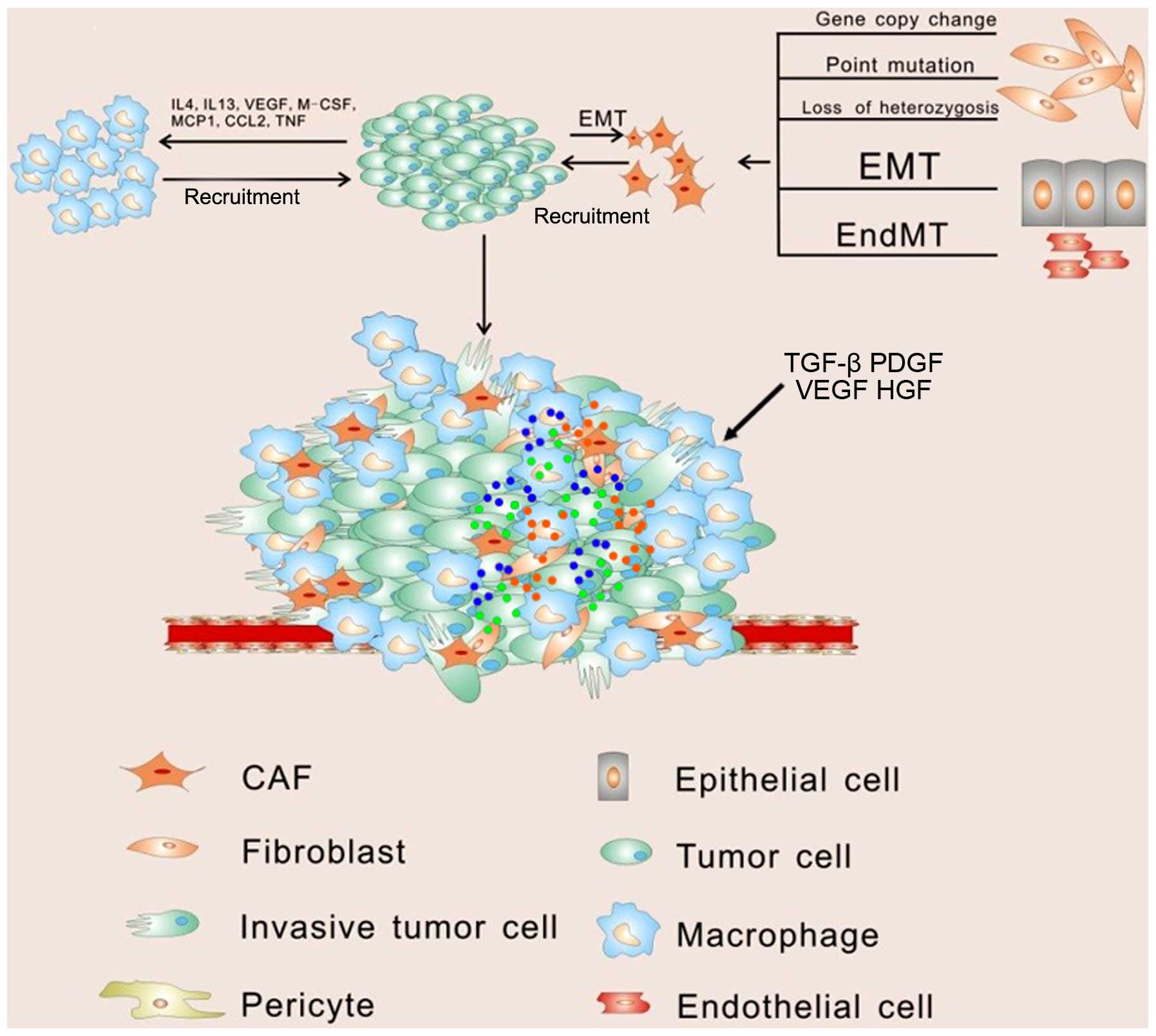
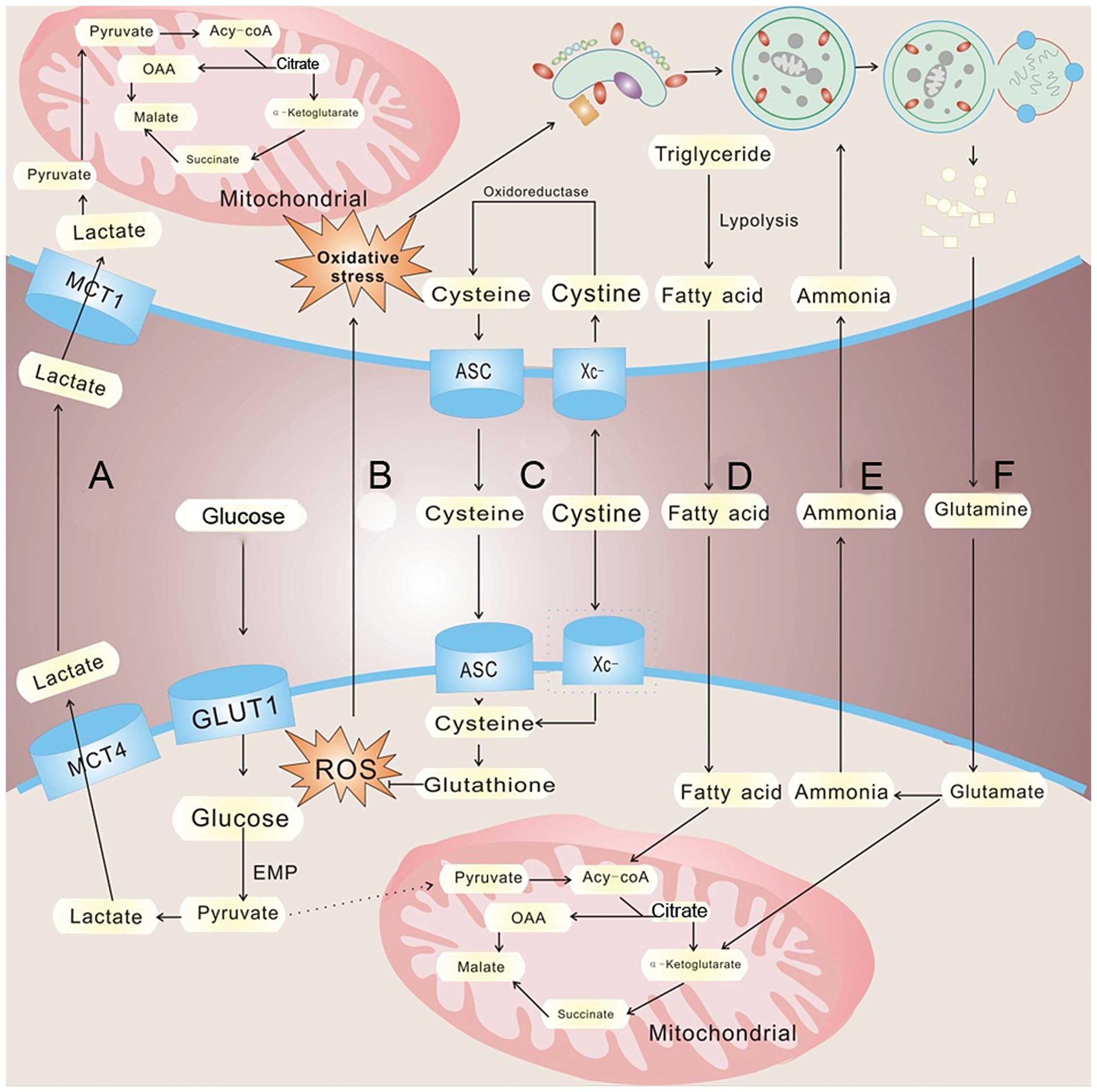
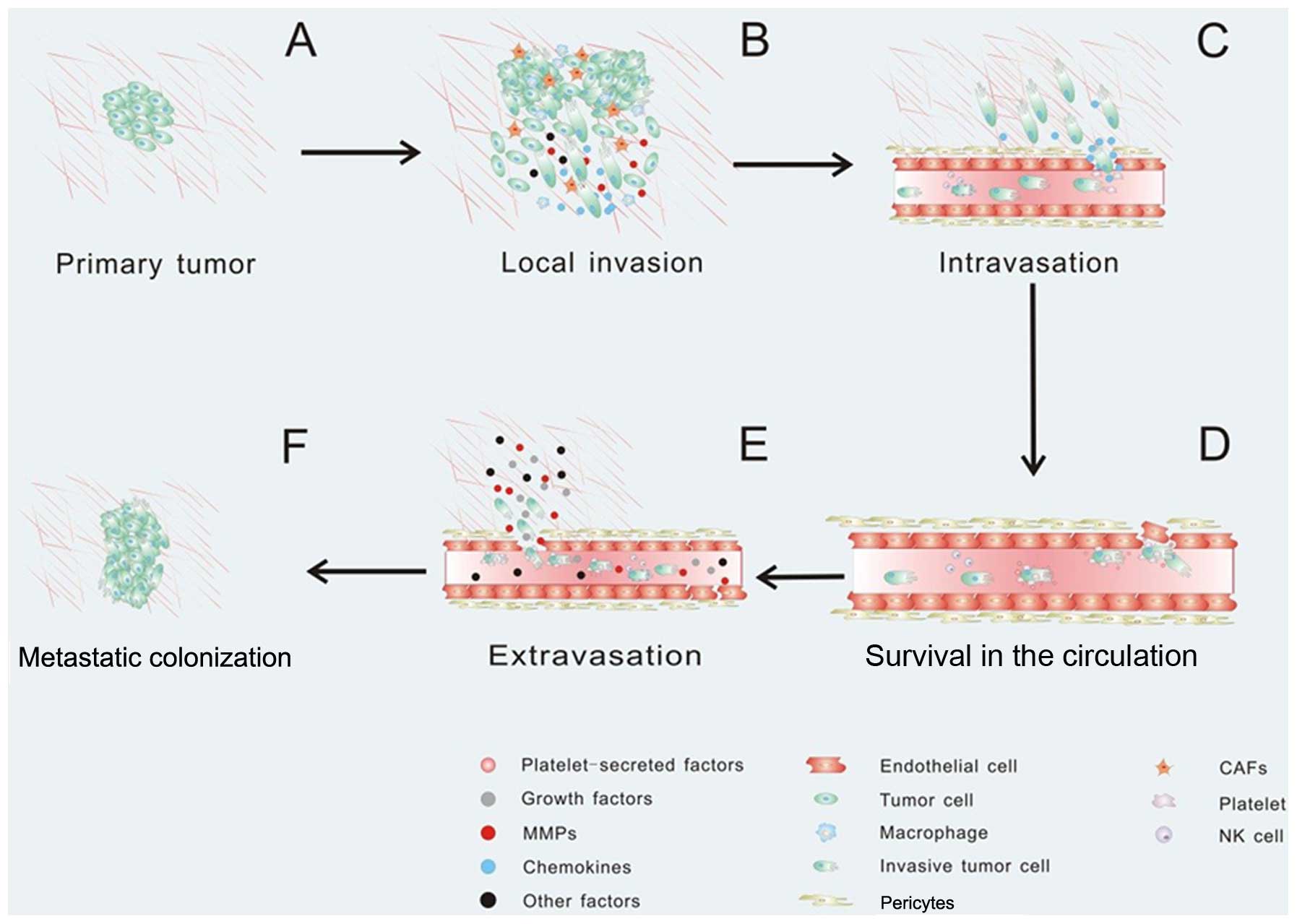
|
1
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: The hallmarks
of cancer. Cell. 100:57–70. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hanahan D and Coussens LM: Accessories to
the crime: Functions of cells recruited to the tumor
microenvironment. Cancer Cell. 21:309–322. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cirri P and Chiarugi P: Cancer associated
fibroblasts: The dark side of the coin. Am J Cancer Res. 1:482–497.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gabrilovich DI, Ostrand-Rosenberg S and
Bronte V: Coordinated regulation of myeloid cells by Tumours. Nat
Rev Immunol. 12:253–268. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cheng L, Huang Z, Zhou W, Wu Q, Donnola S,
Liu JK, Fang X, Sloan AE, Mao Y, Lathia JD, et al: Glioblastoma
stem cells generate vascular pericytes to support vessel function
and tumor growth. Cell. 153:139–152. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Cornil I, Theodorescu D, Man S, Herlyn M,
Jambrosic J and Kerbel RS: Fibroblast cell interactions with human
melanoma cells affect tumor cell growth as a function of tumor
progression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 88:6028–6032. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Räsänen K and Vaheri A: Activation of
fibroblasts in cancer stroma. Exp Cell Res. 316:2713–2722. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lu C, Vickers MF and Kerbel RS:
Interleukin 6: A fibroblast-derived growth inhibitor of human
melanoma cells from early but not advanced stages of tumor
progression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 89:9215–9219. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Leonardi GC, Candido S, Cervello M,
Nicolosi D, Raiti F, Travali S, Spandidos DA and Libra M: The tumor
microenvironment in hepatocellular carcinoma (review). Int J Oncol.
40:1733–1747. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Rønnov-Jessen L and Petersen OW: Induction
of alpha-smooth muscle actin by transforming growth factor-beta 1
in quiescent human breast gland fibroblasts. Implications for
myofibroblast generation in breast neoplasia. Lab Invest.
68:696–707. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Postlethwaite AE, Keski-Oja J, Moses HL
and Kang AH: Stimulation of the chemotactic migration of human
fibroblasts by transforming growth factor beta. J Exp Med.
165:251–256. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Mayo LD, Dixon JE, Durden DL, Tonks NK and
Donner DB: PTEN protects p53 from Mdm2 and sensitizes cancer cells
to chemotherapy. J Biol Chem. 277:5484–5489. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Erez N, Truitt M, Olson P, Arron ST and
Hanahan D: Cancer-associated fibroblasts are activated in incipient
neoplasia to orchestrate tumor-promoting inflammation in an
NF-kappaB-dependent manner. Cancer Cell. 17:135–147. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
De Wever O, Demetter P, Mareel M and
Bracke M: Stromal myofibroblasts are drivers of invasive cancer
growth. Int J Cancer. 123:2229–2238. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Schmitt-Gräff A, Desmoulière A and
