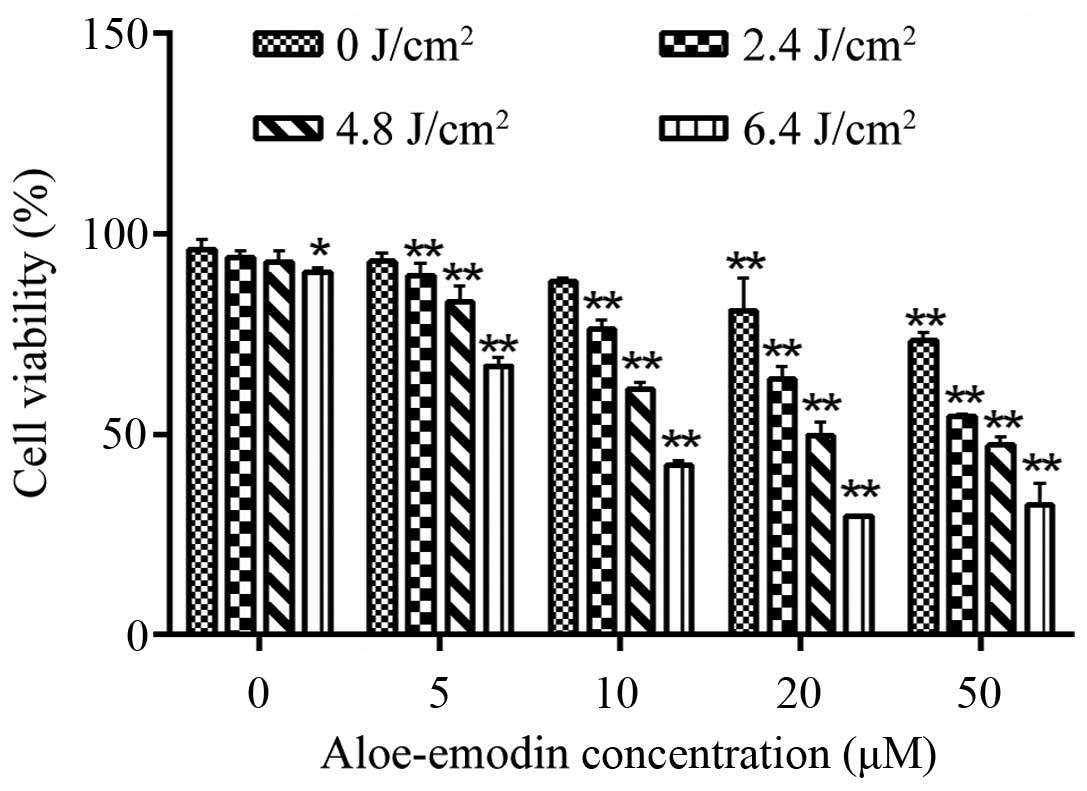
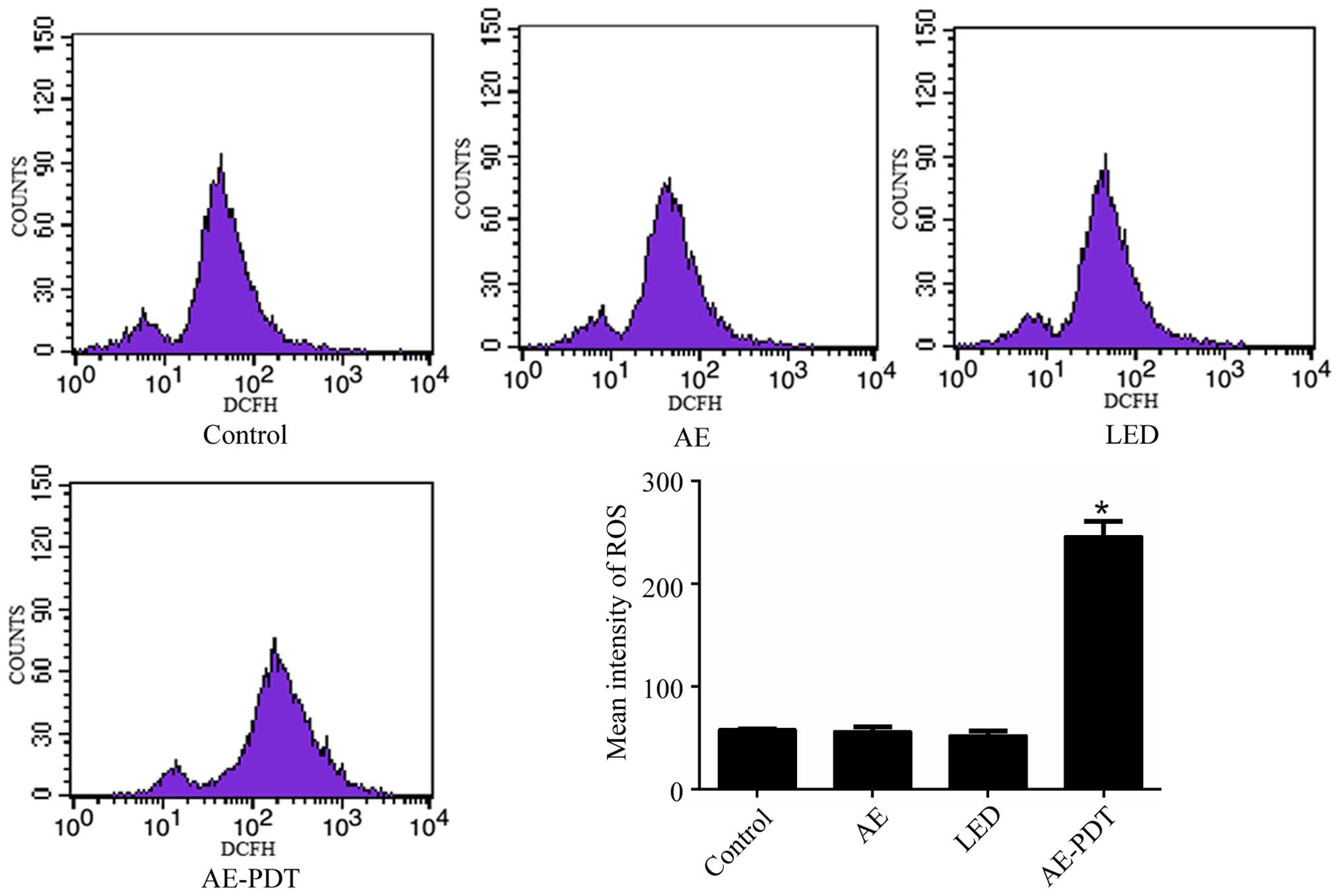
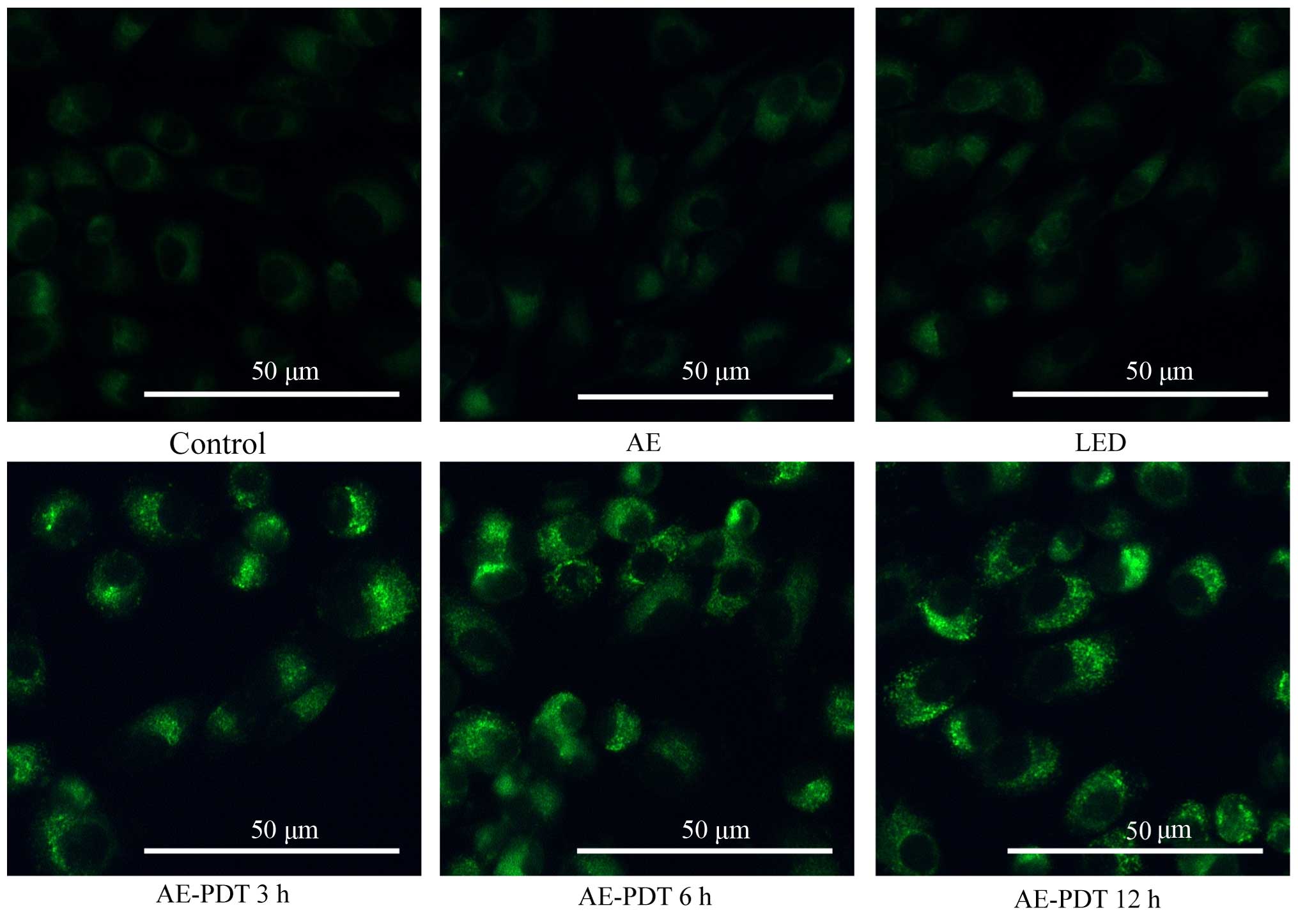
