. Surg Clin North Am.
81:799–813. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wang WS, Zhong HJ, Xiao DW, Huang X, Liao
LD, Xie ZF, Xu XE, Shen ZY, Xu LY and Li EM: The expression of CFL1
and N-WASP in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and its
correlation with clinicopathological features. Dis Esophagus.
23:512–521. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang W, Mouneimne G, Sidani M, Wyckoff J,
Chen X, Makris A, Goswami S, Bresnick AR and Condeelis JS: The
activity status of cofilin is directly related to invasion,
intravasation, and metastasis of mammary tumors. J Cell Biol.
173:395–404. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang W, Eddy R and Condeelis J: The
cofilin pathway in breast cancer invasion and metastasis. Nat Rev
Cancer. 7:429–440. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hotulainen P, Paunola E, Vartiainen MK and
Lappalainen P: Actin-depolymerizing factor and cofilin-1 play
overlapping roles in promoting rapid F-actin depolymerization in
mammalian nonmuscle cells. Mol Biol Cell. 16:649–664. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
10
|
van Rheenen J, Song X, van Roosmalen W,
Cammer M, Chen X, Desmarais V, Yip SC, Backer JM, Eddy RJ and
Condeelis JS: EGF-induced PIP2 hydrolysis releases and
activates cofilin locally in carcinoma cells. J Cell Biol.
179:1247–1259. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lu LI, Fu NI, Luo XU, Li XY and Li XP:
Overexpression of cofilin 1 in prostate cancer and the
corresponding clinical implications. Oncol Lett. 9:2757–2761.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhou J, Wang Y, Fei J and Zhang W:
Expression of cofilin 1 is positively correlated with the
differentiation of human epithelial ovarian cancer. Oncol Lett.
4:1187–1190. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Polachini GM, Sobral LM, Mercante AMC,
Paes-Leme AF, Xavier FC, Henrique T, Guimarães DM, Vidotto A,
Fukuyama EE, Góis-Filho JF, et al: Proteomic approaches identify
members of cofilin pathway involved in oral tumorigenesis. PLoS
One. 7:e505172012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Peng XC, Gong FM, Zhao YW, Zhou LX, Xie
YW, Liao HL, Lin HJ, Li ZY, Tang MH and Tong AP: Comparative
proteomic approach identifies PKM2 and cofilin-1 as potential
diagnostic, prognostic and therapeutic targets for pulmonary
adenocarcinoma. PLoS One. 6:e273092011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ji P, Agrawal S, Diederichs S, Bäumer N,
Becker A, Cauvet T, Kowski S, Beger C, Welte K, Berdel WE, et al:
Cyclin A1, the alternative A-type cyclin, contributes to G1/S cell
cycle progression in somatic cells. Oncogene. 24:2739–2744. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wake MS and Watson CJ: STAT3 the oncogene
- still eluding therapy? FEBS J. 282:2600–2611. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Katoh D, Nishizuka M, Osada S and Imagawa
M: Fad104, a positive regulator of adipocyte differentiation,
suppresses invasion and metastasis of melanoma cells by inhibition
of STAT3 activity. PLoS One. 10:e01171972015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Du YY, Liu X and Shan BE: Periplocin
extracted from cortex periplocae induces apoptosis of SW480 cells
through inhibiting the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Ai
Zheng. 28:456–460. 2009.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhao L, Shan B, Du Y, Wang M, Liu L and
Ren FZ: Periplocin from Cortex periplocae inhibits cell growth and
down-regulates survivin and c-myc expression in colon cancer in
vitro and in vivo via β-catenin/TCF signaling. Oncol Rep.
24:375–383. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lu Z, Song Q, Yang J, Zhao X, Zhang X,
Yang P and Kang J: Comparative proteomic analysis of anti-cancer
mechanism by periplocin treatment in lung cancer cells. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 33:859–868. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|