Gabbiani G: Heterogeneity of myofibroblast phenotypic features: An
example of fibroblastic cell plasticity. Virchows Arch. 425:3–24.
1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tlsty TD and Hein PW: Know thy neighbor:
Stromal cells can contribute oncogenic signals. Curr Opin Genet
Dev. 11:54–59. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Skalli O, Pelte MF, Peclet MC, Gabbiani G,
Gugliotta P, Bussolati G, Ravazzola M and Orci L: Alpha-smooth
muscle actin, a differentiation marker of smooth muscle cells, is
present in microfilamentous bundles of pericytes. J Histochem
Cytochem. 37:315–321. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
De Wever O and Mareel M: Role of tissue
stroma in cancer cell invasion. J Pathol. 200:429–447. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC, Jaiswal
RK, Douglas R, Mosca JD, Moorman MA, Simonetti DW, Craig S and
Marshak DR: Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem
cells. Science. 284:143–147. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Rattigan Y, Hsu JM, Mishra PJ, Glod J and
Banerjee D: Interleukin 6 mediated recruitment of mesenchymal stem
cells to the hypoxic tumor milieu. Exp Cell Res. 316:3417–3424.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Karnoub AE, Dash AB, Vo AP, Sullivan A,
Brooks MW, Bell GW, Richardson AL, Polyak K, Tubo R and Weinberg
RA: Mesenchymal stem cells within tumour stroma promote breast
cancer metastasis. Nature. 449:557–563. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zeisberg EM, Tarnavski O, Zeisberg M,
Dorfman AL, McMullen JR, Gustafsson E, Chandraker A, Yuan X, Pu WT,
Roberts AB, et al: Endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition
contributes to cardiac fibrosis. Nat Med. 13:952–961. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zeisberg EM, Potenta S, Xie L, Zeisberg M
and Kalluri R: Discovery of endothelial to mesenchymal transition
as a source for carcinoma-associated fibroblasts. Cancer Res.
67:10123–10128. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Petersen OW, Lind Nielsen H, Gudjonsson T,
Villadsen R, Rønnov-Jessen L and Bissell MJ: The plasticity of
human breast carcinoma cells is more than epithelial to mesenchymal
conversion. Breast Cancer Res. 3:213–217. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Petersen OW, Nielsen HL, Gudjonsson T,
Villadsen R, Rank F, Niebuhr E, Bissell MJ and Rønnov-Jessen L:
Epithelial to mesenchymal transition in human breast cancer can
provide a nonmalignant stroma. Am J Pathol. 162:391–402. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kurose K, Gilley K, Matsumoto S, Watson
PH, Zhou XP and Eng C: Frequent somatic mutations in PTEN and TP53
are mutually exclusive in the stroma of breast carcinomas. Nat
Genet. 32:355–357. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Orimo A and Weinberg RA: Stromal
fibroblasts in cancer: A novel tumor-promoting cell type. Cell
Cycle. 5:1597–1601. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Bronisz A, Godlewski J, Wallace JA,
Merchant AS, Nowicki MO, Mathsyaraja H, Srinivasan R, Trimboli AJ,
Martin CK, Li F, et al: Reprogramming of the tumour
microenvironment by stromal PTEN-regulated miR-320. Nat Cell Biol.