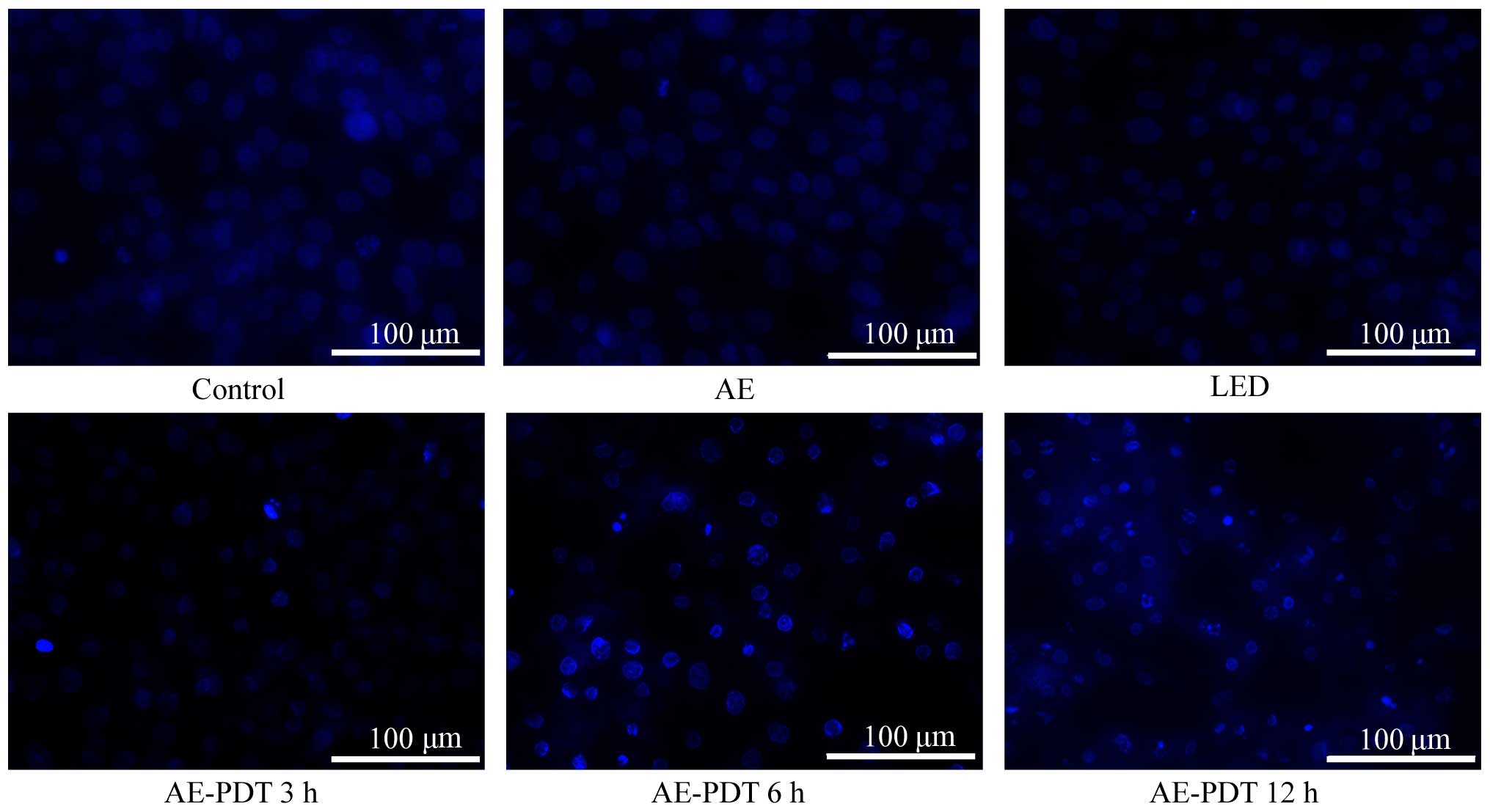
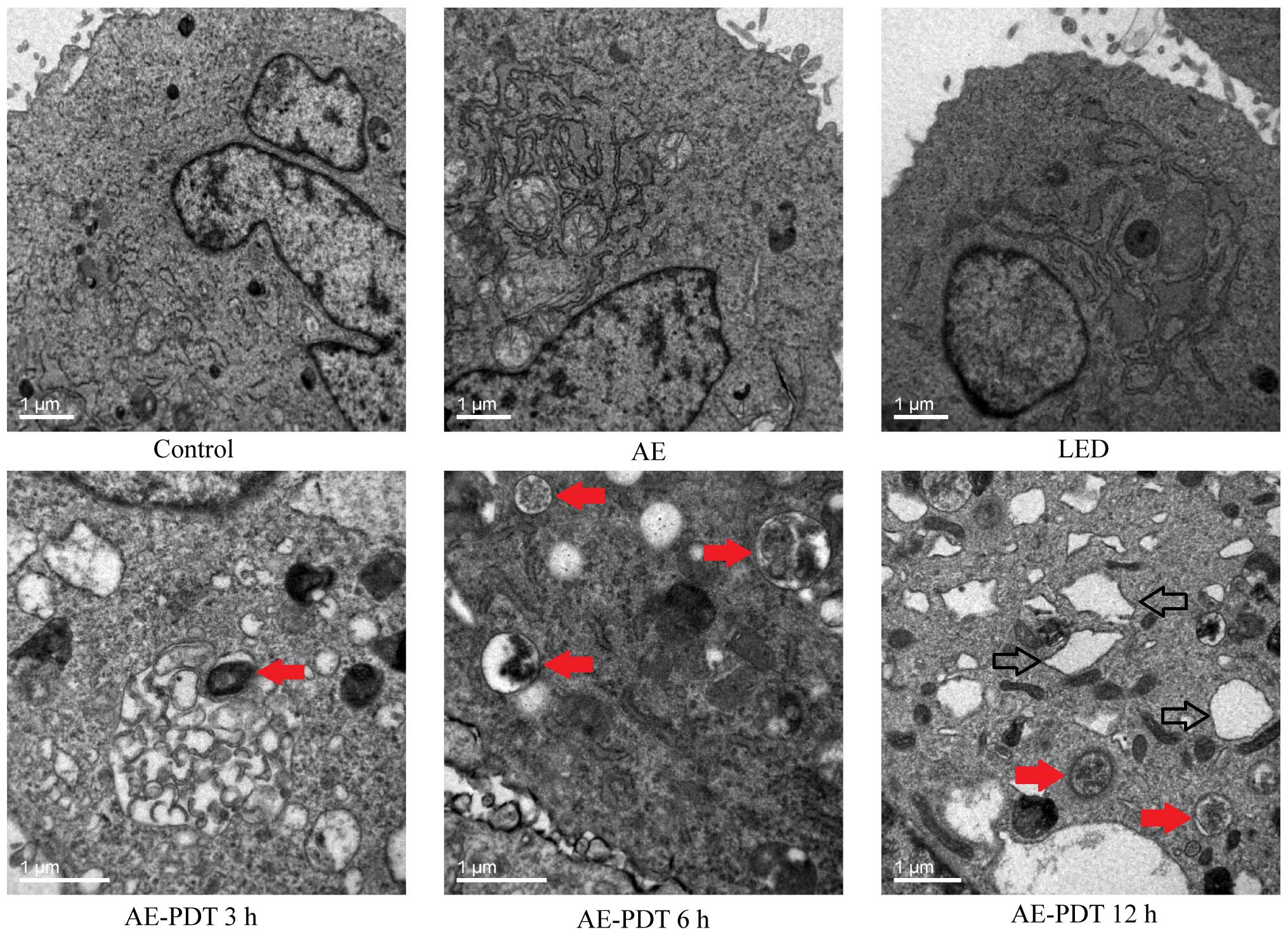
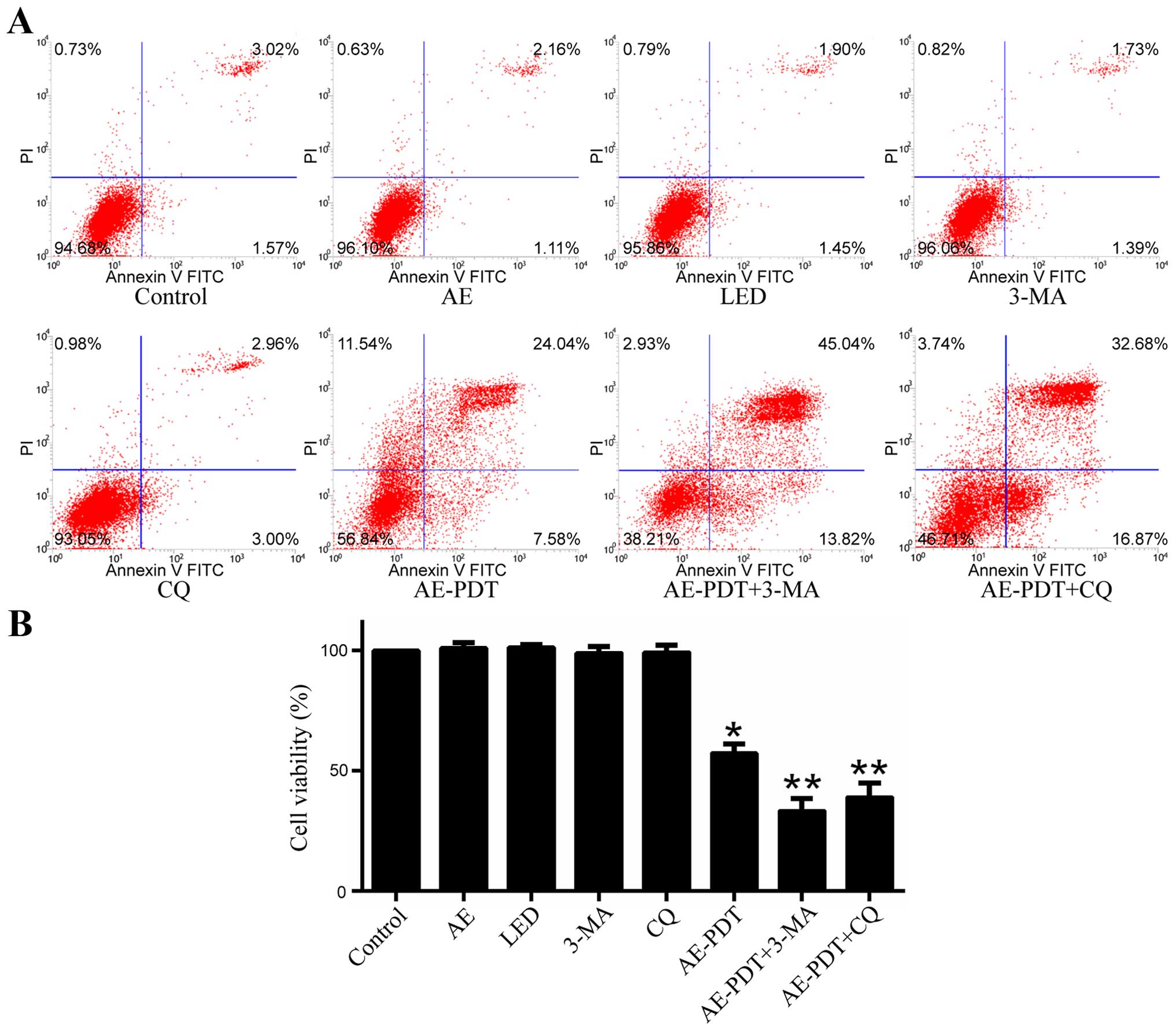
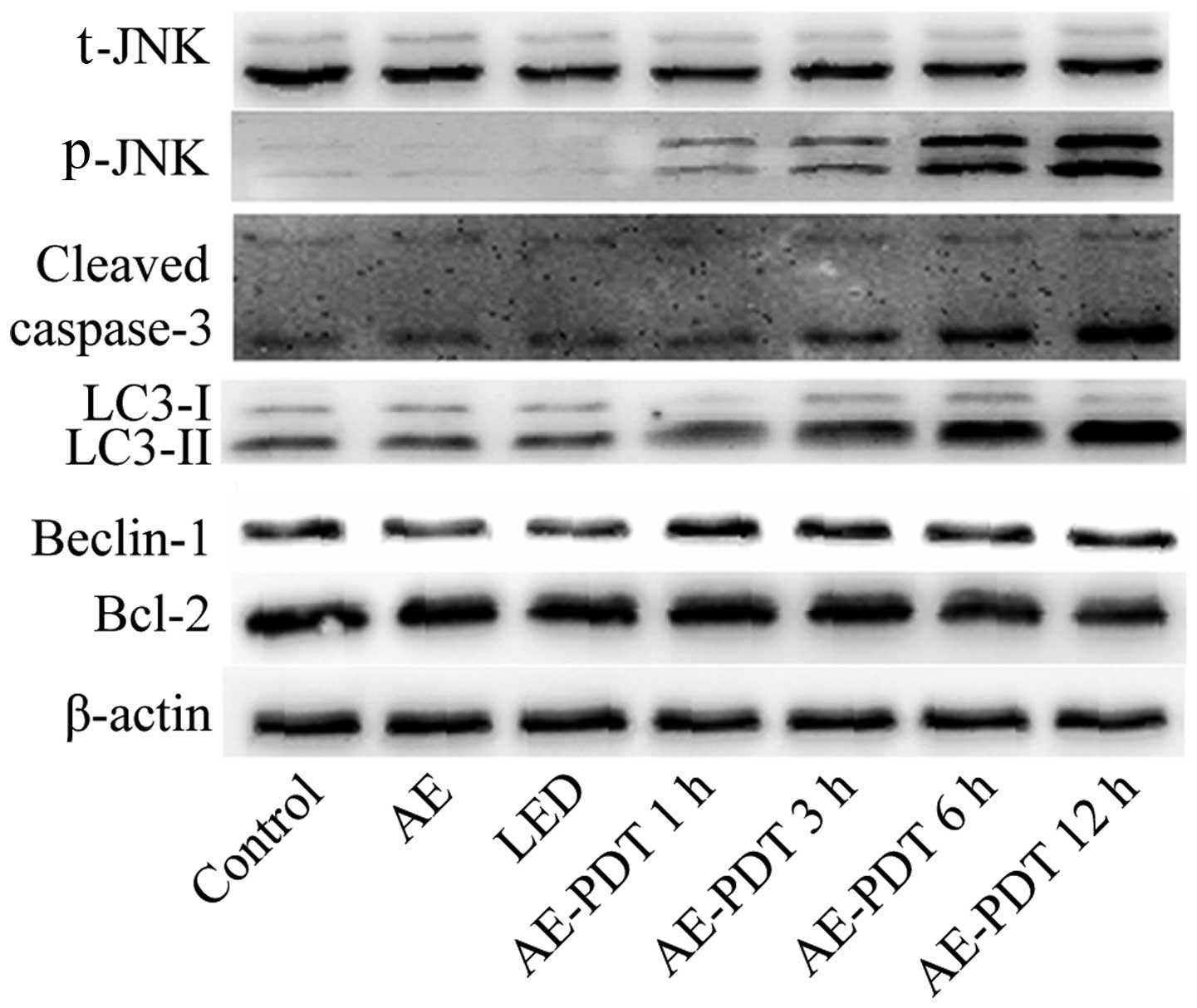