14:159–167. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sun X, Mao Y, Wang J, Zu L, Hao M, Cheng
G, Qu Q, Cui D, Keller ET, Chen X, et al: IL-6 secreted by
cancer-associated fibroblasts induces tamoxifen resistance in
luminal breast cancer. Oncogene. Jun 9–2014.Epub ahead of print.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Sica A: Role of tumour-associated
macrophages in cancer-related inflammation. Exp Oncol. 32:153–158.
2010.
|
|
32
|
Sica A, Larghi P, Mancino A, Rubino L,
Porta C, Totaro MG, Rimoldi M, Biswas SK, Allavena P and Mantovani
A: Macrophage polarization in tumour progression. Semin Cancer
Biol. 18:349–355. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lin EY, Nguyen AV, Russell RG and Pollard
JW: Colony-stimulating factor 1 promotes progression of mammary
tumors to malignancy. J Exp Med. 193:727–740. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Nesbit M, Schaider H, Miller TH and Herlyn
M: Low-level monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 stimulation of
monocytes leads to tumor formation in nontumorigenic melanoma
cells. J Immunol. 166:6483–6490. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Schmid MC, Avraamides CJ, Dippold HC,
Franco I, Foubert P, Ellies LG, Acevedo LM, Manglicmot JR, Song X,
Wrasidlo W, et al: Receptor tyrosine kinases and TLR/IL1Rs
unexpectedly activate myeloid cell PI3kγ, a single convergent point
promoting tumor inflammation and progression. Cancer Cell.
19:715–727. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Balkwill F: Cancer and the chemokine
network. Nat Rev Cancer. 4:540–550. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Qian BZ, Li J, Zhang H, Kitamura T, Zhang
J, Campion LR and Kaiser EA: CCL2 recruits inflammatory monocytes
to facilitate breast-tumour metastasis. Nature. 475:222–225. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Mizutani K, Sud S, McGregor NA,
Martinovski G, Rice BT, Craig MJ, Varsos ZS, Roca H and Pienta KJ:
The chemokine CCL2 increases prostate tumor growth and bone
metastasis through macrophage and osteoclast recruitment.
Neoplasia. 11:1235–1242. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Acharyya S, Oskarsson T, Vanharanta S,
Malladi S, Kim J, Morris PG, Manova-Todorova K, Leversha M, Hogg N,
Seshan VE, et al: A CXCL1 paracrine network links cancer
chemoresistance and metastasis. Cell. 150:165–178. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Shields JD, Kourtis IC, Tomei AA, Roberts
JM and Swartz MA: Induction of lymphoidlike stroma and immune
escape by tumors that express the chemokine CCL21. Science.
328:749–752. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Cremer I, Fridman WH and Sautès-Fridman C:
Tumor microenvironment in NSCLC suppresses NK cells function.
Oncoimmunology. 1:244–246. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zhao X, Rong L, Zhao X, Li X, Liu X, Deng
J, Wu H, Xu X, Erben U, Wu P, et al: TNF signaling drives
myeloid-derived suppressor cell accumulation. J Clin Invest.
122:4094–4104. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Bayne LJ, Beatty GL, Jhala N, Clark CE,
Rhim AD, Stanger BZ and Vonderheide RH: Tumor-derived
granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor regulates myeloid
inflammation and T cell immunity in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Cell.
21:822–835. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Würth R, Bajetto A, Harrison JK, Barbieri
F and Florio T: CXCL12 modulation of CXCR4 and CXCR7 activity in
human glioblastoma stem-like cells and regulation of the tumor
micro-environment. Front Cell Neurosci. 8:1442014.
|
|
45
|
Bergers G and Benjamin LE: Tumorigenesis
and the angiogenic switch. Nat Rev Cancer. 3:401–410. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Bertolini F, Shaked Y, Mancuso P and
Kerbel RS: The multifaceted circulating endothelial cell in cancer:
Towards marker and target identification. Nat Rev Cancer.
6:835–845. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Volm M, Koomägi R and Mattern J:
Prognostic value of vascular endothelial growth factor and its
receptor FLT-1 in squamous cell lung cancer. Int J Cancer.
74:64–68. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Yoshiji H, Gomez DE, Shibuya M and
Thorgeirsson UP: Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor,
its receptor, and other angiogenic factors in human breast cancer.
Cancer Res. 56:2013–2016. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Olson TA, Mohanraj D, Carson LF and
Ramakrishnan S: Vascular permeability factor gene expression in
normal and neoplastic human ovaries. Cancer Res. 54:276–280.
1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Brown LF, Berse B, Jackman RW, Tognazzi K,
Manseau EJ, Dvorak HF and Senger DR: Increased expression of
vascular permeability factor (vascular endothelial growth factor)
and its receptors in kidney and bladder carcinomas. Am J Pathol.
143:1255–1262. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Asahara T, Takahashi T, Masuda H, Kalka C,
Chen D, Iwaguro H, Inai Y, Silver M and Isner JM: VEGF contributes
to postnatal neovascularization by mobilizing bone marrow-derived
endothelial progenitor cells. EMBO J. 18:3964–3972. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Png KJ, Halberg N, Yoshida M and Tavazoie
SF: A microRNA regulon that mediates endothelial recruitment and
metastasis by cancer cells. Nature. 481:190–194. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Zeng Z, Li YC, Jiao ZH, Yao J and Xue Y:
The cross talk between cGMP signal pathway and PKC in pulmonary
endothelial cell angiogenesis. Int J Mol Sci. 15:10185–10198. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Karar J and Maity A: PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway
in angiogenesis. Front Mol Neurosci. 4:512011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Wang Z, Martin D, Molinolo AA, Patel V,
Iglesias-Bartolome R, Degese MS, Vitale-Cross L, Chen Q and Gutkind
JS: mTOR co-targeting in cetuximab resistance in head and neck
cancers harboring PIK3CA and RAS mutations. J Natl Cancer Inst.
106:dju2152014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Patel V, Marsh CA, Dorsam RT, Mikelis CM,
Masedunskas A, Amornphimoltham P, Nathan CA, Singh B, Weigert R,
Molinolo AA, et al: Decreased lymphangiogenesis and lymph node
metastasis by mTOR inhibition in head and neck cancer. Cancer Res.
71:7103–7112. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Oft M, Heider KH and Beug H: TGFbeta
signaling is necessary for carcinoma cell invasiveness and
metastasis. Curr Biol. 8:1243–1252. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Biswas S, Guix M, Rinehart C, Dugger TC,
Chytil A, Moses HL, Freeman ML and Arteaga CL: Inhibition of
TGF-beta with neutralizing antibodies prevents radiation-induced
acceleration of metastatic cancer progression. J Clin Invest.
117:1305–1313. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Padua D, Zhang XH, Wang Q, Nadal C, Gerald
WL, Gomis RR and Massagué J: TGFbeta primes breast tumors for lung
metastasis seeding through angiopoietin-like 4. Cell. 133:66–77.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Siegel PM, Shu W, Cardiff RD, Muller WJ
and Massagué J: Transforming growth factor beta signaling impairs
Neu-induced mammary tumorigenesis while promoting pulmonary
metastasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 100:8430–8435. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Yin JJ, Selander K, Chirgwin JM, Dallas M,
Grubbs BG, Wieser R, Massagué J, Mundy GR and Guise TA: TGF-beta
signaling blockade inhibits PTHrP secretion by breast cancer cells
and bone metastases development. J Clin Invest. 103:197–206. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Kang Y, HE W, Tulley S, Gupta GP,
Serganova I, Chen CR, Manova-Todorova K, Blasberg R, Gerald WL and
Massagué J: Breast cancer bone metastasis mediated by the Smad
tumor suppressor pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:13909–13914.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Labelle M, Begum S and Hynes RO: Direct
signaling between platelets and cancer cells induces an
epithelial-mesenchymal-like transition and promotes metastasis.
Cancer Cell. 20:576–590. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Nakamura T, Nishizawa T, Hagiya M, Seki T,
Shimonishi M, Sugimura A, Tashiro K and Shimizu S: Molecular
cloning and expression of human hepatocyte growth factor. Nature.
342:440–443. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Birchmeier C, Birchmeier W, Gherardi E and
Vande Woude GF: Met, metastasis, motility and more. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 4:915–925. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Matsumoto K and Nakamura T: Hepatocyte
growth factor and the met system as a mediator of tumor-stromal
interactions. Int J Cancer. 119:477–483. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Wilson TR, Fridlyand J, Yan Y, Penuel E,
Burton L, Chan E, Peng J, Lin E, Wang Y, Sosman J, et al:
Widespread potential for growth-factor-driven resistance to
anticancer kinase inhibitors. Nature. 487:505–509. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Straussman R, Morikawa T, Shee K,
Barzily-Rokni M, Qian ZR, Du J, Davis A, Mongare MM, Gould J,
Frederick DT, et al: Tumour micro-environment elicits innate
resistance to RAF inhibitors through HGF secretion. Nature.
487:500–504. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Zhou P, Li H, Wheeler S, Grandis JR,
Stabile LA and Egloff AM: Generation of head and neck cancer
patient-derived xenografts with in vivo acquired cetuximab
resistance. Clin Cancer Res. 21(Suppl 4): B392015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Rossi D and Zlotnik A: The biology of
chemokines and their receptors. Annu Rev Immunol. 18:217–242. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Murphy PM, Baggiolini M, Charo IF, Hébert
CA, Horuk R, Matsushima K, Miller LH, Oppenheim JJ and Power CA:
International union of pharmacology. XXII Nomenclature for
chemokine receptors. Pharmacol Rev. 52:145–176. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Zlotnik A and Yoshie O: Chemokines: A new
classification system and their role in immunity. Immunity.
12:121–127. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Dhawan P and Richmond A: Role of CXCL1 in
tumorigenesis of melanoma. J Leukoc Biol. 72:9–18. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Wang D, Wang H, Brown J, Daikoku T, Ning
W, Shi Q, Richmond A, Strieter R, Dey SK and DuBois RN: CXCL1
induced by prostaglandin E2 promotes angiogenesis in colorectal
cancer. J Exp Med. 203:941–951. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Karunagaran D, Tzahar E, Beerli RR, Chen
X, Graus-Porta D, Ratzkin BJ, Seger R, Hynes NE and Yarden Y:
ErbB-2 is a common auxiliary subunit of NDF and EGF receptors:
Implications for breast cancer. EMBO J. 15:254–264. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Conti I and Rollins BJ: CCL2 (monocyte
chemoattractant protein-1) and cancer. Semin Cancer Biol.
14:149–154. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Craig MJ and Loberg RD: CCL2 (monocyte
chemoattractant protein-1) in cancer bone metastases. Cancer
Metastasis Rev. 25:611–619. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Popivanova BK, Kostadinova FI, Furuichi K,
Shamekh MM, Kondo T, Wada T, Egashira K and Mukaida N: Blockade of
a chemokine, CCL2, reduces chronic colitis-associated
carcinogenesis in mice. Cancer Res. 69:7884–7892. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Rottiers V and Näär AM: MicroRNAs in
metabolism and metabolic disorders. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
13:239–250. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Krützfeldt J and Stoffel M: MicroRNAs: A
new class of regulatory genes affecting metabolism. Cell Metab.
4:9–12. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Calin GA and Croce CM: MicroRNA signatures
in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:857–866. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Kosaka N, Iguchi H, Yoshioka Y, Takeshita
F, Matsuki Y and Ochiya T: Secretory mechanisms and intercellular
transfer of microRNAs in living cells. J Biol Chem.
285:17442–17452. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Zhang J, Zhao H, Gao Y and Zhang W:
Secretory miRNAs as novel cancer biomarkers. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1826:32–43. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Xu D and Tahara H: The role of exosomes
and microRNAs in senescence and aging. Adv Drug Deliv Rev.
65:368–375. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Kosaka N, Iguchi H, Yoshioka Y, Hagiwara
K, Takeshita F and Ochiya T: Competitive interactions of cancer
cells and normal cells via secretory microRNAs. J Biol Chem.
287:1397–1405. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
86
|
Yang M, Chen J, Su F, Yu B, Su F, Lin L,
Liu Y, Huang JD and Song E: Microvesicles secreted by macrophages
shuttle invasion-potentiating microRNAs into breast cancer cells.
Mol Cancer. 10:1172011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Fabbri M, Paone A, Calore F, Galli R,
Gaudio E, Santhanam R, Lovat F, Fadda P, Mao C, Nuovo GJ, et al:
MicroRNAs bind to Toll-like receptors to induce prometastatic
inflammatory response. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 109:E2110–E2116.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Roth C, Rack B, Müller V, Janni W, Pantel
K and Schwarzenbach H: Circulating microRNAs as blood-based markers
for patients with primary and metastatic breast cancer. Breast
Cancer Res. 12:R902010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Mitchell PS, Parkin RK, Kroh EM, Fritz BR,
Wyman SK, Pogosova-Agadjanyan EL, Peterson A, Noteboom J, O'Briant
KC, Allen A, et al: Circulating microRNAs as stable blood-based
markers for cancer detection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
105:10513–10518. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Cairns RA, Harris IS and Mak TW:
Regulation of cancer cell metabolism. Nat Rev Cancer. 11:85–95.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Vander Heiden MG, Cantley LC and Thompson
CB: Understanding the Warburg effect: The metabolic requirements of
cell proliferation. Science. 324:1029–1033. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Lunt SY and Vander Heiden MG: Aerobic
glycolysis: Meeting the metabolic requirements of cell
proliferation. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 27:441–464. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Riemann A, Schneider B, Ihling A, Nowak M,
Sauvant C, Thews O and Gekle M: Acidic environment leads to
ROS-induced MAPK signaling in cancer cells. PLoS One. 6:e224452011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Fischer K, Hoffmann P, Voelkl S,
Meidenbauer N, Ammer J, Edinger M, Gottfried E, Schwarz S, Rothe G,
Hoves S, et al: Inhibitory effect of tumor cell-derived lactic acid
on human t cells. Blood. 109:3812–3819. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Walenta S and Mueller-Klieser WF: Lactate:
Mirror and motor of tumor malignancy. Semin Radiat Oncol.
14:267–274. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Rattigan YI, Patel BB, Ackerstaff E,
Sukenick G, Koutcher JA, Glod JW and Banerjee D: Lactate is a
mediator of metabolic cooperation between stromal carcinoma
associated fibroblasts and glycolytic tumor cells in the tumor
microenvironment. Exp Cell Res. 318:326–335. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
97
|
Végran F, Boidot R, Michiels C, Sonveaux P
and Feron O: Lactate influx through the endothelial cell
monocarboxylate transporter MCT1 supports an NF-κB/IL-8 pathway
that drives tumor angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 71:2550–2560. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
98
|
Semenza GL: Tumor metabolism: Cancer cells
give and take lactate. J Clin Invest. 118:3835–3837.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Feron O: Pyruvate into lactate and back:
From the Warburg effect to symbiotic energy fuel exchange in cancer
cells. Radiother Oncol. 92:329–333. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Sonveaux P, Végran F, Schroeder T, Wergin
MC, Verrax J, Rabbani ZN, De Saedeleer CJ, Kennedy KM, Diepart C,
Jordan BF, et al: Targeting lactate-fueled respiration selectively
kills hypoxic tumor cells in mice. J Clin Invest. 118:3930–3942.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Koukourakis MI, Giatromanolaki A, Harris
AL and Sivridis E: Comparison of metabolic pathways between cancer
cells and stromal cells in colorectal carcinomas: A metabolic
survival role for tumor-associated stroma. Cancer Res. 66:632–637.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Nieman KM, Kenny HA, Penicka CV, Ladanyi
A, Buell-Gutbrod R, Zillhardt MR, Romero IL, Carey MS, Mills GB,
Hotamisligil GS, et al: Adipocytes promote ovarian cancer
metastasis and provide energy for rapid tumor growth. Nat Med.