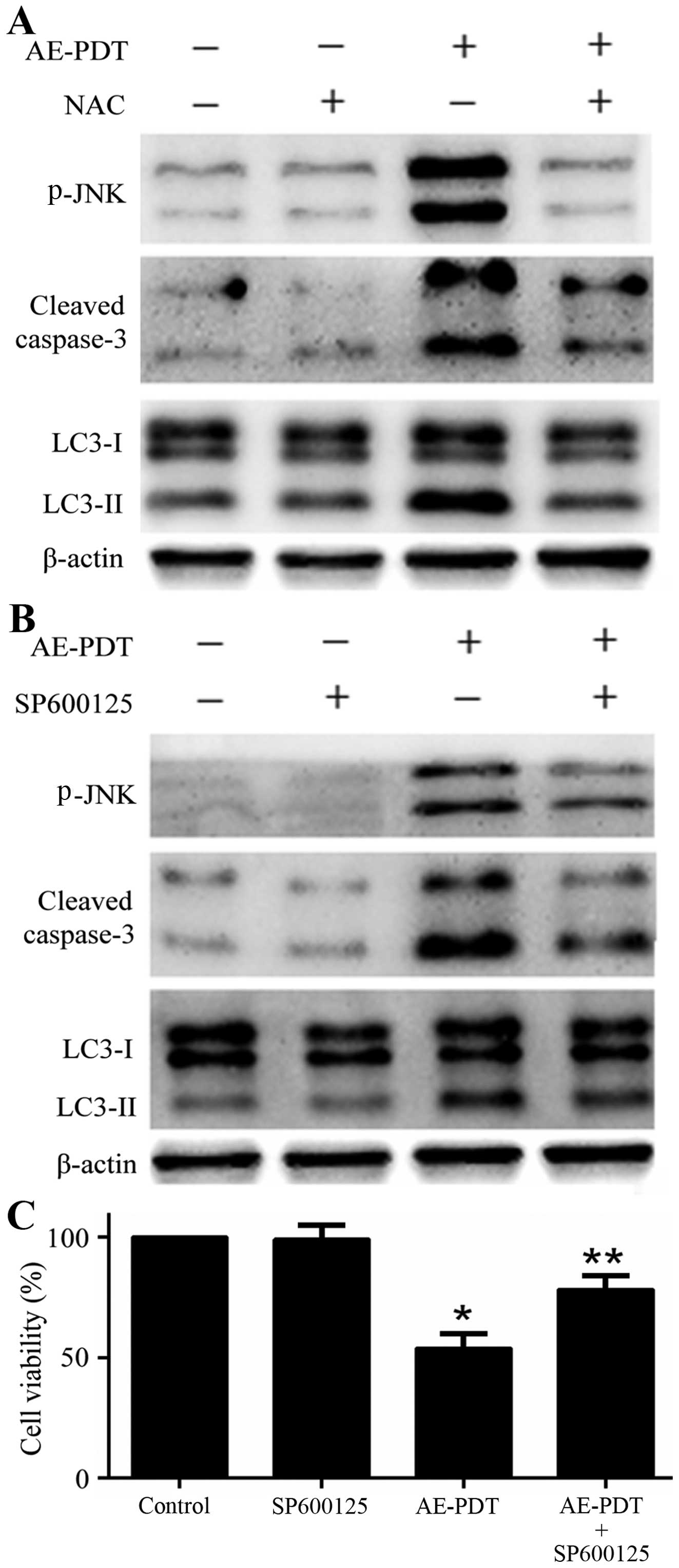
|
1
|
Whelan J, McTiernan A, Cooper N, Wong YK,
Francis M, Vernon S and Strauss SJ: Incidence and survival of
malignant bone sarcomas in England 1979–2007. Int J Cancer1.
31:E508–E517. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Ottaviani G and Jaffe N: The epidemiology
of osteosarcoma. Cancer Treat Res. 152:3–13. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
He H, Ni J and Huang J: Molecular
mechanisms of chemoresistance in osteosarcoma (Review). Oncol Lett.
7:1352–1362. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Mittal N, Kent PM and Ording J: Metastatic
and recurrent bone primary bone cancers. Curr Probl Cancer.