17:1498–1503. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Marie SK and Shinjo SM: Metabolism and
brain cancer. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 66(Suppl 1): 33–43. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
104
|
Hirayama A, Kami K, Sugimoto M, Sugawara
M, Toki N, Onozuka H, Kinoshita T, Saito N, Ochiai A, Tomita M, et
al: Quantitative metabolome profiling of colon and stomach cancer
microenvironment by capillary electrophoresis time-of-flight mass
spectrometry. Cancer Res. 69:4918–4925. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Ko YH, Lin Z, Flomenberg N, Pestell RG,
Howell A, Sotgia F, Lisanti MP and Martinez-Outschoorn UE:
Glutamine fuels a vicious cycle of autophagy in the tumor stroma
and oxidative mitochondrial metabolism in epithelial cancer cells:
Implications for preventing chemotherapy resistance. Cancer Biol
Ther. 12:1085–1097. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
106
|
Filipp FV, Ratnikov B, De Ingeniis J,
Smith JW, Osterman AL and Scott DA: Glutamine-fueled mitochondrial
metabolism is decoupled from glycolysis in melanoma. Pigment Cell
Melanoma Res. 25:732–739. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Jain M, Nilsson R, Sharma S, Madhusudhan
N, Kitami T, Souza AL, Kafri R, Kirschner MW, Clish CB and Mootha
VK: Metabolite profiling identifies a key role for glycine in rapid
cancer cell proliferation. Science. 336:1040–1044. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Okamoto K, Toyokuni S, Kim WJ, Ogawa O,
Kakehi Y, Arao S, Hiai H and Yoshida O: Overexpression of human
mutT homologue gene messenger RNA in renal-cell carcinoma: evidence
of persistent oxidative stress in cancer. Int J Cancer. 65:437–441.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Gackowski D, Banaszkiewicz Z, Rozalski R,
Jawien A and Olinski R: Persistent oxidative stress in colorectal
carcinoma patients. Int J Cancer. 101:395–397. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Toyokuni S, Okamoto K, Yodoi J and Hiai H:
Persistent oxidative stress in cancer. FEBS Lett. 358:1–3. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Zhou Y, Hileman EO, Plunkett W, Keating MJ
and Huang P: Free radical stress in chronic lymphocytic leukemia
cells and its role in cellular sensitivity to ROS-generating
anticancer agents. Blood. 101:4098–4104. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Szatrowski TP and Nathan CF: Production of
large amounts of hydrogen peroxide by human tumor cells. Cancer
Res. 51:794–798. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Grivennikov SI, Greten FR and Karin M:
Immunity, inflammation, and cancer. Cell. 140:883–899. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Ishikawa K, Takenaga K, Akimoto M,
Koshikawa N, Yamaguchi A, Imanishi H, Nakada K, Honma Y and Hayashi
J: ROS-generating mitochondrial DNA mutations can regulate tumor
cell metastasis. Science. 320:661–664. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Trachootham D, Alexandre J and Huang P:
Targeting cancer cells by ROS-mediated mechanisms: A radical
therapeutic approach? Nat Rev Drug Discov. 8:579–591. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Martinez-Outschoorn UE, Lin Z, Trimmer C,
Flomenberg N, Wang C, Pavlides S, Pestell RG, Howell A, Sotgia F
and Lisanti MP: Cancer cells metabolically 'fertilize' the tumor
microenvironment with hydrogen peroxide, driving the Warburg
effect: Implications for Pet imaging of human tumors. Cell Cycle.
10:2504–2520. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Mathew R, Karantza-Wadsworth V and White
E: Role of autophagy in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 7:961–967. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Baehrecke EH: Autophagy: Dual roles in
life and death? Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 6:505–510. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Eisenberg-Lerner A and Kimchi A: The
paradox of autophagy and its implication in cancer etiology and
therapy. Apoptosis. 14:376–391. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Pavlides S, Tsirigos A, Migneco G,
Whitaker-Menezes D, Chiavarina B, Flomenberg N, Frank PG, Casimiro
MC, Wang C, Pestell RG, et al: The autophagic tumor stroma model of
cancer: Role of oxidative stress and ketone production in fueling
tumor cell metabolism. Cell Cycle. 9:3485–3505. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Martinez-Outschoorn UE, Balliet RM,
Rivadeneira DB, Chiavarina B, Pavlides S, Wang C, Whitaker-Menezes
D, Daumer KM, Lin Z, Witkiewicz AK, et al: Oxidative stress in
cancer associated fibroblasts drives tumor-stroma co-evolution: A
new paradigm for understanding tumor metabolism, the field effect
and genomic instability in cancer cells. Cell Cycle. 9:3256–3276.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Bonuccelli G, Tsirigos A, Whitaker-Menezes
D, Pavlides S, Pestell RG, Chiavarina B, Frank PG, Flomenberg N,
Howell A, Martinez-Outschoorn UE, et al: Ketones and lactate 'fuel'
tumor growth and metastasis: Evidence that epithelial cancer cells
use oxidative mitochondrial metabolism. Cell Cycle. 9:3506–3514.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Martinez-Outschoorn UE, Trimmer C, Lin Z,
Whitaker-Menezes D, Chiavarina B, Zhou J, Wang C, Pavlides S,
Martinez-Cantarin MP, Capozza F, et al: Autophagy in cancer
associated fibroblasts promotes tumor cell survival: Role of
hypoxia, HIF1 induction and NFκB activation in the tumor stromal
microenvironment. Cell Cycle. 9:3515–3533. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Chiavarina B, Whitaker-Menezes D, Migneco
G, Martinez-Outschoorn UE, Pavlides S, Howell A, Tanowitz HB,
Casimiro MC, Wang C, Pestell RG, et al: HIF1-alpha functions as a
tumor promoter in cancer associated fibroblasts, and as a tumor
suppressor in breast cancer cells: Autophagy drives
compartment-specific oncogenesis. Cell Cycle. 9:3534–3551. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Martinez-Outschoorn UE, Whitaker-Menezes
D, Pavlides S, Chiavarina B, Bonuccelli G, Casey T, Tsirigos A,
Migneco G, Witkiewicz A, Balliet R, et al: The autophagic tumor
stroma model of cancer or 'battery-operated tumor growth': A simple
solution to the autophagy paradox. Cell Cycle. 9:4297–4306. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Salem AF, Whitaker-Menezes D, Lin Z,
Martinez-Outschoorn UE, Tanowitz HB, Al-Zoubi MS, Howell A, Pestell
RG, Sotgia F and Lisanti MP: Two-compartment tumor metabolism:
Autophagy in the tumor microenvironment and oxidative mitochondrial
metabolism (OXPHOS) in cancer cells. Cell Cycle. 11:2545–2556.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Zhang W, Trachootham D, Liu J, Chen G,
Pelicano H, Garcia-Prieto C, Lu W, Burger JA, Croce CM, Plunkett W,
et al: Stromal control of cystine metabolism promotes cancer cell
survival in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Nat Cell Biol.
14:276–286. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Carmeliet P and Jain RK: Molecular
mechanisms and clinical applications of angiogenesis. Nature.
473:298–307. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Risau W: Mechanisms of angiogenesis.
Nature. 386:671–674. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Carmeliet P and Jain RK: Angiogenesis in
cancer and other diseases. Nature. 407:249–257. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Leek RD, Lewis CE, Whitehouse R, Greenall
M, Clarke J and Harris AL: Association of macrophage infiltration
with angiogenesis and prognosis in invasive breast carcinoma.
Cancer Res. 56:4625–4629. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Polverini PJ and Leibovich SJ: Induction
of neovascularization in vivo and endothelial proliferation in
vitro by tumor-associated macrophages. Lab Invest. 51:635–642.
1984.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
O'Sullivan C, Lewis CE, Harris AL and
McGee JO: Secretion of epidermal growth factor by macrophages
associated with breast carcinoma. Lancet. 342:148–149. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Lewis CE, Leek R, Harris A and McGee JO:
Cytokine regulation of angiogenesis in breast cancer: The role of
tumor-associated macrophages. J Leukoc Biol. 57:747–751.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Harmey JH, Dimitriadis E, Kay E, Redmond
HP and Bouchier-Hayes D: Regulation of macrophage production of
vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) by hypoxia and
transforming growth factor beta-1. Ann Surg Oncol. 5:271–278. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Stockmann C, Doedens A, Weidemann A, Zhang
N, Takeda N, Greenberg JI, Cheresh DA and Johnson RS: Deletion of
vascular endothelial growth factor in myeloid cells accelerates
tumori-genesis. Nature. 456:814–818. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Bingle L, Lewis CE, Corke KP, Reed MW and
Brown NJ: Macrophages promote angiogenesis in human breast tumour
spheroids in vivo. Br J Cancer. 94:101–107. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
Voronov E, Shouval DS, Krelin Y, Cagnano
E, Benharroch D, Iwakura Y, Dinarello CA and Apte RN: IL-1 is
required for tumor invasiveness and angiogenesis. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 100:2645–2650. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Chen P, Huang Y, Bong R, Ding Y, Song N,
Wang X, Song X and Luo Y: Tumor-associated macrophages promote
angiogenesis and melanoma growth via adrenomedullin in a paracrine
and autocrine manner. Clin Cancer Res. 17:7230–7239. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
Mazzieri R, Pucci F, Moi D, Zonari E,
Ranghetti A, Berti A, Politi LS, Gentner B, Brown JL, Naldini L, et
al: Targeting the ANG2/TIE2 axis inhibits tumor growth and
metastasis by impairing angiogenesis and disabling rebounds of
proangiogenic myeloid cells. Cancer Cell. 19:512–526. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Hughes R, Fang HY, Muthana M and Lewis CE:
Role of tumour-associated macrophages in the regulation of
angiogenesis. Tumour-Associated Macrophages. 17–29. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
142
|
Giraudo E, Inoue M and Hanahan D: An
amino-bisphosphonate targets MMP-9-expressing macrophages and
angiogenesis to impair cervical carcinogenesis. J Clin Invest.
114:623–633. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Li ZR, Li YP, Lin ML, Su WR, Zhang WX,
Zhang Y, Yao L and Liang D: Activated macrophages induce
neovascularization through upregulation of MMP-9 and VEGF in rat
corneas. Cornea. 31:1028–1035. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
144
|
Houghton AM, Grisolano JL, Baumann ML,
Kobayashi DK, Hautamaki RD, Nehring LC, Cornelius LA and Shapiro
SD: Macrophage elastase (matrix metalloproteinase-12) suppresses
growth of lung metastases. Cancer Res. 66:6149–6155. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
145
|
Guo X, Oshima H, Kitmura T, Taketo MM and
Oshima M: Stromal fibroblasts activated by tumor cells promote
angiogenesis in mouse gastric cancer. J Biol Chem. 283:19864–19871.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
146
|
Zhang Y, Tang H, Cai J, Zhang T, Guo J,
Feng D and Wang Z: Ovarian cancer-associated fibroblasts contribute
to epithelial ovarian carcinoma metastasis by promoting
angiogenesis, lymphangiogenesis and tumor cell invasion. Cancer
Lett. 303:47–55. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
147
|
Friedl P and Wolf K: Tumour-cell invasion
and migration: Diversity and escape mechanisms. Nat Rev Cancer.
3:362–374. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
148
|
Steeg PS: Tumor metastasis: Mechanistic
insights and clinical challenges. Nat Med. 12:895–904. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
149
|
Valastyan S and Weinberg RA: Tumor
metastasis: Molecular insights and evolving paradigms. Cell.
147:275–292. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
150
|
Liotta LA, Kleinerman J, Catanzaro P and
Rynbrandt D: Degradation of basement membrane by murine tumor
cells. J Natl Cancer Inst. 58:1427–1431. 1977.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
151
|
Liotta LA: Tumor invasion and metastases -
role of the extracellular matrix: Rhoads memorial Award lecture.
Cancer Res. 46:1–7. 1986.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
152
|
Fingleton B, Vargo-Gogola T, Crawford HC
and Matrisian LM: Matrilysin [MMP-7] expression selects for cells
with reduced sensitivity to apoptosis. Neoplasia. 3:459–468. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
153
|
Noë V, Fingleton B, Jacobs K, Crawford HC,
Vermeulen S, Steelant W, Bruyneel E, Matrisian LM and Mareel M:
Release of an invasion promoter E-cadherin fragment by matrilysin
and stromelysin-1. J Cell Sci. 114:111–118. 2001.
|
|
154
|
Sameni M, Dosescu J, Moin K and Sloane BF:
Functional imaging of proteolysis: Stromal and inflammatory cells
increase tumor proteolysis. Mol Imaging. 2:159–175. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
155
|
Grimshaw MJ, Hagemann T, Ayhan A, Gillett
CE, Binder C and Balkwill FR: A role for endothelin-2 and its
receptors in breast tumor cell invasion. Cancer Res. 64:2461–2468.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
156
|
Sahai E: Mechanisms of cancer cell
invasion. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 15:87–96. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
157
|
Gaggioli C, Hooper S, Hidalgo-Carcedo C,
Grosse R, Marshall JF, Harrington K and Sahai E: Fibroblast-led
collective invasion of carcinoma cells with differing roles for
RhoGTPases in leading and following cells. Nat Cell Biol.
9:1392–1400. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
158
|
Provenzano PP, Eliceiri KW, Campbell JM,
Inman DR, White JG and Keely PJ: Collagen reorganization at the
tumor-stromal interface facilitates local invasion. BMC Med.
4:382006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
159
|
Provenzano PP, Inman DR, Eliceiri KW,
Trier SM and Keely PJ: Contact guidance mediated three-dimensional
cell migration is regulated by rho/rock-dependent matrix
reorganization. Biophys J. 95:5374–5384. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
160
|
Goetz JG, Minguet S, Navarro-Lérida I,
Lazcano JJ, Samaniego R, Calvo E, Tello M, Osteso-Ibáñez T,
Pellinen T, Echarri A, et al: Biomechanical remodeling of the
microenvironment by stromal caveolin-1 favors tumor invasion and
metastasis. Cell. 146:148–163. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
161
|
Chen J, Yao Y, Gong C, Yu F, Su S, Chen J,
Liu B, Deng H, Wang F, Lin L, et al: CCL18 from tumor-associated
macrophages promotes breast cancer metastasis via PItPnm3. Cancer
Cell. 19:541–555. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
162
|
Yamaguchi H, Pixley F and Condeelis J:
Invadopodia and podosomes in tumor invasion. Eur J Cell Biol.
85:213–218. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
163
|
Yamaguchi H, Lorenz M, Kempiak S,
Sarmiento C, Coniglio S, Symons M, Segall J, Eddy R, Miki H,
Takenawa T, et al: Molecular mechanisms of invadopodium formation:
The role of the N-WASP-Arp2/3 complex pathway and cofilin. J Cell
Biol. 168:441–452. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
164
|
Buccione R, Orth JD and McNiven MA: Foot
and mouth: Podosomes, invadopodia and circular dorsal ruffles. Nat
Rev Mol Cell Biol. 5:647–657. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
165
|
Calle Y, Chou HC, Thrasher AJ and Jones
GE: Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein and the cytoskeletal dynamics
of dendritic cells. J Pathol. 204:460–469. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
166
|
Linder S and Aepfelbacher M: Podosomes:
Adhesion hot-spots of invasive cells. Trends Cell Biol. 13:376–385.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
167
|
Mizutani K, Miki H, He H, Maruta H and
Takenawa T: Essential role of neural Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome
protein in podosome formation and degradation of extracellular
matrix in src-transformed fibroblasts. Cancer Res. 62:669–674.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
168
|
Moreno-Bueno G, Portillo F and Cano A:
Transcriptional regulation of cell polarity in EMT and cancer.
Oncogene. 27:6958–6969. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
169
|
Thiery JP: Epithelial-mesenchymal
transitions in tumour progression. Nat Rev Cancer. 2:442–454. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
170
|
Liu R, Li J, Xie K, Zhang T, Lei Y, Chen
Y, Zhang L, Huang K, Wang K, Wu H, et al: FGFR4 promotes
stroma-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in colorectal
cancer. Cancer Res. 73:5926–5935. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
171
|
Bergers G, Song S, Meyer-Morse N,
Bergsland E and Hanahan D: Benefits of targeting both pericytes and
endothelial cells in the tumor vasculature with kinase inhibitors.
J Clin Invest. 111:1287–1295. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
172
|
Raza A, Franklin MJ and Dudek AZ:
Pericytes and vessel maturation during tumor angiogenesis and
metastasis. Am J Hematol. 85:593–598. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
173
|
Cooke VG, LeBleu VS, Keskin D, Khan Z,
O'Connell JT, Teng Y, Duncan MB, Xie L, Maeda G, Vong S, et al:
Pericyte depletion results in hypoxia-associated
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and metastasis mediated by met
signaling pathway. Cancer Cell. 21:66–81. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
174
|
Cano A, Pérez-Moreno MA, Rodrigo I,
Locascio A, Blanco MJ, Del Barrio MG, Portillo F and Nieto MA: The
transcription factor snail controls epithelial-mesenchymal
transitions by repressing E-cadherin expression. Nat Cell Biol.