37:215–224. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Shirasu N, Nam SO and Kuroki M:
Tumor-targeted photodynamic therapy. Anticancer Res. 33:2823–2831.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Calabrò G, Patalano A, Lo Conte V and
Chianese C: Photodynamic chemotherapy in the treatment of
superficial mycoses: An evidence-based evaluation. G Ital Dermatol
Venereol. 148:639–648. 2013.
|
|
7
|
Master A, Livingston M and Sen Gupta A:
Photodynamic nanomedicine in the treatment of solid tumors:
Perspectives and challenges. J Control Release. 168:88–102. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mfouo-Tynga I and Abrahamse H: Cell death
pathways and phthalocyanine as an efficient agent for photodynamic
cancer therapy. Int J Mol Sci. 16:10228–10241. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chen R, Zhang J, Hu Y, Wang S, Chen M and
Wang Y: Potential antineoplastic effects of Aloe-emodin: A
comprehensive review. Am J Chin Med. 42:275–288. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tabolacci C, Lentini A, Mattioli P,
Provenzano B, Oliverio S, Carlomosti F and Beninati S: Antitumor
properties of aloe-emodin and induction of transglutaminase 2
activity in B16-F10 melanoma cells. Life Sci. 87:316–324. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sevcovicova A, Bodnarova K, Loderer D,
Imreova P, Galova E and Miadokova E: Dual activities of emodin -
DNA protectivity vs mutagenicity. Neuro Endocrinol Lett. 35(Suppl
2): S149–S154. 2014.
|
|
12
|
Zaffaroni M, Mucignat C, Pecere T, Zagotto
G, Frapolli R, D'Incalci M and Zucchetti M: High-performance liquid
chromatographic assay for the determination of Aloe Emodin in mouse
plasma. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 796:113–119.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Vargas F, Rivas C and Medrano M:
Interaction of emodin, aloe-emodin, and rhein with human serum
albumin: A fluorescence spectroscopic study. Toxicol Mech Methods.
14:227–231. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lee HZ: Effects and mechanisms of emodin
on cell death in human lung squamous cell carcinoma. Br J
Pharmacol. 134:11–20. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lee HZ, Yang WH, Hour MJ, Wu CY, Peng WH,
Bao BY, Han PH and Bau DT: Photodynamic activity of aloe-emodin
induces resensitization of lung cancer cells to anoikis. Eur J
Pharmacol. 648:50–58. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Trachootham D, Lu W, Ogasawara MA, Nilsa
RD and Huang P: Redox regulation of cell survival. Antioxid Redox
Signal. 10:1343–1374. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Rodríguez-Blanco J, Martín V,
García-Santos G, Herrera F, Casado-Zapico S, Antolín I and
Rodriguez C: Cooperative action of JNK and AKT/mTOR in
1-methyl-4-phenylpyri-dinium-induced autophagy of neuronal PC12
cells. J Neurosci Res. 90:1850–1860. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Erikstein BS, Hagland HR, Nikolaisen J,
Kulawiec M, Singh KK, Gjertsen BT and Tronstad KJ: Cellular stress
induced by resazurin leads to autophagy and cell death via
production of reactive oxygen species and mitochondrial impairment.
J Cell Biochem. 111:574–584. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zou P, Xia Y, Chen T, Zhang J, Wang Z,
Chen W, Chen M, Kanchana K, Yang S and Liang G: Selective killing
of gastric cancer cells by a small molecule targeting ROS-mediated
ER stress activation. Mol Carcinog. Jun 18–2015.Epub ahead of
print. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Gewirtz DA: The four faces of autophagy:
Implications for cancer therapy. Cancer Res. 74:647–651. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bincoletto C, Bechara A, Pereira GJ,
Santos CP, Antunes F, Peixoto da-Silva J, Muler M, Gigli RD,
Monteforte PT, Hirata H, et al: Interplay between apoptosis and
autophagy, a challenging puzzle: New perspectives on antitumor
chemotherapies. Chem Biol Interact. 206:279–288. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ahn MY, Yoon HE, Kwon SM, Lee J, Min SK,
Kim YC, Ahn SG and Yoon JH: Synthesized Pheophorbide a-mediated
photodynamic therapy induced apoptosis and autophagy in human oral
squamous carcinoma cells. J Oral Pathol Med. 42:17–25. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Abe A and Kokuba H: Harmol induces
autophagy and subsequent apoptosis in U251MG human glioma cells
through the downregulation of survivin. Oncol Rep. 29:1333–1342.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|