2:76–83. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
175
|
Batlle E, Sancho E, Francí C, Domínguez D,
Monfar M, Baulida J and García De Herreros A: The transcription
factor snail is a repressor of E-cadherin gene expression in
epithelial tumour cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2:84–89. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
176
|
Zhou BP, Deng J, Xia W, Xu J, Li YM,
Gunduz M and Hung MC: Dual regulation of Snail by
GSK-3beta-mediated phosphorylation in control of
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat Cell Biol. 6:931–940. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
177
|
Wu Y, Deng J, Rychahou PG, Qiu S, Evers BM
and Zhou BP: Stabilization of snail by NF-kappaB is required for
inflammation-induced cell migration and invasion. Cancer Cell.
15:416–428. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
178
|
Quigley JP and Armstrong PB: Tumor cell
intravasation alucidated: The chick embryo opens the window. Cell.
94:281–284. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
179
|
Wyckoff JB, Jones JG, Condeelis JS and
Segall JE: A critical step in metastasis: In vivo analysis of
intravasation at the primary tumor. Cancer Res. 60:2504–2511.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
180
|
Wolf MJ, Hoos A, Bauer J, Boettcher S,
Knust M, Weber A, Simonavicius N, Schneider C, Lang M, Stürzl M, et
al: Endothelial CCR2 signaling induced by colon carcinoma cells
enables extravasation via the JAK2-Stat5 and p38MAPk pathway.
Cancer Cell. 22:91–105. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
181
|
Gay LJ and Felding-Habermann B:
Contribution of platelets to tumour metastasis. Nat Rev Cancer.
11:123–134. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
182
|
Nagrath S, Sequist LV, Maheswaran S, Bell
DW, Irimia D, Ulkus L, Smith MR, Kwak EL, Digumarthy S, Muzikansky
A, et al: Isolation of rare circulating tumour cells in cancer
patients by microchip technology. Nature. 450:1235–1239. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
183
|
Huang YY, Hoshino K, Chen P, Wu CH, Lane
N, Huebschman M, Liu H, Sokolov K, Uhr JW, Frenkel EP, et al:
Immunomagnetic nanoscreening of circulating tumor cells with a
motion controlled microfluidic system. Biomed Microdevices.
15:673–681. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
184
|
Cai H and Peng F: 2-NBDG fluorescence
imaging of hyper-metabolic circulating tumor cells in mouse
xenograft model of breast cancer. J Fluoresc. 23:213–220. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
185
|
Nieswandt B, Hafner M, Echtenacher B and
Männel DN: Lysis of tumor cells by natural killer cells in mice is
impeded by platelets. Cancer Res. 59:1295–1300. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
186
|
Mbeunkui F and Johann DJ Jr: Cancer and
the tumor micro-environment: A review of an essential relationship.
Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 63:571–582. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
187
|
Gupta GP, Nguyen DX, Chiang AC, Bos PD,
Kim JY, Nadal C, Gomis RR, Manova-Todorova K and Massagué J:
Mediators of vascular remodelling co-opted for sequential steps in
lung metastasis. Nature. 446:765–770. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
188
|
Psaila B, Kaplan RN, Port ER and Lyden D:
Priming the 'soil' for breast cancer metastasis: The pre-metastatic
niche. Breast Dis. 26:65–74. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
189
|
Psaila B and Lyden D: The metastatic
niche: Adapting the foreign soil. Nat Rev Cancer. 9:285–293. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
190
|
Hiratsuka S, Watanabe A, Aburatani H and
Maru Y: Tumour-mediated upregulation of chemoattractants and
recruitment of myeloid cells predetermines lung metastasis. Nat
Cell Biol. 8:1369–1375. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
191
|
Rafii S and Lyden D: S100 chemokines
mediate bookmarking of premetastatic niches. Nat Cell Biol.
8:1321–1323. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
192
|
Hiratsuka S, Watanabe A, Sakurai Y,
Akashi-Takamura S, Ishibashi S, Miyake K, Shibuya M, Akira S,
Aburatani H and Maru Y: The S100A8-serum amyloid A3-TLR4 paracrine
cascade establishes a pre-metastatic phase. Nat Cell Biol.
10:1349–1355. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
193
|
Kaplan RN, Riba RD, Zacharoulis S, Bramley
AH, Vincent L, Costa C, MacDonald DD, Jin DK, Shido K, Kerns SA, et
al: VEGFR1-positive haematopoietic bone marrow progenitors initiate
the pre-metastatic niche. Nature. 438:820–827. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
194
|
Nakasone ES, Askautrud HA, Kees T, Park
JH, Plaks V, Ewald AJ, Fein M, Rasch MG, Tan YX, Qiu J, et al:
Imaging tumor-stroma interactions during chemotherapy reveals
contributions of the microenvironment to resistance. Cancer Cell.
21:488–503. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
195
|
Roodhart JM, Daenen LG, Stigter EC, Prins
HJ, Gerrits J, Houthuijzen JM, Gerritsen MG, Schipper HS, Backer
MJ, van Amersfoort M, et al: Mesenchymal stem cells induce
resistance to chemotherapy through the release of platinum-induced
fatty acids. Cancer Cell. 20:370–383. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
196
|
Joosse SA and Pantel K: Tumor-educated
platelets as liquid biopsy in cancer patients. Cancer Cell.
28:552–554. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
197
|
Wong HK, Fatimy RE, Onodera C, Wei Z, Yi
M, Mohan A, Gowrisankaran S, Karmali P, Marcusson E, Wakimoto H, et
al: The Cancer Genome Atlas Analysis predicts microRNA for
targeting cancer growth and vascularization in glioblastoma. Mol
Ther. 23:1234–1247. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
198
|
Resnick MJ, Lopatin M, Shore ND, Lam PN,
Helfand B, Abramson RD, Crager M, Bonham M, Tezcan H, Clark-Langone
KM, et al: Analysis of tumor DNA in urine as a highly sensitive
liquid biopsy for patients with non-muscle invasive bladder cancer
(NMIBC). Clin Cancer Res. 22:142016.
|
|
199
|
Mishra RK, Wei C, Hresko RC, Bajpai R,
Heitmeier M, Matulis SM, Nooka AK, Rosen ST, Hruz PW, Schiltz GE,
et al: In Silico modeling-based identification of glucose
transporter 4 (GLUT4)-selective inhibitors for cancer therapy. J
Biol Chem. 290:14441–14453. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
200
|
Tuxhorn JA, McAlhany SJ, Yang F, Dang TD
and Rowley DR: Inhibition of transforming growth factor-beta
activity decreases angiogenesis in a human prostate cancer-reactive
stroma xenograft model. Cancer Res. 62:6021–6025. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
201
|
Carmeliet P: Angiogenesis in health and
disease. Nat Med. 9:653–660. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
202
|
Joyce JA, Freeman C, Meyer-Morse N, Parish
CR and Hanahan D: A functional heparan sulfate mimetic implicates
both heparanase and heparan sulfate in tumor angiogenesis and
invasion in a mouse model of multistage cancer. Oncogene.
24:4037–4051. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
203
|
Hamano Y, Zeisberg M, Sugimoto H, Lively
JC, Maeshima Y, Yang C, Hynes RO, Werb Z, Sudhakar A and Kalluri R:
Physiological levels of tumstatin, a fragment of collagen IV alpha3
chain, are generated by MMP-9 proteolysis and suppress angiogenesis
via alphav beta3 integrin. Cancer Cell. 3:589–601. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
204
|
Rudland PS, Platt-Higgins A, El-Tanani M,
De Silva Rudland S, Barraclough R, Winstanley JH, Howitt R and West
CR: Prognostic significance of the metastasis-associated protein
osteopontin in human breast cancer. Cancer Res. 62:3417–3427.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
205
|
El-Tanani MK, Campbell FC, Kurisetty V,
Jin D, Mccann M and Rudland PS: The regulation and role of
osteopontin in malignant transformation and cancer. Cytokine Growth
Factor Rev. 17:463–474. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
206
|
Tuck AB and Chambers AF: The role of
osteopontin in breast cancer: Clinical and experimental studies. J
Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 6:419–429. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
207
|
Weber GF: The metastasis gene osteopontin:
A candidate target for cancer therapy. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1552:61–85. 2001.
|
|
208
|
Matarrese P, Fusco O, Tinari N, Natoli C,
Liu FT, Semeraro ML, Malorni W and Iacobelli S: Galectin-3
overexpression protects from apoptosis by improving cell adhesion
properties. Int J Cancer. 85:545–554. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
209
|
Inohara H, Honjo Y, Yoshii T, Akahani S,
Yoshida J, Hattori K, Okamoto S, Sawada T, Raz A and Kubo T:
Expression of galectin-3 in fine-needle aspirates as a diagnostic
marker differentiating benign from malignant thyroid neoplasms.
Cancer. 85:2475–2484. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
210
|
Pinedo HM, Verheul HM, D'Amato RJ and
Folkman J: Involvement of platelets in tumour angiogenesis? Lancet.
352:1775–1777. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
211
|
Pai R, Soreghan B, Szabo IL, Pavelka M,
Baatar D and Tarnawski AS: Prostaglandin E2 transactivates EGF
receptor: A novel mechanism for promoting colon cancer growth and
gastrointestinal hypertrophy. Nat Med. 8:289–293. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
212
|
Ikushima H and Miyazono K: TGFbeta
signalling: A complex web in cancer progression. Nat Rev Cancer.
10:415–424. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
213
|
Sierko E and Wojtukiewicz MZ: Platelets
and angiogenesis in malignancy. Semin Thromb Hemost. 30:95–108.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
214
|
Medina VA and Rivera ES: Histamine
receptors and cancer pharmacology. Br J Pharmacol. 161:755–767.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
215
|
Moghaddam A, Zhang HT, Fan TP, HU DE, Lees
VC, Turley H, Fox SB, Gatter KC, Harris AL and Bicknell R:
Thymidine phosphorylase is angiogenic and promotes tumor growth.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 92:998–1002. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
216
|
Bronckaers A, Gago F, Balzarini J and
Liekens S: The dual role of thymidine phosphorylase in cancer
development and chemotherapy. Med Res Rev. 29:903–953. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
217
|
Geiger TR and Peeper DS: Critical role for
TrkB kinase function in anoikis suppression, tumorigenesis, and
metastasis. Cancer Res. 67:6221–6229. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
218
|
Kim YJ, Borsig L, Varki NM and Varki A:
P-selectin deficiency attenuates tumor growth and metastasis. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 95:9325–9330. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
219
|
David M, Wannecq E, Descotes F, Jansen S,
Deux B, Ribeiro J, Serre CM, Grès S, Bendriss-Vermare N, Bollen M,
et al: Cancer cell expression of autotaxin controls bone metastasis
formation in mouse through lysophosphatidic acid-dependent
activation of osteoclasts. PLoS One. 5:e97412010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
220
|
Visentin B, Vekich JA, Sibbald BJ, Cavalli
AL, Moreno KM, Matteo RG, Garland WA, Lu Y, Yu S, Hall HS, et al:
Validation of an anti-sphingosine-1-phosphate antibody as a
potential therapeutic in reducing growth, invasion, and
angiogenesis in multiple tumor lineages. Cancer Cell. 9:225–238.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
221
|
Ruf W and Mueller BM: Thrombin generation
and the pathogenesis of cancer. Semin Thromb Hemost. 32(Suppl 1):
61–68. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
222
|
Bajou K, Noël A, Gerard RD, Masson V,
Brunner N, Holst-Hansen C, Skobe M, Fusenig NE, Carmeliet P, Collen
D, et al: Absence of host plasminogen activator inhibitor 1
prevents cancer invasion and vascularization. Nat Med. 4:923–928.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
223
|
Falcón BL, Hashizume H, Koumoutsakos P,
Chou J, Bready JV, Coxon A, Oliner JD and McDonald DM: Contrasting
actions of selective inhibitors of angiopoietin-1 and
angiopoietin-2 on the normalization of tumor blood vessels. Am J
Pathol. 175:2159–2170. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
224
|
Payne AS and Cornelius LA: The role of
chemokines in melanoma tumor growth and metastasis. J Invest
Dermatol. 118:915–922. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
225
|
Wu Y, Li YY, Matsushima K, Baba T and
Mukaida N: CCL3-CCR5 axis regulates intratumoral accumulation of
leukocytes and fibroblasts and promotes angiogenesis in murine lung
metastasis process. J Immunol. 181:6384–6393. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
226
|
Läubli H, Spanaus KS and Borsig L:
Selectin-mediated activation of endothelial cells induces
expression of CCL5 and promotes metastasis through recruitment of
monocytes. Blood. 114:4583–4591. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
227
|
Yi F, Jaffe R and Prochownik EV: The CCL6
chemokine is differentially regulated by c-Myc and L-Myc, and
promotes tumorigenesis and metastasis. Cancer Res. 63:2923–2932.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
228
|
Keeley EC, Mehrad B and Strieter RM: CXC
chemokines in cancer angiogenesis and metastases. Adv Cancer Res.
106:91–111. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
229
|
Nakamura ES, Koizumi K, Kobayashi M,
Saitoh Y, Arita Y, Nakayama T, Sakurai H, Yoshie O and Saiki I:
RANKL-induced CCL22/macrophage-derived chemokine produced from
osteoclasts potentially promotes the bone metastasis of lung cancer
expressing its receptor CCR4. Clin Exp Metastasis. 23:9–18. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
230
|
Romagnani P, Lasagni L, Annunziato F,
Serio M and Romagnani S: CXC chemokines: The regulatory link
between inflammation and angiogenesis. Trends Immunol. 25:201–209.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
231
|
Strieter RM, Burdick MD, Gomperts BN,
Belperio JA and Keane MP: CXC chemokines in angiogenesis. Cytokine
Growth Factor Rev. 16:593–609. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
232
|
Feliciano P: CXCL1 and CXCL2 link
metastasis and chemoresistance. Nat Genet. 44:8402012.
|
|
233
|
Keane MP, Belperio JA, Xue YY, Burdick MD
and Strieter RM: Depletion of CXCR2 inhibits tumor growth and
angiogenesis in a murine model of lung cancer. J Immunol.
172:2853–2860. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
234
|
White ES, Flaherty KR, Carskadon S, Brant
A, Iannettoni MD, Yee J, Orringer MB and Arenberg DA: Macrophage
migration inhibitory factor and CXC chemokine expression in
non-small cell lung cancer: Role in angiogenesis and prognosis.
Clin Cancer Res. 9:853–860. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
235
|
Strieter RM, Burdick MD, Mestas J,
Gomperts B, Keane MP and Belperio JA: Cancer CXC chemokine networks
and tumour angiogenesis. Eur J Cancer. 42:768–778. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
236
|
Miyazaki H, Patel V, Wanzg H, Edmunzs RK,
Gutkind JS and Yeudall WA: Down-regulation of CXCL5 inhibits
squamous carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 66:4279–4284. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
237
|
Gijsbers K, Gouwy M, Struyf S, Wuyts A,
Proost P, Opdenakker G, Penninckx F, Ectors N, Geboes K and van
Damme J: GCP-2/CXCL6 synergizes with other endothelial cell-derived
chemokines in neutrophil mobilization and is associated with
angiogenesis in gastrointestinal tumors. Exp Cell Res. 303:331–342.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
238
|
Verbeke H, Struyf S, Berghmans N, Van
Coillie E, Opdenakker G, Uyttenhove C, Van Snick J and Van Damme J:
Isotypic neutralizing antibodies against mouse GCP-2/CXCL6 inhibit
melanoma growth and metastasis. Cancer Lett. 302:54–62. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
239
|
Tang Z, Yu M, Miller F, Berk RS, Tromp G
and Kosir MA: Increased invasion through basement membrane by
CXCL7-transfected breast cells. Am J Surg. 196:690–696. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
240
|
Bachelder RE, Wendt MA and Mercurio AM:
Vascular endothelial growth factor promotes breast carcinoma
invasion in an autocrine manner by regulating the chemokine
receptor CXCR4. Cancer Res. 62:7203–7206. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
241
|
Belperio JA, Phillips RJ, Burdick MD, Lutz
M, Keane M and Strieter R: The SDF-1/CXCL 12/CXCR4 biological axis
in non-small cell lung cancer metastases. Chest. 125(Suppl 5):
156S2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
242
|
Pan J, Mestas J, Burdick MD, Phillips RJ,
Thomas GV, Reckamp K, Belperio JA and Strieter RM: Stromal derived
factor-1 (SDF-1/CXCL12) and cXcr4 in renal cell carcinoma
metastasis. Mol Cancer. 5:562006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|